数据结构和算法——用C语言实现所有图状结构及相关算法
文章目录
- 前言
- 图的基本概念
- 图的存储方式
-
- 邻接矩阵
- 邻接表
- 十字链表
- 临界多重表
- 图的遍历
- 最小生成树
-
- 普里姆算法(Prim)
- 克鲁斯卡尔算法(Kruskal)
- 最短路径
-
- BFS求最短路径
- 迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra)
- 弗洛伊德算法(Floyd)
- 有向无环图
-
- AOV网的拓扑结构
-
- 拓扑排序
- 逆拓扑排序
- AOE网的关键路径
前言
本文所有代码均在仓库中,这是一个完整的由纯C语言实现的可以存储任意类型元素的数据结构的工程项目。
![]()
- 首先是极好的工程意识,该项目是一个中大型的CMake项目,结构目录清晰,通过这个项目可以遇见许多工程问题并且可以培养自己的工程意识。
- 其次是优秀的封装性(每个数据结构的头文件中只暴漏少量的信息),以及优秀的代码风格和全面的注释,通过这个项目可以提升自己的封装技巧:
![]()
- 异常处理功能:在使用C语言编写代码的时候不能使用类似Java的异常处理机制是非常难受的,所以我也简单实现了一下。详情可看在C语言中实现类似面向对象语言的异常处理机制
![]()
最后也是最重要的一点,数据结构的通用性和舒适的体验感,下面以平衡二叉树为例:
- 第一步:要想使用平衡二叉树,只需要引入其的头文件:
#include "tree-structure/balanced-binary-tree/BalancedBinaryTree.h"
- 第二步:定义自己任意类型的数据,并构造插入数据(以一个自定义的结构体为例):
#include "tree-structure/balanced-binary-tree/BalancedBinaryTree.h"
int dataCompare(void *, void *);
typedef struct People {
char *name;
int age;
} *People;
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
struct People dataList[] = {
{"张三", 15},
{"李四", 3},
{"王五", 7},
{"赵六", 10},
{"田七", 9},
{"周八", 8},
};
BalancedBinaryTree tree = balancedBinaryTreeConstructor(NULL, 0, dataCompare);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) {
balancedBinaryTreeInsert(&tree, dataList + i, dataCompare);
}
return 0;
}
/**
* 根据人的年龄比较
*/
int dataCompare(void *data1, void *data2) {
int sub = ((People) data1)->age - ((People) data2)->age;
if (sub > 0) {
return 1;
} else if (sub < 0) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
- 第三步:打印一下平衡二叉树:
#include "tree-structure/balanced-binary-tree/BalancedBinaryTree.h"
int dataCompare(void *, void *);
void dataPrint(void *);
typedef struct People {
char *name;
int age;
} *People;
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
struct People dataList[] = {
{"张三", 15},
{"李四", 3},
{"王五", 7},
{"赵六", 10},
{"田七", 9},
{"周八", 8},
};
BalancedBinaryTree tree = balancedBinaryTreeConstructor(NULL, 0, dataCompare);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) {
balancedBinaryTreeInsert(&tree, dataList + i, dataCompare);
balancedBinaryTreePrint(tree, dataPrint);
printf("-------------\n");
}
return 0;
}
/**
* 根据人的年龄比较
*/
int dataCompare(void *data1, void *data2) {
int sub = ((People) data1)->age - ((People) data2)->age;
if (sub > 0) {
return 1;
} else if (sub < 0) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
/**
* 打印人的年龄
* @param data
*/
void dataPrint(void *data) {
People people = (People) data;
printf("%d", people->age);
}
打印的结果如下:
![]()
最后期待大佬们的点赞。
图的基本概念
图 G G G由顶点集 V V V和边集 E E E组成,记为:
G = ( V , E ) G=(V,E) G=(V,E)
若 V = { v 1 , v 2 , … , v n } V=\{v_1,v_2,\dots,v_n\} V={v1,v2,…,vn}则用 ∣ V ∣ |V| ∣V∣表示图 G G G中顶点的个数,也称为图 G G G的阶;若 E = { ( a , b ) ∣ a ∈ V , b ∈ V } E=\{(a,b)|a\in V,b\in V\} E={(a,b)∣a∈V,b∈V}则用 ∣ E ∣ |E| ∣E∣表示图 G G G中边的条数。不存在空图,即一个图的点集是非空的。图的分类如下:
- 无向图:若 E E E为无向边(简称边)的有限集合,则 G G G为无向图。
- 0 < ∣ E ∣ < ∣ V ∣ ( ∣ V ∣ − 1 ) 2 0<|E|<\frac{|V|(|V|-1)}{2} 0<∣E∣<2∣V∣(∣V∣−1)
- 有向图:若 E E E为有向边(简称弧)的有限集合,则 G G G为有向图.
