Promise-异步回调
1.理解Promise
promise是ES6提出的异步编程的新的解决方案,通过链式调用解决ajax回调地狱
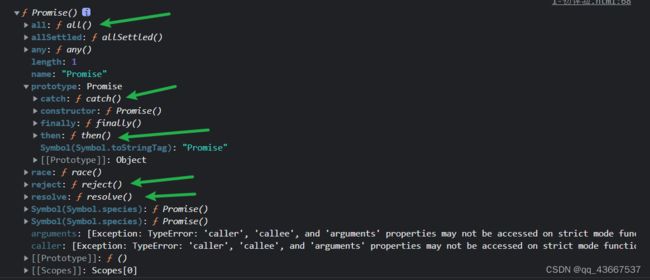
从语法上看,promise是一个构造函数,自己身上有all、reject、resolve方法,原型上有then、catch方法
从功能上看,Promise对象用来封装一个异步请求操作并接受成功/失败时候的结果
2.Promise对象三种状态
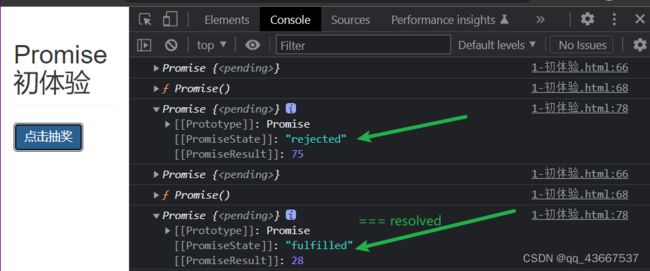
promise对象中 PromiseState属性 ,这个属性有三种状态,分别是一下:
pending:等待中,或者进行中,还没有得到结果
resolved/fullfilled:执行成功
rejected:执行失败
这三种状态不受外界影响,而且状态只能从pending改变为resolved或者rejected,并且不可逆。
Promise对象的值
实例对象中的另外一个属性 PromiseResult
保存着异步任务【成功/失败】的结果,可以被resolve或者reject函数修改,修改后的结果可以被then函数接收到
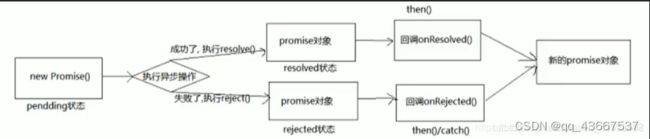
then方法返回一个新的promise对象
①实例化一个Promise对象
②Promise作为一个构造函数,接受一个函数类型的值,这个函数有两个参数,分别是resolve reject
③当异步任务执行成功时候,调用resolve函数,将promise对象的状态修改为resolved,然后调用then方法中的第一个回调函数,并返回一个新的Promise对象
④当异步任务执行失败的时候,调用reject函数,将Promise对象的状态修改为rejected,然后调用then方法中的第二个回调函数,并返回一个新的Promise对象
3.Promise的基本使用
const promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// ... some code
if (/* 异步操作成功 */){
resolve(value);
} else {
reject(reason);
}
});
Promise作为一个构造函数,在实例化一个对象过程中,接受一个参数,这个参数是一个函数类型的值,这个函数里面有两个参数,分别是resolve、reject,当异步任务执行成功的时候,调用resolve函数,将promise对象的状态修改为resolved,并将异步操作的结果作为参数传递出去;异步任务执行失败的时候,调用reject函数,状态修改为rejected,并将异步操作的错误,作为参数reason传递出去
Promise实例 生成之后,可以调用then方法分别指定resolved状态和rejected状态的回调函数
then方法有两个参数,第一个参数是成功时候的回调,第二个参数是失败的时候的回调 接受构造函数中处理的状态的变化,并分别处理
promise.then(function(value) {
// success
}, function(reason) {
// failure
});
实例如下:
// 创建一个新的p对象promise
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { // 执行器函数
// 执行异步操作任务
setTimeout(() => {
const time = Date.now()
// 如果当前时间是偶数代表成功,否则失败
if (time % 2 == 0) {
// 如果成功,调用resolve(value)
resolve('成功的数据,time=' + time)
} else {
// 如果失败,调用reject(reason)
