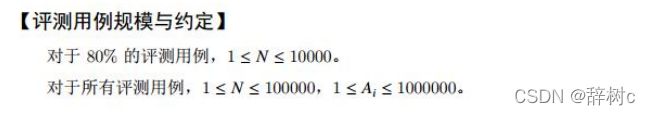【蓝桥杯】第十届软件类省赛(C/C++大学A组)超详细全题解
目录
试题 A:平方和(5分)
试题 B:数列求值(5分)
试题 C:最大降雨量(10分)
试题 D:迷宫(10分)
试题 E:RSA 解密(15分)
试题 F:完全二叉树的权值(15分)
试题 G:外卖店优先级(20分)
试题 H:修改数组(20分)
试题 I:糖果(25分)
试题 J:组合数问题(25分)
试题 A:平方和(5分)
题目链接:平方和
知识点:枚举、数位判断
解题思路:枚举 1 ~ 2019 每个数判断是否出现 2、0、1、9 这四个数字,只要出现至少一个,就将该数平方加入答案。
AC代码:
#include
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair PII;
typedef pair PLL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LLF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
bool check(int x){
if(x == 2 || x == 0 || x == 1 || x == 9) return true;
return false;
}
int main(){
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
ll sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 2019; i++){
int temp = i;
while(temp){
if(check(temp % 10)){
sum += i * i;
break;
}
temp /= 10;
}
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
} 最终答案:2658417853
试题 B:数列求值(5分)
题目链接:数列求值
知识点:递推、取模
解题思路:按照题目递推关系一步一步推即可,可以直接用数组推,也可以像下面代码一样用四个变量推。由于只需要求低四位,所以在推的过程中最多只需要存四位数字。怎么存呢?很简单,只需要每次将前三项之和对 10000 取模就好了。
AC代码:
#include
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair PII;
typedef pair PLL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LLF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
int main(){
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int a = 1, b = 1, c = 1, temp;
for(int i = 4; i <= 20190324; i++){
temp = (a + b + c) % 10000;
a = b;
b = c;
c = temp;
}
cout << c << endl;
return 0;
} 最终答案:4659
试题 C:最大降雨量(10分)
题目链接: 最大降雨量
知识点:思维、数学
解题思路:题目要求的是 7 周能量的中位数,每周能量又是一周中每天能量的中位数,为了使答案尽可能大,那么法术使用的顺序一定是按下面代码中的样子进行排列的,因此比答案值大的数只有 15 个,具体见代码中的分析。
AC代码:
#include
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair PII;
typedef pair PLL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LLF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
int main(){
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
/*
a11 a12 a13 a14 a15 a16 a17
a21 a22 a23 a24 a25 a26 a27
a31 a32 a33 a34 a35 a36 a37
a41 a42 a43 (a44) [a45] [a46] [a47]
a51 a52 a53 [a54] [a55] [a56] [a57]
a61 a62 a63 [a64] [a65] [a66] [a67]
a71 a72 a73 [a74] [a75] [a76] [a77]
*/
// '()'为最终答案的位置,'[]'为比答案大的数
// 因此最终答案为49 - 15 = 34
cout << 34 << endl;
return 0;
} 最终答案:34
试题 D:迷宫(10分)
题目链接:迷宫
知识点:最短路、bfs
解题思路:bfs 求最先到达每个点时上一步走的方向(0 表示下,1 表示左,2 表示右,3 表示上)存入 last 数组中,然后从终点退回起点,将每一步退到的点的 last 数组中的值转为 D、L、R、U 存入ans 数组,逆向输出就是答案。(由于只存第一次到达的情况,因此这样路径一定最短;又由于按 D、L、R、U 的顺序更新去到的点,因此这样得到的答案一定是字典序最小的)
AC代码:
#include
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair PII;
typedef pair PLL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LLF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
const int N = 30 + 5, M = 50 + 5;
char g[N][M], ans[N * M];
bool st[N][M];
int dx[4] = {1, 0, 0, -1};
