什么是MySQL数据库?看这一篇干货文章就够了!
前言
为啥学习MySQL呢?因为MySQL是最流行的关系型数据库管理系统之一,在web应用方面,MySQL是最好的软件。MySQL所使用的sql语言是用于访问数据库的最常用标准化语言。
这篇文章,我会为大家详细梳理MySQL数据库的方方面面。
1.MySQL的入门
什么是数据库呢?
数据库,它是按照数据结构来组织,存储和管理数据的仓库。
数据库管理系统, 指数据库系统中对数据进行管理的软件系统。
细节掌握:
安装配置,常用命令,操作数据库;
整型与浮点型,日期时间型与字符型;
创建与查看数据库表,修改数据库表,删除数据库表;
非空约束,主键约束,唯一约束,默认约束,外键约束;
管理工具:
MySQL Workbench,SQLyog;单表数据记录的插入与自动编号,单表数据记录的更新,单表数据记录的删除,单表数据记录的查询,对查询结果进行分组,对查询结果进行排序,通过limit语句限制查询记录的数量;
mysql的运算符,数值函数,字符函数,日期时间函数,聚合函数,信息函数与加密函数;
使用比较运算符引发的子查询,插入记录时使用的子查询
多表连接,内连接,外连接,自连接,多表更新,多表删除
创建,使用自定义函数
创建存储过程,使用存储过程
mysql官网:

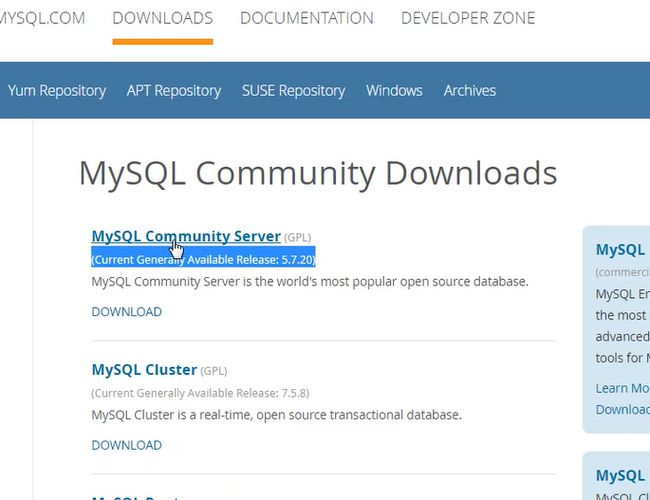
安装包下载:(安装操作)



点击安装:



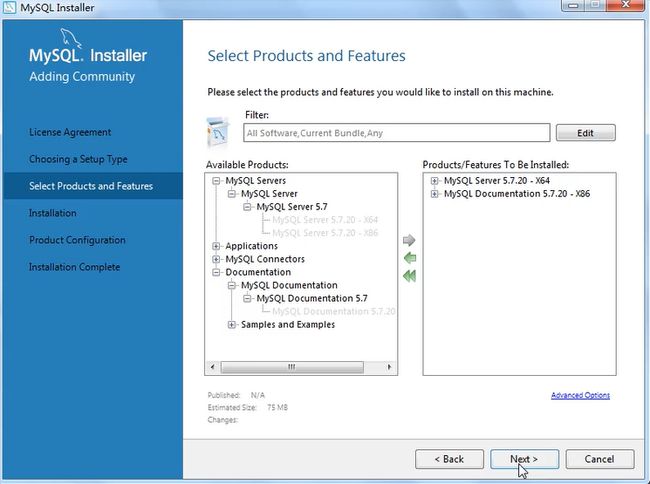

产品配置的操作:
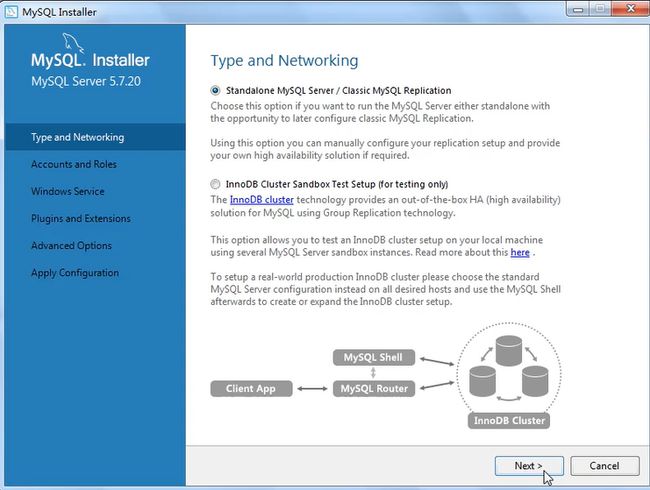




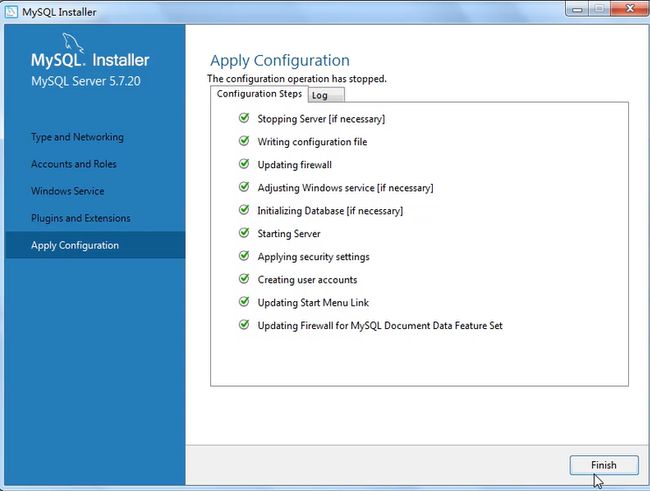
打开服务框用win+r,输入services.msc
2. mysql目录结构
bin目录:用于存储一些可执行文件include目录:用于存储包含的一些头文件lib目录:用于存储一些库文件share目录:用于存储错误信息,字符集文件等data目录:用于放置一些日志文件以及数据库my.ini文件:数据库的配置文件
启动与停止:


mysql参数:
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
-u |
用户名 |
-p |
密码 |
-V |
输出版本信息并且退出 |
-h |
主机地址 |
3.常用命令
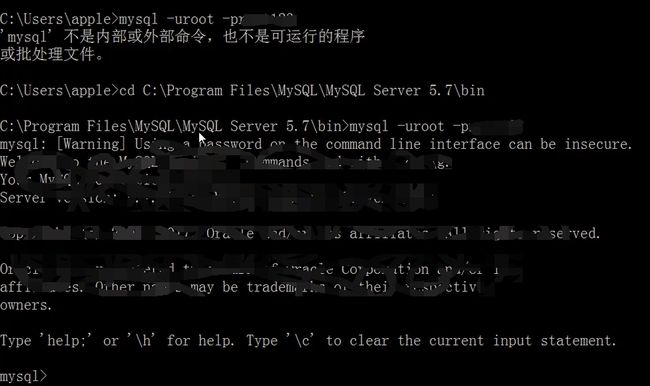
修改用户密码的命令:
mysqladmin 命令用于修改用户密码
mysqladmin 命令格式:
mysqladmin -u用户名 -p旧密码 password新密码