- 0 < ∣ E ∣ < ∣ V ∣ ( ∣ V ∣ − 1 ) 0<|E|<|V|(|V|-1) 0<∣E∣<∣V∣(∣V∣−1)
- 简单图和多重图:如果一个图不存在重复边和顶点到自身的边,那么称图为简单图,否则称为多重图。
图有关的术语如下:
-
顶点的度、入度和出度:
- 对于无向图而言:
- 顶点 v v v的度是指依附于该顶点的边的数目,记为 T D ( v ) TD(v) TD(v)
- ∑ i = 1 n T D ( v i ) = 2 ∣ E ∣ \sum_{i=1}^n TD(v_i)=2|E| i=1∑nTD(vi)=2∣E∣
- 对于有向图而言:
- 入度是指以顶点 v v v为终点的弧的数目,记为 I D ( v ) ID(v) ID(v);
- 出度是以顶点为起点的弧的数目,记为 O D ( v ) OD(v) OD(v);
- 顶点 v v v的度等于其入度和出度之和。
- ∑ i = 1 n I D ( v i ) = ∑ i = 1 n O D ( v i ) = ∣ E ∣ \sum_{i=1}^n ID(v_i)=\sum_{i=1}^n OD(v_i)=|E| i=1∑nID(vi)=i=1∑nOD(vi)=∣E∣
- 对于无向图而言:
-
路径、路径长度和回路:
- 从一个顶点到另一个顶点之间经过的所有顶点的序列称为路径;
- 起点和终点为同一个顶点的路径称为回路。
-
简单路径和简单回路:
- 顶点不重复的路径称为简单路径;
- 除第一个和最后一个顶点外,其余顶点不重复的回路称为简单回路。
-
路径长度:路径上边的数目称为路径长度。
-
距离:两个顶点之间的最短路径长度称为距离,路径不存在则距离为无穷。
-
连通、连通图和连通分量:
- 在无向图中,两个不同顶点之间存在至少一条路径,则称这两个顶点是连通的。若图中任意两个顶点都是连通的,则称该图为连通图,否则称为非连通图;
- 无向图中的极大连通子图称为连通分量。
- 若图是连通的,则 ∣ E ∣ ≥ ∣ V ∣ − 1 |E|\geq|V|-1 ∣E∣≥∣V∣−1
- 若图是非连通的,则 ∣ E ∣ ≤ C ∣ V ∣ − 1 2 |E|\leq C^2_{|V|-1} ∣E∣≤C∣V∣−12
-
强连通图和强连通分量:
- 在有向图中,两个不同顶点之间存在至少一条路径,则称这两个顶点是强连通的。若图中任意两个顶点都是连通的,则称该图为强连通图,否则称为非强连通图;
- 有向图中的极大连通子图称为强连通分量。
- 若图是连通的,则 ∣ E ∣ ≥ ∣ V ∣ |E|\geq|V| ∣E∣≥∣V∣
-
子图和生成子图:
- 顶点集和边集分别是某图顶点集和边集子集的图称为某图的子图。
- 包含某图所有顶点的子图称为生成子图。
-
完全图:任意两个顶点之间都有一条边相连的图称为完全图。
- 对于无向图而言, 0 ≤ ∣ E ∣ ≤ C ∣ V ∣ 2 0\leq|E|\leq C^2_{|V|} 0≤∣E∣≤C∣V∣2
- 对于有向图而言, 0 ≤ ∣ E ∣ ≤ 2 C ∣ V ∣ 2 0\leq |E|\leq 2C^2_{|V|} 0≤∣E∣≤2C∣V∣2
-
连通图的生成树和非连通图的生成森林:
- 包含所有顶点的极小连通子图称为连通图的生成树。
- 连通分量的生成树称为非连通图的生成森林。
-
边的权、网和带权路径长度:
- 为每条边标记的具有一定意义的数值称为边的权值
- 边上带有权值的图称为网
- 一条路径上所有边的权值之和称为该路径的带权路径长度
-
树和有向树:
- 不存在回路且连通的无向图称为树
- 一个顶点的入度为零,其余顶点的入度均为一的有向图称为有向树。
图的存储方式
图一般有以下几种存储方式:
- 邻接矩阵法
- 邻接表法
- 十字链表法
- 邻接多重表
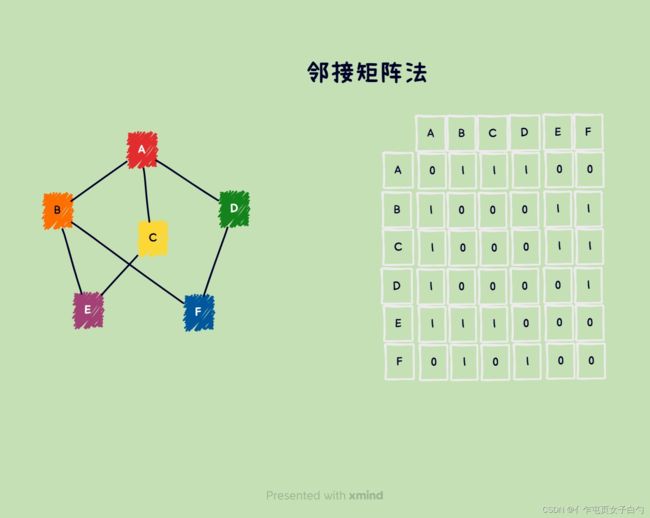
邻接矩阵
邻接矩阵法用一个一维数组存储图中的顶点信息,用一个二维数组存储图中边的信息(即顶点之间的邻接关系),这个二维数组就是邻接矩阵。邻接矩阵法适合存储稠密图。
struct AdjacentMatrixGraph {
void **vertexList;
int **edgeMatrix;
int vertexCount;
int edgeCount;
int size;
int (*compare)(void *, void *);
};
对于图而言:
- e d g e M a t r i x [ i ] [ j ] = { 1 若 ( v i , v j ) 或 ( v j , v i ) 是 G 的边 0 若 ( v i , v j ) 或 ( v j , v i ) 不是 G 的边 edgeMatrix[i][j]= \begin{cases} 1&若(v_i,v_j)或(v_j,v_i)是G的边\\ 0&若(v_i,v_j)或(v_j,v_i)不是G的边 \end{cases} edgeMatrix[i][j]={10若(vi,vj)或(vj,vi)是G的边若(vi,vj)或(vj,vi)不是G的边
