golang学习笔记-go test的使用
golang的单元测试
1 go原生的单元测试
go的标准库自带了单元测试的“框架”,通过go test命令和一些参数可以显示绝大部分的单元测试和函数的性能测试。再配合go的性能测试包pprof能够解决很大一部分的性能的单元测试的问题。testing包含了:testing.T,testing.B和其他的一些函数。
go test命令可以自动执行窗体下的任何以以下开头的函数
func TestXxx(*testing.T){
// todo
// ...
}
但是,Xxx一般不以小写字母开头。函数名称用于表示测试的函数。举个例子,编写求绝对值的Abs函数的测试用例:
func TestAbs(t *testing.T) {
got := Abs(-1)
if got != 1 {
t.Errorf("Abs(-1) = %d; want 1", got)
}
}
在该文件所在的目录下运行go test就可以执行了。
1.1 testing提供的函数
1.1.1 源文件
我们可以对一个函数或者一个对象的函数单独的进行功能行的用例编写,实现对函数的测试覆盖。下面是一个包含多个函数的文件,每个函数有自己的功能,我们就对这个包里面的函数写一下单元测试的代码,尽可能最大的保证用例的覆盖率。之后再对这些函数中的部分函数做性能测试,看看有没有性能的提升空间。
包名为:calculate,包含一个名为sum.go的文件。
// sum.go
package calculate
import (
"fmt"
)
func Sum(a, b int64) int64 {
return a + b
}
func Abs(n int) int {
if n == 0 {
return n
}
return -n
}
type State int
const (
StateRunning = iota
StateStop
StateUnknown
)
func GetState(nState int) State {
switch nState {
case StateRunning:
return StateRunning
case StateStop:
return StateStop
default:
return StateUnknown
}
}
func Loops(size int) {
var (
num int64 = 0
)
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
num++
}
}
func Format(size int) {
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
_ = fmt.Sprintf("No.%d", i)
}
}
1.1.2 testing.T基础
对1.1.1中的源文件进行功能性的用例覆盖我们使用的是testing.T。在calculate目录下新建一个名为sum_test.go的文件,_test.go是固定的,必须以此结尾,前面的部分尽可能与包测试包的名字相同,为了能够快速识别包的含义。并且引入标准库的testing包,新建后的文件为:
//calculate/sum_test.go
package calculate
import (
"testing"
)
创建对应函数的测试用例时,需要以TestXxx开头,Xxx一般为被测试函数的名字,主要是为了能够快速识别和防止冲突。
测试用例编写完后,进入到calculate的目录下,直接执行go test运行测试用例,在终端上就能显示到运行的结果。
1.1.2.1 Sum函数
在sum_test.go中创建Sum的测试用例函数,表示a=1加b=2时,预期结果为3:
func TestSum(t *testing.T) {
var a, b, c int64 = 1, 2, 3
s := Sum(a, b)
if s != c {
t.Errorf("Error of Sum,%v+%v!=%v", a, b, c)
}
}
在calculate目录下执行go test运行结果如下,表示执行这个用例花费了0.222s的时间。
$ go test
PASS
ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate 0.222s
如果想查看详细的运行信息,在go test后加上-v参数即可,如下:
$ go test -v
=== RUN TestSum
--- PASS: TestSum (0.00s)
PASS
ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate 0.225s
上述结果运行结果是通过的,运行结果符合预期。
修改测试用例中预期结果c的值为4,此时运行时应该是失败的,如下:
$ go test -v
=== RUN TestSum
TestSum: sum_test.go:17: Error of Sum,1+2!=4
--- FAIL: TestSum (0.00s)
FAIL
exit status 1
FAIL github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate 0.218s
TestSum: sum_test.go:17: Error of Sum,1+2!=4:是用例的第5行打印。
FAIL:运行结果为失败。
1.1.2.2 其他的函数
以GetState和Abs函数为例,书写一下测试用例:
// TestGetState 函数GetState的测试用例
func TestGetState(t *testing.T) {
var n int
var state State
n = 0
state = GetState(n)
if state != StateRunning {
t.Errorf("Error of GetState StateRunning")
}
n = 1
state = GetState(n)
if state != StateStop {
t.Errorf("Error of GetState StateStop")
}
n = 2
state = GetState(n)
if state != StateUnknown {
t.Errorf("Error of GetState StateUnknown")
}
}
// TestAbs 函数Abs的测试用例
func TestAbs(t *testing.T) {
var got int
got = Abs(-1)
if got != 1 {
t.Errorf("Abs(-1) = %d; want 1", got)
}
}
执行go test -v得到运行的结果:
$ go test -v
=== RUN TestSum
--- PASS: TestSum (0.00s)
=== RUN TestGetState
--- PASS: TestGetState (0.00s)
=== RUN TestAbs
--- PASS: TestAbs (0.00s)
PASS
ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate 0.232s
1.1.2.3 小结
通过上面2个小节的示例,我们了解了go testing的基础用法:
- 如何命名测试文件
- 如何命令函数的测试用例
- 如何运行
go testing,并查看结果
1.1.3 testing.T高级
有这样一个常见的例子,我们有一个数据库操作的api函数,里面有对数据的CURD操作,这些函数之间是有先后的逻辑关系,只有create之后才能query或者delete。如果用1.1.2描述的方式去写测试用例的话,再写除了C之外的都要先写一个数据到数据库里面,然后才能写真实的用例。这样做起来是非常麻烦的,并且有很多冗余的代码。那么,除了1.1.2中描述的方法还有没有更简便的方式呢?
testing提供了一些“流处理”的方式,可以将几个测试用例按照顺序去执行,先看一下需要测试的包。
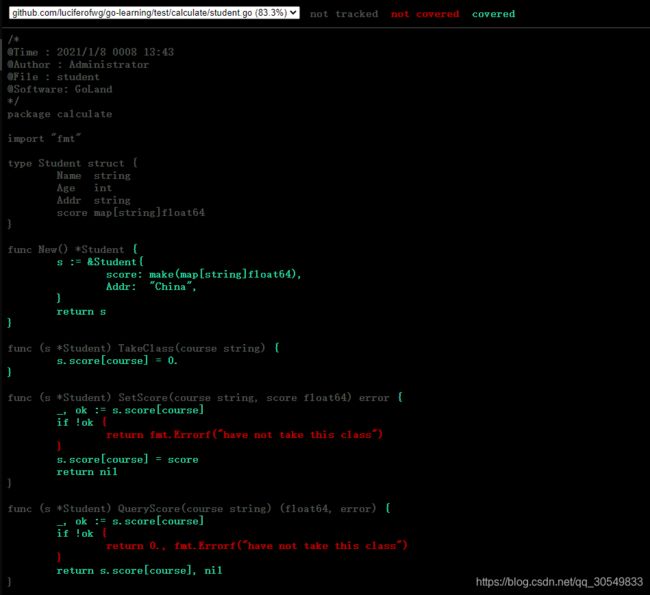
// student.go
package calculate
import "fmt"
type Student struct {
Name string
Age int
Addr string
score map[string]float64
}
func New() *Student {
s := &Student{
score: make(map[string]float64),
Addr: "China",
}
return s
}
func (s *Student) TakeClass(course string) {
s.score[course] = 0.
