Mysql 函数
命令行终端
连接服务端
打开cmd程序,进入到mysql安装目录的bin目录下
1、进入mysql的bin目录
cd C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.1\bin
2、连接mysql
mysql -uroot -p
show databases;
使用数据库
use 数据库名;
查看当前使用的数据库
select database();
创建数据库
create database 数据库名 charset=utf8;
例:
create database ceshi charset=utf8;
删除数据库
drop database 数据库名;
例:
drop database ceshi;
查看当前数据库
select database();
数据表
查看当前数据库中所有表
show tables;
查看表结构
desc 表名;
查看表的创建语句
show create table 表名;
例:
show create table students;
备份
以管理员身份运行cmd程序
运行mysqldump命令
cd C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.1\bin
mysqldump –uroot –p 数据库名 > ceshi.sql
# 按提示输入mysql的密码
恢复
先创建新的数据库
mysql -uroot –p 新数据库名 < ceshi.sql
# 根据提示输入mysql密码
内置函数
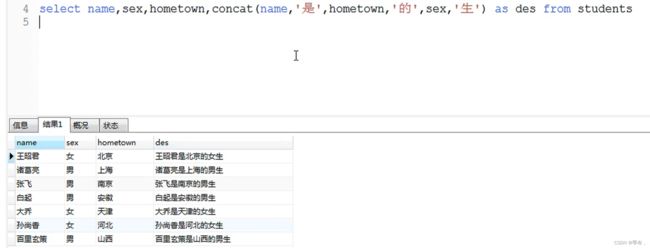
拼接字符串concat(str1,str2…)
select concat(12,34,'ab');
包含字符个数length(str)
select length('abc');
截取字符串
- left(str,len)返回字符串str的左端len个字符
- right(str,len)返回字符串str的右端len个字符
- substring(str,pos,len)返回字符串str的位置pos起len个字符
select substring('abc123',2,3);
去除空格
- ltrim(str)返回删除了左空格的字符串str
- rtrim(str)返回删除了右空格的字符串str
select ltrim(' bar ');
大小写转换,函数如下
- lower(str)
- upper(str)
select lower('aBcD');
数学函数
求四舍五入值round(n,d),n表示原数,d表示小数位置,默认为0
select round(1.6);
求x的y次幂pow(x,y)
select pow(2,3);
获取圆周率PI()
