linux 驱动开发之platform设备驱动一(4)
前言
Linux 设备和驱动通常都需要挂接在一种总线上,例如PCI、USB、I2C、SPI 等的设备存在真实的总线,这自然不是问题,但是SOC上的外设控制器、挂接在SoC内存空间的外设等却不依附于此类总线。基于这一背景,linux形成了一种虚拟的总线,称为platform 总线,相应的设备称为platform_device,而驱动成为platform_driver。
platform总线的出现提高了代码的重用性、实现了设备与驱动的分离,增强了可移植性。之前的驱动开发是把驱动信息和设备信息都写在一起,当模块很多时,就大大增加了冗余代码,不易于维护开发。
本篇章将对platform总线涉及的基础知识进行讲解,下篇章再通过阅读内核platform源码文件疏通具体工作过程。
1 总线、设备和驱动模型
1.1 驱动分离
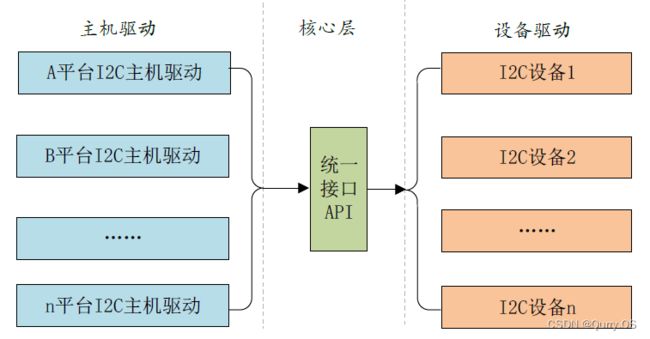
驱动开发中,为了提高代码的重用性,采取了驱动分离的方法,每个平台驱动都会对应有主机驱动和设备驱动,主机驱动就是平台下相应控制器的驱动。
拿I2C来举例,I2C主机控制器的驱动每个平台都不一样,由soc芯片厂家编写,中间有个核心层提供统一接口,设备驱动调用统一接口编写,这样设备驱动就可以适用于任何平台了,一般设备驱动由设备器件厂家编写提供。
1.2 驱动、设备分离
在设备驱动中不填写任何设备信息,驱动使用中通过标准方法获取设备信息(例如从设备树中获取),然后根据设备信息初始化设备;可以在设备树中填入设备信息,像设备挂接在哪个I2C接口上、名字、物理地址、速率设置多少等;这样就把设备信息从设备驱动中分离出来了。设备、驱动分离后就需要有方法将它们连接匹配上,此时总线(bus)就充当这个角色。
当我们向系统注册一个驱动的时候,总线就会在右侧的设备中查找,看看有没有与之匹配的设备,如果有的话就将两者联系起来。同样的,当向系统中注册一个设备的时候,总线就会在左侧的驱动中查找看有没有与之匹配的设备,有的话也联系起来。
2 platform 框架模型
linux中为了解决有些外设没有总线这个概念的问题,故引出了虚拟总线(platform)这个概念。相应的驱动、设备叫platform_driver、platform_device。
2.1 platform总线
结构体bus_type描述总线,定义在include/linux/device.h中;
struct bus_type {
const char *name;
const char *dev_name;
struct device *dev_root;
struct device_attribute *dev_attrs; /* use dev_groups instead */
const struct attribute_group **bus_groups; //总线属性
const struct attribute_group **dev_groups; //设备属性
const struct attribute_group **drv_groups; //驱动属性
int (*match)(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv);
int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);
int (*probe)(struct device *dev);
int (*remove)(struct device *dev);
void (*shutdown)(struct device *dev);
int (*online)(struct device *dev);
int (*offline)(struct device *dev);
int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct device *dev);
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
const struct iommu_ops *iommu_ops;
struct subsys_private *p;
struct lock_class_key lock_key;
};参数name:定义总线的名字;
参数match函数:完成设备与驱动间的匹配,该函数有两个参数(dev、drv)分别表示设备 和驱动对应的结构体;
2.2 platform驱动
结构体platform_driver表示platform驱动,定义在include/linux/platform_device.h中;
struct platform_driver {
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
bool prevent_deferred_probe;
};参数probe函数:当driver 和device 匹配成功的时候,就会执行probe 函数;
参数remove函数:当driver 和device 任意一个remove 的时候,就会执行这个函数;
参数id_table:保存了很多id 信息。id 信息存放着这个platformd 驱动所支持的驱动类型。
device_driver结构体定义在 include/linux/device.h;着重关注of_device_id结构体;
struct device_driver {
const char *name;
struct bus_type *bus;
struct module *owner;
const char *mod_name; /* used for built-in modules */
bool suppress_bind_attrs; /* disables bind/unbind via sysfs */
enum probe_type probe_type;
const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;
const struct acpi_device_id *acpi_match_table;
int (*probe) (struct device *dev);
int (*remove) (struct device *dev);
void (*shutdown) (struct device *dev);
int (*suspend) (struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume) (struct device *dev);
const struct attribute_group **groups;
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
struct driver_private *p;
};结构体platform_device_id、of_device_id定义在/linux/mod_devicetable.h;
