力扣每日一题
一.简单题
1.两数之和
1. 两数之和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
(1)暴力求解
int* twoSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize)
{
int i=0,j=0;
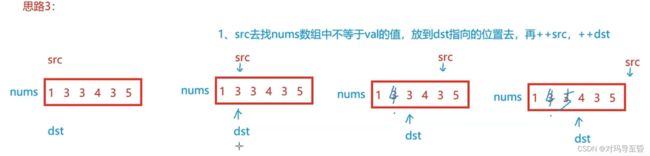
for(i=0;i(2)哈希表
2.回文数
9. 回文数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
bool isPalindrome(int x)
{
if(x<0)
return false;
char arr[20],brr[20];
itoa(x, arr);
char i = 0,tmp=0;
int m = strlen(arr);
strcpy( brr, arr );
for (i = 0; i <=(m - 1)/2; i++)
{
tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[m - 1 - i];
arr[strlen(arr) - 1 - i] = tmp;
}
int f=strcmp( arr, brr );
if(f==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}3.罗马数字转整数
13. 罗马数字转整数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
int romanToInt(char* s)
{
int n=strlen(s);
int i=0;
int sum=0;
for(i=0;i4.
5. 有效括号
20. 有效的括号 - 力扣(LeetCode)
bool isValid(char * s)
{
ST st;
StackInit(&st);
while(*s)
{
if(*s=='('||*s=='['||*s=='{')
{
StackPush(&st,*s);//入栈,栈里不存右括号
s++;
}
else
{
//遇到右括号了,但是栈里面没有数据,说明前面没有左括号,也要返回flase
if(StackEmpty(&st))
{
StackDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
STDataType top=StackTop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
if((*s==')'&&top!='(')||(*s==']'&&top!='[')||(*s=='}'&&top!='{'))
{
StackDestroy(&st); //不销毁会导致内存泄漏
return false;
}
else
{
s++;
}
}
}
//只要栈不是空,就说明里面还有还有左括号没有被匹配
bool ret=StackEmpty(&st);
StackDestroy(&st); //不销毁会导致内存泄漏
return ret;
}.相同的树
100. 相同的树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if(p==NULL && q==NULL)
return true;
if(p==NULL || q==NULL) //这里不能用异或,因为异或是个值运算
return false;
if(p->val != q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
经典的前序:先判断根,再是左子树,右子树.杨辉三角
118. 杨辉三角 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution
{
public:
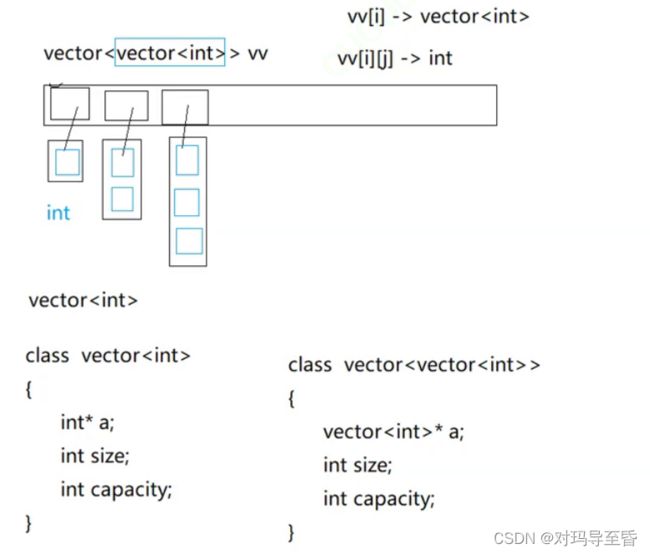
vector> generate(int numRows)
{
vector> vv;
vv.resize(numRows,vector()); //vector()是用匿名对象来初始化
for(size_t i=0;i .反转链表
206. 反转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
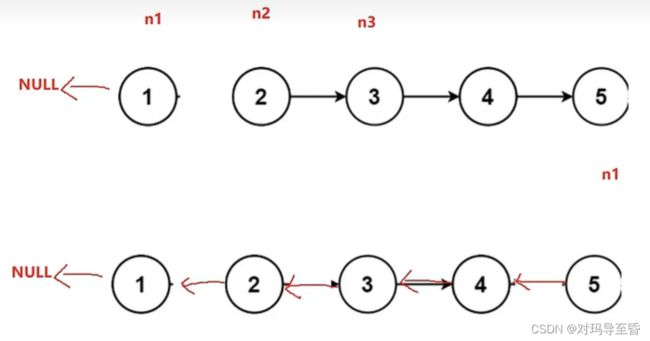
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
if(head==NULL)
{
return head;
}
struct ListNode *n1,*n2,*n3;
n1=NULL;
n2=head;
n3=head->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next=n1; //翻转指针
n1=n2; //让n1==n2
n2=n3; //让n2==n3
if(n3)
{
n3=n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}
运用三指针的方法,关键是画图.链表的中间结点
876. 链表的中间结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode *fast,*slow;
fast=head;
slow=head;
while(fast!=NULL&&fast->next!=NULL)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
运用快慢指针,快指针比慢指针多走一步,最终slow会在head和fast的中间位置拓展:找倒数第k个结点
struct ListNode* FindNode(struct ListNode* head,int k)
{
struct ListNode *fast,*slow;
fast=head;
slow=head;
int i=0;
for(i=0;inext;
}
while(fast)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
也是用快慢指针,不过是fast先走k步;
之后slow与fast一起走,当fast==NULL时,slow指向的是倒数第k个 .合并两个有序链表