- 无向图的邻接矩阵是一个对称矩阵,因此在存储时可以使用压缩矩阵存储。
对于网而言:
- e d g e M a t r i x [ i ] [ j ] = { 权值 若 ( v i , v j ) 或 ( v j , v i ) 是 G 的边 0 或 ∞ 若 ( v i , v j ) 或 ( v j , v i ) 不是 G 的边 edgeMatrix[i][j]= \begin{cases} 权值&若(v_i,v_j)或(v_j,v_i)是G的边\\ 0或\infty&若(v_i,v_j)或(v_j,v_i)不是G的边 \end{cases} edgeMatrix[i][j]={权值0或∞若(vi,vj)或(vj,vi)是G的边若(vi,vj)或(vj,vi)不是G的边
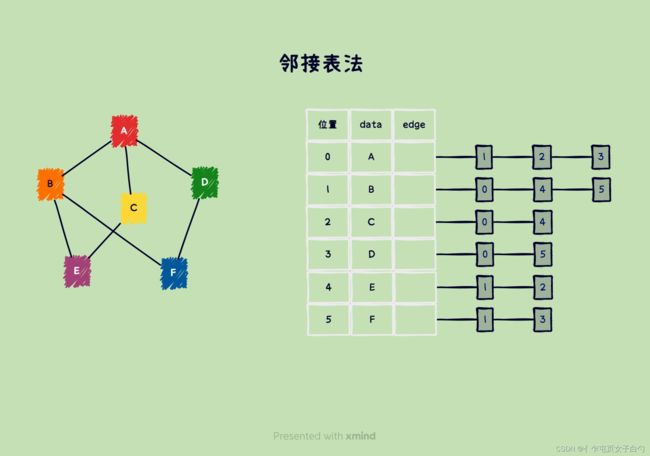
邻接表
邻接表法为每个顶点建立一个单链表,这个链表中的结点表示依附于该顶点的边,这个单链表称为顶点的边表。邻接表法适合存储稀疏图。
typedef struct Edge {
int weight;
int vertexIndex;
struct Edge *next;
} *Edge;
typedef struct Vertex {
void *data;
Edge firstEdge;
} *Vertex, *VertexList;
struct AdjacentListGraph {
VertexList *vertexList;
int vertexCount;
int edgeCount;
int size;
int (*compare)(void *, void *);
};
十字链表
十字链表法是有向图的一种链式存储结构,一个十字链表可以唯一确定一个图。
typedef struct ArcNode{
ArcType data;
int tailVex; //弧头顶点位置
int headVex; //弧尾顶点位置
int headLink; //弧头相同的下一条弧
int tailLink; //弧尾相同的下一条弧
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VexNode {
VertexType data;
ArcNode * firstIn; //以该顶点为弧头的第一个弧顶点
ArcNode * firstOut; //以该顶点为为弧尾的第一个弧顶点
}VexNode,* VexList;
typedef struct OLGraph{
VexList vexList;
int vexNum;
int arcNum;
}* OLGraph;
临界多重表
邻接多重表是无向图的一种链式存储结构。
typedef struct EdgeNode {
bool mark; //是否被搜搜过
int iVex; //该边依附的一个顶点位置
int jVex; //该边依附的另一个顶点位置
int iLink; //下一个依附顶点iVex的边
int jLink; //下一个依附顶点jVex的边
} EdgeNode;
typedef struct VexNode {
VexType data;
EdgeNode *firstEdge; //第一个依附该顶点的边
} VexNode, *VexList;
typedef struct AMLGraph {
VexList vexList;
int vexNum;
int edgeNum;
} *AMLGraph;
图的遍历
图的遍历是指从图中的某一顶点出发,按照某种搜索方法沿着图中的边对图中的所有顶点访问一次且仅访问一次的过程。图的遍历方式主要有以下两种:
- 广度优先搜索(BFS):
- 从图的某一顶点出发,依次访问该顶点的所有邻接顶点;
- 再从这些访问过的邻接顶点出发,依次访问它们的邻接顶点,直到图中所有顶点都被访问为止;
- 若图中还有顶点尚未被访问,则选择一个尚未被访问的顶点重复上述过程。
void BFS(AdjacentListGraph graph, bool isVisited[], LinkedQueue queue, LinkedQueue BFSDataQueue) {
while (!linkedQueueIsEmpty(queue)) {
Vertex vertex = linkedQueueDeQueue(queue);
linkedQueueEnQueue(BFSDataQueue, vertex->data);
isVisited[getVertexIndex(graph, vertex->data) - 1] = true;
for (Vertex j = firstVertex(graph, vertex->data); j != NULL; j = nextVertex(graph, vertex->data, j->data)) {
