《JAVASE系列》牛客网java入门题集题解第一篇
《JAVASE系列》牛客网java入门题集题解第一篇
前言
本章讲解牛客网的java初级编程入门的前十五道题目。作为初学者,无论是已经学习了c语言去适应java语言的编程入门者,还是将java作为入门语言的新手,都适合将这个系列刷完。
刷题链接:编程语法练习-Java初级语法_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
JAVA1 类型转换
题目:
题解:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double d = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.println(Main.typeConversion(d));
}
public static int typeConversion(double d){
return (int) d;
较为简单,需要掌握基本的强制类型转换。
JAVA2 简单运算
题目
题解:
public static void incloud(int a,int b){
int c = a + b;
int d = a - b;
int e = a * b;
int f = a / b;
int g = a % b;
System.out.println(c+" "+d+" "+e+" "+f+" "+g+" ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.close();
if(a>b){
incloud(a,b);
}
else{
incloud(b,a);
}
}
本题用if else 语句实现,如果不用方法的话必须将实现内容放在两个代码块中,较为麻烦,用一个方法来实现a与b的功能。然后再使用if else判断 a b的大小,再放入方法中去。
JAVA3 四舍五入
题目
题解:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double d= scanner.nextDouble();
int b = (int)Math.round(d);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
需要知道能做到浮点数实现四舍五入的方法:Math.round。可以将浮点数四舍五入,返回long 类型,所以可以long类型接收,如果用其他类型,则需要强制类型转化。
JAVA4 交换变量
题目
题解:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
a = a ^ b;
b = a ^ b;
a = a ^ b;
System.out.println(a+" "+b);
}
这里需要掌握逻辑运算符,这是讲解一下逻辑运算符异或的计算技巧:“对于一个数a,如果异或它本身,得到的是 0 。而任何数字异或 0 都会得到其自身的值。”所以 第一句:a = a ^ b,即第二句: b = (a ^ b) ^ b = a ^ (b ^ b) = b ^ 0 = b; 得到第三句: a = a ^ b = (a ^ b) ^ a = (a ^ a) ^ b = b; (注意由于第二句的赋值,所以此时的b已经是a了)。
JAVA5 计算商场折扣
题目
题解
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);
int price = console.nextInt();
int cost = 0;
//write your code here......
if(price>=100&&price<500){
cost = (int)(price * 0.9);
}
else if (price>=500&&price<2000) {
cost = (int)(price * 0.8);
}
else if(price>=2000&&price<5000){
cost = (int)(price * 0.7);
}
else if(price>=5000)
{
cost = (int)(price * 0.6);
}
else{
cost = price;
}
System.out.println(cost);
}
本题需要掌握强制类型转换(因为一个整数*一个浮点数,得到的是浮点数。)以及分支语句if else。
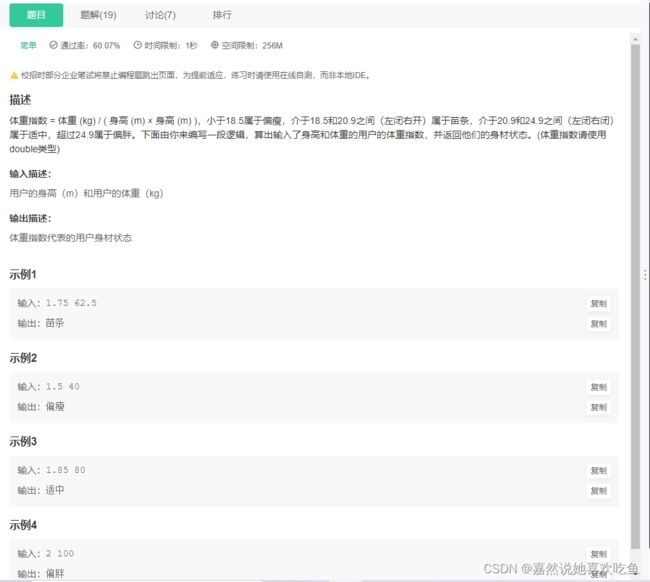
JAVA6 判断体重指数
题目:
题解
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double height = scanner.nextDouble();
double weight = scanner.nextDouble();
//write your code here......