select PI();
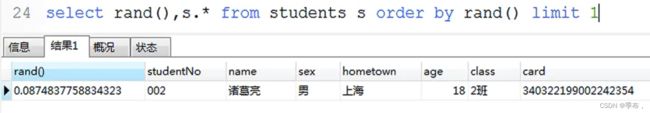
随机数rand(),值为0-1.0的浮点数
select rand();
日期时间函数
当前日期current_date()
select current_date();
当前时间current_time()
select current_time();
当前日期时间now()
select now();
日期格式化date_format(date,format)
- 参数format可选值如下
%Y 获取年,返回完整年份
%y 获取年,返回简写年份
%m 获取月,返回月份
%d 获取日,返回天值
%H 获取时,返回24进制的小时数
%h 获取时,返回12进制的小时数
%i 获取分,返回分钟数
%s 获取秒,返回秒数
例:将使用-拼接的日期转换为使用空格拼接
select date_format('2016-12-21','%Y %m %d');
流程控制
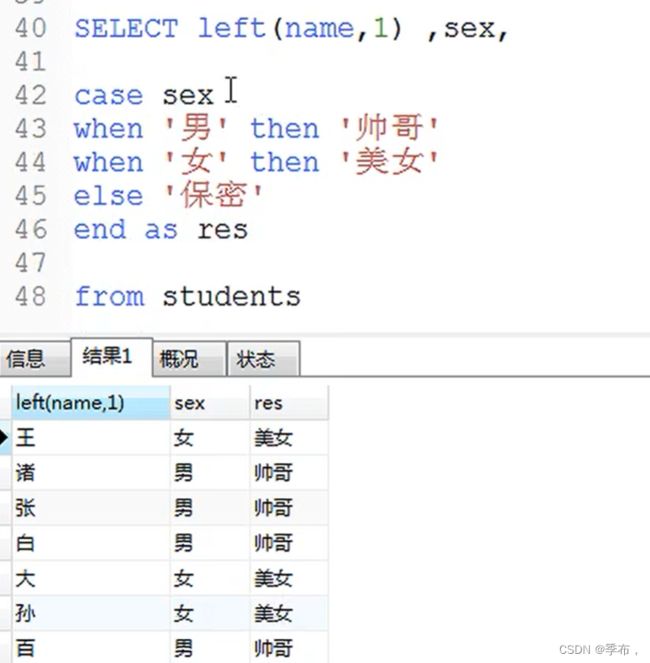
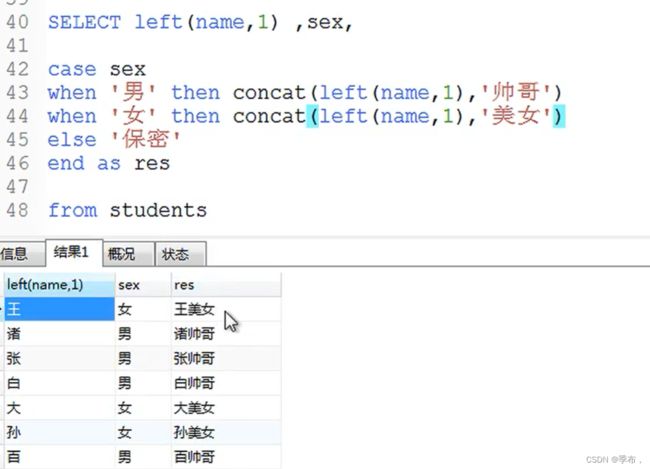
- case语法:等值判断
- 说明:当值等于某个比较值的时候,对应的结果会被返回;如果所有的比较值都不相等则返回else的结果;如果没有else并且所有比较值都不相等则返回null
case 值 when 比较值1 then 结果1 when 比较值2 then 结果2 ... else 结果 end
例:
select case 1 when 1 then 'one' when 2 then 'two' else 'zero' end as result;
自定义函数
命令行中使用
- 语法如下
delimiter $$
create function 函数名称(参数列表) returns 返回类型
begin
sql语句
end
$$
delimiter ;
- 说明:delimiter用于设置分割符,默认为分号
- 在“sql语句”部分编写的语句需要以分号结尾,此时回车会直接执行,所以要创建存储过程前需要指定其它符号作为分割符,此处使用//,也可以使用其它字符
示例
- 要求:创建函数py_trim,用于删除字符串左右两侧的空格
- step1:设置分割符
delimiter $$
- step2:创建函数
create function my_trim(str varchar(100)) returns varchar(100)
begin
return ltrim(rtrim(str));
end
$$
- step3:还原分割符
delimiter ;
使用自定义函数
select ' abc ',my_trim(' abc ')
索引
- 思考:在图书馆中是如何找到一本书的?