}
func (s *Student) SetScore(course string, score float64) error {
_, ok := s.score[course]
if !ok {
return fmt.Errorf("have not take this class")
}
s.score[course] = score
return nil
}
func (s *Student) QueryScore(course string) (float64, error) {
_, ok := s.score[course]
if !ok {
return 0., fmt.Errorf("have not take this class")
}
return s.score[course], nil
}
在这个student.go的文件中主要描述了三个函数,TakeCourese、SetScore和QueryScore。分别对应选修课程,设置学分,查询学分的功能,其中后面的2个函数是依赖第一个函数的,如果没有选修,设置和查询就不会成功的。先看测试用例:
package calculate
import (
"fmt"
"testing"
)
var (
s *Student
course = "c1"
score = 5.2
)
func TestStudentScoreFlow(t *testing.T) {
fmt.Println(">>>>>> flow start")
t.Run("TakeCourse", testTakeCourse)
t.Run("SetScore", testSetScore)
t.Run("QueryScore", testQueryScore)
fmt.Println("<<<<<< flow end")
}
func testTakeCourse(t *testing.T) {
s.TakeClass(course)
}
func testSetScore(t *testing.T) {
if err := s.SetScore(course, score); err != nil {
t.Errorf("Error of SetScore,%v", err)
}
}
func testQueryScore(t *testing.T) {
rs, err := s.QueryScore(course)
if err != nil {
t.Errorf("Error of Query Score,%v", err)
}
if rs != score {
t.Errorf("Error of Query score,real score:%v not equl expection score:%v", rs, score)
}
}
func TestMain(m *testing.M) {
s = New()
m.Run()
}
在上面的实现中,以TestXxx开头的有两个函数,TestMain(m *testing.M)和TestStudentScoreFlow(t *testing.T)。是testing规定了TestMain(m*testing.M)是testing包提供的入口函数,可以给测试用例提供额外的设置和资源释放的的必须的函数,不实现时会自动调用这个函数,类似于go中普通包中的func init(){}函数。因此在我们这个例子中只是示例化了全局变量s而已,真正的用例执行的函数任然是``TestStudentScoreFlow`。
定义了一个名为TestStudentScoreFlow(t *testing.T)的函数,在这个函数中使用t.Run(name string, f func(t *T))bool{}函数,第一个参数为子用例的唯一标识,第二个参数为调用的3个子用例,这3个子用例的函数名字都不是Test开头,默认不会被tesing执行。
需要注意的是在TestStudentScoreFlow()中的3个子用例的顺序必须按照业务流程编写。同样在calculate目录下运行go test -v执行所有的测试用例,结果如下:
$ go test -v
=== RUN TestStudentScoreFlow
>>>>>> flow start
=== RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/TakeCourse
=== RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/SetScore
=== RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/QueryScore
<<<<<< flow end
--- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow (0.00s)
--- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/TakeCourse (0.00s)
--- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/SetScore (0.00s)
--- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/QueryScore (0.00s)
=== RUN TestSum
--- PASS: TestSum (0.00s)
=== RUN TestGetState
--- PASS: TestGetState (0.00s)
=== RUN TestAbs
--- PASS: TestAbs (0.00s)
PASS
ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate 0.215s
上面的运行结果中有几个需要注意的地方:
- 8~11行,是子用例和执行花费的时间
- 12~行,是其他的用例文件的执行结果
注意:
TestMain(m *testing.M)在一个包下的测试用例中只能出现一次,他可以提供这个包下所有_test.go文件中的资源初始化或者释放的工作。
1.1.4 testing.B
一些函数可能在使用的过程中频繁的调用,那么就引出了一个问题,这个函数的运行的性能是怎么样的,如何去得出这个函数具体的运行的数值呢?testing包提供了一个名为testing.B的类型,来解决这一问题。
在1.1.1的源文件中有2个函数Loops和Format,这两个函数都是循环的做一些指令,在calculate目录下新建bench_test.go文件,里面实现这两个函数的性能测试用例,代码如下:
package calculate
import "testing"
// 性能
func BenchmarkLoops(b *testing.B) {
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
Loops(100)
}
}
// 并发
func BenchmarkLoopsParallel(b *testing.B) {
b.RunParallel(func(pb *testing.PB) {
for pb.Next() {
Loops(100)
}
})
}
func BenchmarkFormat(b *testing.B) {
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
Loops(10000)
}
}
上面的代码中函数BenchmarkLoops,测试Loops函数的性能,b.N动态调整调用的次数,就是只执行了b.N次的Loops(100)调用。
BenchmarkLoopsParallel()和“性能”不同的是,b.RunParallel(func(*testing.PB){})表示并发的执行Loops(100),testing会自动调整并发的个数。
1.1.4.1 纯性能测试
需要指出的是,性能测试的指令和普通的函数指令是不同的。用go test -v -bench=.执行当目录下的测试用例,对于testing.T执行普通的测试用例,对于testing.B执行性能计算的用例,执行go test -v -bench=.指令的结果为:
$ go test -v -bench=.
