NIO之ByteBuffer_NIO之网络IO_与ChannelNetty初窥门径
NIO之ByteBuffer与Channel
传统IO:
byte[] <= inputStream <= 文件 => outputStream => byte[]
NIO:
文件 => inputChannel <=> buffer <=> outputChannel => 文件
文件 <= inputChannel <=> outputChannel => 文件
- 文件复制, 并测试ByteBuffer常用API
position: 当前指针位置; limit: 当前内容的最大位置(例如: buffer内容为"hello", 容量为20, limit就是5); capacity: 最大容量
/**
* 测试Buffer的position, limit, capacity, clear, flip
* @author regotto
*/
public class NioTest1 {
/**
* 下面的代码中, clear与flip效果一样.
* 没有clear,flip,position的位置将会一直等于limit, 根据各属性之间的大小关系, position一定不会大于limit,
* 所以在下面的read中, 读取到的值将一直都是0(代表当前读取到的位置), read一直不会等于-1, 代码出现死循环
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileChannel inputChannel = new FileInputStream("input.txt").getChannel();
FileChannel outputChannel = new FileOutputStream("output.txt").getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
while(true){
//此处不进行clear, 此时position还是处于limit的位置, read将一直保持当前位置出现
//死循环
buffer.clear();
int read = inputChannel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("read: " + read);
if (-1 == read){
break;
}
//重置buffer
buffer.flip();
outputChannel.write(buffer);
}
inputChannel.close();
outputChannel.close();
}
}
clear, flip源码如下:
public final Buffer clear() {
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
public final Buffer flip() {
limit = position;
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
- DirectByteBuffer
ByteBuffer.allocate(1024) => HeapByteBuffer, 内部使用的就是byte[], 底层源码如下
public static ByteBuffer allocate(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
return new HeapByteBuffer(capacity, capacity);
}
//HeapByteBuffer extends ByteBuffer
//ByteBuffer构造函数如下:
ByteBuffer(int mark, int pos, int lim, int cap, // package-private
byte[] hb, int offset){
super(mark, pos, lim, cap);
this.hb = hb;
this.offset = offset;
}
HeapByteBuffer位于JVM堆空间, 当使用HeapByteBuffer进行内容复制时, 存在2个复制过程: 应用程序 => 应用程序缓冲区 => 内核缓冲区 => 文件; 这种情况下, 2个复制过程存在一定的性能问题;
ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024) => DirectByteBuffer, DirectByteBuffer使用native方法创建数组, 数组不再位于JVM的Heap中, 而是位于内核内存中, 这样就避免了一次数据拷贝(拷贝的原因在于JVM中数据的地址会改变, 在GC下): 应用程序缓冲区 -> 内核缓冲区; 所谓的零拷贝, 加快速度, C/C++开辟的数组空间都是位于内核缓冲区
DirectByteBuffer底层源码:
public static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity) {
return new DirectByteBuffer(capacity);
}
//unsafe中底层内存分配
base = unsafe.allocateMemory(size);
public native long allocateMemory(long var1);
使用DirectByteBuffer进行文件复制:
/**
* 测试DirectByteBuffer
* @author regotto
*/
public class NioTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileChannel inputChannel = new FileInputStream("input.txt").getChannel();
FileChannel outputChannel = new FileOutputStream("output.txt").getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(4);
while(true){
buffer.clear();
int read = inputChannel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("read: " + read);
if (-1 == read){
break;
}
buffer.flip();
outputChannel.write(buffer);
// buffer.flip();
}
inputChannel.close();
outputChannel.close();
}
/**
* 进行文件复制
*/
public void test() throws Exception {
FileChannel fisChannel = new FileInputStream("text1.txt").getChannel();
FileChannel fosChannel = new FileOutputStream("text2.txt").getChannel();
//transferTo与transferFrom效果一样
fisChannel.transferTo(0, fisChannel.size(), fosChannel);
fisChannel.close();
fosChannel.close();
}
}
- 使用堆外内存进行文件内容复制(使用块内存提高性能)
/**
* 测试MappedByteBuffer
* 使用堆外内存对文件内容进行修改
* @author regotto
*/
public class NioTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//下面的0, 4代表从0号位开始,将4个大小的空间映射到堆外内存
MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = new RandomAccessFile("input.txt", "rw").