double index = weight / (height*height);
if(index<18.5){
System.out.println("偏瘦");
}
else if(index>=18.5&&index<20.9) {
System.out.println("苗条");
}
else if(index>=20.9&&index<24.9) {
System.out.println("适中");
}
else{
System.out.println("偏胖");
}
}
较为简单,本题掌握 if else 语句与基本的运算即可。
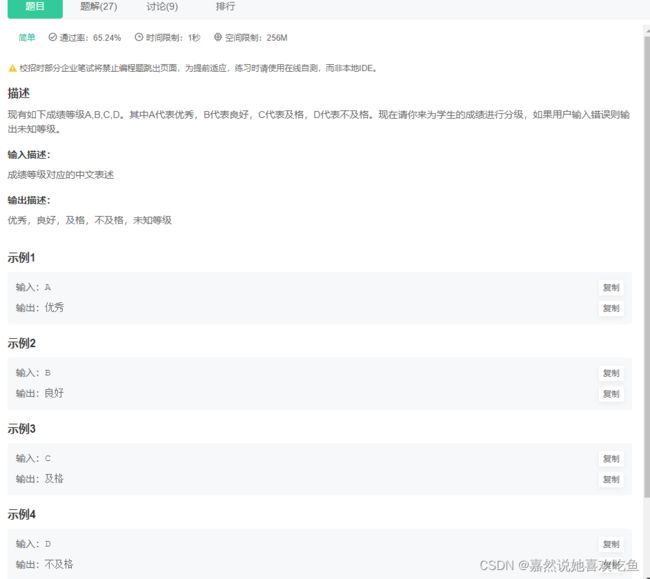
JAVA7 判断学生成绩等级
题目:
题解
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double height = scanner.nextDouble();
double weight = scanner.nextDouble();
//write your code here......
double index = weight / (height*height);
if(index<18.5){
System.out.println("偏瘦");
}
else if(index>=18.5&&index<20.9) {
System.out.println("苗条");
}
else if(index>=20.9&&index<24.9) {
System.out.println("适中");
}
else{
System.out.println("偏胖");
}
}
较为简单,本题掌握 if else 语句即可,当然对于本题而言,使用switch可以更加简单。
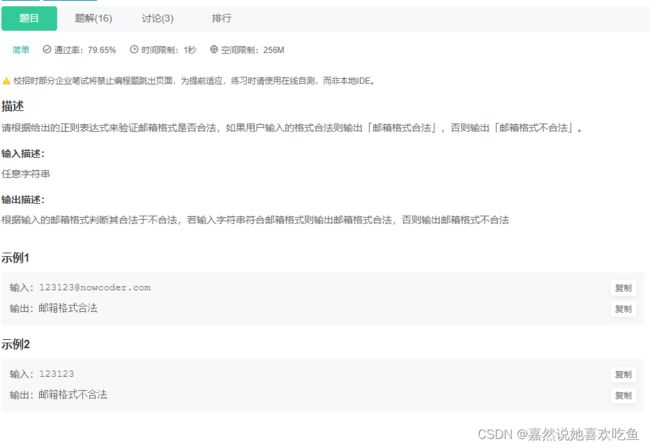
JAVA8 邮箱验证
题目
题解:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scanner.next();
String emailMatcher="[a-zA-Z0-9]+@[a-zA-Z0-9]+\\.[a-zA-Z0-9]+";
System.out.println(str.matches(emailMatcher)?"邮箱格式合法":"邮箱格式不合法");
本题需要知道什么是正则表达式以及:
正则表达式(regular expression)描述了一种字符串匹配的模式(pattern),可以用来检查一个串是否含有某种子串、将匹配的子串替换或者从某个串中取出符合某个条件的子串等。
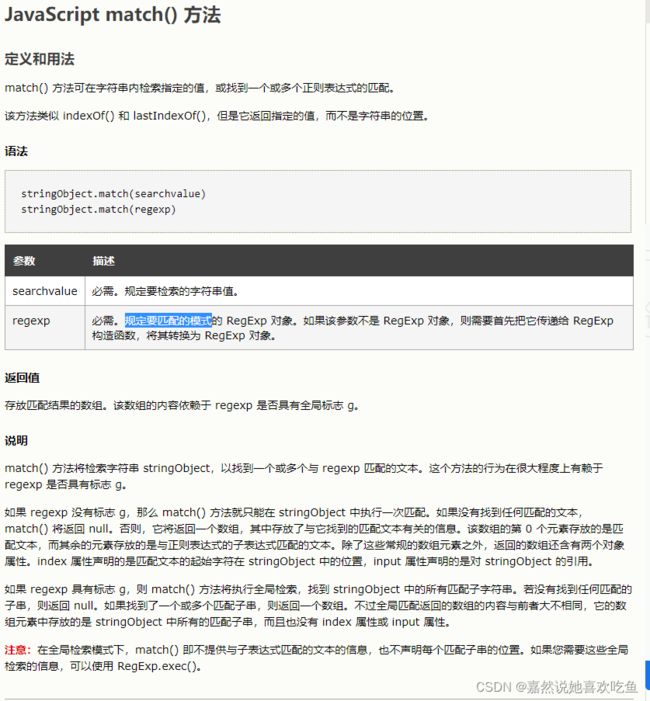
简单讲解 matches方法的使用:(不讲解原理)
字符串1 matches (字符串2)
字符串1 规定要检索的字符串值。即str,我们输入的字符串。
字符串2 规定要匹配的模式对象。即emailMatcher。
提供该方法的学习文档:
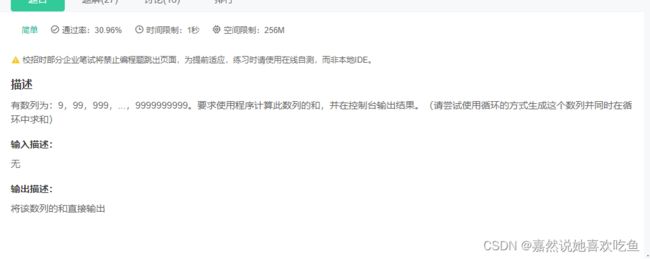
JAVA9 数列求和
题目
题解:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//write your code here........