21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2)
{
if(l1==NULL)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2==NULL)
{
return l1;
}
//如果其中一个链表为空,返回另一个链表
struct ListNode *head,*tail;
head=NULL;
tail=NULL;
while(l1&&l2)
{
if(l1->valval)
{
if(head==NULL) //第一次的判断
{
head=l1;
tail=l1;
}
else
{
tail->next=l1;
tail=l1;
}
l1=l1->next;
}
else
{
if(head==NULL) //第一次的判断
{
head=l2;
tail=l2;
}
else
{
tail->next=l2;
tail=l2;
}
l2=l2->next;
}
}
//连接剩下的
if(l1)
{
tail->next=l1;
}
if(l2)
{
tail->next=l2;
}
return head;
}
依次比较链表结点,每次取小的结点,尾插到新的链表即可 . 回文链表
LCR 027. 回文链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* mid=middleNode(head);
struct ListNode* rhead=reverseList(mid);
struct ListNode* cur1=head; //尽量不要乱动头指针
struct ListNode* cur2=rhead;
while(cur1&&cur2)
{
if(cur1->val!=cur2->val)
{
return false;
}
else
{
cur1=cur1->next;
cur2=cur2->next;
}
}
return true;
}
先找到中间结点,然后逆置后面的链表,之后再和前面的链表比较。.相交链表
LCR 027. 回文链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
struct ListNode* tail1=headA;
struct ListNode* tail2=headB;
int len1=1,len2=1; //因为没有把尾算进去,所以初始为一比较好
while(tail1->next!=NULL)
{
len1++;
tail1=tail1->next;
}
while(tail2->next!=NULL)
{
len2++;
tail2=tail2->next;
}
if(tail1!=tail2) //最好用地址去比较,用值可能会误判
{
return NULL; //不相交
}
int gap=abs(len1-len2);
struct ListNode* longlist=headA;
struct ListNode* shortlist=headB;
if(len1next;
}
while(longlist!=shortlist)
{
longlist=longlist->next;
shortlist=shortlist->next;
}
return longlist;
} .环形链表
LCR 027. 回文链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
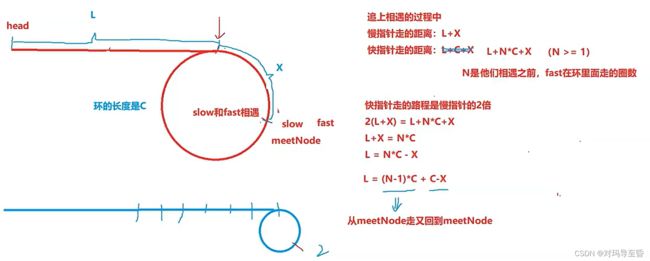
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode* fast=head;
struct ListNode* slow=head;
struct ListNode* A=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
if(slow==fast) //当相遇时
{
struct ListNode* meet=slow;
while(A!=meet)
{
A=A->next;
meet=meet->next;
}
return meet;
}
}
return NULL;
}
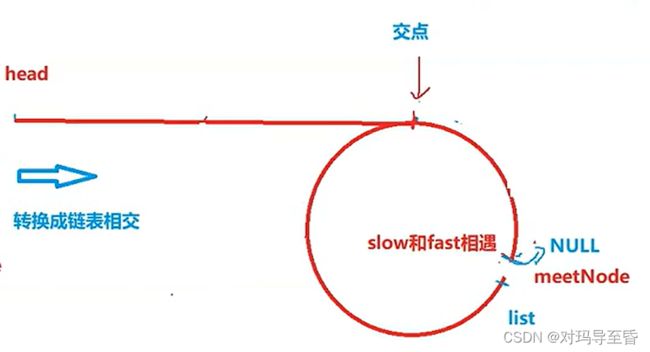
使用快慢指针,快比慢多一步
根据图和公式分析,结论是L==从meet到环入口的距离
法2:
还可以成链表相交求交点
list1:从head到meet (让meet做两个链表的尾巴)
list2:从meet前一个到meet.用队列实现栈
225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
typedef struct
{
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate()
{
MyStack* st =(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&st->q1);
QueueInit(&st->q2);
return st;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
{
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) //->已经解引用过一次了,所以还是要加&
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
//我们需要判断那个队列是空,则将另一个队列的前n-1个数据进行出队到空队列
Queue* emptyQ = &obj->q1;
Queue* noemptyQ = &obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
emptyQ = &obj->q2;
noemptyQ = &obj->q1;
}
// 把非空队列的前N个数据,导入空队列,剩下一个删掉
// 就实现了后进先出
while(QueueSize(noemptyQ)>1)
{
int front =QueueFront(noemptyQ);
QueuePush(emptyQ,front);
QueuePop(noemptyQ);
}
int top=QueueFront(noemptyQ); //先保存一下,不然被pop掉找不到数据了
