1 模板
1.1 模板的概念

1.2 函数的模板

1.2.1 函数的模板语法
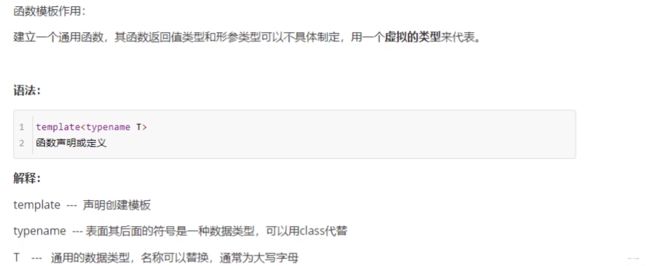
template<typename T>
void mySwap(T &a, T &b) {
T temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void test() {
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
string c = "c";
string d = "d";
mySwap(a, b);
mySwap(c, d);
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
cout << "d = " << d << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
1.2.2 函数模板注意事项

1.2.3 函数模板案例

template<class T>
void mySwap(T &a, T &b) {
T temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
template<class T>
void mySort(T arr,int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int max = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[max]) {
max = j;
}
}
if (max != i) {
mySwap(arr[max], arr[i]);
}
}
}
template<class T>
void myPrint(T arr,int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cout << arr[i] ;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
int arr1[] = { 1,5,9,0,2,8,4 };
char arr2[] = "asdwfg";
int len1;
int len2;
len1 = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(arr1[0]);
len2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
mySort(arr1, len1);
myPrint(arr1, len1);
mySort(arr2,len2);
myPrint(arr2, len2);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
1.2.4 普通函数与函数模板的区别

mySwap<int>(a, b);
1.2.5 普通函数与函数模板的调用规则

mySwap<>(a, b);
1.2.6 模板的局限性
class person {
public:
int m_age;
string m_name;
person(int age, string name) {
this->m_age = age;
this->m_name = name;
}
};
template<class T>
bool myCompare(T &a, T &b) {
if (a == b) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
template<> bool myCompare(person &p1, person &p2) {
if (p1.m_age == p2.m_age&&p1.m_name == p2.m_name) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
void myPrint(bool &ret) {
if (ret) {
cout << "相同" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "不同" << endl;
}
}
void test() {
person p1 = { 18,"Tom" };
person p2 = { 28,"Tom" };
bool ret1 = myCompare(p1, p2);
myPrint(ret1);
bool ret2 = myCompare(p1.m_name, p2.m_name);
myPrint(ret2);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
1.3 类模板
1.3.1 类模板语法
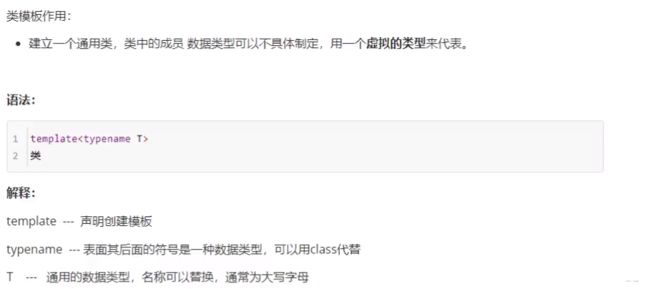
template<class nameType, class ageType>
class person{
public:
nameType m_name;
ageType m_age;
}
void test(){
person<string,int> p1("Tom",18);
}
1.3.2 类模板与函数模板区别

template<class nameType, class ageType = int>
class person{
public:
nameType m_name;
ageType m_age;
}
void test(){
person<string> p1("Tom",18);
}
1.3.3 类模板中成员函数创建时机

1.3.4 类模板对象做函数参数

cout << typeid(T).name() << endl;
template<class T1, class T2>
class person {
public:
T1 m_age;
T2 m_name;
person(T1 age, T2 name) {
this->m_age = age;
this->m_name = name;
}
void person_print() {
cout << this->m_age << endl;
cout << this->m_name << endl;
}
};
void myPrint01(person<int, string> &p1) {
p1.person_print();
}
void test01() {
person<int, string> p1(18, "Tom");
myPrint01(p1);
}
template<class T1,class T2>
void myPrint02(person<T1, T2> &p2) {
p2.person_print();
cout << typeid(T1).name() << endl;
}
void test02() {
person<int, string> p2(28, "Jack");
myPrint02(p2);
}
template<class T>
void myPrint03(T &p3) {
p3.person_print();
cout << typeid(T).name() << endl;
}
void test03() {
person<int, string> p3(38, "John");
myPrint03(p3);
}
int main() {
test01();
test02();
test03();
return 0;
}
1.3.5 类模板与继承

template<class T>
class Base {
public:
T m;
};
template<class T1,class T2>
class Son :public Base<T1> {
public:
T2 n;
Son() {
cout << typeid(T1).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(T2).name() << endl;
}
};
void test() {
Son<int, string> s1;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
1.3.6 类模板成员函数类外实现
template<class T1, class T2>
class person {
public:
T1 m_age;
T2 m_name;
person(T1 age, T2 name);
void person_print();
};
template<class T1, class T2>
person<T1, T2>::person(T1 age, T2 name) {
this->m_age = age;
this->m_name = name;
}
template<class T1, class T2>
void person<T1, T2>::person_print() {
cout << this->m_age << endl;
cout << this->m_name << endl;
}
void test() {
person<int, string> p1(18,"Tom");
p1.person_print();
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
1.3.7 类模板分文件编写