int dy[4] = {0, -1, 1, 0};
char dir[4] = {'D', 'L', 'R', 'U'};
int last[N][M];
int n = 30, m = 50, cnt;
void bfs(){
queue q;
q.push({1, 1});
st[1][1] = true;
while(q.size()){
int x = q.front().first, y = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int xi = x + dx[i];
int yi = y + dy[i];
if(xi < 1 || xi > n || yi < 1 || yi > m || g[xi][yi] == '1' || st[xi][yi]) continue;
q.push({xi, yi});
st[xi][yi] = true;
last[xi][yi] = i;
}
}
int x = n, y = m;
while(x != 1 || y != 1){
int la = last[x][y];
ans[cnt++] = dir[last[x][y]];
x -= dx[la];
y -= dy[la];
}
}
int main(){
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
cin >> g[i][j];
}
}
bfs();
for(int i = cnt - 1; i >= 0; i--){
cout << ans[i];
}
return 0;
} 最终答案:DDDDRRURRRRRRDRRRRDDDLDDRDDDDDDDDDDDDRDDRRRURRUURRDDDDRDRRRRRRDR
试题 E:RSA 解密(15分)
题目链接:RSA 解密
知识点:分解质因数、扩展欧几里得、快速幂、快速乘
解题思路:
根据问题描述,![]() 且
且 ![]() 为质数,那么可以先将 p 和 q 算出来,计算代码如下注释部分。得到 p = 891234941,q = 1123984201;
为质数,那么可以先将 p 和 q 算出来,计算代码如下注释部分。得到 p = 891234941,q = 1123984201;
然后根据 ,可以得到同余方程 ![]() ,其中 e 是未知数。这就可以借助扩展欧几里得求出这个同余方程的解,得到 e = 823816093931522017;
,其中 e 是未知数。这就可以借助扩展欧几里得求出这个同余方程的解,得到 e = 823816093931522017;
最后用快速幂求 ![]() ,由于数据过大,快速幂中的乘法需要使用快速乘进行计算。
,由于数据过大,快速幂中的乘法需要使用快速乘进行计算。
AC代码:
#include
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair PII;
typedef pair PLL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LLF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
ll quick_mul(ll a, ll b, ll m){
ll res = 0;
while(b){
if(b & 1) res = (res + a) % m;
a = (a + a) % m;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
ll quick_pow(ll a, ll b, ll m){
ll res = 1;
while(b){
if(b & 1) res = quick_mul(res, a, m) % m;
a = quick_mul(a, a, m) % m;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
ll ex_gcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y){
if(!b){
x = 1, y = 0;
return a;
}
ll d = ex_gcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= a / b * x;
return d;
}
ll cal(ll d, ll m){
ll x, y;
ex_gcd(d, m, x, y);
return (x % m + m) % m;
}
int main(){
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
ll n = 1001733993063167141, p, q, d = 212353, e, C = 20190324, X;
//for(int i = 2; i * i <= n; i++){
// if(n % i == 0){
// p = i;
// q = n / i;
// break;
// }
//}
p = 891234941, q = 1123984201;
e = cal(d, (p - 1) * (q - 1));
X = quick_pow(C, e, n);
cout << X << endl;
return 0;
} 最终答案:579706994112328949
试题 F:完全二叉树的权值(15分)
题目链接:完全二叉树的权值
知识点:树形结构
解题思路:由于是完全二叉树,第 ![]() 层的开始结点为
层的开始结点为 ![]() ,根据这个性质,计算每层的权值和,然后遍历一遍找到最大权值和,将层数输出即可。
,根据这个性质,计算每层的权值和,然后遍历一遍找到最大权值和,将层数输出即可。
AC代码:
#include
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair PII;
typedef pair PLL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LLF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
