java的Thread类start0方法源码
带着几个问题去看源码
1、如何找到native方法的源码
2、Java的Thread对象、JavaThread、OSThread、操作系统线程
3、Java线程与操作系统线程的关联
4、Java线程保存了哪些操作系统线程数据
5、怎么执行到run方法的
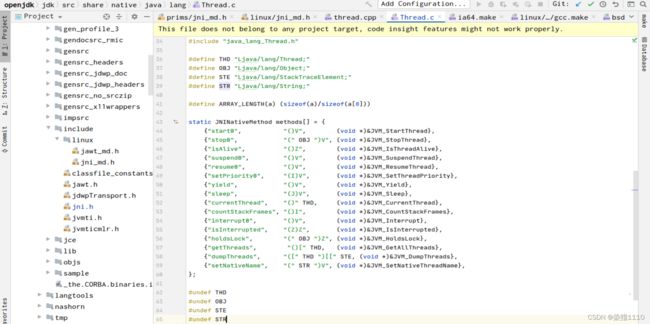
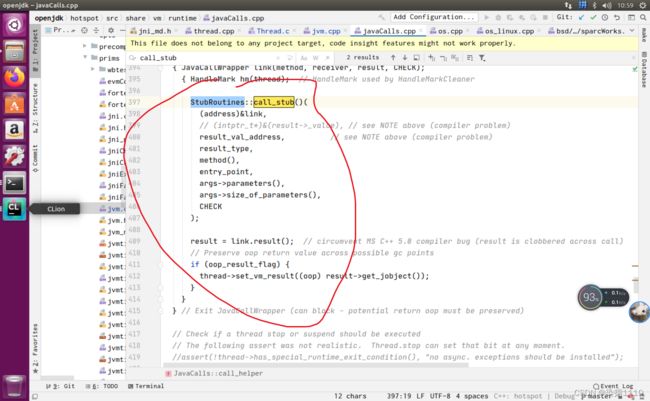
首先第一个问题native的方法是通过jni与c/c++进行通信的jni有个规则一个java类中有native方法那么就会有一个.h的文件.h文件是c/c++用来定义变量、方法的所以想看native方法的源码可以直接去jdk源码搜索类名找它的.c或.cpp文件 这两个文件是c/c++写代码实现的 然后Thread的start方法最终会调用start0这个native方法 所以去jdk源码中搜索Thread找它的.c或.cpp文件,我使用的是openJDK8的源码
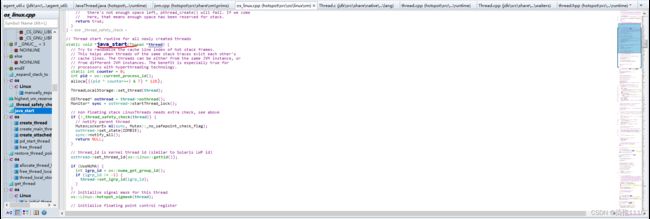
Thread.c中的逻辑
找native方法方式二(图二)
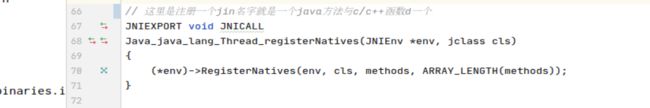
就这两个东西 通过上面的图可以看出 java的native方法与c语言函数中间隔着一层,这一层是jni,可以看出start0是java中的native方法用来启动线程而start0最终调用的是JVM_StartThread函数,然后去通过start0启动线程的方法去追怎么实现的线程创建然后就进入JVM_StartThread
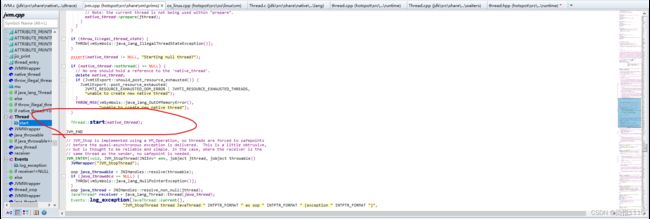
前缀是jvm也就是在jvm.c中实现的 然后进入jvm.c文件中 然后在jvm.c文件中搜索JVM_StartThread会来到这个thread_entry函数,换句话说如果想扩展jdk,比如扩展Class类,给Class类增加一个新的方法,首先找到Class.h文件,这个文件中也有图一与图二这样子的代码,即可在Class.java中写一个native方法,然后在图一的数组中把此方法注册到jdk中,然后再用c/c++写一个实现即可。
JVM_ENTRY(void, JVM_StartThread(JNIEnv* env, jobject jthread))
JVMWrapper("JVM_StartThread");
JavaThread *native_thread = NULL; // 声明一个javaThread用于保存线程
// We cannot hold the Threads_lock when we throw an exception,
// due to rank ordering issues. Example: we might need to grab the
// Heap_lock while we construct the exception.
bool throw_illegal_thread_state = false;
// We must release the Threads_lock before we can post a jvmti event
// in Thread::start.
{
// Ensure that the C++ Thread and OSThread structures aren't freed before
// we operate.