reject('失败的数据,time=' + time)
}
}, 1000);
})
p.then(
value => { // 接收得到成功的value数据 onResolved
console.log('成功的回调', value) // 成功的回调 成功的数据,time=1615015043258
},
reason => { // 接收得到失败的reason数据 onRejected
console.log('失败的回调', reason) // 失败的回调 失败的数据,time=1615014995315
}
)
Promise的封装AJAX请求
4. Promise的API
1.Promise构造函数:Promise(executor){}
executor函数:同步执行(resolve,reject)=>{}
resolve函数:内部定义成功时候调用的函数resolve(value)
reject函数:内部定义失败时候调用的函数reject(reason)
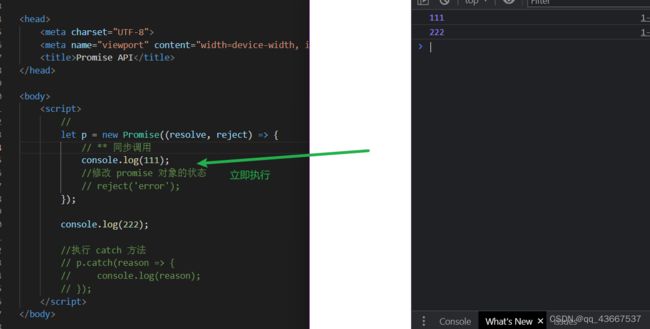
executor是执行器函数,会在Promise内部立即同步回调,异步操作resolve/reject就在executor中执行
2.Promise.prototype.then 方法:p.then(onResolved, onRejected)
onResolved 函数:成功的回调函数 (value) => {}
onRejected 函数:失败的回调函数 (reason) => {}
不管成功还是失败,都会返回一个新的Promise对象
3.Promise.prototype.catch 方法:p.catch(onRejected)
只能指定失败的回调
catch()相当于then(null,onRejected)
//
console.dir(Promise)
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// ** 同步调用
console.log(111);
//修改 promise 对象的状态
// reject('error');
});
console.log(222);
//执行 catch 方法
// p.catch(reason => {
// console.log(reason);
// });
4.Promise.resolve方法:Promise.resolve(value)
value:将被Promise对象解析的参数,或者是一个成功/失败的Promise对象
返回:返回一个带着给定值解析过的 Promise 对象,如果参数本身就是一个 Promise 对象,则直接返回这个 Promise 对象。
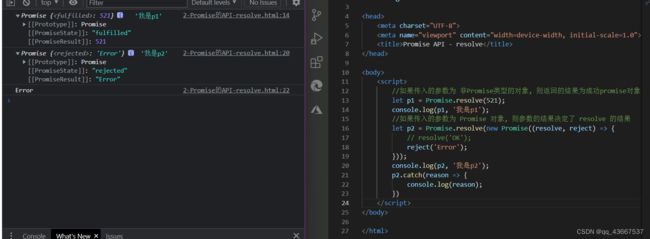
如果resolve() 中的参数是非Promise对象,那么返回一个成功状态的Promise对象
如果resolve() 中的参数是Promise对象,那么返回的结果由这个Promise对象的返回结果决定
只有resolve()或者reject()函数才能改变PromiseResult的值,then()或者catch()能够接收到这个值
5.Promise.reject方法:Promise.reject(reason)
reason失败的原因,reject总是返回失败状态的Promise对象
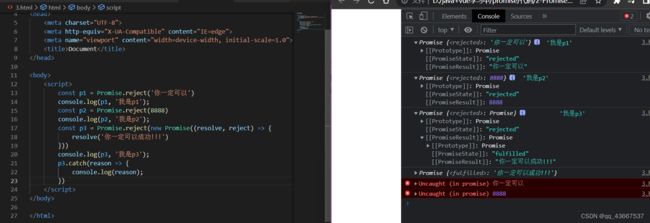
总之,Promise.resolve()/Promise.reject() 用来快速得到Promise对象
//产生一个成功值为1的promise对象
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(1)
})
//相当于
const p1 = Promise.resolve(1)