#pragma once
#include
#include
using namespace std;
template<class T1, class T2>
class tree {
public:
T1 m_age;
T2 m_name;
tree(T1 age, T2 name);
void tree_print();
};
template<class T1, class T2>
tree<T1, T2>::tree(T1 age, T2 name) {
this->m_age = age;
this->m_name = name;
}
template<class T1, class T2>
void tree<T1, T2>::tree_print() {
cout << this->m_age << endl;
cout << this->m_name << endl;
}
#include"tree.hpp"
void test() {
tree<int, string> t1(180,"银杏");
t1.tree_print();
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
1.3.8 类模板与友元

template<class T1, class T2>
class person;
template<class T1, class T2>
void person_print2(person<T1, T2> p) {
cout << " 类外实现 " << p.m_name << endl;
}
template<class T1, class T2>
class person {
friend void person_print1(person<T1,T2> p) {
cout << " 类内实现 " << p.m_name << endl;
}
friend void person_print2<>(person<T1, T2> p);
public:
person(T1 age, T2 name) {
this->m_age = age;
this->m_name = name;
}
private:
T1 m_age;
T2 m_name;
};
void test() {
person<int, string> p1(18,"Tom");
person_print1(p1);
person<int, string> p2(28, "Rose");
person_print2(p2);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
1.3.9 类模板案例 — 通用数组

class person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
person() {};
person(string name, int age) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
};
void printArray(myArray<person> & arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.get_size(); i++) {
cout << arr[i].m_name << "\n" << arr[i].m_age << endl;
}
}
void test() {
myArray<person> arr1(3);
person p1("A", 18);
person p2("B", 28);
person p3("C", 38);
arr1.push_back(p1);
arr1.push_back(p2);
arr1.push_back(p3);
printArray(arr1);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
#pragma once
#include
#include
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class myArray {
public:
myArray(int capacity) {
this->m_Capacity = capacity;
this->m_size = 0;
this->pAddress = new T[this->m_Capacity];
}
myArray(const myArray & arr) {
this->m_Capacity = arr.m_Capacity;
this->m_size = arr.m_size;
this->pAddress = new T[arr.m_Capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < this->m_size; i++) {
this->pAddress[i] = arr.pAddress[i];
}
}
myArray & operator=(const myArray & arr) {
if (this->pAddress != NULL) {
delete[] this->pAddress;
this->pAddress = NULL;
this->m_Capacity = 0;
this->m_size = 0;
}
this->m_Capacity = arr.m_Capacity;
this->m_size = arr.m_size;
this->pAddress = new T[arr.m_Capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < this->m_size; i++) {
this->pAddress[i] = arr.pAddress[i];
}
return *this;
}
void push_back(const T & val) {
if (this->m_size == this->m_Capacity) {
return;
}
this->pAddress[this->m_size] = val;
this->m_size++;
}
void pop_back() {
if (this->m_size == 0) {
return;
}
this->m_size--;
}
T& operator[](int index) {
return this->pAddress[index];
}
int get_Capacity() {
return this->m_Capacity;
}
int get_size() {
return this->m_size;
}
~myArray() {
if (this->pAddress != NULL) {
delete[] this->pAddress;
this->pAddress = NULL;
}
}
private:
T * pAddress;
int m_Capacity;
int m_size;
};
2 STL初识
2.1 STL的诞生

2.2 STL基本概念

2.3 STL六大组件

2.4 STL中容器、算法、迭代器




2.5 容器、算法、迭代器初识
2.5.1 vector存放内置数据类型

#include
#include
void myPrint(int val) {
cout << val << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(3);
vector<int>::iterator itBegin = v1.begin();
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = v1.end();
while (itBegin != itEnd) {
myPrint(*itBegin);
itBegin++;
}
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); it++) {
myPrint(*it);
}
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), myPrint);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
2.5.2 vector存放自定义数据类型

#include
class person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
person(string name,int age) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
};
void myPrint(person &p) {
cout << p.m_name << "\t" << p.m_age << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<person> p;
person p1("张三", 18);
person p2("李四", 28);
person p3("王五", 38);
p.push_back(p1);
p.push_back(p2);
p.push_back(p3);
for (vector<person>::iterator it1 = p.begin(); it1 != p.end(); it1++) {
myPrint(*it1);
}
vector<person*> v;
person p4("张三", 19);
person p5("李四", 29);
person p6("王五", 39);
v.push_back(&p4);
v.push_back(&p5);
v.push_back(&p6);
for (vector<person*>::iterator it2 = v.begin(); it2 != v.end(); it2++) {
myPrint(**it2);
}
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
2.5.3 vector容器嵌套容器