=== RUN TestStudentScoreFlow
>>>>>> flow start
=== RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/TakeCourse
=== RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/SetScore
=== RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/QueryScore
<<<<<< flow end
--- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow (0.00s)
--- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/TakeCourse (0.00s)
--- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/SetScore (0.00s)
--- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/QueryScore (0.00s)
=== RUN TestSum
--- PASS: TestSum (0.00s)
=== RUN TestGetState
--- PASS: TestGetState (0.00s)
=== RUN TestAbs
--- PASS: TestAbs (0.00s)
goos: windows
goarch: amd64
pkg: github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate
BenchmarkLoops
BenchmarkLoops-8 29919739 38.4 ns/op
BenchmarkLoopsParallel
BenchmarkLoopsParallel-8 155734327 7.71 ns/op
BenchmarkFormat
BenchmarkFormat-8 412695 2928 ns/op
PASS
ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate 4.381s
说明:18~27行,为性能测试的结果打印:
第一列是性能测试的名称,第二列是动态调整执行的次数,第三列是性能测试函数每次执行的花费的时间。
1.1.4.2 内存分配
在性能测试的同时显示内存分配的情况,go test -v -bench=. -benchmem,运行结果:
goos: windows
goarch: amd64
pkg: github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate
BenchmarkLoops
BenchmarkLoops-8 29919739 38.5 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
BenchmarkLoopsParallel
BenchmarkLoopsParallel-8 156038534 7.69 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
BenchmarkFormat
BenchmarkFormat-8 412695 2935 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
PASS
ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate 4.642s
第四列:每次执行函数时分配的空间
第五列:每次执行函数的分配内存的次数
1.2 go test命令
在go环境下,用go help testflag查看帮助文档,下面为摘录的部分文档:
> go help testflag
The following flags are recognized by the 'go test' command and
control the execution of any test:
-bench regexp
Run only those benchmarks matching a regular expression.
By default, no benchmarks are run.
To run all benchmarks, use '-bench .' or '-bench=.'.
The regular expression is split by unbracketed slash (/)
characters into a sequence of regular expressions, and each
part of a benchmark's identifier must match the corresponding
element in the sequence, if any. Possible parents of matches
are run with b.N=1 to identify sub-benchmarks. For example,
given -bench=X/Y, top-level benchmarks matching X are run
with b.N=1 to find any sub-benchmarks matching Y, which are
then run in full.
-run regexp
Run only those tests and examples matching the regular expression.
For tests, the regular expression is split by unbracketed slash (/)
characters into a sequence of regular expressions, and each part
of a test's identifier must match the corresponding element in
the sequence, if any. Note that possible parents of matches are
run too, so that -run=X/Y matches and runs and reports the result
of all tests matching X, even those without sub-tests matching Y,
because it must run them to look for those sub-tests.
-covermode set,count,atomic
Set the mode for coverage analysis for the package[s]
being tested. The default is "set" unless -race is enabled,
in which case it is "atomic".
The values:
set: bool: does this statement run?
count: int: how many times does this statement run?
atomic: int: count, but correct in multithreaded tests;
significantly more expensive.
Sets -cover.
-coverprofile cover.out
Write a coverage profile to the file after all tests have passed.
Sets -cover.
