牛客剑指offer刷题链表篇
文章目录
-
-
- 从尾到头打印链表
-
- 题目
- 思路
- 代码实现
- 反转链表
-
- 题目
- 思路
- 代码实现
- 合并两个有序链表
-
- 题目
- 思路
- 代码实现
- 两个链表的第一个共同结点
-
- 题目
- 思路
- 代码实现
- 链表中环的入口结点
-
- 题目
- 思路
- 代码实现
- 链表中倒数第K个节点
-
- 题目
- 思路
- 复杂链表的复制
-
- 题目
- 思路1【时间复杂度和空间复杂度均为O(n)】
- 实现代码1
- 思路2【直接复制链表】
- 代码实现2
- 删除链表中的重复结点
-
- 题目
- 思路
- 代码实现
- 删除链表的节点
-
- 题目
- 代码实现
-
从尾到头打印链表
题目
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来打印出每个节点的值。
思路
利用栈后进先出的性质实现;
代码实现
private static void printReverseNode(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
ListNode pNode = head;
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while (pNode != null) {
stack.add(pNode);
pNode = pNode.next;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(stack.pop().value);
}
}
private static class ListNode {
public ListNode next;
public int value;
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
反转链表
题目
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
思路
遍历各个节点,修改指针指向前一节点实现,需要定义两个变量记录前一节点以及当前节点;
代码实现
/**
* 反转链表
*
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
//前一节点
ListNode prev = null;
//当前节点
ListNode current = null;
while (head != null) {
//取出当前节点
current = head;
//移动到下一个节点
head = head.next;
//当前界面的next指向前一节点
current.next = prev;
//赋值给前一节点
prev = current;
}
return prev;
}
合并两个有序链表
题目
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
思路
从头依次比较各个节点大小,哪个链表当前节点小,则取出当前节点,移动到下一个节点处,继续递归比较得到最终结果;
代码实现
private static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if (list1 == null) {
return list2;
}
if (list2 == null) {
return list1;
}
ListNode result = null;
if (list1.value < list2.value) {
result = list1;
result.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);
} else {
result = list2;
result.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next);
}
return result;
}
两个链表的第一个共同结点
题目
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
思路
由题目可知,当存在共同结点时,结构如下:
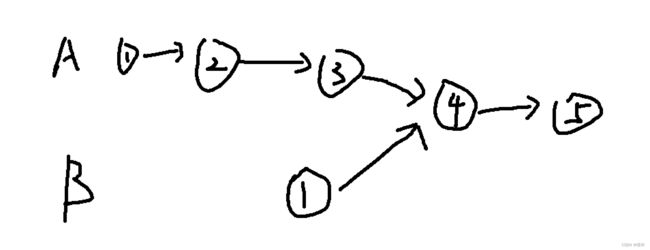
则首先需要计算两条链表的长度得到长度差,而从将链表移动到相同长度位置,然后同时遍历两条链表,则第一个相同节点即为所求节点;
代码实现
public static ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
int headALength = getListNodeLength(headA);
int headBLength = getListNodeLength(headB);
ListNode currentA = headA;
ListNode currentB = headB;
if (headALength > headBLength) {
// headA 移动到相同长度位置
int num = headALength - headBLength;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
currentA = currentA.next;
}
} else {
int num = headBLength - headALength;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
currentB = currentB.next;
}
}
while (currentA != null && currentB != null) {
if (currentA == currentB) {
return currentA;
} else {
currentA = currentA.next;
currentB = currentB.next;
}
}
return null;
}
private static int getListNodeLength(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
int length = 0;
ListNode current = head;
while (current != null) {
length++;
current = current.next;
}
return length;
}
链表中环的入口结点
题目
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
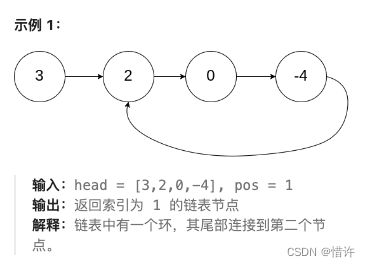
思路
- 首先使用快慢指针移动得到环上相遇节点;
- 然后将快指针移动到头节点处;
- 同时移动快慢指针,一次移动一步,再次相遇即为入环节点;
代码实现
public static ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head.next;
if (fast == null) {
return null;
}
fast = fast.next;
if (fast == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head.next;
while (fast != slow) {
if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null) {
return null;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
fast = head;
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
链表中倒数第K个节点
题目
实现一种算法,找出单向链表中倒数第 k 个节点。返回该节点的值。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5 和 k = 2
输出: 4
说明:
给定的 k 保证是有效的。
思路
- 倒数第k个节点,假设链表有n个节点,则从头节点出发应该走n-k+1步;
- 若正向走则需要两次遍历,一次得到链表长度,然后在从头走n-k+1步;
- 可以定义2个指针,第一个指针先走k-1步,第二个指针再和第一个指针同时走,当第一个指针到达尾节点时,此时第二个指针到达位置即为所求节点【因为此时第二个指针走的步数正好为n-(k-1)步】。
public static int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || k < 1) {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
ListNode first = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) {
if (first.next != null) {
first = first.next;
} else {
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
}
ListNode result = head;
while (first.next != null) {
first = first.next;
result = result.next;
}
return result.val;
}
复杂链表的复制
题目
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
思路1【时间复杂度和空间复杂度均为O(n)】
利用HashMap依次复制各个节点进行存储,然后再次遍历设置next以及random节点;
实现代码1
public static Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
//声明一个map用于存储<节点,节点>映射关系
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
Node cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
思路2【直接复制链表】
- 首先对每个节点进行拷贝,并拼接到各个对应节点后面,如1->2->3 变成 1->1’->2->2’->3->3’;
- 将拷贝节点对应的random指针添加上;
- 分离拷贝节点以及原始节点,最终拆分为1->2->3 和1’->2’->3’;
代码实现2
public static Node copyRandomList2(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
//1.将拷贝节点放到原节点后面,例如1->2->3的链表变成 1->1'->2->2'->3->3'
for (Node node = head, copyNode = null; node != null; node = node.next) {
copyNode = new Node(node.val);
copyNode.next = node.next;
node.next = copyNode;
}
//2.将拷贝节点的random指针添加上
for (Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next.next) {
if (node.random != null) {
node.next.random = node.random.next;
}
}
//3.分离拷贝节点和原节点,变成1->2->3和1'->2'->3'两个链表,返回后一个链表
Node newHead = head.next;
for (Node node = head, copy = null; node != null && node.next != null; ) {
copy = node.next;
node.next = copy.next;
node = copy;
}
return newHead;
}
删除链表中的重复结点
题目
给定一个已排序的链表的头 head , 删除原始链表中所有重复数字的节点,只留下不同的数字 。返回已排序的链表 。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/description/
思路
新建虚拟结点插入头结点,依次遍历各个节点比较值,如果一致,则跳过当前节点;
代码实现
public static ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode result = new ListNode();
result.next = head;
ListNode temp = result;
while (temp.next != null && temp.next.next != null) {
if (temp.next.val == temp.next.next.val) {
int value = temp.next.val;
while (temp.next != null && temp.next.val == value) {
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}
} else {
temp = temp.next;
}
}
return result.next;
}
删除链表的节点
题目
给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/shan-chu-lian-biao-de-jie-dian-lcof/
代码实现
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode result = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
result.next = head;
ListNode cur = result;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return result.next;
}