const p2 = Promise.resolve(2)
const p3 = Promise.reject(3)
p1.then(value => {console.log(value)}) // 1
p2.then(value => {console.log(value)}) // 2
p3.catch(reason => {console.log(reason)}) // 3
6.Promise.all方法:Promise.all()
参数是包含n个promise的数组
返回一个新的promise,只有所有的promise都成功才成功,只要有一个失败了就直接失败
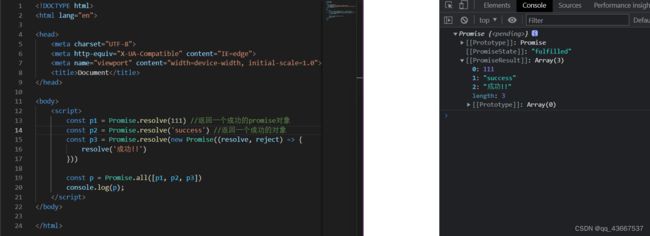
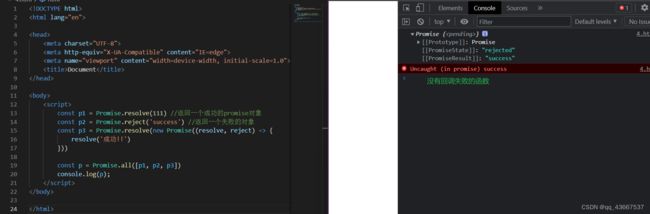
应用
getUserProfile() {
//获取行业ids
getUserProfile().then((res) => {
console.log(res, "获取用户的信息");
this.foodTypeIds = res.data.dept.foodTypeIds
.split(",")
.map((item) => parseInt(item));
console.log(this.foodTypeIds, "foodTypeIds");
});
},
getFoodType() {
//获取行业信息
getFoodType().then((res) => {
this.allFoodTypeIds = res.data;
console.log(this.allFoodTypeIds, "获取行业信息");
});
},
//执行两个异步任务之后 然后调用 树形结构处理函数
handleIt() {
const fun1 = getUserProfile();
const fun2 = getFoodType();
Promise.all([fun1, fun2]).then((res) => {
console.log(res, "两个异步有没有执行完");
const [res1, res2] = res;
this.foodTypeIds = res1.data.dept.foodTypeIds
.split(",")
.map((item) => parseInt(item));
this.allFoodTypeIds = res2.data;
this.handleIdsAndLabel();
});
},
7.Promise.race方法:Promise.race()
参数是,包含n个promise对象的数组
返回一个新的promise对象,第一个完成的promise的状态结果就是最终的结果状态,总之,谁先完成就输出谁,不管他是成功or失败
5.promise中的重要问题
1.修改Promise对象状态的三种方法
1.resolve将promise对象状态:pending=>resolved/fullfilled
2.reject pending => rejected
3.throw 抛出一个异常 pending => rejected
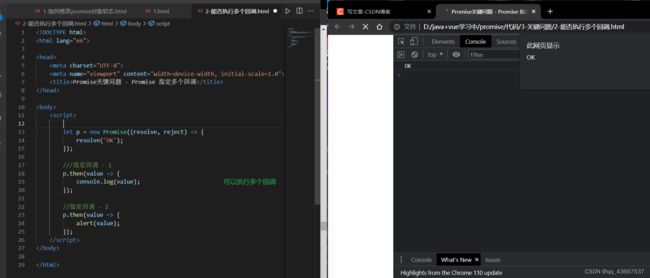
2.Promise对象可以指定多个回调
3.改变promise对象的状态和指定回调函数的先后顺序
resolve()、reject()改变promise对象的状态,then/catch指定回调函数
执行器函数会在promise中同步回调,执行器函数中的resolve reject是异步操作

如果先指定回调,会先保存当前指定的回调函数,当状态改变时(同时指定数据),执行回调函数
如果先改变状态(同时指定数据),后指定回调,直接执行回调函数
4.promise.then() 返回的新 promise 的结果状态由什么决定?