1.2.1 场景
-
指定目录下的测试用例,只执行当前目录下的测试用例
go test -v ./ -
指定目录下所有的测试用例,会执行当前目录下的所有文件夹中的测试用例
go test -v ./... -
运行目录下测试用例文件的函数中(子目录下./…)包含某关键字的函数,下面表示运行函数中包含
FLow关键字的用测go test -v -run=Flow ./例如:
$ ll total 19 -rw-r--r-- 1 Administrator 197121 218 1月 8 17:33 bench_fib_test.go -rw-r--r-- 1 Administrator 197121 440 1月 8 13:32 bench_sum_test.go -rw-r--r-- 1 Administrator 197121 185 1月 8 17:30 fib.go -rw-r--r-- 1 Administrator 197121 769 1月 8 14:24 student.go -rw-r--r-- 1 Administrator 197121 1398 1月 8 15:34 student_test.go -rw-r--r-- 1 Administrator 197121 655 1月 8 10:51 sum.go -rw-r--r-- 1 Administrator 197121 1175 1月 8 15:48 sum_test.go # 运行指令 $ go test -v -run=Flow ./... === RUN TestStudentScoreFlow >>>>>> flow start === RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/TakeCourse === RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/SetScore === RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/QueryScore <<<<<< flow end --- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow (0.00s) --- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/TakeCourse (0.00s) --- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/SetScore (0.00s) --- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/QueryScore (0.00s) PASS ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate (cached)
1.2.2 性能测试
- 只运行当前目录下的所有测试用例
go test -v -bench=./
加了-v指令后,这个命令不仅会执行bench用例,也会执行普通的用例,结果如下:
$ go test -v -bench=.
=== RUN TestStudentScoreFlow
>>>>>> flow start
=== RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/TakeCourse
=== RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/SetScore
=== RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/QueryScore
<<<<<< flow end
--- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow (0.00s)
--- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/TakeCourse (0.00s)
--- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/SetScore (0.00s)
--- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/QueryScore (0.00s)
=== RUN TestSum
--- PASS: TestSum (0.00s)
=== RUN TestGetState
--- PASS: TestGetState (0.00s)
=== RUN TestAbs
--- PASS: TestAbs (0.00s)
goos: windows
goarch: amd64
pkg: github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate
BenchmarkFib10
BenchmarkFib10-8 3371280 361 ns/op
BenchmarkLoops
BenchmarkLoops-8 29928022 39.2 ns/op
BenchmarkLoopsParallel
BenchmarkLoopsParallel-8 155125220 7.70 ns/op
BenchmarkFormat
BenchmarkFormat-8 398947 2976 ns/op
PASS
ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate 5.920s
-
只测试包含某个字段的
bench函数,例如只运行Loops的函数:go test -v -bench=Loops,运行的结果:$ go test -v -bench=Loops === RUN TestStudentScoreFlow >>>>>> flow start === RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/TakeCourse === RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/SetScore === RUN TestStudentScoreFlow/QueryScore <<<<<< flow end --- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow (0.00s) --- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/TakeCourse (0.00s) --- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/SetScore (0.00s) --- PASS: TestStudentScoreFlow/QueryScore (0.00s) === RUN TestSum --- PASS: TestSum (0.00s) === RUN TestGetState --- PASS: TestGetState (0.00s) === RUN TestAbs --- PASS: TestAbs (0.00s) goos: windows goarch: amd64 pkg: github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate BenchmarkLoops BenchmarkLoops-8 29920186 38.8 ns/op BenchmarkLoopsParallel BenchmarkLoopsParallel-8 154316836 7.72 ns/op PASS ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate 3.188s -
不加
-v时的指令:go test -bench=.,结果为:$ go test -bench=. >>>>>> flow start <<<<<< flow end goos: windows goarch: amd64 pkg: github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate BenchmarkFib10-8 3399787 354 ns/op BenchmarkLoops-8 29910492 39.1 ns/op BenchmarkLoopsParallel-8 155366329 7.74 ns/op BenchmarkFormat-8 398938 2948 ns/op PASS ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate 5.890sgo test -bench=Loops,结果为:$ go test -bench=Loops >>>>>> flow start <<<<<< flow end goos: windows goarch: amd64 pkg: github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate BenchmarkLoops-8 32320707 39.1 ns/op BenchmarkLoopsParallel-8 155126396 7.71 ns/op PASS ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate 3.231s
1.2.3 Example
除了上面的两类外,go test还提供了Example的测试方式。这种里面的函数需要以Example开头,里调用需要测试的函数,并用fmt.Println()函数“打印”输出的结果,最下面还要写对应的fmt.Println()的预期输出结果。
还是以上面的几个文件中函数为例,编写一个example_test.go的文件,在这个文件中写一个函数func ExampleSums(){},如下:
//example_test.go
package calculate
import "fmt"
func ExampleSum() {
var a, b int64 = 1, 2
// 测试sum函数,
fmt.Println(Sum(a, b))
// 测试Fib函数,
fmt.Println(Fib(2))
// 纯测试,输出hello,
fmt.Println("hello")
/* 以下为上面fmt.Printlen输出函数的期望输出,分别期望输出3,1,hello,需要注意的是下面的期望并不需要指定类型*/
//Output:
//3
//1
//hello
}
上面的代码//Output:为固定的字符,不能做任何的修改,//Output:下面是对应的fmt.Println()函数的预期输出值,运行的结果:
$ go test -v -run=Sum ./...