#include
void test() {
vector<vector<int>> v;
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
vector<int> v3;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i * 10 + 1);
v3.push_back((i + 2) * 7);
}
v.push_back(v1);
v.push_back(v2);
v.push_back(v3);
for (vector<vector<int>>::iterator it1 = v.begin(); it1 != v.end(); it1++) {
for (vector<int>::iterator it2 = (*it1).begin(); (it2) != (*it1).end(); it2++) {
cout << *it2 << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3 STL-常用容器
3.1 string容器
3.1.1 string基本概念

3.1.2 string构造函数

void test() {
string s1;
const char* str = "hello world";
string s2(str);
string s3(s2);
string s4(5, 'a');
cout << s1 << endl
<< s2 << endl
<< s3 << endl
<< s4 << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.1.3 string赋值操作

void test() {
string str1;
str1.assign("hello world");
cout << str1 << endl;
string str2;
str2.assign("hello world", 8);
cout << str2 << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.1.4 string字符串拼接

void test() {
string str1 = "~$root:";
str1 += "zxy";
cout << str1 << endl;
string str2 = ":";
str1 += str2;
cout << str1 << endl;
str1.append("sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-moveit",10);
cout << str1 << endl;
string str3 = "sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-moveit";
str1.append(str3, 10,-1);
cout << str1 << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.1.5 string查找与替换
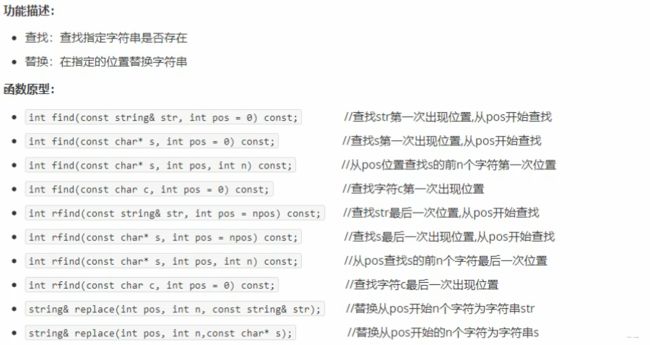
void test() {
string str = "abcdab";
int pos;
pos = str.find("ab");
cout << "find : " << pos << endl;
pos = str.rfind("ab");
cout << "rfind: " << pos << endl;
string str2 = " ab ** ab ";
str.replace(2, 2, str2);
cout << str << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.1.6 string字符串比较

string str1 = "abc";
string str2 = "bbc";
int ret = str1.compare(str2);
3.1.7 string字符存取

void test() {
string str1 = "abcdefg";
for (int i = 0; i < str1.size(); i++) {
cout << str1[i] ;
cout << str1.at(i) ;
}
for (int i = 0; i < str1.size(); i++) {
str1.at(i) = 'x';
}
cout << str1 << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.1.8 string插入与删除

void test() {
string str1 = "abcde";
string str2 = "123";
str1.insert(2, str2);
cout << str1 << endl;
str1.erase(2, 3);
cout << str1 << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.1.9 string子串

void test() {
string email = "[email protected]";
int pos = email.find('@');
string sub_name = email.substr(0, pos);
cout << sub_name << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.2 vector容器
3.2.1 vector基本概念

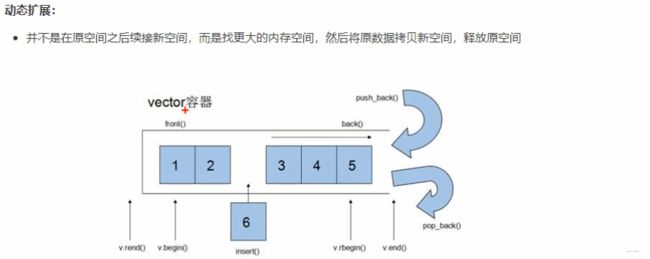
3.2.2 vector构造函数

#include
void printVector(vector<int> &v) {
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i * 6 + 8);
}
printVector(v1);
vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());
printVector(v2);
vector<int> v3(10,100);
printVector(v3);
vector<int> v4(v3);
printVector(v4);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.2.3 vector赋值操作

vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i * 6 + 8);
}
vector<int> v2;
v2 = v1;
vector<int> v3;
v3.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end());
vector<int> v4;
v4.assign(10,100);
3.2.4 vector容量和大小

#include
void printVector(vector<int> &v) {
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "v1的容量为: " << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v1的大小为: " << v.size() << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i * 9 + 8);
}
if (v1.empty()) {
cout << "v1 is empty" << endl;
}
else {
printVector(v1);
v1.resize(15,100);
printVector(v1);
v1.resize(5);
printVector(v1);
}
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.2.5 vector插入与删除

#include
void printVector(vector<int> &v) {
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i * 8 + 8);
}
printVector(v1);
v1.pop_back();
printVector(v1);
v1.insert(v1.begin() + 1, 2, 99);
printVector(v1);
v1.erase(v1.begin() + 2);
printVector(v1);
v1.clear();
printVector(v1);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.2.6 vector数据存取

#include
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i * 11 + 45);
}
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++) {
cout << v1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++) {
cout << v1.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "第一个元素 : " << v1.front() << endl;
cout << "最后一个元素: " << v1.back() << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.2.7 vector互换容器