if (!isVisited[getVertexIndex(graph, j->data) - 1]) {
linkedQueueEnQueue(queue, j);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 广度优先遍历
* @param graph
* @param BFSDataQueue
*/
void BFSTraverse(AdjacentListGraph graph, void *data, LinkedQueue BFSDataQueue) {
bool *isVisited = calloc(graph->vertexCount, sizeof(bool));
LinkedQueue queue = linkedQueueConstructor();
linkedQueueEnQueue(queue, graph->vertexList[getVertexIndex(graph, data) - 1]);
BFS(graph, isVisited, queue, BFSDataQueue);
for (int i = 1; i <= graph->vertexCount; ++i) {
if (!isVisited[i - 1]) {
BFS(graph, isVisited, queue, BFSDataQueue);
}
}
}
- 深度优先搜索(DFS):
- 从图的某一顶点出发,访问它的任一邻接顶点;再从邻接顶点出发,访问邻接顶点的任一邻接顶点;如此往复直到访问到一个所有邻接顶点都被访问的顶点为止;
- 接着回退一步,看看前一次访问的顶点是否还有其它没有被访问的邻接顶点;如果有,则访问此邻接顶点,之后再进行前述过程;如果没有,则再回退一步,重复上述过程,直到连通图中所顶点都被访问过为止。
void DFS(AdjacentListGraph graph, int vertexIndex, bool isVisited[], LinkedQueue DFSDataQueue) {
Vertex vertex = graph->vertexList[vertexIndex - 1];
linkedQueueEnQueue(DFSDataQueue, vertex->data);
isVisited[vertexIndex - 1] = true;
for (Vertex j = firstVertex(graph, vertex->data); j != NULL; j = nextVertex(graph, vertex->data, j->data)) {
int index = getVertexIndex(graph, j->data);
if (!isVisited[index - 1]) {
DFS(graph, index, isVisited, DFSDataQueue);
}
}
}
/**
* 深度优先遍历
* @param graph
* @param data
* @param DFSDataQueue
*/
void DFSTraverse(AdjacentListGraph graph, void *data, LinkedQueue DFSDataQueue) {
bool *isVisited = calloc(graph->vertexCount, sizeof(bool));
int index = getVertexIndex(graph, data);
DFS(graph, index, isVisited, DFSDataQueue);
for (int i = 1; i <= graph->vertexCount; ++i) {
if (!isVisited[i - 1]) {
DFS(graph, i, isVisited, DFSDataQueue);
}
}
}
最小生成树
对于一个带权连通无向图 G G G,生成树不同,每棵树的权值也可能不同,若 T T T为权值最小的生成树,则 T T T称为 G G G的最小生成树(MST)。最小生成树的性质如下:
- 如果 G G G中有权值相等的边,则最小生成树不是唯一的,若 G G G的边数比顶点数少一,则 G G G的生成树就是它本身。
- 最小生成树的边的权值是唯一的,且是最小的。
- 最小生成树的边数为顶点数减一。
- U U U是V的一个子集,若 ( u , v ) (u,v) (u,v)是一条具有最小权值的边,其中 u ∈ U , v ∈ V − U u∈U,v∈V-U u∈U,v∈V−U,则必存在一棵包含 ( u , v ) (u,v) (u,v)的最小生成树。
普里姆算法(Prim)
普里姆算法的步骤:
- 初始时从图中选择一个顶点加入树 T T T,此时树中只有这一个顶点;
- 之后选择一个与当前 T T T中顶点集合距离最近的顶点,并将该顶点和相应的边加入 T T T;