const int N = 100005;
int a[N], sum[N];
int main(){
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int n;
cin >> n;
int cnt = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(i == (1 << cnt)) cnt++;
cin >> a[i];
sum[cnt] += a[i];
}
int ma = -INF, ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++){
if(sum[i] > ma){
ma = sum[i];
ans = i;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
} 试题 G:外卖店优先级(20分)
题目链接:外卖店优先级
知识点:思维、模拟
解题思路:将订单按时间进行排序,遍历所有订单,每个订单的这家店当前的优先级需要减去当前时间到这家店上一次收到订单的时间之差(最多减至 0),然后记录这家店是否在优先缓存中。最后再遍历一遍每家店,如果这家店最后一次收到订单不是在 T 时刻,就需要更新一下这家店的优先级,并判断是否在优先缓存中,如果在,就将答案 +1。
AC代码:
#include
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair PII;
typedef pair PLL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LLF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
const int N = 1000005;
int prio[N], last[N];
bool st[N];
struct bill{
int ts, id;
bool operator < (const bill &u) const{
return ts < u.ts;
}
}b[N];
int main(){
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int n, m, t;
cin >> n >> m >> t;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
cin >> b[i].ts >> b[i].id;
}
sort(b + 1, b + m + 1);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int ts = b[i].ts, id = b[i].id;
if(ts != last[id]){
prio[id] = max(0, prio[id] - (ts - last[id] - 1));
}
if(prio[id] <= 3) st[id] = false;
prio[id] += 2;
if(prio[id] > 5) st[id] = true;
last[id] = ts;
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(last[i] < t){
prio[i] -= t - last[i];
if(prio[i] <= 3) st[i] = false;
}
if(st[i]) ans++;
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
} 试题 H:修改数组(20分)
题目链接:修改数组
知识点:并查集
解题思路:由于数据范围较大,正常遍历和记录一个数是否存在的方法就不好用了。这就需要用到一种特殊的数据结构——单链表式的并查集。并查集的根结点表示大于等于当前这个数并且在之前没出现过的数;查询过程同时更新每个点的根结点,也就是一般并查集的 find() 函数。
举个例子:2 1 1 3 4,一开始先预处理 fa[i] = i。
输入第一个数 2,由于 fa[2] = 2,说明这个数前面没有出现过,不变直接输出 2,让 fa[2] = 3,(这样下次如果遇到 2 这个数,就直接置为 3 输出);
接着输入 1,由于fa[1] = 1,不变直接输出 1,让 fa[1] = 2;
接着输入 1,由于 fa[1] = 2,fa[2] = 3,fa[3] = 3,fa[1] 就更新为 3,输出 3,让 fa[3] = 4;
接着输入 3,由于 fa[3] = 4,fa[4] = 4,输出 4,让 fa[4] = 5;
最后输入 4,由于 fa[4] = 5,fa[5] = 5,输出 5,让 fa[5] = 6。
这样最终就输出了 2 1 3 4 5。
AC代码:
#include
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair PII;
typedef pair PLL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LLF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
const int N = 1000005;
int a[N], fa[N];
int find(int x){
if(fa[x] != x) fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
return fa[x];
}
int main(){
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++){
fa[i] = i;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x;
cin >> x;
x = find(x);
cout << x << ' ';
fa[x] = x + 1;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
} 试题 I:糖果(25分)
题目链接:糖果
知识点:二进制、状压dp
