计算机毕业设计选题推荐-篮球人才管理系统-Python项目实战
✨作者主页:IT研究室✨
个人简介:曾从事计算机专业培训教学,擅长Java、Python、微信小程序、Golang、安卓Android等项目实战。接项目定制开发、代码讲解、答辩教学、文档编写、降重等。
☑文末获取源码☑
精彩专栏推荐⬇⬇⬇
Java项目
Python项目
安卓项目
微信小程序项目
文章目录
- 一、前言
- 二、开发环境
- 三、系统界面展示
- 四、代码参考
- 五、论文参考
- 六、系统视频
- 结语
一、前言
随着社会的进步和人们对幼儿教育的重视,幼儿教育管理系统逐渐成为了教育领域的重要研究对象。然而,现有的幼儿教育管理系统并不能完全满足用户的需求,无法实现对幼儿信息、班级、缴费、考勤等功能的实时监控和管理,因此,提高幼儿教育管理工作的质量和效率,增进幼儿教育事业的发展,研究幼儿教育管理系统是必要的。
目前,虽然已经有一些幼儿教育管理系统,但是它们存在一些问题。首先,它们无法实现对幼儿信息的实时更新和管理,无法满足用户对数据准确性的需求。其次,它们无法对班级、缴费、考勤等功能进行实时监控和管理,无法满足用户对工作效率的需求。再次,它们无法提供实时的数据分析报告,无法满足用户研究背景和意义
在篮球人才管理系统的研究中,我们致力于利用信息化的手段优化和提升篮球人才管理的效率和品质。这个课题的产生源于几个背景:首先,随着全球篮球产业的飞速发展,无论是职业联赛还是青少年培训,篮球人才的管理已经成为一个重要且具有挑战性的问题。传统的纸质档案管理方式已经无法满足实时、便捷的人才管理需求。其次,科技的进步,特别是信息技术和人工智能的发展,为我们提供了解决这个问题的可能性。通过构建一个集球员信息录入、赛程信息录入、新闻资讯等功能模块于一体的篮球人才管理系统,我们能够实现对球员信息、赛程信息等信息的实时监控和管理。
现有解决方案存在的问题
尽管存在一些现有的解决方案,但它们都存在一些问题。首先,许多解决方案依赖于手工录入和更新数据,这不仅效率低下,而且容易出错。其次,它们无法实现数据的实时更新和监控,导致管理效率的低下和信息的滞后。再次,它们缺乏对球员个体差异和特殊情况的考虑,无法实现个性化管理和培训。因此,我们需要一个全新的、能够实时处理和管理球员信息的系统,以提高篮球人才管理工作的质量和效率,增进篮球信息化建设。
我们的研究目的是开发一个功能强大、操作便捷的篮球人才管理系统。这个系统将包括球员信息录入、赛程信息录入、新闻资讯等功能模块。通过这些模块,用户可以轻松地录入和管理球员的各类信息,包括基本信息、训练情况、比赛数据等。此外,新闻资讯模块将提供实时的篮球新闻和赛事信息,帮助用户更好地了解篮球界的动态。
篮球人才管理系统的研究意义重大。首先,它将提高篮球人才管理的效率和品质,为球队的教练团队提供球员信息和深入的数据分析,帮助教练团队做出更准确、更及时的决策。其次,它将推动篮球信息化建设的发展,通过利用先进的信息技术和人工智能技术,实现对球员信息的实时监控和管理,这将为篮球行业的数字化转型提供强大的支持。再次,它将增进篮球行业的可持续发展,通过提供实时的新闻资讯和赛事信息,帮助公众更好地了解和参与篮球运动,进一步推动篮球产业的发展。对决策支持的需求。
本研究旨在开发一个幼儿教育管理系统,该系统能够实现对幼儿信息、班级、缴费、考勤等功能的实时监控和管理,提高幼儿教育管理工作的质量和效率,增进幼儿教育事业的发展。具体来说,本研究将实现以下目标:
实现对幼儿信息的实时更新和管理,提高数据准确性;
对班级、缴费、考勤等功能进行实时监控和管理,提高工作效率;
提供实时的数据分析报告,支持决策制定;
提高幼儿教育管理工作的质量和效率,增进幼儿教育事业的发展。
本研究的意义在于通过开发一个具有实时监控和管理功能的幼儿教育管理系统,实现对幼儿信息、班级、缴费、考勤等功能的全局管理,提高幼儿教育管理工作的质量和效率,增进幼儿教育事业的发展。具体来说,本研究的意义包括:
提高数据准确性:通过对幼儿信息的实时更新和管理,可以提高数据的准确性,为后续的数据分析提供可靠的基础。
提高工作效率:通过对班级、缴费、考勤等功能的实时监控和管理,可以提高工作效率,减少人工操作的成本和错误率。
支持决策制定:通过提供实时的数据分析报告,可以帮助管理人员做出更加科学合理的决策,提高决策的准确性和及时性。
增进幼儿教育事业的发展:通过提高幼儿教育管理工作的质量和效率,可以进一步增进幼儿教育事业的发展,提高整体教育水平。
二、开发环境
- 开发语言:Python
- 数据库:MySQL
- 系统架构:B/S
- 后端:Django
- 前端:Vue
三、系统界面展示
四、代码参考
- Java项目实战代码参考:
class Vec2d(object):
"""2d vector class, supports vector and scalar operators,
and also provides a bunch of high level functions
"""
__slots__ = ['x', 'y']
def __init__(self, x_or_pair, y = None):
if y == None:
self.x = x_or_pair[0]
self.y = x_or_pair[1]
else:
self.x = x_or_pair
self.y = y
def __len__(self):
return 2
def __getitem__(self, key):
if key == 0:
return self.x
elif key == 1:
return self.y
else:
raise IndexError("Invalid subscript "+str(key)+" to Vec2d")
def __setitem__(self, key, value):