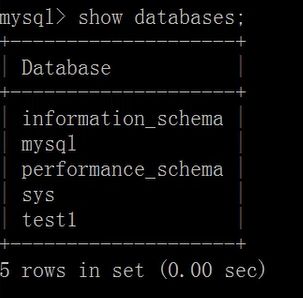
显示数据库的命令
show databases;

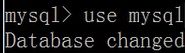
使用数据库的命令
use 数据库的名称
显示当前连接的信息
显示当前连接的数据库:
select database();显示当前服务器版本:
select version();显示当前日期时间:
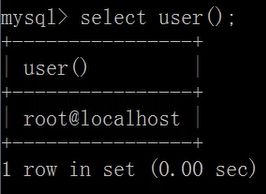
select now();显示当前用户:
select user();


4.操作数据库(创建,修改,删除)
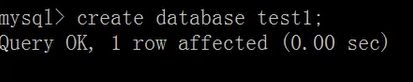
创建数据库SQL:
create database [if not exists] db_name
[default] character set [=] charset_name
create database database_name;

修改数据库的语法格式:
alter database db_name
[default] character set [=] charset_name


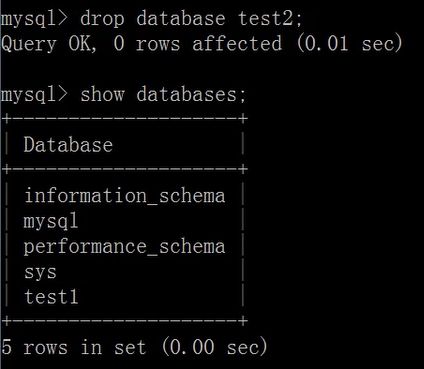
删除数据库语法格式:
drop database [if exitsts] db_name;
5.数据库-数据类型
了解数据类型:(借助图书管理系统)
图书类别表:
类别编号(category_id) 类别名称(category) 父类别(parent_id)
1 计算机 0
2 医学 0
图书信息表:
图书编号(book_id) 类别编号(book_category_id) 书名(book_name) 作者(author) 价格(price) 出版社(press) 出版时间(pubdate) 库存(store)
借阅信息表:
图书编号(book_id) 身份证号(card_id) 借出日期(borrow_date) 归还日期(return_date) 是否归还(status)
读者信息表
身份证号(card_id) 姓名(name) 性别(sex) 年龄(age) 联系电话(tel) 余额(balance)
数据类型:
整型:TINYINT-1字节 SMALLINT-2字节 MEDIUMINT-3字节 INT-4字节 BIGINT-8字节
浮点数类型和定点数类型:
float-4个字节
double-8个字节
decimal
日期时间类型:

字符型:

6.数据库表结构的操作
创建和查看数据表
创建数据表:create table
create table <表名>
(
列名1 数据类型[列级别约束条件][默认值],
列名2 数据类型[列级别约束条件][默认值],
...
[表级别约束条件]
);
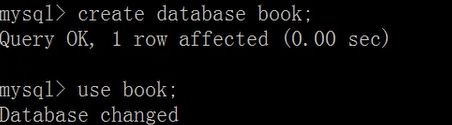


查看数据库表:
show tables [from db_name];
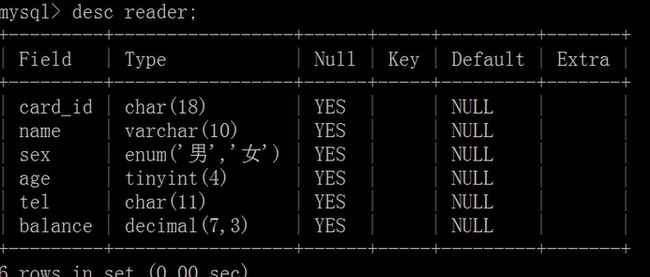
查看数据表基本结构:
show columns from tbl_name;
describe <表名> /DESC<表名>

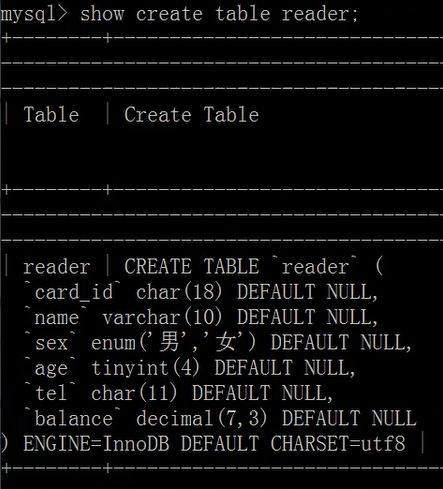
show create table tbl_name;
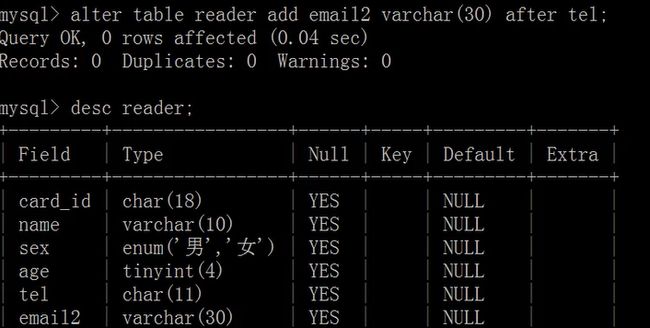
修改数据库表
添加列:
alter table <表名>
add <新列名> <数据类型>
[ 约束条件 ] [first | after 已存在列名];

修改列名:
alter table <表名>
change <旧列名> <新列名> <新数据类型>;