解题思路:可以看得出来,这题的思路很可能是 dfs 或者状压dp(看数据范围做题)。考虑每包糖果用一个 ![]() ~
~ ![]() 的 m 位二进制表示,第
的 m 位二进制表示,第 ![]() 位是 1 表示有第
位是 1 表示有第 ![]() 种口味的糖果。这样样例中的 6 包糖果就可以表示为 00011、00111、00101、10110、11010、10011。这样就可以用状压dp进行解题了。令
种口味的糖果。这样样例中的 6 包糖果就可以表示为 00011、00111、00101、10110、11010、10011。这样就可以用状压dp进行解题了。令 ![]() 表示考虑到第
表示考虑到第 ![]() 包糖果,已经得到的口味种类的二进制表示为
包糖果,已经得到的口味种类的二进制表示为 ![]() 。那么可以得到状态转移方程:
。那么可以得到状态转移方程:![]() 。
。
然后考虑初始化,由于求的最小值,将 dp 数组初始化为大于等于 n + 1 的数(因为能够吃到所有种类的糖果的最坏情况是将 n 包全部买下),然后由于每包糖果都有不同种类的糖果,初始化 dp[i][a[i]] = 1。
由于数据较大,数组需要开到 ![]() 的大小(数量级达到了
的大小(数量级达到了 ![]() ),这是做不了的,因此就需要进行空间优化。类似于背包问题,将 dp 数组优化成一维,遍历二进制时从后往前,这样就解决了空间问题。
),这是做不了的,因此就需要进行空间优化。类似于背包问题,将 dp 数组优化成一维,遍历二进制时从后往前,这样就解决了空间问题。
AC代码:
#include
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair PII;
typedef pair PLL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LLF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
const int N = 105;
int a[N], dp[1 << 20];
int main(){
freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int n, m, k;
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= k; j++){
int x;
cin >> x;
a[i] |= 1 << (x - 1);
}
}
memset(dp, 0x3f, sizeof dp);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
dp[a[i]] = 1;
for(int j = (1 << m) - 1; j >= 0; j--){
dp[j | a[i]] = min(dp[j | a[i]], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
if(dp[(1 << m) - 1] == INF) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << dp[(1 << m) - 1] << endl;
return 0;
} 试题 J:组合数问题(25分)
题目链接:组合数问题
知识点:组合数、Lucas定理、数位dp
解题思路:求 ![]() 即求 ,由于 i 和 j 会达到
即求 ,由于 i 和 j 会达到 ![]() 的级别,求组合数就需要考虑到 Lucas 定理了。
的级别,求组合数就需要考虑到 Lucas 定理了。
(Lucas 定理:)
假设 a = 69,b = 47,k = 5,那么 。
将 a 和 b 用 k 进制表示一下,可以发现 ![]() ,
,![]() 。这恰好和上面分解后的组合数对应。
。这恰好和上面分解后的组合数对应。
再根据组合数 ![]() 的性质,当 n < m 的时候,
的性质,当 n < m 的时候,![]() ,那么就只需要分析 k 进制下的 a 和 b,如果 a 的某一位 p 小于 b 的该位 q,那么式子中一定会出现一个
,那么就只需要分析 k 进制下的 a 和 b,如果 a 的某一位 p 小于 b 的该位 q,那么式子中一定会出现一个 ![]() ,则 。
,则 。
这样就将原题转换成分析数位的问题了,这就可以用数位dp来解决。
但是仔细考虑后会发现如果只找某一位的关系是非常复杂的,因此可以将其转换为总数减去 i 的每一位都大于等于 j 的数量。
这样数位dp就比较好考虑了:
令 dp[i][0] 表示:a 的前 i 位未全取到上限值,b 的前 i 位也未全取到上限值;
dp[i][1] 表示:a 的前 i 位全取到上限值,b 的前 i 位未全取到上限值;
dp[i][2] 表示:a 的前 i 位未全取到上限值,b 的前 i 位全取到上限值;
dp[i][3] 表示:a 的前 i 位全取到上限值,b 的前 i 位也全取到上限值。
令 cal1(x, y) 表示:x 取值 [0, x],y 取值 [0, y] 时 x ≥ y 的数量;
cal2(x, y) 表示:x 取定值 x,y 取值 [0, y] 时 x ≥ y 的数量;
cal3(x, y) 表示:x 取值 [0, x],y 取定值 y 时 x ≥ y 的数量。
考虑状态转移:
![]()
![]()
![]()
分析一下这四个方程:
1.dp[i][0]:前 i 位 a 和 b 都没全取到上限值,
(1)可以由前 i + 1 位 a 和 b 都没全取到上限值转移,此时 a 和 b 的第 i 位均可以取 0 ~ k - 1;
(2)也可以由前 i + 1 位 a 全取到上限值,b没全取到上限值转移,此时 a 的第 i 位只能取 0 ~ a[i] - 1,b 的第 i 位可以取 0 ~ k - 1;
(3)也可以由前 i + 1 位 a 没全取到上限值,b 全取到上限值转移,此时 a 的第 i 位可以取 0 ~ k - 1,b 的第 i 位只能取 0 ~ b[i] - 1;
(4)还可以由前 i + 1 位 a 和 b 全取到上限值转移,此时 a 的第 i 位只能取 0 ~ a[i] - 1,b 的第 i 位只能取到 0 ~ b[i] - 1。