if key == 0:
self.x = value
elif key == 1:
self.y = value
else:
raise IndexError("Invalid subscript "+str(key)+" to Vec2d")
# String representaion (for debugging)
def __repr__(self):
return 'Vec2d(%s, %s)' % (self.x, self.y)
# Comparison
def __eq__(self, other):
if hasattr(other, "__getitem__") and len(other) == 2:
return self.x == other[0] and self.y == other[1]
else:
return False
def __ne__(self, other):
if hasattr(other, "__getitem__") and len(other) == 2:
return self.x != other[0] or self.y != other[1]
else:
return True
def __nonzero__(self):
return bool(self.x or self.y)
# Generic operator handlers
def _o2(self, other, f):
"Any two-operator operation where the left operand is a Vec2d"
if isinstance(other, Vec2d):
return Vec2d(f(self.x, other.x),
f(self.y, other.y))
elif (hasattr(other, "__getitem__")):
return Vec2d(f(self.x, other[0]),
f(self.y, other[1]))
else:
return Vec2d(f(self.x, other),
f(self.y, other))
def _r_o2(self, other, f):
"Any two-operator operation where the right operand is a Vec2d"
if (hasattr(other, "__getitem__")):
return Vec2d(f(other[0], self.x),
f(other[1], self.y))
else:
return Vec2d(f(other, self.x),
f(other, self.y))
def _io(self, other, f):
"inplace operator"
if (hasattr(other, "__getitem__")):
self.x = f(self.x, other[0])
self.y = f(self.y, other[1])
else:
self.x = f(self.x, other)
self.y = f(self.y, other)
return self
# Addition
def __add__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, Vec2d):
return Vec2d(self.x + other.x, self.y + other.y)
elif hasattr(other, "__getitem__"):
return Vec2d(self.x + other[0], self.y + other[1])
else:
return Vec2d(self.x + other, self.y + other)
__radd__ = __add__
def __iadd__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, Vec2d):
self.x += other.x
self.y += other.y
elif hasattr(other, "__getitem__"):
self.x += other[0]
self.y += other[1]
else:
self.x += other
self.y += other
return self
# Subtraction
def __sub__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, Vec2d):
return Vec2d(self.x - other.x, self.y - other.y)
elif (hasattr(other, "__getitem__")):
return Vec2d(self.x - other[0], self.y - other[1])
else:
return Vec2d(self.x - other, self.y - other)
def __rsub__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, Vec2d):
return Vec2d(other.x - self.x, other.y - self.y)
if (hasattr(other, "__getitem__")):
return Vec2d(other[0] - self.x, other[1] - self.y)
else:
return Vec2d(other - self.x, other - self.y)
def __isub__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, Vec2d):