=== RUN TestSum
--- PASS: TestSum (0.00s)
=== RUN ExampleSum
--- PASS: ExampleSum (0.00s)
PASS
ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate (cached)
修改返回的预期结果,修改为:
//Output:
//3
//2
//helle
运行后:
$ go test -v -run=Sum ./...
=== RUN TestSum
--- PASS: TestSum (0.00s)
=== RUN ExampleSum
--- FAIL: ExampleSum (0.00s)
got:
3
1
hello
want:
3
2
helle
FAIL
ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate 0.218s
很明确的显示出了那个地方预期值不满足。
1.3 生成测试报告
知道了怎么写测试用例,怎么执行测试用例,我们也需要将测试用例的结果集中,然后以可视化的方式导出,方便开发人员的查看或者一些其他的自动化的管理等。
-cover参数可以查看测试用例的覆盖率:
$ go test -cover ./...
? github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test [no test files]
ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate (cached) coverage: 75.0% of statements
ok github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/dbops (cached) coverage: 74.2% of statements
go test的参数中有名为-covermode和-coverprofile的参数,通过这两个参数可以将产生的结果写入到一定的文件中,例如下面的指令:
go test -v -covermode=set -coverprofile=cover.out ./...
表示将测试用例执行时按照set的模式执行,并且将结果导出到文件cover.out中,执行后cover.out的文件看起来并不友好,如下:
mode: set
github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate/fib.go:9.21,10.11 1 0
github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate/fib.go:13.2,13.28 1 0
github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate/fib.go:10.11,12.3 1 0
github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate/student.go:18.21,24.2 2 1
github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate/student.go:26.44,28.2 1 1
github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate/student.go:30.64,32.9 2 1
github.com/luciferofwg/go-learning/test/calculate/student.go:35.2,36.12 2 1
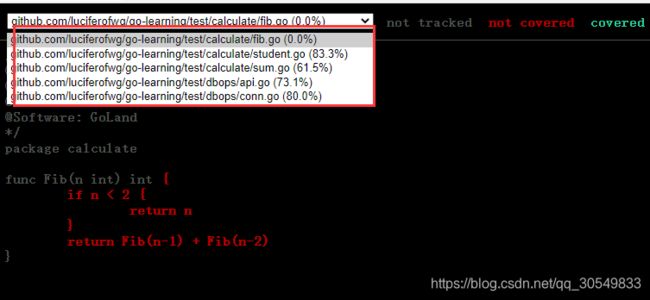
再用指令go tool cover -html=cover.out -o cover.html将生产的cover.out文件导出为html格式,html文件就会很友好,很直观。
不仅仅有每一个文件的测试用例覆盖率,还能看到具体的文件的测试用例覆盖情况,比如下面的fib.go的测试覆盖率为0%,sdutend.go测试覆盖率为83.3%。
[Package testing]https://golang.org/pkg/testing/#pkg-examples
[go test命令(Go语言测试命令)完全攻略]http://c.biancheng.net/view/124.html
[Golang Testing单元测试指南]https://www.cnblogs.com/sunsky303/p/11818480.html
[An Introduction to Benchmarking Your Go Programs]https://tutorialedge.net/golang/benchmarking-your-go-programs/
[Go多个pkg的单元测试覆盖率]http://singlecool.com/2017/06/11/golang-test/
[go 性能优化之 benchmark + pprof]https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/332613357