QueuePop(noemptyQ);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
{
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
{
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2); //都不为空才行
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
{
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
obj==NULL;
}
核心思路:
1.入数据,往不为空的队列里入数据,保持另外一个队列为空
2.出数据,把前n-1个数据转移到另外一个队列里存起来,把最后一个数据出出去.用栈实现队列
typedef struct
{
ST pushST;
ST popST;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate()
{
MyQueue* q=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
StackInit(&q->pushST);
StackInit(&q->popST);
return q;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x)
{
StackPush(&obj->pushST,x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{
if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST))
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST))
{
StackPush(&obj->popST,StackTop(&obj->pushST));
StackPop(&obj->pushST);
}
}
int front=StackTop(&obj->popST);
StackPop(&obj->popST);
return front;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj)
{
if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST))
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST))
{
StackPush(&obj->popST,StackTop(&obj->pushST));
StackPop(&obj->pushST);
}
}
return StackTop(&obj->popST);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj)
{
return StackEmpty(&obj->pushST) && StackEmpty(&obj->popST);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj)
{
StackDestroy(&obj->pushST);
StackDestroy(&obj->popST);
free(obj); //不要忘了把MyQueue释放掉
obj==NULL;
}.单值二叉树
965. 单值二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(root->left && root->left->val!=root->val) //跟左子树比较
{
return false;
}
if(root->right && root->right->val!=root->val) //跟右子树比较
{
return false;
}
return isUnivalTree(root->left) && isUnivalTree(root->right);
//不能是
return isUnivalTree(root->left);
return isUnivalTree(root->right);
}
每次递归都是比较孩子(子树)与父亲,只要不是单值二叉树,肯定在某个地方孩子与父亲不相等.对称二叉树
101. 对称二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
bool _isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* leftRoot,struct TreeNode* rightRoot)
{
if(leftRoot==NULL && rightRoot==NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(leftRoot==NULL || rightRoot==NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(leftRoot->val != rightRoot->val)
{
return false; //最好写题意不满足的条件
}
return _isSymmetric(leftRoot->left,rightRoot->right)
&& _isSymmetric(leftRoot->right,rightRoot->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return _isSymmetric(root->left,root->right); //当给的函数不合适的时候,可以自己再编一个
}.二叉树的前序遍历
144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return (root==NULL) ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left)+TreeSize(root->right)+1;
}
void _preorder(struct TreeNode* root,int* a,int *i) //递归中传数值,基本都是传址
{
if(root==NULL)
return ;
a[(*i)++]=root->val;
_preorder(root->left,a,i);