详细:
①throw抛出一个异常,那么then返回的新promise对象的状态变为rejected,reason为抛出的异常
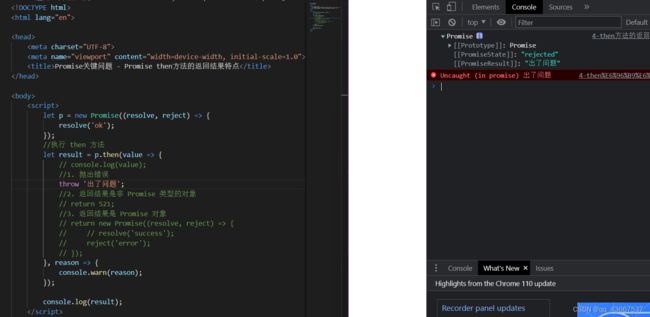
②回调函数的返回结果是一个非promise对象,新promise对象的状态变为resolved,value为返回的结果
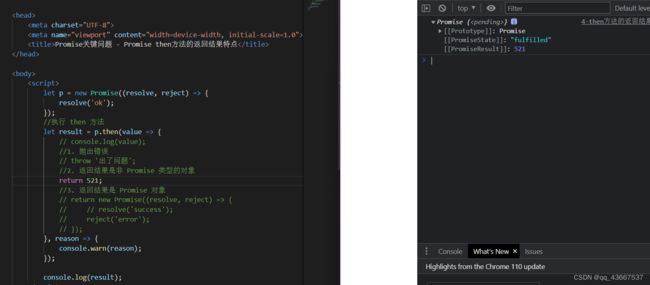
③如果回调函数返回的结果是一个新promise对象,那么then函数返回的promise对象的结果同这个新promise对象的结果
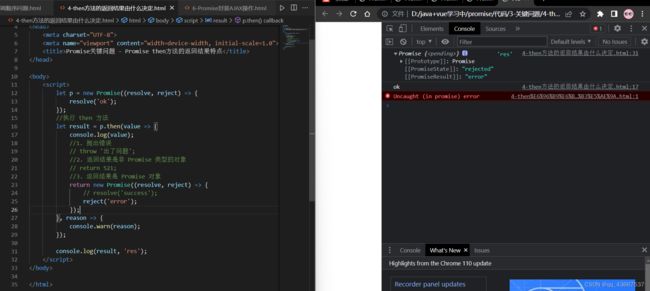
// 应用
getNationalList() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
listCollect("national", this.queryParams1).then(response => {
let res = response.rows.length == 0 ? [] : response.rows
if (this.collectList[0]) { //手动对数组进行操作,以解决vue2对数组某一项改变不监听的问题
this.collectList.splice(0, 1)
this.collectList.unshift(res)
} else {
this.collectList.push(res)
}
this.total1 = response.total
resolve("国家法规列表获取成功") //执行成功
});
})
},
getLocalList() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
listCollect("local", this.queryParams2).then(response => {
let res = response.rows.length == 0 ? [] : response.rows
this.total2 = response.total
if (this.collectList[1]) {
this.collectList.splice(1, 1)
this.collectList.push(res)
} else {
this.collectList.push(res)
}
resolve("地方法规列表获取成功")
});
})
},
// 执行异步
handleIt() {
//promise串联多个任务
this.getNationalList().then(() => {
return this.getLocalList();
}).then(() => {
this.setSwiperHeight();
});
},
5.promise如何串联多个操作任务
(1)promise 的 then() 返回一个新的 promise,可以并成 then() 的链式调用
(2)通过 then 的链式调用串联多个同步/异步任务
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('OK');
}, 1000);
});
p.then(value => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("success");
});
}).then(value => {
console.log(value); // success
}).then(value => {
console.log(value); // undefined
})
6.promise异常穿透(传透)
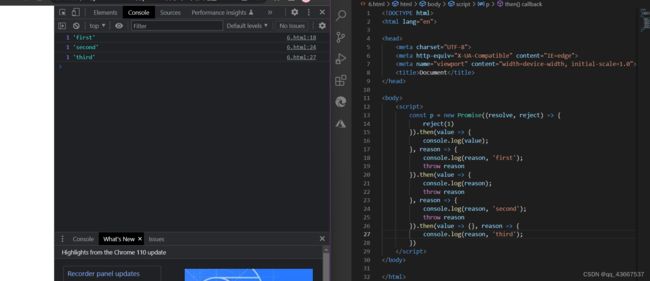
所以失败的结果是一层一层处理下来的,最后传递到 catch 中。
或者,将 reason => {throw reason} 替换为 reason => Promise.reject(reason) 也是一样的
7.中断promise链
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//resolve(1)
reject(1)
}).then(
value => {
console.log('onResolved1()', value)
return 2
}
).then(
value => {
console.log('onResolved2()', value)
return 3
}
).then(
value => {
console.log('onResolved3()', value)
}
).catch(
reason => {
console.log('onRejected1()', reason)
return new Promise(() => {}) // 返回一个pending的promise
}
).then(
value => {
console.log('onResolved4()', value)
},
reason => {
console.log('onRejected2()', reason)
}
)
// onRejected1() 1
在 catch 中返回一个新的 promise,且这个 promise 没有结果。
由于,返回的新的 promise 结果决定了后面 then 中的结果,所以后面的 then 中也没有结果。
这就实现了中断 promise链的效果。
参考
参考大佬的promise
尚硅谷 promise教程
Event loop js中事件循环机制