self.x -= other.x
self.y -= other.y
elif (hasattr(other, "__getitem__")):
self.x -= other[0]
self.y -= other[1]
else:
self.x -= other
self.y -= other
return self
# Multiplication
def __mul__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, Vec2d):
return Vec2d(self.x*other.x, self.y*other.y)
if (hasattr(other, "__getitem__")):
return Vec2d(self.x*other[0], self.y*other[1])
else:
return Vec2d(self.x*other, self.y*other)
__rmul__ = __mul__
def __imul__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, Vec2d):
self.x *= other.x
self.y *= other.y
elif (hasattr(other, "__getitem__")):
self.x *= other[0]
self.y *= other[1]
else:
self.x *= other
self.y *= other
return self
# Division
def __div__(self, other):
return self._o2(other, operator.div)
def __rdiv__(self, other):
return self._r_o2(other, operator.div)
def __idiv__(self, other):
return self._io(other, operator.div)
def __floordiv__(self, other):
return self._o2(other, operator.floordiv)
def __rfloordiv__(self, other):
return self._r_o2(other, operator.floordiv)
def __ifloordiv__(self, other):
return self._io(other, operator.floordiv)
def __truediv__(self, other):
return self._o2(other, operator.truediv)
def __rtruediv__(self, other):
return self._r_o2(other, operator.truediv)
def __itruediv__(self, other):
return self._io(other, operator.floordiv)
# Modulo
def __mod__(self, other):
return self._o2(other, operator.mod)
def __rmod__(self, other):
return self._r_o2(other, operator.mod)
def __divmod__(self, other):
return self._o2(other, operator.divmod)
def __rdivmod__(self, other):
return self._r_o2(other, operator.divmod)
# Exponentation
def __pow__(self, other):
return self._o2(other, operator.pow)
def __rpow__(self, other):
return self._r_o2(other, operator.pow)
# Bitwise operators
def __lshift__(self, other):
return self._o2(other, operator.lshift)
def __rlshift__(self, other):
return self._r_o2(other, operator.lshift)
def __rshift__(self, other):
return self._o2(other, operator.rshift)
def __rrshift__(self, other):
return self._r_o2(other, operator.rshift)
def __and__(self, other):
return self._o2(other, operator.and_)
__rand__ = __and__
def __or__(self, other):
return self._o2(other, operator.or_)
__ror__ = __or__
def __xor__(self, other):
return self._o2(other, operator.xor)
__rxor__ = __xor__
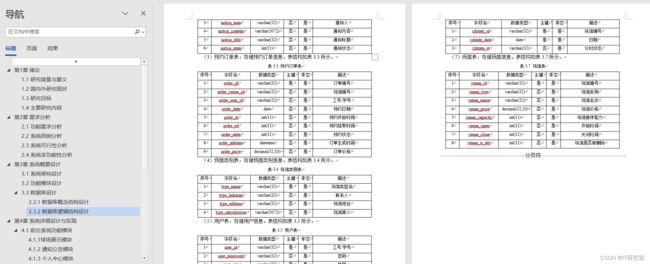
五、论文参考
六、系统视频
篮球人才管理系统项目视频:
计算机毕业设计选题推荐-篮球人才管理系统-Python项目
结语
计算机毕业设计选题推荐-篮球人才管理系统-Java项目实战
大家可以帮忙点赞、收藏、关注、评论啦~
源码获取:私信我
精彩专栏推荐⬇⬇⬇
Java项目
Python项目
安卓项目
微信小程序项目