_preorder(root->right,a,i);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize=TreeSize(root);
int *a=(int*)malloc((*returnSize)*sizeof(int));
int i=0;
_preorder(root,a,&i); //要保证每个栈帧都只有一个i
return a;
}.字符串中的第一个唯一字符
387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution
{
public:
int firstUniqChar(string s)
{
//用计数来统计次数
int count[26]={0};
for(auto ch:s)
{
count[ch-'a']++;
}
for(int i=0;i.字符串相加
415. 字符串相加 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution
{
public:
string addStrings(string num1, string num2)
{
int end1=num1.size()-1,end2=num2.size()-1;
int next=0;
string str;
while(end1>=0||end2>=0)
{
int val1=0;
if(end1>=0)
{
val1=num1[end1]-'0';
}
int val2=0;
if(end2>=0)
{
val2=num2[end2]-'0';
}
int ret=val1+val2+next;
if(ret>9)
{
ret -= 10;
next=1;
}
else
{
next=0;
}
str.insert(0,1,'0'+ret);
--end1;
--end2;
}
if(next==1)
{
str.insert(0,1,'0'+1);
}
return str;
}
};
//可以用来处理大数相加.另一颗树的子树
572. 另一棵树的子树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) //第100题的函数
{
if(p==NULL && q==NULL)
return true;
if(p==NULL || q==NULL)
return false;
if(p->val != q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(isSameTree(root,subRoot))
{
return true;
}
return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot) || isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
//return isSameTree(root->left,subRoot) || isSameTree(root->right,subRoot) 是错的
}.仅仅反转字母
917. 仅仅反转字母 - 力扣(LeetCode)
bool isletter(char a)
{
if((a>='a'&&a<='z')||(a>='A'&&a<='Z'))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
class Solution
{
public:
string reverseOnlyLetters(string s)
{
size_t begin=0;
size_t end=s.size()-1;
while(begin二.中等题
1.整数反转
7. 整数反转 - 力扣(LeetCode)
int reverse(int x)
{
int m=0;
long int sum=0;
int flag=0;
if(x<0)
{
if(x==-2147483648)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
x=-x;
flag=1;
}
}
while(x)
{
m=x%10;
sum=sum*10+m;
x=x/10;
}
if(sum>=2147483648||sum<=-2147483648)
{
return 0;
}
if(flag==1)
{
sum=-sum;
}
return sum;
}2.链表分割(牛客网)
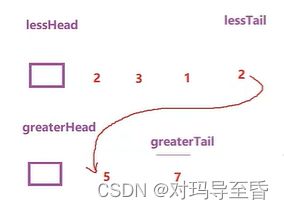
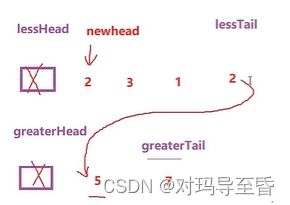
typedef struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
}ListNode;
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x)
{
struct ListNode* A_head, * A_tail, * B_head, * B_tail;
//开一个哨兵卫的头结点,方便之后的分别尾插
A_head = A_tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
A_tail = NULL;
B_head = B_tail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
B_tail = NULL;
ListNode* cur = pHead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val < x)
{
A_tail->next = cur; //A_tail的下一个指向cur
A_tail = cur;
}
else
{
B_tail->next = cur; //A_tail的下一个指向cur
B_tail = cur;
}
cur = cur->next; //因为cur没有被改变,所以依然可以继续往下走
}
A_tail->next = B_head->next;
B_tail = NULL; // 要把b_tail指向空,不然有可能B的最后一个还连着A的下一个呢
ListNode* head=A_head->next;
//不要忘了释放内存
free(A_head);
free(B_head);
return A_head->next;
}.电话号码的字母组合