long a = 9;
int i = 0;
long sum = 0;
for(i=0;i<10;i++){
sum += a;
a = a*10 + 9;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
由于题目最终的答案会超过int类型的长度,所以我们采用long类型,总共有10个数字相加,并且每一个数字都是前一位数字的9倍加一,所以我们采用for循环以及此规律来完成这道题目
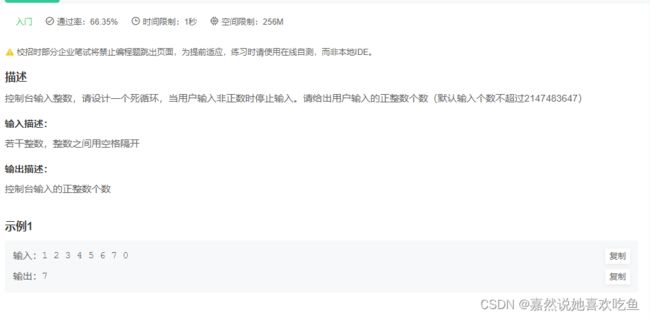
JAVA10 统计输入正数个数
题目
题解:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//write your code here......
while(true){
int num = scanner.nextInt();
if(num>0){
count ++;
}
else{
break;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
计算输入的正数个数,用一个死循环来实现,如果输入的是负数或者0,则跳出循环,否则则将一直统计正数的个数。
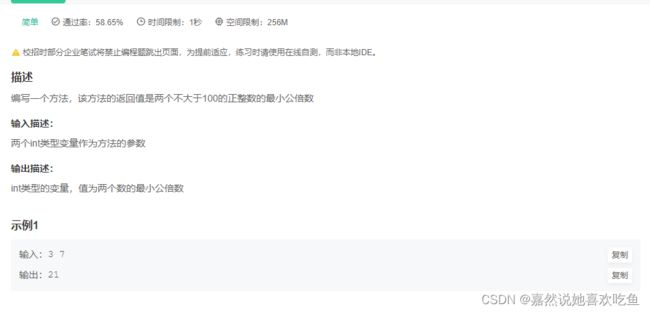
JAVA11 求最小公倍数
题目
题解:
public static int getCM(int m, int n){
//write your code here......
int i= 0;
for(i=m;i<=m*n;i++){
if(i%m==0&&i%n==0){
break;
}
}
return i;
}
较为简单也易理解的代码,用一个for循环一 一地去测试。当然也可以用辗转相除法计算出最大公约数,再有两数之积去除以最大公约数,也是可以得到最小公倍数的。
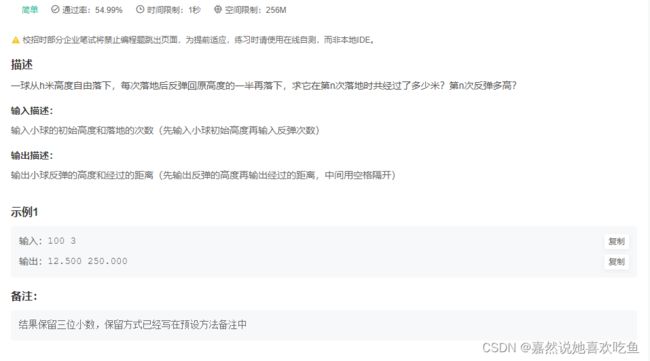
JAVA12 小球走过路程计算
题目
题解:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
float h=scanner.nextFloat();
int n =scanner.nextInt();
//write your code here......