#include
void printVector(vector<int> &v,string index) {
cout << index << ": ";
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i * 13 + 24);
}
printVector(v1,"v1");
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v2.push_back(i * 56 + 2);
}
printVector(v2, "v2");
v1.swap(v2);
printVector(v1, "v1");
printVector(v2, "v2");
vector<int> v3;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
v3.push_back(i * 13 + 24);
}
cout << "v3的容量为: " << v3.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v3的大小为: " << v3.size() << endl;
v3.resize(10);
cout << "v3的容量为: " << v3.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v3的大小为: " << v3.size() << endl;
vector<int>(v3).swap(v3);
cout << "v3的容量为: " << v3.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v3的大小为: " << v3.size() << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.2.8 vector预留空间

#include
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
int num = 0;
int * p = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
if (p != &v1[0]) {
p = &v1[0];
num++;
}
}
cout << "v1开辟内存空间次数: " << num << endl;
vector<int> v2;
v2.reserve(1000);
int re_num = 0;
int * re_p = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
v2.push_back(i);
if (re_p != &v2[0]) {
re_p = &v2[0];
re_num++;
}
}
cout << "v2开辟内存空间次数: " << re_num << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.3 deque容器
3.3.1 deque容器基本概念
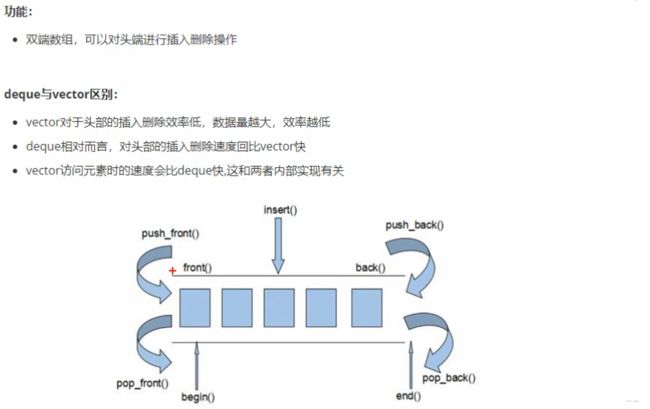

3.3.2 deque构造函数

#include
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d) {
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
deque<int> d1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
d1.push_back(i * 11);
d1.push_front(i * 10);
}
printDeque(d1);
deque<int> d2(d1.begin() + 1, d1.end()-1);
printDeque(d2);
deque<int> d3(20,99);
printDeque(d3);
deque<int> d4(d3);
printDeque(d4);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.3.3 deque赋值操作

3.3.4 deque大小操作

3.3.5 deque插入与删除

deque<int> d1;
deque<int> d2;
d1.insert(d1.begin(),d2.begin(),d2.end())
3.3.6 deque数据存取

3.3.7 deque排序

#include
#include
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d) {
for (int i = 0; i < d.size(); i++) {
cout << d[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
deque<int> d1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
d1.push_back(i * 11);
d1.push_front(i * 10);
}
printDeque(d1);
sort(d1.begin(), d1.end());
printDeque(d1);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.4 案例 – 评委打分
3.4.1 案例描述
3.4.2 实现步骤

3.4.3 案例实现
#include
#include
#include
#include
class player {
public:
int m_id;
int m_score;
deque<int> score;
player(int m_id,int m_score){
this->m_id = m_id;
this->m_score = m_score;
}
void printScore() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
cout << this->score[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
};
void pushPlayer(vector<player> &play) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
player p(i + 1, 0);
play.push_back(p);
}
}
void test() {
vector<player> play;
play.reserve(5);
pushPlayer(play);
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
for (vector<player>::iterator it = play.begin(); it != play.end(); it++) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int score_rand = rand() % 41 + 60;
it->score.push_back(score_rand);
}
sort(it->score.begin(), it->score.end());
it->printScore();
it->score.pop_back();
it->score.pop_front();
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < it->score.size(); i++) {
sum += it->score[i];
}
int avg = sum / it->score.size();
it->m_score = avg;
cout << "id: " << it->m_id << " 成绩为: " << it->m_score << endl << endl;
}
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.5 stack容器
3.5.1 stack基本概念

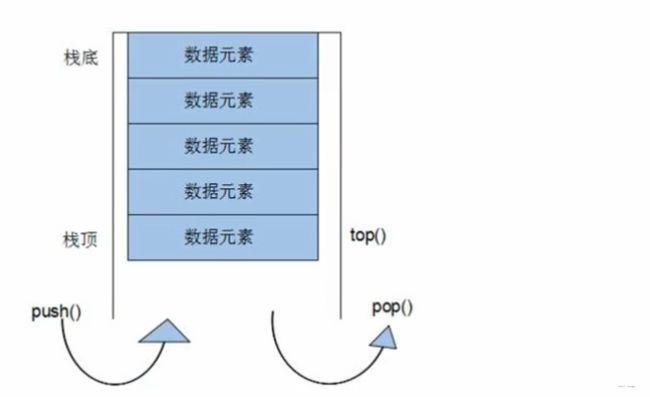
- 栈不允许有遍历行为
- 栈可以判断容器是否为空 empty()
- 栈可以返回元素个数 size()
3.5.2 stack常用接口