struct platform_device_id {
char name[PLATFORM_NAME_SIZE];
kernel_ulong_t driver_data;
};
struct of_device_id {
char name[32];
char type[32];
char compatible[128];
const void *data;
};2.2.1 platform驱动注册函数
int platform_driver_register (struct platform_driver *driver)
参数driver:要注册的 platform驱动,定义好的platform_driver结构体变量;
返回值: 负数,失败; 0,成功。
2.2.2 platform 驱动卸载函数
void platform_driver_unregister(struct platform_driver *drv)
参数drv:要卸载的 platform驱动。
2.3 platform设备
platform_device这个结构体表示 platform设备,如果内核使用设备树来描述设备信息,就不需要使用platform_device结构体描述了。(现在的开发中很多都是使用设备树来描述了)
struct platform_device {
const char *name;
int id;
bool id_auto;
struct device dev;
u32 num_resources;
struct resource *resource;
const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;
char *driver_override; /* Driver name to force a match */
/* MFD cell pointer */
struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;
/* arch specific additions */
struct pdev_archdata archdata;
};
参数name:platform设备的名字,用来和platform驱动相匹配。名字相同才能匹配成功;
参数id:是用来区分如果设备名字相同的时候(通过在后面添加一个数字来代表不同的设 备),通常为 -1 ;
参数resource:资源结构体,描述设备信息;
参数num_resource:资源结构体数量。
resource结构体定义再/linux/ioport.h中;
flag表示资源类型,内核定义了可选的资源类型,常用类型有IORESOURCE_IO(IO 的内存)、IORESOURCE_MEM( 表述一段物理内存)、IORESOURCE_IRQ (表示中断),如下代码:
struct resource {
resource_size_t start;
resource_size_t end;
const char *name;
unsigned long flags;
struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child;
};
/*
* IO resources have these defined flags.
*/
#define IORESOURCE_BITS 0x000000ff /* Bus-specific bits */
#define IORESOURCE_TYPE_BITS 0x00001f00 /* Resource type */
#define IORESOURCE_IO 0x00000100 /* PCI/ISA I/O ports */
#define IORESOURCE_MEM 0x00000200
#define IORESOURCE_REG 0x00000300 /* Register offsets */
#define IORESOURCE_IRQ 0x00000400
#define IORESOURCE_DMA 0x00000800
#define IORESOURCE_BUS 0x00001000
#define IORESOURCE_PREFETCH 0x00002000 /* No side effects */
#define IORESOURCE_READONLY 0x00004000
#define IORESOURCE_CACHEABLE 0x00008000
#define IORESOURCE_RANGELENGTH 0x00010000
#define IORESOURCE_SHADOWABLE 0x00020000
#define IORESOURCE_SIZEALIGN 0x00040000 /* size indicates alignment */
#define IORESOURCE_STARTALIGN 0x00080000 /* start field is alignment */
#define IORESOURCE_MEM_64 0x00100000
#define IORESOURCE_WINDOW 0x00200000 /* forwarded by bridge */
#define IORESOURCE_MUXED 0x00400000 /* Resource is software muxed */
#define IORESOURCE_EXCLUSIVE 0x08000000 /* Userland may not map this resource */
#define IORESOURCE_DISABLED 0x10000000
#define IORESOURCE_UNSET 0x20000000 /* No address assigned yet */
2.3.1 platform设备注册函数
int platform_device_register(struct platform_device *pdev)
参数pdev:要注册的 platform设备。
返回值: 负数,失败; 0,成功。
2.3.2 platform设备卸载函数
void platform_device_unregister(struct platform_device *pdev)
参数pdev:要注销的 platform设备。
2.3.3 获取资源函数
struct resource *platform_get_resource(struct platform_device *,unsigned int, unsigned int);
第一个参数:平台设备变量;
第二个参数:资源类型;
第三个参数:索引号,资源处在同类资源的哪个位置上,大家注意理解同类资源是指flags 一模一样。
2.3.4 申请IO内存
#define request_mem_region(start,n,name) \
__request_region(&iomem_resource, (start), (n), (name), 0)
第一个参数:起始地址;
第二个参数:长度;
第三个参数:名字。