- 以此类推,直到图中所有的顶点都加入 T T T,得到的 T T T就是最小生成树。
/**
* Prim算法
* @param graph
* @return
*/
AdjacentListGraph Prim(AdjacentListGraph graph) {
AdjacentListGraph MST = adjacentListGraphConstructor(graph->vertexCount, graph->compare);
//是否加入最小生成树
bool isJoin[graph->vertexCount];
//路径长度
int distance[graph->vertexCount];
//路径前驱
int path[graph->vertexCount];
for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexCount; ++i) {
isJoin[i] = false;
distance[i] = INFINITY;
path[i] = -1;
}
while (MST->size != graph->vertexCount) {
int fromIndex = -1, toIndex = -1, minDistance = 0;
if (MST->vertexCount == 0) {
toIndex = 1;
} else {
for (int i = 1; i <= graph->vertexCount; ++i) {
if (isJoin[i - 1] == false && distance[i - 1] < minDistance) {
fromIndex = path[i - 1];
toIndex = i;
minDistance = distance[i - 1];
}
}
if (toIndex == -1) {
break;
}
}
isJoin[toIndex - 1] = true;
distance[toIndex - 1] = minDistance;
path[toIndex - 1] = fromIndex;
for (Edge edge = graph->vertexList[toIndex - 1]->firstEdge; edge != NULL; edge = edge->next) {
if (edge->weight < distance[edge->vertexIndex - 1]) {
distance[edge->vertexIndex - 1] = edge->weight;
path[edge->vertexIndex - 1] = toIndex;
}
}
insertVertex(MST, graph->vertexList[toIndex - 1]->data);
MST->vertexCount++;
addEdge(MST, graph->vertexList[fromIndex - 1]->data, graph->vertexList[toIndex - 1]->data);
MST->edgeCount++;
fromIndex = -1;
toIndex = -1;
minDistance = 0;
}
return MST;
}
克鲁斯卡尔算法(Kruskal)
克鲁斯卡尔算法的步骤:
- 将所有顶点都加入树 T T T,但是不加入边信息;
- 然后在图中寻找权值最小的边,若该边依附的顶点落在树 T T T的顶点上,且不形成环,那么就把该边加入到树 T T T中,否则就舍弃该边;
- 依次类推,直至T中所有顶点都连通。
/**
* 克鲁斯卡尔算法
* @param graph
* @return
*/
AdjacentListGraph Kruskal(AdjacentListGraph graph) {
AdjacentListGraph MST = adjacentListGraphConstructor(graph->vertexCount, graph->compare);
PriorityQueue queue = priorityQueueConstructor(graph->compare);
DisjointSet set = disjointSetConstructor(graph->vertexCount, graph->compare);
for (int i = 1; i <= graph->vertexCount; ++i) {
Vertex vertex = graph->vertexList[i - 1];
disjointSetInsert(set, vertex->data);
insertVertex(MST, vertex->data);
for (Edge edge = graph->vertexList[i - 1]->firstEdge; edge != NULL; edge = edge->next) {