#include
void test() {
stack<int> s;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
s.push(i * 4 + 1);
}
cout << "出栈前栈的大小: " << s.size() << endl;
while (!s.empty()) {
cout << s.top() << endl;
s.pop();
}
cout << "出栈后栈的大小: " << s.size() << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.6 queue容器
3.6.1 queue基本概念

- 队列不允许有遍历行为
- 队列可以判断容器是否为空 empty()
- 队列可以返回元素个数 size()
3.6.2 queue常用接口

#include
void test() {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
q.push(i * 7 + 2);
}
while (!q.empty()) {
cout << "队列的队头: " << q.front() << endl;
cout << "队列的队尾: " << q.back() << endl;
q.pop();
}
cout << "" << q.size() << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.7 list容器
3.7.1 list基本概念


- 链表可以在任意位置进行快速的插入或删除元素
- 链表动态分配存储,不会造成内存浪费
- 链表遍历速度慢
- 链表占用空间大
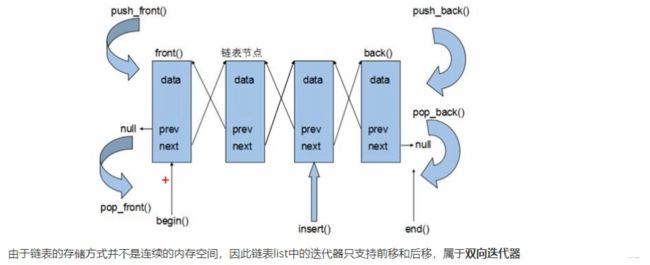
- List链表中,插入和删除元素不会造成原有list迭代器的失效,而vector是不成立的(内存满了之后另开一处空间进行存储)
3.7.2 list构造函数

#include
void printList(const list<int> &L) {
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
list<int> L1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
L1.push_back(i * 2 + 3);
}
printList(L1);
list<int> L2(L1.begin(), L1.end());
printList(L2);
list<int> L3(L2);
printList(L3);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.7.3 list赋值与交换

3.7.4 list大小操作

3.7.5 list插入与删除

#include
void printList(const list<int> &L) {
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
list<int> L1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
L1.push_back(i % 2 );
}
printList(L1);
L1.insert(++L1.begin(), 2, 3);
printList(L1);
L1.erase(++L1.begin());
printList(L1);
L1.remove(0);
printList(L1);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.7.6 list数据存取

3.7.7 list反转与排序

#include
void printList(const list<int> &L) {
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
bool myCompare(int v1, int v2) {
return v1 > v2;
}
void test() {
list<int> L1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
L1.push_back((i % 2) * 6 + i);
}
printList(L1);
L1.reverse();
cout << "反转后的链表: " << endl;
printList(L1);
L1.sort();
cout << "排序后的链表: " << endl;
printList(L1);
L1.sort(myCompare);
printList(L1);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.7.8 list排序案例

#include
#include
class person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
int m_height;
person() {};
person(string name, int age,int height) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
this->m_height = height;
}
};
void creatPerson(list<person> &L,int num) {
string nameSeed = "ABCDEFGHIJK";
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
person p;
p.m_name += nameSeed[i];
p.m_age = 20 + rand() % 5;
p.m_height = 180 + rand() % 10;
L.push_back(p);
}
}
void printList(const list<person> &L) {
for (list<person>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++) {
cout << "姓名: " << (*it).m_name << " 年龄: " << (*it).m_age << " 身高: " << (*it).m_height << endl;
}
}
bool myCompare(person &p1,person &p2) {
if (p1.m_age != p2.m_age) {
return p1.m_age < p2.m_age;
}
else {
return p1.m_height > p2.m_height;
}
}
void test() {
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
list<person> L1;
creatPerson(L1, 10);
cout << "排序前:" << endl;
printList(L1);
cout << "排序后:" << endl;
L1.sort(myCompare);
printList(L1);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.8 set/multiset容器
3.8.1 set基本概念

3.8.2 set构造和赋值

#include
#include
void printSet(const set<int> &s) {
for (set<int>::const_iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void printSet(const multiset<int> &s) {
for (multiset<int>::const_iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
set<int> s1;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
s1.insert(rand() % 10);
}
printSet(s1);
multiset<int> s2;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
s2.insert(rand() % 10);
}
printSet(s2);
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.8.3 set大小和交换

3.8.4 set插入与删除

3.8.5 set查找和统计

#include
#include
void test() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
set<int> s1;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
s1.insert(rand() % 10);
}
set<int>::iterator pos = s1.find(5);
if (pos != s1.end()) {
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
multiset<int> s2;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
s2.insert(rand() % 10);
}
int num = s2.count(5);
cout << "元素个数为: " << num << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.8.6 set和multiset区别

#include
#include
void test() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
set<int> s1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> ret = s1.insert(rand() % 10);
if (ret.second) {
cout << "数据插入成功 " << *ret.first << endl;
}
else {
cout << "数据插入失败 " << *ret.first << endl;
}
}
multiset<int> s2;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
s2.insert(rand() % 10);
}
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.8.7 pair对组创建

void test() {
pair<int, string> p1(1, "a");
cout << p1.first << " " << p1.second << endl;
pair<int, string> p2 = make_pair(2, "b");
cout << p2.first << " " << p2.second << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}
3.8.8 set容器排序

