Google单元测试sample分析(三)
本文介绍关于模版类该如何设置单元测试
源码目录在googletest/googletest/目录下的prime_tables.h和sample6_unittest.cc
prime_tables.h
// Copyright 2008 Google Inc.
// All Rights Reserved.
//
// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
// met:
//
// * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
// * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
// copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer
// in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
// distribution.
// * Neither the name of Google Inc. nor the names of its
// contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
// this software without specific prior written permission.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
// This provides interface PrimeTable that determines whether a number is a
// prime and determines a next prime number. This interface is used
// in Google Test samples demonstrating use of parameterized tests.
#ifndef GTEST_SAMPLES_PRIME_TABLES_H_
#define GTEST_SAMPLES_PRIME_TABLES_H_
#include 该文件定义了一个抽象类PrimeTable ,OnTheFlyPrimeTable 和PreCalculatedPrimeTable 分别实现该类。
sample6_unittest.cc
#include "prime_tables.h"
#include "gtest/gtest.h"
namespace {
// First, we define some factory functions for creating instances of
// the implementations. You may be able to skip this step if all your
// implementations can be constructed the same way.
template <class T>
PrimeTable* CreatePrimeTable();
template <>
PrimeTable* CreatePrimeTable<OnTheFlyPrimeTable>() {
return new OnTheFlyPrimeTable;
}
template <>
PrimeTable* CreatePrimeTable<PreCalculatedPrimeTable>() {
return new PreCalculatedPrimeTable(10000);
}
// Then we define a test fixture class template.
template <class T>
class PrimeTableTest : public testing::Test {
protected:
// The ctor calls the factory function to create a prime table
// implemented by T.
PrimeTableTest() : table_(CreatePrimeTable<T>()) {}
~PrimeTableTest() override { delete table_; }
// Note that we test an implementation via the base interface
// instead of the actual implementation class. This is important
// for keeping the tests close to the real world scenario, where the
// implementation is invoked via the base interface. It avoids
// got-yas where the implementation class has a method that shadows
// a method with the same name (but slightly different argument
// types) in the base interface, for example.
PrimeTable* const table_;
};
#if GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST
using testing::Types;
// Google Test offers two ways for reusing tests for different types.
// The first is called "typed tests". You should use it if you
// already know *all* the types you are gonna exercise when you write
// the tests.
// To write a typed test case, first use
//
// TYPED_TEST_SUITE(TestCaseName, TypeList);
//
// to declare it and specify the type parameters. As with TEST_F,
// TestCaseName must match the test fixture name.
// The list of types we want to test.
typedef Types<OnTheFlyPrimeTable, PreCalculatedPrimeTable> Implementations;
TYPED_TEST_SUITE(PrimeTableTest, Implementations);
// Then use TYPED_TEST(TestCaseName, TestName) to define a typed test,
// similar to TEST_F.
TYPED_TEST(PrimeTableTest, ReturnsFalseForNonPrimes) {
// Inside the test body, you can refer to the type parameter by
// TypeParam, and refer to the fixture class by TestFixture. We
// don't need them in this example.
// Since we are in the template world, C++ requires explicitly
// writing 'this->' when referring to members of the fixture class.
// This is something you have to learn to live with.
