C/C++开发资源及下载汇总
开个新帖子,记录需要用到的网络资源
runtime官网
Latest supported Visual C++ Redistributable downloads | Microsoft DocsThis article lists the download links for the latest versions of Visual C++ Redistributable packages.![]() https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-CN/cpp/windows/latest-supported-vc-redist?view=msvc-170
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-CN/cpp/windows/latest-supported-vc-redist?view=msvc-170
Using GCC with MinGW
In this tutorial, you configure Visual Studio Code to use the GCC C++ compiler (g++) and GDB debugger from mingw-w64 to create programs that run on Windows.
MinGW-w64GCC for Windows 64 & 32 bitshttps://www.mingw-w64.org/我选的是MSYS2
MSYS2
安装完成,运行MSYS2 64bit
First run pacman -Syu 进行升级
Run "MSYS2 MSYS" from Start menu. Update the rest of the base packages with pacman -Su:
Now MSYS2 is ready for you. You will probably want to install some tools and the mingw-w64 GCC to start compiling:
pacman -S --needed base-devel mingw-w64-x86_64-toolchain配置VSCODE
Prerequisites#
To successfully complete this tutorial, you must do the following steps:
Check your MinGW installation#
-
Install Visual Studio Code.
-
Install the C/C++ extension for VS Code. You can install the C/C++ extension by searching for 'c++' in the Extensions view (Ctrl+Shift+X).
-
Get the latest version of Mingw-w64 via MSYS2, which provides up-to-date native builds of GCC, Mingw-w64, and other helpful C++ tools and libraries. Click here to download the MSYS2 installer. Then follow the instructions on the MSYS2 website to install Mingw-w64.
-
Add the path to your Mingw-w64
binfolder to the WindowsPATHenvironment variable by using the following steps:- In the Windows search bar, type 'settings' to open your Windows Settings.
- Search for Edit environment variables for your account.
- Choose the
Pathvariable and then select Edit. - Select New and add the Mingw-w64 destination folder path to the system path. The exact path depends on which version of Mingw-w64 you have installed and where you installed it. If you used the settings above to install Mingw-w64, then add this to the path:
C:\msys64\mingw64\bin. - Select OK to save the updated PATH. You will need to reopen any console windows for the new PATH location to be available.
To check that your Mingw-w64 tools are correctly installed and available, open a new Command Prompt and type:
g++ --version
gdb --versionIf you don't see the expected output or g++ or gdb is not a recognized command, make sure your PATH entry matches the Mingw-w64 binary location where the compilers are located. If the compilers do not exist at that PATH entry, make sure you followed the instructions on the MSYS2 website to install Mingw-w64.
Create Hello World#
From a Windows command prompt, create an empty folder called projects where you can place all your VS Code projects. Then create a sub-folder called helloworld, navigate into it, and open VS Code in that folder by entering the following commands:
mkdir projects
cd projects
mkdir helloworld
cd helloworld
code .The "code ." command opens VS Code in the current working folder, which becomes your "workspace". As you go through the tutorial, you will see three files created in a .vscode folder in the workspace:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector msg {"Hello", "C++", "World", "from", "VS Code", "and the C++ extension!"};
for (const string& word : msg)
{
cout << word << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} tasks.json(build instructions)launch.json(debugger settings)c_cpp_properties.json(compiler path and IntelliSense settings)
Add a source code file#
In the File Explorer title bar, select the New File button and name the file helloworld.cpp.
Build helloworld.cpp#
Next, you'll create a tasks.json file to tell VS Code how to build (compile) the program. This task will invoke the g++ compiler to create an executable file based on the source code.
From the main menu, choose Terminal > Configure Default Build Task. In the dropdown, which will display a tasks dropdown listing various predefined build tasks for C++ compilers. Choose g++.exe build active file, which will build the file that is currently displayed (active) in the editor.
This will create a tasks.json file in a .vscode folder and open it in the editor.
Your new tasks.json file should look similar to the JSON below:
{
"tasks": [
{
"type": "cppbuild",
"label": "C/C++: g++.exe build active file",
"command": "C:/msys64/mingw64/bin/g++.exe",
"args": ["-g", "${file}", "-o", "${fileDirname}\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe"],
"options": {
"cwd": "${fileDirname}"
},
"problemMatcher": ["$gcc"],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"detail": "compiler: C:/msys64/mingw64/bin/g++.exe"
}
],
"version": "2.0.0"
}The command setting specifies the program to run; in this case that is g++. The args array specifies the command-line arguments that will be passed to g++. These arguments must be specified in the order expected by the compiler. This task tells g++ to take the active file (${file}), compile it, and create an executable file in the current directory (${fileDirname}) with the same name as the active file but with the .exe extension (${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe), resulting in helloworld.exe for our example.