#include
class person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
int m_height;
person() {};
person(string name, int age, int height) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
this->m_height = height;
}
};
class myCompare1 {
public:
bool operator()(int v1, int v2) {
return v1 > v2;
}
};
class myCompare2 {
public:
bool operator()(const person &p1, const person &p2) {
if (p1.m_age == p2.m_age) {
return p1.m_height > p2.m_height;
}
else {
return p1.m_age > p2.m_age;
}
}
};
void creatPerson(int num, set<person, myCompare2> &s) {
string nameSeed = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMN";
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
person p;
p.m_name += nameSeed[i];
p.m_age = 20 + rand() % 10;
p.m_height = 170 + rand() % 10;
s.insert(p);
}
}
void printSet(set<person, myCompare2> &s) {
for (set<person, myCompare2>::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++) {
cout << " 姓名: " << (*it).m_name << " 年龄: " << (*it).m_age << " 身高: " << (*it).m_height << endl;
}
}
void test() {
set<int, myCompare1> s1;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
s1.insert(rand() % 10);
}
for (set<int, myCompare1>::iterator it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
set<person, myCompare2> s2;
creatPerson(9, s2);
printSet(s2);
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
3.9 map/multimap容器
3.9.1 map基本概念

3.9.2 map构造和赋值

#include
void printMap(const map<int, int> &m) {
for (map<int, int>::const_iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) {
cout << it->first << "\t" << it->second << endl;
}
}
void test() {
map<int, int> m1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
m1.insert(pair<int, int>(i, rand() % 41 + 60));
}
printMap(m1);
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
3.9.3 map大小和交换

3.9.4 map插入与删除

#include
void printMap(const map<int, int> &m) {
for (map<int, int>::const_iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) {
cout << it->first << "\t" << it->second << endl;
}
}
void test() {
map<int, int> m1;
m1.insert(pair<int, int>(5, 10));
m1.insert(make_pair(4, 20));
m1.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30));
printMap(m1);
m1.erase(m1.begin());
printMap(m1);
m1.erase(4);
printMap(m1);
m1.erase(m1.begin(),m1.end());
printMap(m1);
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
3.9.5 map查找和统计

3.9.6 map容器排序

#include
class mapCompare {
public:
bool operator()(int v1, int v2) {
return v1 > v2;
}
};
void printMap(const map<int, int, mapCompare> &m) {
for (map<int, int, mapCompare>::const_iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) {
cout << it->first << "\t" << it->second << endl;
}
}
void test() {
map<int, int, mapCompare> m1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
m1.insert(make_pair(i, rand() % 41 + 60));
}
printMap(m1);
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
3.10 案例 – 员工分组
3.10.1 案例描述

3.10.2 实现步骤

3.10.3 案例实现
#include
#include
#include
#define CEHUA 0
#define MEISHU 1
#define YANFA 2
class stuff {
public:
string m_name;
int m_salary;
stuff() {};
stuff(string name, int salary) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_salary = salary;
}
};
void creatStuff(vector<stuff> &v) {
string nameSeed = "ABCDEFGHIJ";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
stuff s;
s.m_name += nameSeed[i];
s.m_salary = 5000 + (rand() % 10) * 500;
v.push_back(s);
}
}
void printStuff(const multimap<int, stuff> &m) {
cout << "------------------------" << endl;
cout << "策划部门:" << endl;
multimap<int, stuff>::const_iterator pos = m.find(CEHUA);
int num = m.count(CEHUA);
int index = 0;
for (; pos != m.end() && index < num; pos++, index++) {
cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_name << " 工资:" << pos->second.m_salary << endl;
}
cout << "------------------------" << endl;
cout << "美术部门:" << endl;
pos = m.find(MEISHU);
num = m.count(MEISHU);
index = 0;
for (; pos != m.end() && index < num; pos++, index++) {
cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_name << " 工资:" << pos->second.m_salary << endl;
}
cout << "------------------------" << endl;
cout << "研发部门:" << endl;
pos = m.find(YANFA);
num = m.count(YANFA);
index = 0;
for (; pos != m.end() && index < num; pos++, index++) {
cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_name << " 工资:" << pos->second.m_salary << endl;
}
}
void allocateDepart(const vector<stuff> &v, multimap<int, stuff> &m) {
for (vector<stuff>::const_iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) {
m.insert(make_pair(rand() % 3 , *it));
}
}
void test() {
vector<stuff> v;
creatStuff(v);
multimap<int, stuff> m;
allocateDepart(v,m);
printStuff(m);
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
4 STL-函数对象
4.1 函数对象
4.1.1 函数对象概念

4.1.2 函数对象使用

class myPrint {
public:
int count;
myPrint() {
this->count = 0;
}
void operator()(string text) {
cout << text << endl;
count++;
}
};
void print_test(myPrint &mP, string text) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
mP(text);
}
cout << mP.count << endl;
}
void test() {
myPrint mP;
string text = "hello world";
print_test(mP, text);
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
4.2 谓词
4.2.1 谓词概念