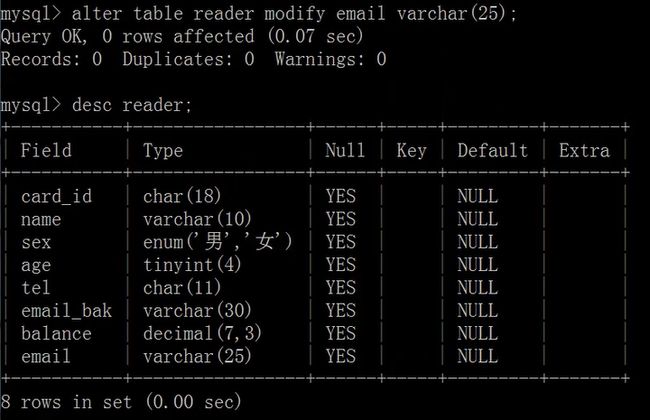
修改列的数据类型:
alter table <表名> MODIFY <列名> <数据类型>
修改列的排列位置
alter table<表名>
MODIFY <列1> <数据类型> FIRST|AFTER<列2>
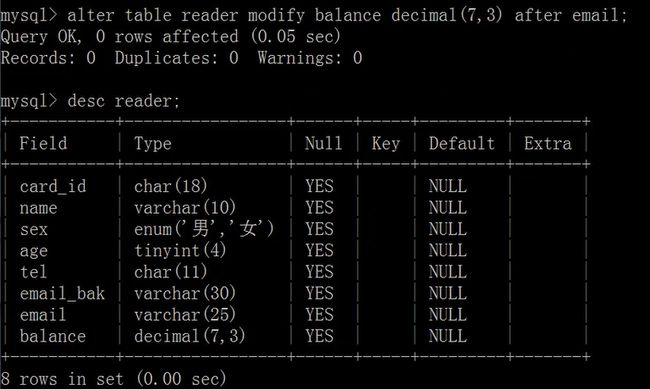
删除列:
alter table <表名> drop <列名>;
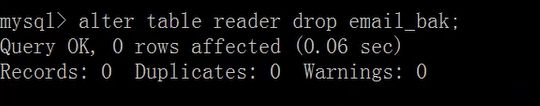
修改表名:
alter table <旧表名> RENAME [TO] <新表名>;
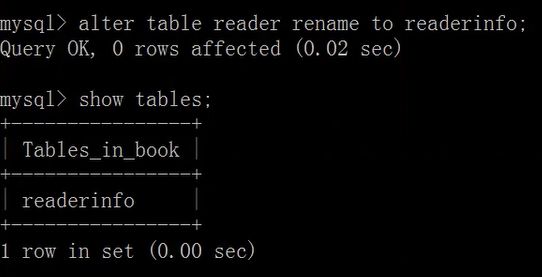
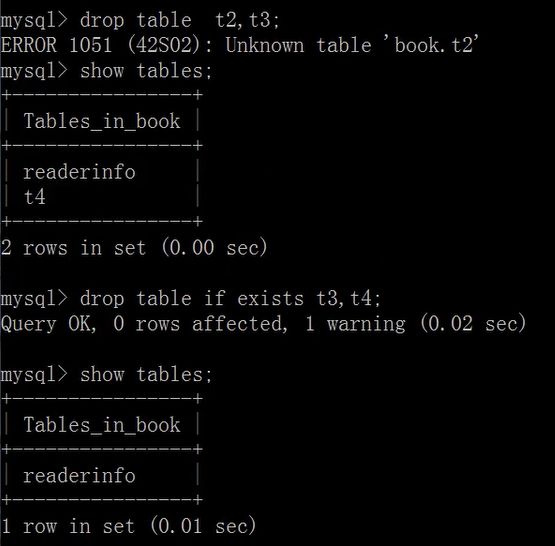
删除数据库表
drop table [if exists] 表1,表2,...表n;


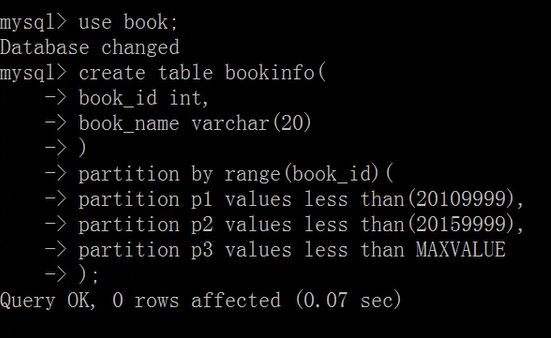
查看表分区

创建表分区:使用partition by类型(字段)
使用values less than操作符定义分区
create table bookinfo(
book_id int,
book_name varchar(20)
)
partition by range(book_id)(
partition p1 values less than(20101010),
partition p3 values less than MAXVALUE
);

7.子查询
select price from bookinfo where book_id = 20101010;
select * from readerinfo;
update readerinfo set balance = balance-(select price from bookinfo where book_id = 20101010) * 0.05 where card_id = '2323232342sxxxxx';
什么是子查询呢?
它是指嵌套在其他sql语句内的查询语句。
select * from table1 where col1 = (select col2 from table2);
insert into bookcategory(category,parent_id)values('x',2),('y',2);
insert into bookinfo(book_id,book_category_id,book_name,author,price,press,pubdate,store)
values
(45245244, 6, 'x', '1,2,3 等', 115, '出版社', '2020-06-01',10),
(45342545, 6, 'y', '1, 2',27.8, '出版社', '2020-07-01', 5);
update readerinfo set balance = 500 where card_id = '683246';
insert into borrowinfo(book_id,card_id,borrow_date,return_date,status)
values
(35452455,'5724154','2020-10-10','2020-11-10','否');
查询借阅信息表, 显示借 xx这本书的借阅记录
select * from borrowinfo where book_id = (select book_id from bookinfo where book_name = 'xx');
查询图书信息表, 显示图书价格小于图书平均价格的所有图书信息
select * from bookinfo where price < (select round(avg(price),2) from bookinfo);
查询图书信息表,显示图书类别不是’数据库’的所有图书信息
select * from bookinfo where book_category_id<>(select category_id from bookcategory where category = '数据库');
查询图书信息表,显示图书类别为’计算机’的所有图书信息
select * from bookcategory;
select * from bookinfo where book_category_id = ANY(select category_id from bookcategory where parent_id = 1);
select * from bookinfo where price > ANY (select price from bookinfo where book_category_id =4);
select * from bookinfo where price > ALL (select price from bookinfo where book_category_id =4);
查询图书信息表,显示图书类别为’2’的所有图书信息
in 后面的子查询返回一个数据列,等于数据列里的任意一个值都是满足条件的
select * from bookinfo where book_category_id in (select category_id from bookcategory where parent_id = 2);
select * from bookinfo where book_category_id = any (select category_id from bookcategory where parent_id = 2);
查看图书类别表中是否有’y’的类别,如果有,则查看图书信息表
select * from bookinfo where exists (select category_id from bookcategory where category='y');
select * from bookinfo where exists (select category_id from bookcategory where category='x');
insert into select 语句从一个表复制数据,然后把数据插入到一个已存在的表中。
insert into table2 select * from table1;
需要创建一张罚款记录信息表,包含如下信息:图书编号、身份证号、应还日期、实际还书日期,罚款金额
记录来源于借阅信息表超出还书时间还未还书的读者
create table readerfee(
book_id int,
card_id char(18),
return_date date,
actual_return_date date,
book_fee decimal(7,3),
primary key(book_id,card_id)
);
select book_id,card_id,return_date from borrowinfo where datediff(sysdate(),return_date)>0 and status = '否';
insert into readerfee(book_id,card_id,return_date) select book_id,card_id,return_date from borrowinfo where datediff(sysdate(),return_date)>0 and status = '否';
select * from readerfee;
身份证号为5461xxxxxxx的读者将超限的图书20201101归还,根据描述实现如下需求:
更新借阅信息表,将借阅状态(status)更新为‘是’。
更新罚款记录信息表,更新实际还书日期和罚款金额,罚款金额为每超出一天扣0.2元。
update borrowinfo set status = '是' where book_id = 20201101 and card_id = '5461xxxxxxx';
select * from borrowinfo;
update readerfee set actual_return_date=sysdate(), book_fee=datediff(sysdate(),return_date)*0.2 where book_id = 20201101 and card_id = '5461xxxxxxx';
select * from readerfee;
8.mysql的约束
它事一种限制,通过对表的行或列的数据做出限制,来确保表的数据的完整性,唯一性。
表结构:
图书(图书编号book_id,类别编号book_category_id,书名book_name,作者author)
在mysql中常用的几种约束类型:
| 约束类型 | 非空约束 | 主键约束 | 唯一约束 | 默认约束 | 外键约束 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 关键字 | not null |
primary key |
unique |
default |
foreign key |
图书信息表:
(图书编号book_id,类别编号book_category_id,书名book_name,作者author,价格price,出版社press,出版时间pubdate,库存store)
图书类别表:
(类别编号category_id - 主键,类别名称category - 唯一,父类别parent_id -非空)
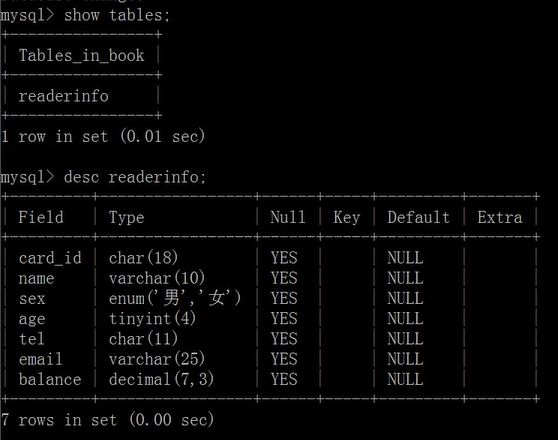
读者信息表:
(身份证号card_id,姓名name,性别sex,年龄age,联系电话tel,余额balance)
借阅信息表:
(图书编号book_id,身份证号card_id,借出日期borrow_date,归还日期return_date,是否归还status)
非空约束
null字段值可以为空
not null字段值禁止为空
非空约束
非空约束指字段的值不能为空。对于使用了非空约束的字段如果用户在添加数据时,没有指定值,数据库系统会报错。
列名 数据类型 not null
创建表时添加非空约束
create table bookinfo(
book_id int,
book_name varchar(20) not null
);
删除非空约束
alter table bookinfo modify book_name varchar(20);
通过修改表添加非空约束
alter table bookinfo modify book_name varchar(20) not null;