int *tuple = calloc(3, sizeof(int));
tuple[0] = i;
tuple[1] = edge->vertexIndex;
tuple[2] = edge->weight;
priorityQueueEnQueue(queue, tuple);
}
}
while (!priorityQueueIsEmpty(queue)) {
int *tuple = priorityQueueDeQueue(queue);
Vertex fromVertex = graph->vertexList[tuple[0] - 1];
Vertex toVertex = graph->vertexList[tuple[1] - 1];
int weight = tuple[2];
if (graph->compare(disjointSetFind(set, fromVertex->data), disjointSetFind(set, toVertex->data)) != 0) {
addEdge(MST, fromVertex->data, toVertex->data);
setWeight(MST, fromVertex->data, toVertex->data, weight);
disjointSetUnion(set, fromVertex, toVertex);
}
}
return MST;
}
最短路径
在图中,把一个顶点到另一个顶点的一条路径所经过边上的权值 (无权图视为权为 1 1 1)之和称为该路径的带权路径长度,带权路径长度最短的路径称为最短路径。两点之间的最短路径一定包含路径上其它顶点之间的最短路径。其中:
- 无权图的单源最短路径问题可由 B F S BFS BFS算法和 D i j k s t r a Dijkstra Dijkstra算法解决
- 带权图的单源最短路径问题可由 D i j k s t r a Dijkstra Dijkstra算法解决
- 带权图和无权图的各顶点最短路径问题可由 F l o y d Floyd Floyd算法解决
BFS求最短路径
/**
* BFS求无权图最短路径
* @param graph
* @param startVertex
* @param endVertex
* @param stack
*/
void BFSMinPath(AdjacentListGraph graph, void *startVertex, void *endVertex, SequenceStack stack) {
//起始顶点到各个顶点的最短路径
int distance[graph->vertexCount];
//最短路径从哪个顶点过来
int path[graph->vertexCount];
bool isVisited[graph->vertexCount];
for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexCount; ++i) {
distance[i] = INFINITY;
path[i] = -1;
isVisited[i] = false;
}
int startIndex = getVertexIndex(graph, startVertex);
LinkedQueue queue = linkedQueueConstructor();
distance[startIndex - 1] = 0;
isVisited[startIndex - 1] = true;
linkedQueueEnQueue(queue, startVertex);
while (linkedQueueIsEmpty(queue)) {
Vertex vertex = linkedQueueDeQueue(queue);
for (Vertex near = firstVertex(graph, vertex->data); near != NULL; near = nextVertex(graph, vertex->data, near->data)) {
int nearIndex = getVertexIndex(graph, near->data);
if (!isVisited[nearIndex - 1]) {
distance[nearIndex - 1] = distance[startIndex - 1] + 1;
path[nearIndex - 1] = startIndex;
isVisited[nearIndex - 1] = true;
linkedQueueEnQueue(queue, near);
}
}
}
int minPath = getVertexIndex(graph, endVertex);
while (path[minPath - 1] != -1) {