4.2.1 一元谓词
#include
#include
class score {
public:
bool operator()(int value) {
return value > 90;
}
};
void test() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v.push_back(60 + rand() % 41);
}
vector<int>::iterator pos = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), score());
if (pos == v.end()) {
cout << "failed" << endl;
}
else {
cout << *pos << endl;
}
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
4.2.1 二元谓词
#include
#include
class sortRules {
public:
bool operator()(int v1, int v2) {
return v1 > v2;
}
};
void printVector(vector<int> &v) {
for (vector<int>::iterator pos = v.begin(); pos != v.end(); pos++) {
cout << *pos << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v.push_back(60 + rand() % 41);
}
cout << "修改规则前:" << endl;
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
printVector(v);
cout << "修改规则后: " << endl;
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), sortRules());
printVector(v);
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test(); return 0;
}
4.3 内建函数对象
4.3.1 内建函数对象意义

4.3.2 算术仿函数

#include
void test() {
negate<int> n;
cout << n(10) << endl;
modulus<int> m;
cout << m(50, 7) << endl;
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
4.3.3 关系仿函数

#include
#include
#include
void test() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v.push_back(60 + rand() % 41);
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());
for (vector<int>::iterator pos = v.begin(); pos != v.end(); pos++) {
cout << *pos << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
4.3.4 逻辑仿函数

#include
#include
#include
void test() {
vector<bool> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(rand() % 2);
}
vector<bool> v2;
v2.resize(v1.size());
transform(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), logical_not<bool>());
for (vector<bool>::iterator pos = v2.begin(); pos != v2.end(); pos++) {
cout << *pos << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
5 STL-常用算法

5.1 常用遍历算法

5.1.1 for_each

#include
#include
void printVector1(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
class printVector2 {
public:
void operator()(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
};
void test() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v.push_back(rand() % 100);
}
cout << "普通函数:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), printVector1);
cout << endl;
cout << "仿函数:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), printVector2());
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
5.1.2 transform

#include
#include
void printVector(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
class transRules {
public:
int operator()(int val) {
return ++val;
}
};
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
}
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), printVector);
cout << endl;
vector<int> v2;
v2.resize(v1.size());
transform(v1.begin(),v1.end(),v2.begin(),transRules());
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), printVector);
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
5.2 常用查找算法

5.2.1 find

#include
#include
class person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
person() {};
person(string name,int age) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
bool operator==(const person &p) {
if (this->m_name == p.m_name&&this->m_age == p.m_age) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
};
void test() {
vector<person> v;
string nameSeed = "ABCDEFGHIJK";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
person p;
p.m_name += nameSeed[i];
p.m_age = 23 + rand() % 3;
v.push_back(p);
}
person pFind("A",25);
vector<person>::iterator pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), pFind);
if (pos == v.end()) {
cout << "未找到一样的人" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "找到一样的人" << endl;
}
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
5.2.2 find_if

#include
#include
class person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
person() {};
person(string name, int age) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
};
class Greater {
public:
bool operator()(const person &p) {
if (p.m_age > 25) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
};
void test() {
vector<person> v;
string nameSeed = "ABCDEFGHIJK";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
person p;
p.m_name += nameSeed[i];
p.m_age = 23 + rand() % 4;
v.push_back(p);
}
vector<person>::iterator pos = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater());
if (pos == v.end()) {
cout << "未找到年龄大于25的人" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "找到年龄大于25的人" << endl;
}
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
5.2.3 adjacent_find

5.2.4 binary_search

5.2.5 count

#include
#include
class person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
person() {};
person(string name, int age) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
bool operator==(const person &p) {
if (this->m_age == p.m_age) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
};
void test() {
vector<person> v;
string nameSeed = "ABCDEFJHISAHJDJSAKLHFCVSDL";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
person p;
p.m_name = nameSeed[i];
p.m_age = rand() % 3 + 20;
v.push_back(p);
}
person pCount("Z", 21);
int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), pCount);
cout << "年龄相同的人数:" << num << endl;
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
5.2.6 count_find

#include
#include
class person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
person() {};
person(string name, int age) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
};
class PCount {
public:
bool operator()(const person &p) {
return p.m_age == 20;
}
};
void test() {
vector<person> v;
string nameSeed = "ABCDEFJHISAHJDJSAKLHFCVSDL";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
person p;
p.m_name = nameSeed[i];
p.m_age = rand() % 3 + 20;
v.push_back(p);
}
int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), PCount());
cout << "年龄相同的人数:" << num << endl;
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
5.3 常用排序算法

5.3.1 sort

#include
#include
class person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
person() {};
person(string name, int age) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
};
class sortRules {
public:
bool operator()(const person &p1, const person &p2) {
return p1.m_age > p2.m_age;
}
};
void printVector(const person &p) {
cout << "姓名:" << p.m_name << " 年龄:" << p.m_age << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<person> v;
string nameSeed = "ABCDEFJHISAHJDJSAKLHFCVSDL";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
person p;
p.m_name = nameSeed[i];
p.m_age = rand() % 10 + 20;
v.push_back(p);
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), sortRules());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), printVector);
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
5.3.2 random_shuffle
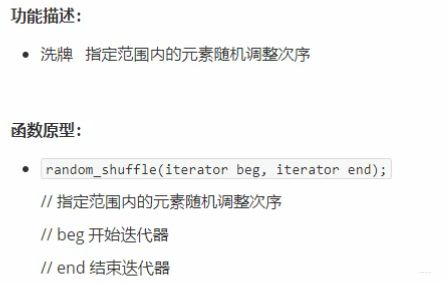
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
5.3.3 merge