getChannel().map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 4);
mappedByteBuffer.put(0, (byte) 'a');
mappedByteBuffer.put(0, (byte) 'a');
mappedByteBuffer.put(0, (byte) 'a');
}
}
NIO之网络IO
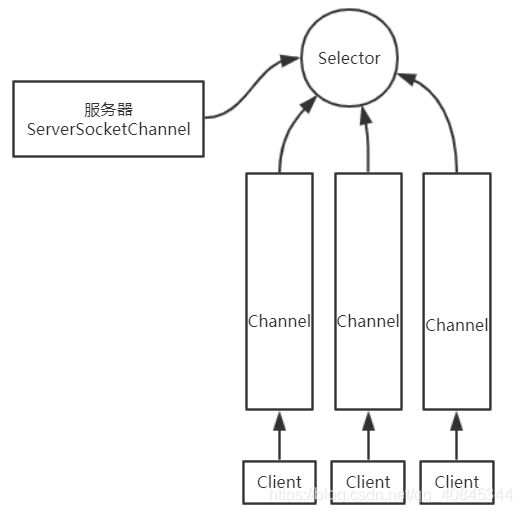
Selector: 检测Channel是否存在事件发生
ServerSocketChannel: 服务器
Channel: 管道
Client: 客户端
selectionKey的4种状态:
OP_ACCEPT: 网络已连接 value = 16
OP_CONNECT: 连接已建立 value = 8
OP_READ OP_WRITE: 读/写操作, value = 1 或value = 4
根据上面结构图编写简单案例代码:
NioServer
/**
* server
*/
public class NioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
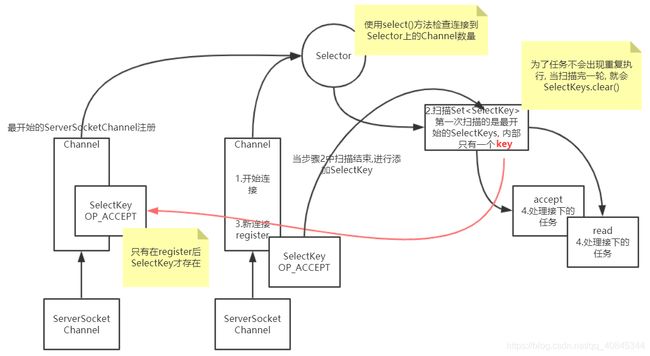
Selector selector = Selector.open();
SelectionKey selectionKey = serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
//设置selector监控, 监控Channel的连接情况, 此处除去第一次的ServerSocketChannel注册, 监控时长2s
if (selector.select(2000) == 0) {
System.out.println("------当前没有要处理的Channel, 我去处理其他事------");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
continue;
}
//此时有Channel进行连接, 获取selectedKeys, 处理每一个Channel的对象事件
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
selectionKeys.forEach(key -> {
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
System.out.println("OP_ACCEPT");
//说明此处的key对应的是最开始前面register的ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
//此处对象的hash值相同
System.out.println("(ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(): " + server.hashCode());
System.out.println("ServerSocketChannel.open(): " + serverSocketChannel.hashCode());
try {
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//此处注册的时候就附加一个缓冲区, 可用于传输对象
//当执行register的时候, 就会生成一个对应的SelectionKey事件, 当前的selectionKeys遍历完成, 就会将该selectionKey添加到set集合中
SelectionKey socketChannelReadRegister = socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
try {
socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
System.out.println("客户端内容: " + new String(byteBuffer.array(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//这里使用remove与下面使用clear效果一样, 都是清除当前已经执行过的Channel, 避免重复执行
//当前的Channel对应的事件被处理过, 就不再被处理, 使用这种写法较为恰当
selectionKeys.remove(key);
});
// selectionKeys.clear();
}
}
}
NioClient
/**
* client
*/
public class NioClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
if (!socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9999))) {
//连接服务端失败, 使用finishConnect进行连接, 此处finishConnect非阻塞
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