主键约束
主键约束:要求主键列的数据唯一,并且不允许为空,主键能够唯一地标识表中的一条记录。
主键的类型:
主键分为单字段主键和多字段联合主键
单字段主键:是由一个字段组成
在定义列的同时指定主键
列名 数据类型 primary key;
在列定义的后边指定主键
[constraint<约束名>] primary key(列名);
创建表时添加主键约束
create table bookinfo(
book_id int primary key,
book_name varchar(20) not null
);
create table bookinfo(
book_id int,
book_name varchar(20) not null,
constraint pk_id primary key(book_id)
);
删除主键约束
ALTER TABLE bookinfo DROP PRIMARY KEY;
通过修改表的方式添加主键约束
ALTER TABLE bookinfo ADD PRIMARY KEY(book_id);


多字段联合主键,复合主键
主键有多个字段联合组成。primary key(字段1,字段2,...字段n);
create table borrowinfo(
book_id int,
card_id char(18),
primary key(book_id,card_id)
);
通过修改表为列添加主键
create table bookinfo(
book_id int,
book_name varchar(20) not null
);
alter table bookinfo modify book_id int primary key;
alter table bookinfo add primary key(book_id);
alter table bookinfo add constraint pk_id primary key(book_id);

唯一约束
唯一约束要求该列唯一,允许为空,唯一约束可以确保一列或者几列不出现重复值。
语法规则:
列名 数据类型 unique
[constraint <约束名>] unique(<列名>)
创建表时添加唯一约束
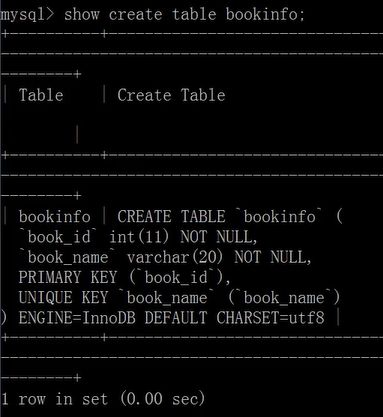
CREATE TABLE bookinfo(
book_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
book_name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL UNIQUE
);
或:
create table bookinfo(
book_id int primary key,
book_name varchar(20) not null,
constraint uk_bname unique(book_name)
);
通过修改表的方式添加唯一约束
alter table bookinfo modify book_name varchar(20) unique;
ALTER TABLE bookinfo ADD UNIQUE(book_name);
alter table bookinfo
add constraint uk_bname unique(book_name);
删除唯一约束
ALTER TABLE book_info DROP KEY uk_bname;
ALTER TABLE book_info DROP INDEX uk_bname;


唯一约束和主键约束的区别
一个表中可以有多个
unique声明,但只能有一个primary key声明声明为
primary key的列不允许有空值声明为
unique的列允许空值
默认约束
默认约束是指某列的默认值
列名 数据类型 default 默认值
创建表时添加默认约束
CREATE TABLE bookinfo(
book_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
press VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT '出版社'
);
通过修改表的方式添加默认约束
ALTER TABLE bookinfo
ALTER COLUMN press SET DEFAULT '出版社';
alter table bookinfo
modify press varchar(10) default '出版社';
删除默认约束
alter table bookinfo modify press varchar(20);
ALTER TABLE bookinfo
ALTER COLUMN press DROP DEFAULT;
外键约束
外键是用来在两个表的数据之间建立链接,可以是一列或者多列,一个表可以有一个或者多个外键。
外键对应的是参照完整性,一个表的外键可以为空值,若不为空值,则每一个外键必须等于另一个表中主键的某个值。
作用:保持数据的一致性,完整性。
创建表时添加外键约束
图书类别表(父表)
CREATE TABLE bookcategory(
category_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
category VARCHAR(20),
parent_id INT
);
图书信息表(子表)
CREATE TABLE bookinfo(
book_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
book_category_id INT,
CONSTRAINT fk_cid FOREIGN KEY(book_category_id) REFERENCES bookcategory(category_id)
);
通过修改表的方式添加外键约束
ALTER TABLE bookinfo
ADD FOREIGN KEY(book_category_id) REFERENCES bookcategory(category_id);
删除外键约束
ALTER TABLE bookinfo DROP FOREIGN KEY fk_cid;

外键约束的参照操作
cascade,从父表删除或更新且自动删除或更新子表中匹配的行
create table bookinfo(
book_id int primary key,
book_category_id int,
constraint fk_cid foreign key (book_category_id) references bookcategory(category_id) on delete cascade);
创建图书管理系统表