EXPECT_FALSE(this->table_->IsPrime(-5));
EXPECT_FALSE(this->table_->IsPrime(0));
EXPECT_FALSE(this->table_->IsPrime(1));
EXPECT_FALSE(this->table_->IsPrime(4));
EXPECT_FALSE(this->table_->IsPrime(6));
EXPECT_FALSE(this->table_->IsPrime(100));
}
TYPED_TEST(PrimeTableTest, ReturnsTrueForPrimes) {
EXPECT_TRUE(this->table_->IsPrime(2));
EXPECT_TRUE(this->table_->IsPrime(3));
EXPECT_TRUE(this->table_->IsPrime(5));
EXPECT_TRUE(this->table_->IsPrime(7));
EXPECT_TRUE(this->table_->IsPrime(11));
EXPECT_TRUE(this->table_->IsPrime(131));
}
TYPED_TEST(PrimeTableTest, CanGetNextPrime) {
EXPECT_EQ(2, this->table_->GetNextPrime(0));
EXPECT_EQ(3, this->table_->GetNextPrime(2));
EXPECT_EQ(5, this->table_->GetNextPrime(3));
EXPECT_EQ(7, this->table_->GetNextPrime(5));
EXPECT_EQ(11, this->table_->GetNextPrime(7));
EXPECT_EQ(131, this->table_->GetNextPrime(128));
}
// That's it! Google Test will repeat each TYPED_TEST for each type
// in the type list specified in TYPED_TEST_SUITE. Sit back and be
// happy that you don't have to define them multiple times.
#endif // GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST
以上代码中PrimeTableTest类继承自testing::Test,类内部定义个PrimeTable类型指针。
如下是Google Test框架中的Typed Test(带类型的测试)功能,在testing::Types命名空间中
#if GTEST_HAS_TYPED_TEST
using testing::Types;
如下Implementations是一个模板参数,它包含了两种实现的类型。
typedef Types
TYPED_TEST_SUITE(PrimeTableTest, Implementations);
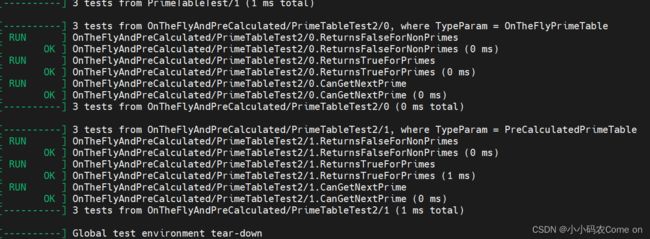
最后运行结果如下:
可以看出PrimeTableTest测试夹具中,针对OnTheFlyPrimeTable和PreCalculatedPrimeTable两种类型都测试一次。
template <class T>
class PrimeTableTest2 : public PrimeTableTest<T> {
};
// Then, declare the test case. The argument is the name of the test
// fixture, and also the name of the test case (as usual). The _P
// suffix is for "parameterized" or "pattern".
TYPED_TEST_SUITE_P(PrimeTableTest2);
// Next, use TYPED_TEST_P(TestCaseName, TestName) to define a test,
// similar to what you do with TEST_F.
TYPED_TEST_P(PrimeTableTest2, ReturnsFalseForNonPrimes) {
EXPECT_FALSE(this->table_->IsPrime(-5));
EXPECT_FALSE(this->table_->IsPrime(0));
EXPECT_FALSE(this->table_->IsPrime(1));
EXPECT_FALSE(this->table_->IsPrime(4));
EXPECT_FALSE(this->table_->IsPrime(6));
EXPECT_FALSE(this->table_->IsPrime(100));
}
TYPED_TEST_P(PrimeTableTest2, ReturnsTrueForPrimes) {
EXPECT_TRUE(this->table_->IsPrime(2));
EXPECT_TRUE(this->table_->IsPrime(3));
EXPECT_TRUE(this->table_->IsPrime(5));
EXPECT_TRUE(this->table_->IsPrime(7));
EXPECT_TRUE(this->table_->IsPrime(11));
EXPECT_TRUE(this->table_->IsPrime(131));
}
TYPED_TEST_P(PrimeTableTest2, CanGetNextPrime) {
EXPECT_EQ(2, this->table_->GetNextPrime(0));
EXPECT_EQ(3, this->table_->GetNextPrime(2));
EXPECT_EQ(5, this->table_->GetNextPrime(3));
EXPECT_EQ(7, this->table_->GetNextPrime(5));
EXPECT_EQ(11, this->table_->GetNextPrime(7));
EXPECT_EQ(131, this->table_->GetNextPrime(128));
}