2.dp[i][1]:前 i 位 a 全取到上限值,b 没全取到上限值,
(1)可以由前 i + 1 位 a 全取到上限值,b 没全取到上限值转移,此时 a 的第 i 位只能取 a[i],b 的第 i 位能取 0 ~ k - 1;
(2)也可以由前 i + 1 位 a 和 b 全取到上限值转移,此时 a 的第 i 位只能取 a[i],b 的第 i 位只能取 0 ~ b[i] - 1。
3.dp[i][2]:前 i 位 a 没全取到上限值,b 全取到上限值,
(1)可以由前 i + 1 位 a 没全取到上限值,b 全取到上限值转移,此时 a 的第 i 位能取 0 ~ k - 1,b 的第 i 位只能取 b[i];
(2)也可以由前 i + 1 位 a 和 b 全取到上限值转移,此时 a 的第 i 位只能取 0 ~ a[i] - 1,b 的第 i 位只能取 b[i]。
4.dp[i][3]:前 i 位 a 和 b 都全取到上限值,只能由前 i + 1 位 a 和 b 都全取到上限值转移,此时 a 的第 i 位只能取 a[i],b 的第 i 位只能取 b[i],如果 a[i] >= b[i],那么个数为 1,反之个数为 0。
最后解释一下 cal1()、cal2()、cal3() 的计算过程:
1.cal1():由于 x 能取 [0, x],y 能取 [0, y],那么要求 x ≥ y 的个数,有两种情况:
(1)x < y:当 x 取 0 时,y 能取 [0, 0],x 取 1 时,y 能取 [0, 1],……,x 取 x 时,y 能取 [0, x],对这些取值个数求和,即 1 + 2 + ... + (x + 1),也就是 (x + 2)(x + 1) / 2;
(2)x ≥ y:当 x 取 0 时,y 能取 [0, 0],x 取 1 时,y 能取 [0, 1],……,x 取 y 时,y 能取 [0, y],x 取 y + 1 时,y 还是只能取 [0, y]……,对这些取值个数求和,即 1 + 2 + ... + (y + 1) + (x - y)(y + 1),也就是 (y + 2)(y + 1) / 2 + (x - y)(y + 1);
2.cal2():由于 x 取定值 x,y 能取 [0, y],那么要求 x ≥ y 的个数,有两种情况:
(1)x < y:y 只能取 [0, x];
(2)x ≥ y:y 能取 [0, y]。
整合一下,总个数为 min(x, y) + 1;
3.cal3():由于 x 能取 [0, x],y 取定值 y,那么要求 x ≥ y 的个数,有两种情况:
(1)x < y:无论 x 怎么取,均是 x < y,个数为 0;
(2)x ≥ y:x 只能取 [y, x],个数为 x - y + 1。
AC代码:
#include
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair PII;
typedef pair PLL;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll LLF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
const int inv2 = 500000004;
const int N = 105;
int a[N], b[N];
ll dp[N][4];
ll cal1(ll x, ll y){
if(x < 0 || y < 0) return 0;
ll xx = x, yy = y;
x %= mod; y %= mod;
if(xx < yy) return (x + 2) * (x + 1) % mod * inv2 % mod;
return ((y + 2) * (y + 1) % mod * inv2 % mod + (x - y) * (y + 1) % mod) % mod;
}
ll cal2(ll x, ll y){
return min(x, y) + 1;
}
ll cal3(ll x, ll y){
return x < y ? 0 : x - y + 1;
}
int main(){
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int t, k;
cin >> t >> k;
while(t--){
memset(dp, 0, sizeof dp);
memset(a, 0, sizeof a);
memset(b, 0, sizeof b);
ll n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
if(m > n) m = n;
ll ans = cal1(n, m);
int alen = 0, blen = 0;
while(n){
a[alen++] = n % k;
n /= k;
}
while(m){
b[blen++] = m % k;
m /= k;
}
dp[alen][3] = 1;
for(int i = alen - 1; i >= 0; i--){
dp[i][0] = (dp[i + 1][0] * cal1(k - 1, k - 1) + dp[i + 1][1] * cal1(a[i] - 1, k - 1) + dp[i + 1][2] * cal1(k - 1, b[i] - 1) + dp[i + 1][3] * cal1(a[i] - 1, b[i] - 1)) % mod;
dp[i][1] = (dp[i + 1][1] * cal2(a[i], k - 1) + dp[i + 1][3] * cal2(a[i], b[i] - 1)) % mod;
dp[i][2] = (dp[i + 1][2] * cal3(k - 1, b[i]) + dp[i + 1][3] * cal3(a[i] - 1, b[i])) % mod;
dp[i][3] = dp[i + 1][3] & (a[i] >= b[i]);
}
ans -= dp[0][0] + dp[0][1] + dp[0][2] + dp[0][3];
ans = (ans % mod + mod) % mod;
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}