System.out.println("连接同时, 干其他事情");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
}
}
//return new HeapByteBuffer(capacity, capacity);
// ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//return new HeapByteBuffer(array, offset, length);
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello world".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
socketChannel.write(buffer);
//此处阻塞, 若关闭连接, server会抛出异常
System.out.println("进入睡眠");
Thread.currentThread().join();
}
}
Netty初窥门径
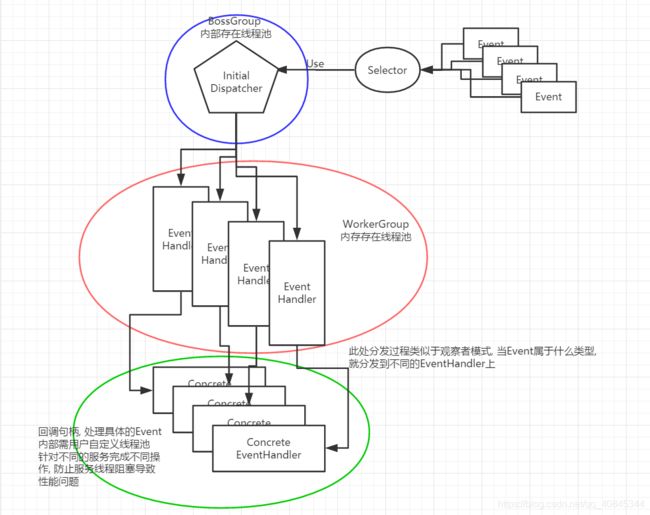
BossGroup: 处理客户端连接请求
WorkGroup: 处理网络读写操作
二者使用NioEventLoopGroup不断循环处理任务线程, NioEventLoopGroup内部都有一个selector, 监听每个Channel连接情况
NioEventLoopGroup内部使用串行化设计: 消息读取->解码->处理->编码->发送
一个NioEventLoopGroup包含多个NioEventLoop
一个NioEventLoop包含一个Selector, 一个任务队列
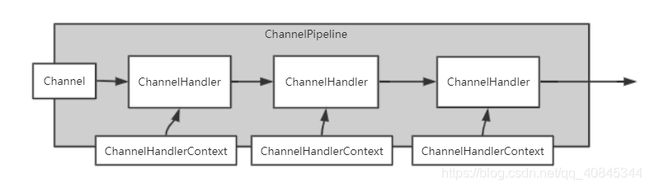
每个NioChannel都会绑定一个自己的ChannelPipeline
ChannelPipeline: Handler集合, 负责处理/拦截inbound, outbound操作
ChannelHandlerContext: 事件处理器上下文对象, 内部包含每个具体的ChannelHandler, 也绑定对应Channel, pipeline信息
- 简单入门案例:
NettyServer:
/**
* 服务器端
*/
public class NettyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//线程池中任务队列数: ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128
//让连接保持活动状态: ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap().
group(bossGroup, workGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new NettyServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9999).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
NettyServerHandler:
public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("客户端发送的内容: " + byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
/**
* 数据读取完成
* @param ctx Channel上下文对象
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("就是没钱", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//出现异常, 直接关闭上下文对象
ctx.close();
}
}
NettyClient
/**
* 客户端
*/
public class NettyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap().group(workGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new NettyClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 9999).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}
}
NettyClientHandler:
public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/**
* 通道准备就绪, 当前已经连接
* @param ctx
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("老板, 还钱吧".getBytes(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)));
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
}