#include
#include
class person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
person() {};
person(string name, int age) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
};
class sortRules {
public:
bool operator()(const person &p1, const person &p2) {
return p1.m_age > p2.m_age;
}
};
void printVector(const person &p) {
cout << "姓名:" << p.m_name << " 年龄:" << p.m_age << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<person> v1;
vector<person> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
person p1;
p1.m_name = "A";
p1.m_age = 20 + rand() % 10;
v1.push_back(p1);
person p2;
p2.m_name = "B";
p2.m_age = 20 + rand() % 10;
v1.push_back(p2);
}
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end(), sortRules());
sort(v2.begin(), v2.end(), sortRules());
vector<person> vTarget;
vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin(), sortRules());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), printVector);
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
5.3.4 reverse

5.4 常用拷贝和替换算法

5.4.1 copy

5.4.2 replace

#include
#include
class person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
person() {};
person(string name, int age) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
bool operator==(const person &p) {
return(this->m_name == p.m_name&&this->m_age == p.m_age);
}
};
class printVector {
public:
void operator()(const person &p) {
cout << "姓名:" << p.m_name << " 年龄:" << p.m_age << endl;
}
};
void test() {
vector<person> v;
string nameSeed = "ABCDEFJHISAHJDJSAKLHFCVSDL";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
person p;
p.m_name = nameSeed[0];
p.m_age = rand() % 3 + 20;
v.push_back(p);
}
cout << "替换前:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), printVector());
person pOLD("A",22);
person pNEW("a", 22000);
replace(v.begin(), v.end(), pOLD, pNEW);
cout << "替换后:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), printVector());
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
5.4.3 replace_if

#include
#include
class person {
public:
string m_name;
int m_age;
person() {};
person(string name, int age) {
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
void operator=(string name) {
this->m_name = name;
}
};
class printVector {
public:
void operator()(const person &p) {
cout << "姓名:" << p.m_name << " 年龄:" << p.m_age << endl;
}
};
class replaceRules {
public:
bool operator()(const person&p) {
return p.m_age > 30;
}
};
void test() {
vector<person> v;
string nameSeed = "ABCDEFJHISAHJDJSAKLHFCVSDL";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
person p;
p.m_name = nameSeed[i];
p.m_age = rand() % 10 + 25;
v.push_back(p);
}
cout << "替换前:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), printVector());
replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), replaceRules(), "大龄青年");
cout << "替换后:" << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), printVector());
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
5.4.4 swap

5.5 常用算术生成算法

5.5.1 accumulate

#include
accumulate(v.begin(),v.end(),0);
5.5.2 fill

5.6 常用集合算法

5.6.1 set_intersection
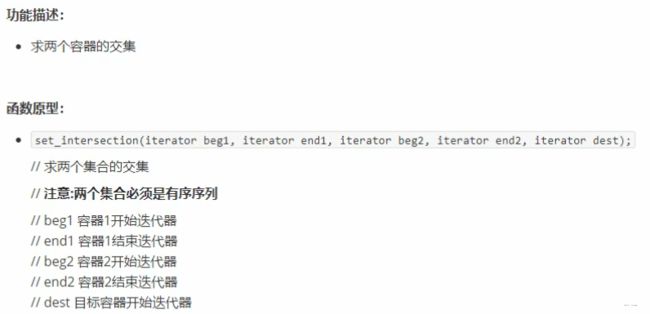
#include
#include
void printVector(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 5);
}
vector<int> vTarget;
vTarget.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));
vector<int>::iterator it_end = set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
cout << "交集为:" << endl;
for_each(vTarget.begin(), it_end, printVector);
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
test();
return 0;
}
5.6.2 set_union

vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
5.6.3 set_difference
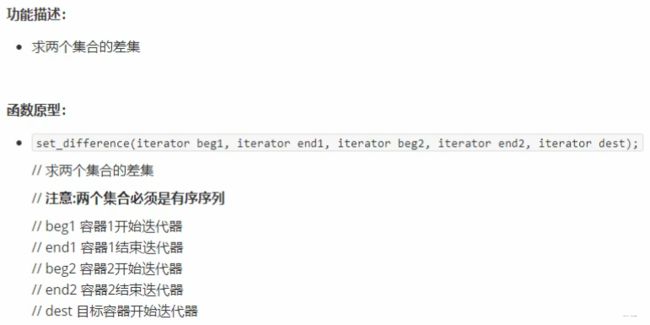
- 差集是所有元素除去交集部分后剩下的元素
- v1与v2的差集 和 v2对与v1的差集 结果不同
vTarget.resize(max(v1.size(), v2.size()));
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()










































































