图书类别表
create table bookcategory(
category_id int primary key,
category varchar(20) not null unique,
parent_id int not null
);
图书信息表
create table bookinfo(
book_id int primary key,
book_category_id int,
book_name varchar(20) not null unique,
author varchar(20) not null,
price float(5,2) not null,
press varchar(20) default '机械工业出版社',
pubdate date not null,
store int not null,
constraint fk_bcid foreign key(book_category_id) references bookcategory(category_id)
);
读者信息表
create table readerinfo(
card_id char(18) primary key,
name varchar(20) not null,
sex enum('男','女','保密') default '保密',
age tinyint,
tel char(11) not null,
balance decimal(7,3) default 200
);
借阅信息表
create table borrowinfo(
book_id int,
card_id char(18),
borrow_date date not null,
return_date date not null,
status char(11) not null,
primary key(book_id,card_id)
);
9.数据库表记录的操作
单表数据记录的插入
语法格式:
insert into table_name(column_list) values(value_list);
为表的所有列插入数据
insert into bookcategory
(category_id,category,parent_id)values
(1,'x',0);
insert into bookcategory values(2,'y',0);
为表的指定列插入数据
insert into readerinfo
(card_id,name,tel)values('4562135465','张飞','4651354651');
同时插入多条记录
insert into bookcategory(category_id,category,parent_id)values(3,'x',1),(4,'y',1),(5,'z',2);
将查询结果插入的表中
insert into bookcategory select * from test where id>5;
自动增加
设置表的属性值自动增加:
列名 数据类型 auto_increment
创建表时添加自增列
create table bookcategory_tmp(
category_id int primary key auto_increment,
category varchar(20) not null unique,
parent_id int not null
)auto_increment=5;
测试自增列
insert into bookcategory_tmp(category,parent_id)values('dadaqianduan',0);
去掉自增列
alter table bookcategory_tmp modify category_id int;
添加自增列
alter table bookcategory_tmp modify category_id int auto_increment;
修改自增列的起始值
alter table bookcategory_tmp auto_increment = 15;
insert into bookcategory_tmp(category,parent_id)values('文学',0);
删除图书信息表的外键
alter table bookinfo drop foreign key fk_bcid;
为图书类别表添加自动编号的功能
alter table bookcategory modify category_id int auto_increment;
恢复关联
alter table bookinfo add constraint fk_bcid foreign key(book_category_id)references bookcategory(category_id);
单表数据记录的更新
向借阅信息表插入一条借阅信息
insert into borrowinfo(book_id,card_id,borrow_date,return_date,status)values(20202010,46516874,'2020-11-29','2020-12-29','否');
更新读者信息表中的余额
查看书的价格 79.80
select price from bookinfo where book_id = 20202010;
更新余额
update readerinfo set balance = balance - 79.80*0.05 where card_id = '46516874';
select * from readerinfo;
更新图书信息表的库存
update bookinfo set store = store -1 where book_id = 20150201;
select * from bookinfo;
单表数据记录的删除
删除指定条件的记录
delete from readerinfo where card_id = '46461265464565';
删除表中所有记录
delete from readerinfo;
truncate table readerinfo;快
想要删除表中的所有记录,可以使用truncate table语句,truncate将直接删除原来的表,并重新创建一个表,其语法结构:
truncate table table_name
查询儿科学的类别编号
select category_id from bookcategory where category='儿科学';
删除图书编号为5的图书信息
delete from bookinfo where book_category_id = 5;
删除图书类别表中儿科学这个类别
delete from bookcategory where category = '儿科学';
单表数据记录的查询
查询所有列
select * from bookcategory;
select category_id,category,parent_id from bookcategory;
查询指定列
select category from bookcategory;
select category_id,category from bookcategory;
查询指定条件的记录
select book_id,book_name,price from bookinfo where press='出版社';
查询结果不重复的记录
select distinct press from bookinfo;
查看空值
select * from readerinfo where age is null;
分组
统计读者信息表中男读者的人数
select count(*) from readerinfo where sex='男';
将读者信息表中的记录按性别进行分组
select sex from readerinfo group by sex;
将读者信息表中的记录按性别进行分组,并统计每种性别的人数
select sex,count(*) from readerinfo group by sex;
将读者信息表中的记录按性别进行分组,分组后人数大于的性别
select sex from readerinfo group by sex having count(sex)>2;
排序
通过order by子句对查询的结果进行排序
order by 列名 [asc|desc]
排序方向:
排序分为升序和降序,默认为升序
升序
asc降序
desc
单列排序
select * from bookinfo order by price;
多列排序
select * from bookinfo order by price,store;
指定排序方向
select * from bookinfo order by price,store desc;
limit语句限制查询记录的数量
前3行记录
select * from bookinfo limit 3;
从第3条记录开始的后2条记录
select * from bookinfo limit 2,2;
select * from bookinfo limit 2 offset 2;
insert into bookinfo(book_id,book_category_id,book_name,author,price,press,pubdate,store)
values
(454235424,4, '123', 'xxx',85.8, '出版社', '2020-04-01', 10),
(452454542,4, '456', 'xxx', 35.5, '出版社', '2020-08-01', 20),
(454578754,4, '789', 'xxx', 46.6, '出版社', '2020-05-01',8);
将图书信息按照库存进行分组,统计每组库存下的个数,然后按库存进行降序排序,并查看结果中的前四条记录
select store,count(*)from bookinfo
group by store
order by store desc