sequenceStackPush(stack, graph->vertexList[minPath - 1]);
minPath = path[minPath - 1];
}
}
迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra)
算法思想:
- 首先找出源顶点到达其它顶点的直达路径,不能直达记为无穷大。
- 从这些路径中挑选一条长度最短的路径。并将该顶点加入集合S。
- 对其余的路径进行调整,若能经过找到的最短路径到达其它顶点并且该路径之和比直达路径小,那么就是用该路径替代原来的直达路径。并将该顶点加入集合S。
- 之后重复上述步骤直到所有顶点都加入到S集合。
缺陷:不适用于负权值带权图
/**
* 迪杰斯特拉算法
* @param graph
* @param startVertex
* @param endVertex
* @param stack
*/
void Dijkstra(AdjacentListGraph graph, void *startVertex, void *endVertex, SequenceStack stack) {
int findCount = 0;
//标记各顶点是否找到最短路径
bool isFind[graph->vertexCount];
//最短路径长度
int distance[graph->vertexCount];
//路径前驱
int path[graph->vertexCount];
for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertexCount; ++i) {
isFind[i] = false;
distance[i] = INFINITY;
path[i] = -1;
}
while (findCount != graph->vertexCount) {
int fromIndex = -1, toIndex = -1, minDistance = 0;
if (findCount == 0) {
toIndex = getVertexIndex(graph, startVertex);
} else {
for (int i = 1; i <= graph->vertexCount; ++i) {
if (isFind[i - 1] == false && distance[i - 1] < minDistance) {
fromIndex = path[i - 1];
toIndex = i;
minDistance = distance[i - 1];
}
}
if (toIndex == -1) {
break;
}
}
isFind[toIndex - 1] = true;
distance[toIndex - 1] = minDistance;
path[toIndex - 1] = fromIndex;
for (Edge edge = graph->vertexList[toIndex - 1]->firstEdge; edge != NULL; edge = edge->next) {
if (distance[toIndex - 1] + edge->weight < distance[edge->vertexIndex - 1]) {
distance[edge->vertexIndex - 1] = distance[toIndex - 1] + edge->weight;
path[edge->vertexIndex - 1] = toIndex;
}
}
findCount++;
fromIndex = -1;
toIndex = -1;
minDistance = 0;
}
int minPath = getVertexIndex(graph, endVertex);
while (path[minPath - 1] != -1) {
sequenceStackPush(stack, graph->vertexList[minPath - 1]);
minPath = path[minPath - 1];
}
}
弗洛伊德算法(Floyd)
- 逐个顶点试探,选出一条路径长度最短的。
- 初始时用一个矩阵存储各个顶点之间的距离,如果存在直达路径则记录直达路径,否则记录为无穷大。
- 逐步在原直接路径中增加中间顶点,若加入中间顶点后路径变短,则修改矩阵中的值,否则矩阵中的值不变。
- 所有顶点试探完毕,算法结束。
有向无环图
若一个有向图中不存在环,则称该图为有向无环图,简称DAG图。若用DAG图表示一个工程的各个子工程及其相互制约的关系:
-
其中以顶点表示活动,弧表示活动之间的优先制约关系。则将这样的图称为AOV网。AOV网的特点如下:
- 若从A到B有一条有向路径,则A是B的前驱,B是A的后继。
- 若AB是网中的有向边,则A是B的直接前驱,B是A的直接后继。