Note: You can learn more about
tasks.jsonvariables in the variables reference.
The label value is what you will see in the tasks list; you can name this whatever you like.
The "isDefault": true value in the group object specifies that this task will be run when you press Ctrl+Shift+B. This property is for convenience only; if you set it to false, you can still run it from the Terminal menu with Tasks: Run Build Task.
Running the build#
-
Go back to
helloworld.cpp. Your task builds the active file and you want to buildhelloworld.cpp. -
To run the build task defined in
tasks.json, press Ctrl+Shift+B or from the Terminal main menu choose Run Build Task. -
When the task starts, you should see the Integrated Terminal panel appear below the source code editor. After the task completes, the terminal shows output from the compiler that indicates whether the build succeeded or failed. For a successful g++ build, the output looks something like this:
-
Create a new terminal using the + button and you'll have a new terminal with the
helloworldfolder as the working directory. Rundirand you should now see the executablehelloworld.exe.
-
You can run
helloworldin the terminal by typinghelloworld.exe(or.\helloworld.exeif you use a PowerShell terminal).
Note: You might need to press Enter a couple of times initially to see the PowerShell prompt in the terminal. This issue should be fixed in a future release of Windows.
Modifying tasks.json#
You can modify your tasks.json to build multiple C++ files by using an argument like "${workspaceFolder}\\*.cpp" instead of ${file}. This will build all .cpp files in your current folder. You can also modify the output filename by replacing "${fileDirname}\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe" with a hard-coded filename (for example "${workspaceFolder}\\myProgram.exe").
Debug helloworld.cpp#
Next, you'll create a launch.json file to configure VS Code to launch the GDB debugger when you press F5 to debug the program.
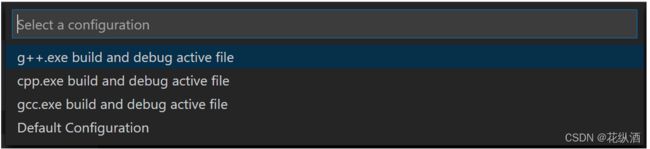
- From the main menu, choose Run > Add Configuration... and then choose C++ (GDB/LLDB).
- You'll then see a dropdown for various predefined debugging configurations. Choose g++.exe build and debug active file.
VS Code creates a launch.json file, opens it in the editor, and builds and runs 'helloworld'.
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "g++.exe - Build and debug active file",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${fileDirname}\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${fileDirname}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"miDebuggerPath": "C:\\msys64\\mingw64\\bin\\gdb.exe",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
],
"preLaunchTask": "C/C++: g++.exe build active file"
}
]
}The program setting specifies the program you want to debug. Here it is set to the active file folder ${fileDirname} and active filename with the .exe extension ${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe, which if helloworld.cpp is the active file will be helloworld.exe.
By default, the C++ extension won't add any breakpoints to your source code and the stopAtEntry value is set to false.
Change the stopAtEntry value to true to cause the debugger to stop on the main method when you start debugging.
Note: The
preLaunchTasksetting is used to specify task to be executed before launch. Make sure it is consistent with thetasks.jsonfilelabelsetting.
Start a debugging session#
- Go back to
helloworld.cppso that it is the active file. - Press F5 or from the main menu choose Run > Start Debugging. Before you start stepping through the source code, let's take a moment to notice several changes in the user interface:
-
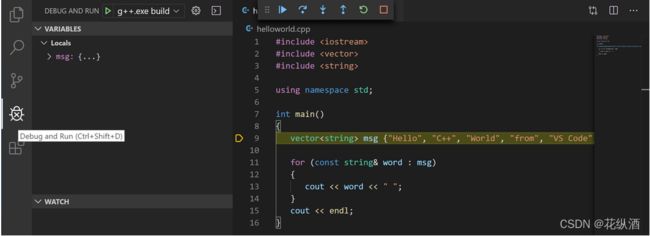
The Integrated Terminal appears at the bottom of the source code editor. In the Debug Output tab, you see output that indicates the debugger is up and running.
-
The editor highlights the first statement in the
mainmethod. This is a breakpoint that the C++ extension automatically sets for you:
-
The Run view on the left shows debugging information. You'll see an example later in the tutorial.
-
At the top of the code editor, a debugging control panel appears. You can move this around the screen by grabbing the dots on the left side.