limit 4;
10.运算符与函数
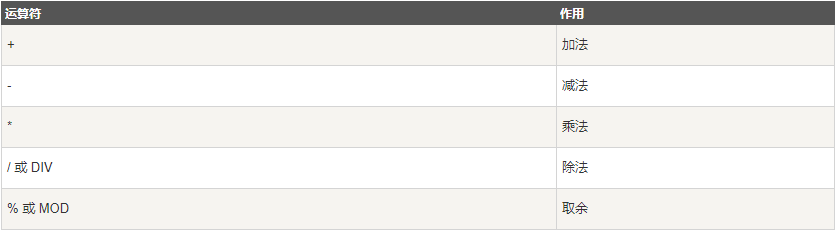
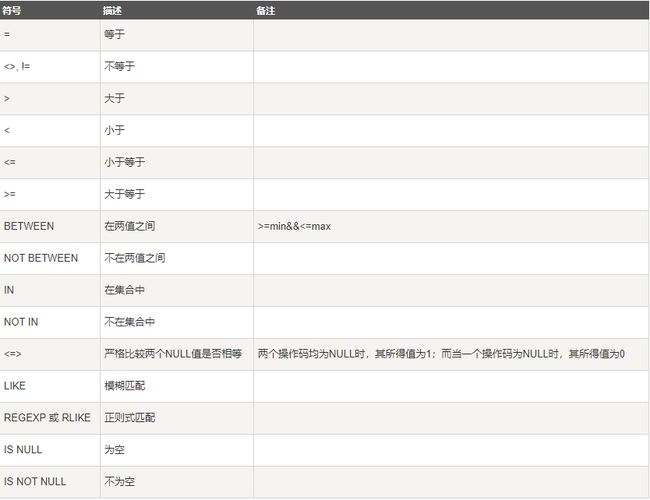
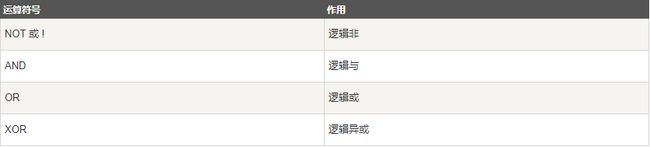
MySQL 主要有以下几种运算符:
算术运算符
比较运算符
逻辑运算符
位运算符
算术运算符
比较运算符
逻辑运算符
位运算符
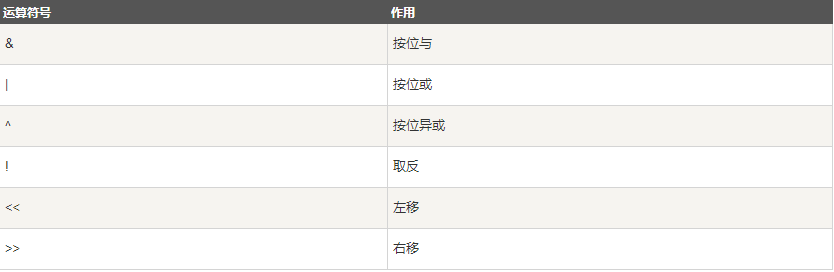
运算符优先级
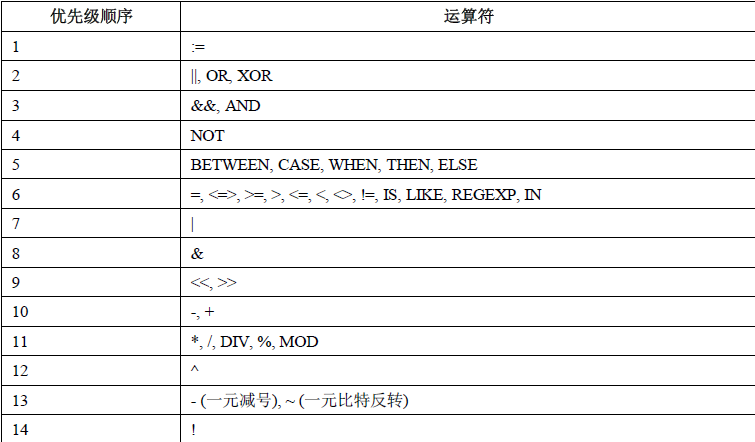
读者的身份证号,姓名,电话,余额。
select card_id, name, tel, balance from readerinfo where balance-200<=0;
查看读者信息表中,余额大于200的读者信息。
select * from readerinfo where balance>200;
查看读者信息表中,余额不等于200的读者信息。
select * from readerinfo where balance <> 200;
查看读者信息表中,年龄不为空的读者信息。
select * from readerinfo where age is not null;
查看读者信息表中,余额在350到450之间的读者信息。
select * from readerinfo where balance between 350 and 450;
select * from readerinfo where name in('dada','dada1','dada2');
select * from readerinfo where name like '张_';
select * from readerinfo where tel like '135%';
select * from bookinfo where price>50 and store<5;
select * from bookinfo where price>80 or press = '出版社';
select * from bookinfo where price not between 50 and 100;
数值函数
ceil返回大于x的最小整数值
select ceil(28.55); // 29
floor返回小于x的最大整数值
select floor(28.55); // 28
四舍五入 round返回最接近于参数x的整数,对参数x进行四舍五入
select round(28.55); // 29
select round(28.55,1),round(28.55,0),round(28.55,-1);
// 28.6 29 30
截断函数
select truncate(28.55,1),truncate(28.55,0),truncate(28.55,-1);
// 28.5 28 20
取模,返回x被y除后的余数
select mod(11,2); // 1
select book_id,book_name,price, round(price) from bookinfo;
select * from bookinfo where mod(book_id,2)=0;
字符函数
字符串连接
select concat('hello','world');
select concat_ws('-','hello','world');
字母转换大小写
select lower('Hello World');
select upper('Hello World');
求长度
select length(' hello ');
删除空格
select ltrim(' hello '),length(ltrim(' hello '));
select rtrim(' hello '),length(rtrim(' hello '));
select trim(' hello '),length(trim(' hello '));
截取字符串
select substring('hello world',1,5);
select substring('hello world',-5,2);
获取指定长度的字符串
select left('hello world', 5); // hello
select right('hello world', 5); // world
替换函数
select replace('hello world','world','mysql'); // hello mysql
格式化函数
select format(1234.5678,2),format(1234.5,2),format(1234.5678,0);
//1234.57 1234.50 12345
select book_id,book_name,format(price,2)from bookinfo;
日期和时间函数
查看当前的系统日期
select curdate();
// 2020-02-02
select curdate()+0;
select curtime()+0;
查看当前的系统日期和时间
select now(); // 2020-10-10 12:12:12
select sysdate(); // 2020-10-10 12:12:12
date_add(date,interval expr type): year,month,day,week,hour
日期的加运算
select date_add('2020-01-01', interval 5 month); // 2020-06-01
计算两个日期之间间隔的天数
select datediff('2020-02-10','2020-02-01');
日期格式化
select date_format('2020-02-01', '%Y%m');
聚合函数(分组函数)
| 名称 | 描述 | | avg() | 返回某列的平均值 | | count() | 返回某列的行数 | | max() | 返回某列的最大值 | | min() | 返回某列的最小值 | | sum() | 返回某列值的和 |
求图书信息表中,所有图书的平均价格。
select avg(price) from bookinfo;
求图书信息表中,所有图书的总价格。
select sum(price) from bookinfo;
求图书信息表中的最大库存。
select max(store) from bookinfo;
求图书信息表中的最小库存。
select min(store) from bookinfo;
求图书信息表中有多少种图书。
select count(*) from bookinfo;
按类别进行分组, 查询每种类别下有多少种图书以及每种类别图书的库存总和。
select book_category_id as '图书类别',count(book_id) as '图书种类', sum(store) as '库存总和' from bookinfo group by book_category_id;
信息函数与加密函数
系统信息函数
查看当前MySQL服务器版本的版本号
select version();
查看MySQL服务器当前连接的次数
select connection_id();
查看当前的数据库名
select schema();
查看当前登录的用户名
select user();
加密函数
select md5('test');
create table myuser(
username varchar(10),
password varchar(35)
);
insert into myuser values('user1',md5('pwd1'));
select * from myuser;
select * from myuser where username = 'user1' and password = md5('pwd1');
select password('rootpwd');
set password = password('rootpwd');
select user,authentication_string from mysql.user;
11.多表连接查询
多表连接查询是从多个表中获取数据。
由图书信息表:(图书编号book_id,类别编号book_category_id,书名book_name)
由图书类别表:(类别编号category_id,类别名称category,父类别parent_id)
获取表:(图书编号book_id,书名book_name,类别名称category)
多表连接的语法结构:
table_reference
[INNER] JOIN | {LEFT|RIGHT} [OUTER] JOIN
table_reference
on conditional_expr
多表连接 通过查看图书信息表和图书类别表 来获取图书编号、图书名称、图书类别
select book_id,book_name,category from bookinfo inner join bookcategory on bookinfo.book_category_id = bookcategory.category_id;
内连接
根据连接条件从多个表中查询选择数据,显示这些表中与连接条件相匹配的数据行,组合成新记录。(内连接就是两者共同都有的)
内连接的语法结构:
select column_list
from t1
[INNER] JOIN t2 ON join_condition1
[INNER] JOIN t3 ON join_condition2
...]
where where_conditions;
由于图书借阅统计的需要,想查询未归还图书的图书编号,图书名称,身份证号,姓名,电话,归还日期, 是否归还。
select borrowinfo.book_id,book_name,borrowinfo.card_id, name, tel, return_date, status from borrowinfo