double sum = h;
while(n>0){
h = h / 2;
sum += h*2;
n--;
}
sum -= h*2;
System.out.println(String.format("%.3f", h)+" "+String.format("%.3f", sum));
}
优秀的解法很多,这里是个人的解法,即第一次掉落触底时,球走了h米,
同时第一次反弹并在第二次触底之前,弹起与掉落的高度均为 h/2,所以sum = h +(h/2)* 2,
第二次反弹并在第三次触底之前,弹起与掉落的高度均为 h/4,所以sum = h+(h/2)* 2+(h/4)*2,
到了这里,sum就已经是答案了,但是我们为了计算出h在第三次弹起的高度,所以继续执行一次循环,得到答案h,但是sum也多加了第三次弹起到第四次掉落的高度,所以减掉这一部分。
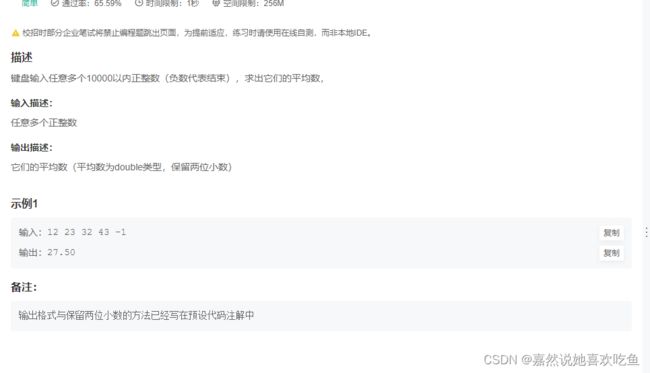
JAVA13 求平均数
题目
题解:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
//write your code here......
int sum = 0;
int n = 0;
while(true){
int num = scan.nextInt();
if(num>=0){
sum+=num;
n++;
}
else{
break;
}
}
double avg = (double)sum/n;
System.out.println(String.format("%.2f",avg));
较为简单,实现重复输入与第十题一样。
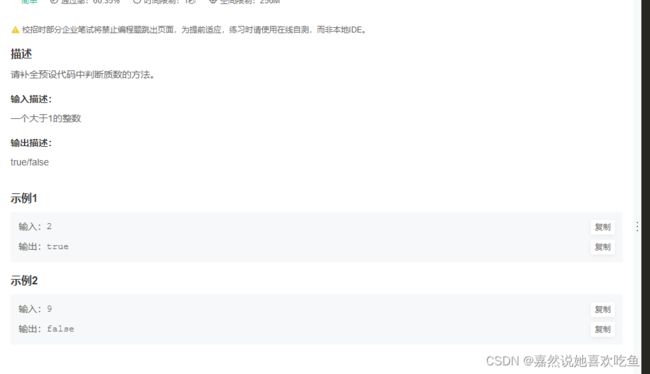
JAVA14 判断质数
题目
题解:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main main = new Main();
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int number = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println(main.isPrimeNumber(number));
}
public Boolean isPrimeNumber(int number) {
//write your code here......
int i = 0;
for(i=2;i<number-1;i++){
if(number%i==0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
求算质数,也就是素数,可以用for循环将2到number-1重复测试,只要有一个能将number整除,就不是素数,就可以结束这个方法返回flase了,如果都没有可以整除的,那就是素数了,返回true。
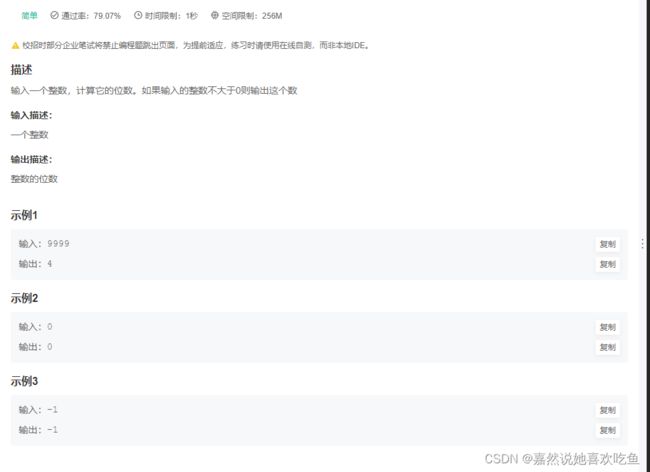
JAVA15 计算整数位数
题目
题解:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = scan.nextInt();
scan.close();
//write code here......
int n = 0;
int i = 0;
for(i=0;;i++){
if(num>0){
n++;
num = num/10;
}
else{
break;
}
}
System.out.println(n);
}
用一个for循环的死循环,来重复计算num的位数,如果num>0,即计数器n+1,同时num/10,使num的位数减一。如果num=0,即统计完毕,循环结束,跳出循环。
总结
这15道题主要涉及java语法的基本数据类型,运算符,分支,循环
其中较为值得理解的是 异或的计算技巧,matches 方法的使用,如何做到循环输入。
感谢阅读!