-
其中以弧表示活动,顶点表示活动之的开始和结束事件。则将这样的图称为AOE网。AOE网的性质如下:
- 只有在某顶点所代表的事件发生后,从该顶点出发的各有向边所代表的活动才能开始。
- 只有在进入某顶点的各有向边所代表的活动都已结束时,该顶点所代表的事件才能发生。
AOV网的拓扑结构
在AOV网中,我们将全部活动排列成一个线性序列,使得若AOV网中有边AB存在,则在这个序列中,A一定排在B的前面,具有这种性质的线性序列称为拓扑有序序列。即做事的先后顺序。用于求解拓扑序列的算法称为拓扑排序算法,拓扑排序算法可以用于检测图中是否含有环:如果拓扑序列中含有所有图中的结点,那么该图就没有环,否则就含有环。
拓扑排序
拓扑排序的算法思想如下:
- 在AOV网中选一个没有前驱的顶点,然后从图网中删除该顶点以及以这个顶点为起点的边。
- 重复上面的步骤,直到网为空或网中不存在无前驱的顶点为止。
/**
* 拓扑排序
* @param graph
* @param queue
*/
void topologicalSort(AdjacentListGraph graph, LinkedQueue queue) {
SequenceStack stack = sequenceStackConstructor(graph->vertexCount);
int inDegreeList[graph->vertexCount];
for (int i = 1; i <= graph->vertexCount; ++i) {
inDegreeList[i - 1] = getInDegree(graph, graph->vertexList[i - 1]->data);
if (inDegreeList[i - 1] == 0) {
sequenceStackPush(stack, graph->vertexList[i - 1]);
}
}
while (!sequenceStackIsEmpty(stack)) {
Vertex vertex = sequenceStackPop(stack);
linkedQueueEnQueue(queue, vertex->data);
for (Edge edge = vertex->firstEdge; edge != NULL; edge = edge->next) {
if (--inDegreeList[edge->vertexIndex - 1] == 0) {
sequenceStackPush(stack, graph->vertexList[edge->vertexIndex - 1]);
}
}
}
}
逆拓扑排序
逆拓扑排序的算法思想如下:
- 在AOV网中选一个没有后继的顶点,然后从图网中删除该顶点以及以这个顶点为终点的边。
- 重复上面的步骤,直到网为空或网中不存在无后继的顶点为止。
void DFS(AdjacentListGraph graph, int index, int isVisited[], LinkedQueue queue) {
isVisited[index - 1] += 2;
Vertex vertex = graph->vertexList[index - 1];
for (Edge edge = vertex->firstEdge; edge != NULL; edge = edge->next) {
if (isVisited[edge->vertexIndex - 1] == 0) {
DFS(graph, edge->vertexIndex, isVisited, queue);
}
if (isVisited[edge->vertexIndex - 1] == 2) {
throw Error(CYCLIC_GRAPH_ERROR, "图中含有环,逆拓扑排序失败");
}
}
isVisited[index - 1]--;
linkedQueueEnQueue(queue, vertex->data);
}
/**
* 深度优先算法求逆拓扑排序
* @param graph
* @param queue
*/
void DFSInTopologicalSort(AdjacentListGraph graph, LinkedQueue queue) {
int *isVisited = calloc(graph->vertexCount, sizeof(bool));
for (int i = 1; i <= graph->vertexCount; ++i) {
if (isVisited[i - 1] == 0) {
DFS(graph, i, isVisited, queue);
}
}
}
AOE网的关键路径
在AOE网中,入度为零的顶点称为源点,出度为零的顶点称为汇点,关键路径是指从源点到汇点路径长度最长的路径。关键路径上的活动称为关键活动。完成整个工程最短的时间就是关键路径的长度。