inner join bookinfo on borrowinfo.book_id = bookinfo.book_id
inner join readerinfo on borrowinfo.card_id = readerinfo.card_id
where borrowinfo.status = '否';
select t1.book_id,book_name,t1.card_id, name, tel, return_date, status from borrowinfo t1
join bookinfo t2 on t1.book_id = t2.book_id
join readerinfo t3 on t1.card_id = t3.card_id
where t1.status = '否';
外连接
外连接将查询多个表中相关联的行。
外连接分为:左外连接 left outer join;右外连接right outer join
根据业务需要,我们需要查看图书类别表中的所有类别下都有哪些图书。
select book_id, book_name, category from bookcategory
left join bookinfo on bookcategory.category_id = bookinfo.book_category_id
where parent_id<>0;
select book_id, book_name, category from bookinfo a
right join bookcategory b on b.category_id = a.book_category_id;
select * from bookcategory;
左外连接:显示左表全部记录,右表满足连接条件的记录。
右外连接:显示右表全部记录,左表满足连接条件的记录。
语法结构:
select column_list
from t1
left | right [outer] join t2 on join_condition1;
自连接
如果在一个连接查询中,涉及的两个表都是同一个表,这种查询称为自连接
查询所有图书类别的图书类别编号,类别名称,上级分类名称。
select * from bookcategory;
select s.category_id as'图书类别编号', s.category as '图书类别名称', p.category as'图书的上级分类名称' from bookcategory s
inner join bookcategory p
on s.parent_id = p.category_id;
多表更新
update
table1 {[inner] join | {left|right} [outer] join} table2
on conditional_expr
set col1 = {expr1|default}
[,col2 = {expr2|default}]...
[where where_condition]
身份证号为432xxxxxx的读者将超时的图书86154归还,根据描述实现如下需求:
更新借阅信息表,将借阅状态(status)更新为‘是’。
更新罚款记录信息表,更新实际还书日期和罚款金额,罚款金额为每超出一天扣0.2元。
同时更新读者信息表的余额。(在余额中扣除罚款金额)
update readerfee t1 join readerinfo t2 on t1.card_id = t2.card_id
set actual_return_date = sysdate(),book_fee=datediff(sysdate(),return_date)*0.2,balance = balance - book_fee
where t1.book_id = 86154 and t1.card_id = '432xxxxxx';
select * from readerinfo;
多表删除
delete table1[.*], table2[.*]
from table1 {[inner]join|{left|right}[outer]join} table2
on conditional_expr
[where where_condition]
图书类别表,图书信息表:
由于业务需求,需要删除图书类别表中在图书信息表中没有图书记录的类别。
select book_id,book_name,category from bookcategory_bak t1
left join bookinfo_bak t2
on t1.category_id = t2.book_category_id
where parent_id<>0;
delete t1 from bookcategory_bak t1
left join bookinfo_bak t2
on t1.category_id = t2.book_category_id
where parent_id<>0 and book_id is null;
select * from bookcategory_bak;
需要删除图书类别表的编程语言的类别,以及图书信息表中关于编程语言的图书记录。
select book_id,book_name,category_id,category from bookcategory_bak t1
inner join bookinfo_bak t2
on t1.category_id = t2.book_category_id;
delete t1,t2 from bookcategory_bak t1
inner join bookinfo_bak t2
on t1.category_id = t2.book_category_id
where t1.category_id = 3;
多表连接
根据连接查询返回的结果:内连接(inner join),外连接(outer join),交叉连接(cross join)。
根据连接条件所使用的操作符:相等连接,不等连接。
12.自定义函数
创建函数
CREATE FUNCTION 函数名(参数列表) RETURNS 返回类型
BEGIN
函数体
END
调用函数
SELECT 函数名(参数列表)
查看函数
SHOW FUNCTION STATUS;
删除函数
DROP FUNCTION IF EXISTS function_name;
函数:需要有返回值,可以指定0~n个参数
创建自定义函数:
create function function_name([func_parameter])
returns type
[characteristics..] routine_body
Characteristics指定存储函数的特性,取值举例:
sql security{definer|invoker}指明谁有权限来执行。
definer表示只有定义者才能执行。
invoker表示拥有权限的调用者才可以执行,默认情况下,系统指定为definer。
comment 'string':注释信息,可以用来描述存储函数。
函数体是由sql代码构成,可以简单的sql语句。如果为复合结构需要使用begin...end语句,复合结构可以包含声明,流程控制。
select length('hello');
select date_format(pubdate,'%Y-%m') from bookinfo;
delimiter //
create function ym_date(mydate date)
returns varchar(15)
begin
return date_format(mydate,'%Y-%m');
end//
delimiter;
select ym_date(pubdate) from bookinfo;
创建自定义函数:
语法格式:
create function function_name([func_parameter])
returns type
[characteristics...] routine_body
select length('hello');
select date_format(pubdate,'%Y-%m') from bookinfo;
delimiter //
create function ym_date(mydate date)
returns varchar(15)
begin
return date_format(mydate,'%Y-%m');
end//
delimiter ;
使用(调用)自定义函数
select ym_date(pubdate) from bookinfo;
实例分析函数:
创建一个函数
delimiter $$ --定界符
--- 开始创建函数
create function user_main_fn(v_id int)
returns varchar(50)
begin
--定义变量
declare v_userName varchar(50);
--给定义的变量赋值
select f_userName info v_userName from t_user_main
where f_userId = v_id;
--返回函数处理结果
return v_userName;
end $$ --函数创建定界符
delimiter;
自定义函数两个必要条件:参数,返回值
创建自定义函数
create function function_name
returns
{string|integer|real|decimal}
routine_body
语法格式:
CREATE FUNCTION function_name([func_parameter])
RETURNS type
[characteristics … ] routine_body
function_name : 函数名称
func_parameter : 函数的参数列表
RETURNS type : 指定返回值的类型
Characteristics : 指定存储函数的特性
routine_body : 函数体
创建无参的自定义函数:

删除自定义函数
DROP FUNCTION [IF EXISTS] func_name;

SELECT DATE_FORMAT(NOW(), '%Y年%m月%d日 %H点:%i分:%s秒')
CREATE FUNCTION f1() RETURNS VARCHAR(30)
RETURN DATE_FORMAT(NOW(), '%Y年%m月%d日 %H点:%i分:%s秒');
SELECT f1();
复合结构体的函数
-- 将语句结束符改为$$,为了防止下面的函数将;看成是语句的结束
DELIMITER $$
CREATE FUNCTION adduser(username VARCHAR(20))
RETURNS INT UNSIGNED
RETURN
BEGIN
INSERT INTO table_1(username) VALUES(username);
LAST_INSERT_ID();
END;
-- 将分隔符改回来
DELIMITER ;
流程控制的使用
常用的流程控制语句:
IF条件判断语句-if
CASE条件判断语句-case
WHILE循环语句-while
LOOP循环语句-loop
REPEAT循环语句-repeat
13.存储过程

局部变量以关键字DECLARE声明
DECLARE var_name [, varname2, varname3 …] date_type [DEFAULT value];
例:DECARE num INT DEFAULE 10;
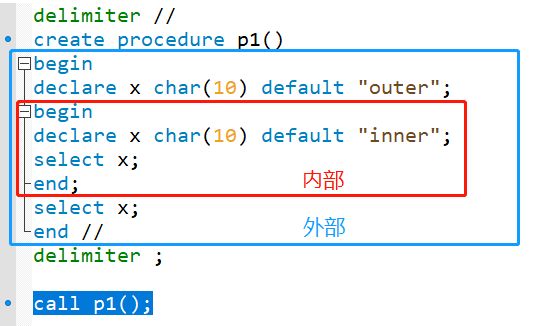

内部BEGIN…END块中定义的变量只在该块内有效
会话变量的作用范围为整个程序


语法结果
create procedure proc_name([proc_parameter])
[characteristics...] routine_body
delimiter //
create procedure selectproc1()
begin
select book_id, book_name, price, store from bookinfo;
end //
delimiter;
call selectproc();
删除存储过程:
drop procedure [if exists] proc_name;
创建一个查询图书的编号、书名、价格和库存的存储过程。
delimiter //
create procedure selectproc1()
begin
select book_id,book_name,price,store from bookinfo;
end//
delimiter ;
调用存储过程
call selectproc1();
创建查询图书编号、书名、图书类别的存储过程
delimiter //
create procedure proc1()
begin
select book_id,book_name,category from bookinfo t1
join bookcategory t2
on t1.book_category_id = t2.category_id;
end//
delimiter ;
call proc1();
设计一个存储过程,删除一个读者,并输出剩余读者的个数。
delimiter //
create procedure proc2(in cid char(18), out num int)
begin
delete from readerinfo where card_id = cid;
select count(card_id) into num from readerinfo;
end//
delimiter ;
select * from readerinfo;
call proc2('6545xx', @num);
select @num;
设计一个存储过程,实现交换两个数的处理。
delimiter //
create procedure proc3(inout num1 int, inout num2 int)
begin
declare t int default 0;
set t = num1;
set num1 = num2;
set num2 = t;
end//
delimiter ;
set @n1 = 3, @n2 = 5;
call proc3(@n1,@n2);
select @n1,@n2;
删除存储过程
drop procedure proc1;
drop procedure if exists proc2;
存储过程和函数的区别
存储过程,存储过程实现的功能比较复制,功能强大,可以执行包括修改表等一系列数据库操作。
存储函数,实现的功能针对性比较强。
返回值上的不同
存储过程:可以返回多个值,也可以不返回值,只是实现某种效果或动作。
存储函数:必须有返回值,而且只能有一个返回值。
参数不同
存储过程:存储过程的参数类型有三种,in,out,inout。
存储函数:参数类型只有一种,类似于in参数,调用函数时需要按照参数的类型指定值即可。
语法结构
存储过程,存储过程声明时不需要指定返回类型。
存储函数,函数声明时需要指定返回类型,且在函数体中必须包含一个有效的return语句。
调用方式
存储过程,用call语句进行调用
存储函数,嵌入在sql中使用的,可以在select中调用
14.事务
事务必须满足的四个条件:
atomicity 原子性
consistency 一致性
lsolation 隔离性
durability 持久性
控制事务处理
rollback,回滚会结束用户的事务,并撤销正在进行的所有未提交的修改
commit,会提交事务,并使已对数据库进行的所有修改称为永久性的
savepoint identifier,允许在事务中创建一个保存点,一个事务中可以有多个savepoint
rollback to identifier,把事务回滚到标记点
事务处理主要有两种方法
用begin, rollback, commit来实现
begin,start transaction开始一个事务rollback事务回滚commit事务确认
set autocommit = 0禁止自动提交set autocommit = 1开始自动提交
innodb使用事务
从Mysql5.5版本开始,InnoDB是默认的表存储引擎。
innodb是事务型数据库的首选引擎,支持事务安全表。

MySql中 delimiter
默认下,delimiter是分号,在命令行客户端中,如果有一行命令以分号结束,那么回车后,mysql将会执行该命令。
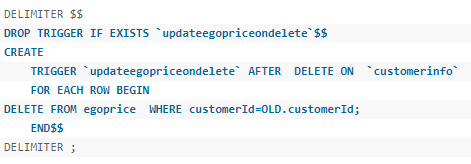 (告诉mysql解释器,该段命令是否已经结束了,mysql是否可以执行了。)
(告诉mysql解释器,该段命令是否已经结束了,mysql是否可以执行了。)
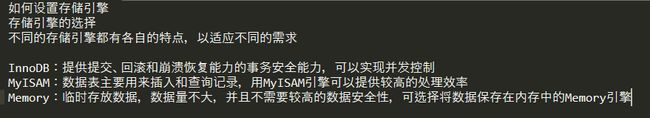
什么是存储引擎:数据库存储引擎是数据库底层软件组件。数据库管理系统使用数据引擎进行创建,查询,更新和删除数据的操作。
mysql的核心就是存储引擎。
innodb存储引擎
它为
mysql提供了具有提交,回滚和崩溃恢复能力的事务安全存储引擎。对于处理巨大数据量的数据拥有很好的性能
innodb存储引擎支持外键完整性约束innodb被用在众多需要高性能的大型数据库站点上
设置存储引擎:
设置服务器的存储引擎
在配置文件my.ini中的mysqld下面设置需要的存储引擎
default-storage-engine=InnoDB重启mysql服务器
创建表(单个)设置存储引擎
create table mytest(
id int primary key,
name varchar(10)
) engine = innodb default charset = utf8;

修改表的存储引擎
alter table tablename engine = engineName







15.管理与维护
管理用户
USE mysql;
select user from user;
权限表:存储账号的权限信息表:user,db,host,tables_priv,columns_priv和procs_priv
各个权限表的作用
tables_priv表用来对表设置操作权限;columns_priv表用来对表的某一列设置权限;procs_priv表可以对存储过程和存储函数设置操作权限。

使用CREATE USER语句创建新用户
语法格式:
CREATE USER “user”@“host” [IDENTIFIED BY “password”];
使用DROP USER 语句删除用户
语法格式:
DROP USER user[, user];
例:使用DROP USER删除账户"rose"@"localhost":
DROP USER "rose"@"localhost";
示例:
查看日志文件的路径
show variables like 'log_error';
创建新的日志信息表
flush logs;
创建新的日志信息表
mysqladmin -uroot -p flush-logs
点关注,不迷路
好了各位,以上就是这篇文章的全部内容,能看到这里的人都是人才。我后面会不断更新技术相关的文章,如果觉得文章对你有用,欢迎给个“在看”,也欢迎分享,感谢大家 !!
—————END—————
喜欢本文的朋友,欢迎关注公众号 程序员小灰,收看更多精彩内容
![]()
点个[在看],是对小灰最大的支持!