17. 电话号码的字母组合 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution
{
string _numToStr[10]={"","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"};
public:
void Combinations(const string& digits,size_t di,string conbineStr,vector& strV)
//这里用传值是为了往下调用的时候不影响上面的数字
{
if(di==digits.size())
{
strV.push_back(conbineStr);
return;
}
int num=digits[di]-'0';
string str=_numToStr[num];
for(auto ch:str)
{
Combinations(digits,di+1,conbineStr+ch,strV);
//这里不能是 di++和conbineStr += ch 因为会改变di和conbineStr
}
}
vector letterCombinations(string digits)
{
vector strV;
if(digits.size()==0)
{
return strV;
}
Combinations(digits,0,"",strV);
return strV;
}
}; 3.复制带随机指针的链表
138. 复制带随机指针的链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{
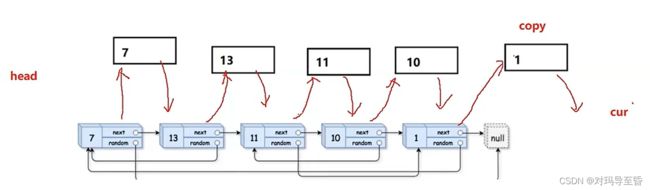
//1.拷贝结点,插入原节点的后面
struct Node* cur=head;
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val=cur->val;
//插入copy节点
copy->next=cur->next;
cur->next=copy;
cur=copy->next; //cur移动到下一个原节点
}
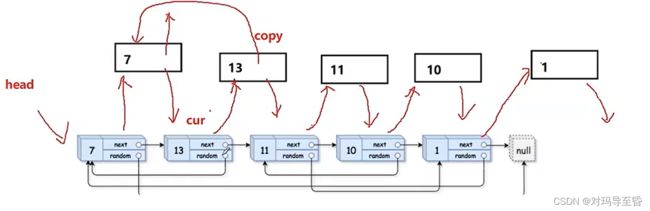
//2.根据原节点,处理copy节点的random
cur=head;
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=cur->next;
if(cur->random==NULL)
{
copy->random=NULL;
}
else
{
copy->random=cur->random->next;
}
cur=copy->next;
}
//3.取出复制的链表出来
cur=head;
struct Node* copyhead=NULL;
struct Node* copytail=NULL;
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copy=cur->next;
struct Node* next=copy->next;
if(copytail==NULL)
{
copyhead=copytail=copy;
}
else
{
copytail->next=copy;
copytail=copy;
}
cur->next=next; //恢复原链表
cur=next;
}
return copyhead; //别忘了返回
}
最重要的还是画图.设计循环队列
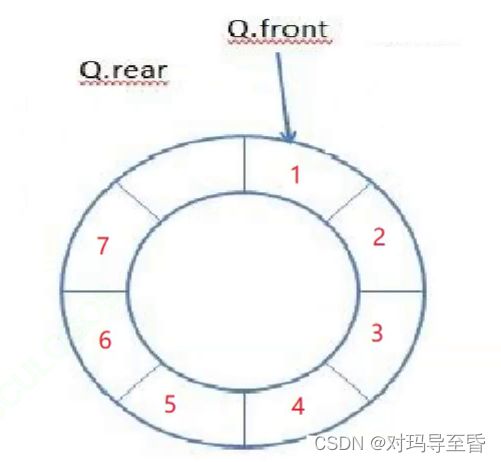
622. 设计循环队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
(1)链表判满
(2)数组判满 (rear是下标,开辟空间数==k+1)
typedef struct
{
int *a;
int front;
int tail;
int k;
} MyCircularQueue;
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
return obj->tail==obj->front;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
return (obj->tail+1)%(obj->k+1)==obj->front;
}
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k)
{
MyCircularQueue* obj =(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
obj->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
obj->front=obj->tail=0;
obj->k=k;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value)
{
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->a[obj->tail]=value;
obj->tail++; //别忘了放完之后,tail才++
obj->tail=(obj->tail)%(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->front++;
obj->front=(obj->front)%(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->a[obj->front];
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
if(obj->tail==0)
{
return obj->a[obj->k];
}
else
{
return obj->a[obj->tail-1]; //别忘了tail-1,因为push完之后tail要+1;
}
// return obj->a[(obj->tail+obj->k)%(obj->k+1)]; 也可以
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
free(obj->a); //从小往大释放
free(obj);
}
1.也符合先进先出
2.空间大小固定
3.就结果而言,数组更好用