- 一般的应用系统对比数据库的读写比例在10:1左右,而且插入操作和更新操作很少出现性能问题,遇到最多的,也是最容易出问题的,还是一些复杂的查询操作,所以查询语句的优化显然是重中之重
- 当数据库中数据量很大时,查找数据会变得很慢
- 优化方案:索引
语法
查看索引
show index from 表名;
创建索引
方式一:建表时创建索引
create table create_index(
id int primary key,
name varchar(10) unique,
age int,
key (age)
);
方式二:对于已经存在的表,添加索引
如果指定字段是字符串,需要指定长度,建议长度与定义字段时的长度一致
字段类型如果不是字符串,可以不填写长度部分
create index 索引名称 on 表名(字段名称(长度))
例:
create index age_index on create_index(age);
create index name_index on create_index(name(10));
删除索引:
drop index 索引名称 on 表名;
示例
创建测试表testindex
create table test_index(title varchar(10));
向表中加入十万条数据
- 创建存储过程proc_test,在存储过程中实现插入数据的操作
- step1:定义分割符
delimiter //
step2:定义存储过程
create procedure proc_test()
begin
declare i int default 0;
while i<100000 do
insert into test_index(title) values(concat('test',i));
set i=i+1;
end while;
end
//
step3:还原分割符
delimiter ;
执行存储过程proc_test
call proc_test();
查询
开启运行时间监测:
set profiling=1;
查找第1万条数据test10000
select * from test_index where title='test10000';
查看执行的时间:
show profiles;
为表title_index的title列创建索引:
create index title_index on test_index(title(10));
执行查询语句:
select * from test_index where title='test10000';
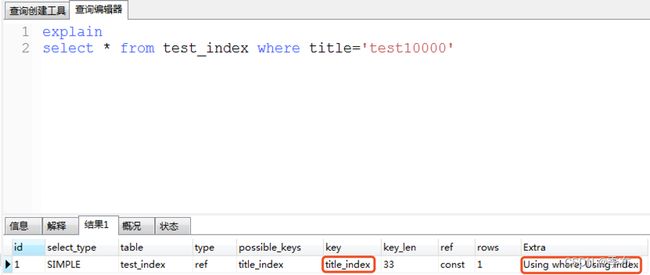
再次查看执行的时间
show profiles;
缺点
- 虽然索引大大提高了查询速度,同时却会降低更新表的速度,如对表进行INSERT、UPDATE和DELETE,因为更新表时,MySQL不仅要保存数据,还要保存一下索引文件
- 但是,在互联网应用中,查询的语句远远大于增删改的语句,甚至可以占到80%~90%,所以也不要太在意,只是在大数据导入时,可以先删除索引,再批量插入数据,最后再添加索引
分析查询
explain
select * from test_index where title='test10000'
外键foreign key
- 如果一个实体的某个字段指向另一个实体的主键,就称为外键。被指向的实体,称之为主实体(主表),也叫父实体(父表)。负责指向的实体,称之为从实体(从表),也叫子实体(子表)
- 对关系字段进行约束,当为从表中的关系字段填写值时,会到关联的主表中查询此值是否存在,如果存在则填写成功,如果不存在则填写失败并报错
查看外键
show create table 表名
设置外键约束
方式一:创建数据表的时候设置外键约束
注意: goods 中的 cate_id 的类型一定要和 goods_cates 表中的 cate_id 类型一致
create table goods_fk(
id int unsigned primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(150),
cate_id int unsigned,
brand_id int unsigned,
price decimal(10,3) default 0,
is_show bit default 1,
is_saleoff bit default 0,
foreign key(cate_id) references goods_cates(cate_id),
foreign key(brand_id) references goods_brands(brand_id)
);
foreign key(自己的字段) references 主表(主表字段)
方式二:对于已经存在的数据表设置外键约束
alter table 从表名 add foreign key (从表字段) references 主表(主表字段);
alter table goods add foreign key (cate_id) references goods_cates(cate_id);
alter table goods add foreign key (brand_id) references goods_brands(brand_id);
删除外键
-- 需要先获取外键约束名称
show create table goods;
-- 获取名称之后就可以根据名称来删除外键约束
alter table goods drop foreign key 外键名称;
alter table goods drop foreign key goods_ibfk_1;
alter table goods drop foreign key goods_ibfk_2;
从表中插入数据
insert into goods_fk (name,cate_id,brand_id,price)
values('LaserJet Pro P1606dn 黑白激光打印机','20','20','1849'); -- 插入不成功,因为主表中没有20这个值
insert into goods_fk (name,cate_id,brand_id,price)
values('LaserJet Pro P1606dn 黑白激光打印机','1','1','1849'); -- 可以插入成功
在实际开发中,很少会使用到外键约束,会极大的降低表更新的效率