MutexLocker mu(Threads_lock);
// Since JDK 5 the java.lang.Thread threadStatus is used to prevent
// re-starting an already started thread, so we should usually find
// that the JavaThread is null. However for a JNI attached thread
// there is a small window between the Thread object being created
// (with its JavaThread set) and the update to its threadStatus, so we
// have to check for this
if (java_lang_Thread::thread(JNIHandles::resolve_non_null(jthread)) != NULL) {
throw_illegal_thread_state = true;
} else {
// We could also check the stillborn flag to see if this thread was already stopped, but
// for historical reasons we let the thread detect that itself when it starts running
jlong size =
java_lang_Thread::stackSize(JNIHandles::resolve_non_null(jthread));
// Allocate the C++ Thread structure and create the native thread. The
// stack size retrieved from java is signed, but the constructor takes
// size_t (an unsigned type), so avoid passing negative values which would
// result in really large stacks.
size_t sz = size > 0 ? (size_t) size : 0;
native_thread = new JavaThread(&thread_entry, sz);
// At this point it may be possible that no osthread was created for the
// JavaThread due to lack of memory. Check for this situation and throw
// an exception if necessary. Eventually we may want to change this so
// that we only grab the lock if the thread was created successfully -
// then we can also do this check and throw the exception in the
// JavaThread constructor.
if (native_thread->osthread() != NULL) {
// Note: the current thread is not being used within "prepare".
native_thread->prepare(jthread);
}
}
}
if (throw_illegal_thread_state) {
THROW(vmSymbols::java_lang_IllegalThreadStateException());
}
assert(native_thread != NULL, "Starting null thread?");
if (native_thread->osthread() == NULL) {
// No one should hold a reference to the 'native_thread'.
delete native_thread;
if (JvmtiExport::should_post_resource_exhausted()) {
JvmtiExport::post_resource_exhausted(
JVMTI_RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED_OOM_ERROR | JVMTI_RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED_THREADS,
"unable to create new native thread");
}
THROW_MSG(vmSymbols::java_lang_OutOfMemoryError(),
"unable to create new native thread");
}
Thread::start(native_thread);
JVM_END
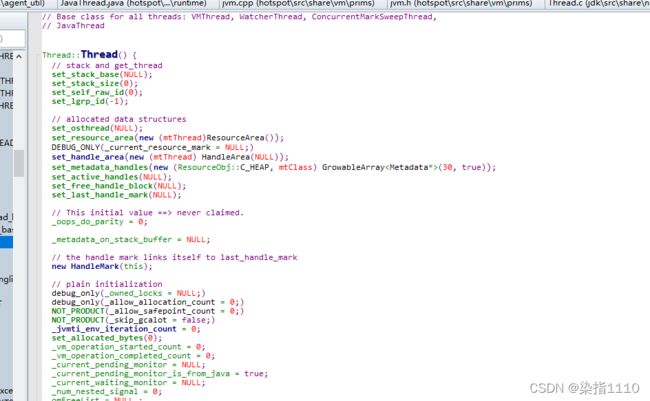
根据 native_thread = new JavaThread(&thread_entry, sz);可以猜测出thread_entry就是run方法跟进去看JavaThread的代码
JavaThread
/*
* Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS FILE HEADER.
*
* This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 only, as
* published by the Free Software Foundation.
*
* This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
* version 2 for more details (a copy is included in the LICENSE file that
* accompanied this code).
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License version
* 2 along with this work; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,
* Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*
* Please contact Oracle, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065 USA
* or visit www.oracle.com if you need additional information or have any
* questions.
*
*/
package sun.jvm.hotspot.runtime;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import sun.jvm.hotspot.debugger.*;
import sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.*;
import sun.jvm.hotspot.types.*;
import sun.jvm.hotspot.utilities.*;
/** This is an abstract class because there are certain OS- and
CPU-specific operations (like the setting and getting of the last
Java frame pointer) which need to be factored out. These
operations are implemented by, for example,
SolarisSPARCJavaThread, and the concrete subclasses are
instantiated by the JavaThreadFactory in the Threads class. */
public class JavaThread extends Thread {
private static final boolean DEBUG = System.getProperty("sun.jvm.hotspot.runtime.JavaThread.DEBUG") != null;
private static AddressField nextField;
private static sun.jvm.hotspot.types.OopField threadObjField;
private static AddressField anchorField;
private static AddressField lastJavaSPField;
private static AddressField lastJavaPCField;
private static CIntegerField threadStateField;
private static AddressField osThreadField;
private static AddressField stackBaseField;
private static CIntegerField stackSizeField;
private static JavaThreadPDAccess access;
// JavaThreadStates read from underlying process
private static int UNINITIALIZED;
private static int NEW;
private static int NEW_TRANS;
private static int IN_NATIVE;
private static int IN_NATIVE_TRANS;
private static int IN_VM;
private static int IN_VM_TRANS;
private static int IN_JAVA;
private static int IN_JAVA_TRANS;
private static int BLOCKED;
private static int BLOCKED_TRANS;
static {
VM.registerVMInitializedObserver(new Observer() {
public void update(Observable o, Object data) {
initialize(VM.getVM().getTypeDataBase());
}
});
}
private static synchronized void initialize(TypeDataBase db) {
Type type = db.lookupType("JavaThread");
Type anchorType = db.lookupType("JavaFrameAnchor");
nextField = type.getAddressField("_next");
threadObjField = type.getOopField("_threadObj");
anchorField = type.getAddressField("_anchor");
lastJavaSPField = anchorType.getAddressField("_last_Java_sp");
lastJavaPCField = anchorType.getAddressField("_last_Java_pc");
threadStateField = type.getCIntegerField("_thread_state");
osThreadField = type.getAddressField("_osthread");
stackBaseField = type.getAddressField("_stack_base");
stackSizeField = type.getCIntegerField("_stack_size");
UNINITIALIZED = db.lookupIntConstant("_thread_uninitialized").intValue();
NEW = db.lookupIntConstant("_thread_new").intValue();
NEW_TRANS = db.lookupIntConstant("_thread_new_trans").intValue();
IN_NATIVE = db.lookupIntConstant("_thread_in_native").intValue();
IN_NATIVE_TRANS = db.lookupIntConstant("_thread_in_native_trans").intValue();
IN_VM = db.lookupIntConstant("_thread_in_vm").intValue();
IN_VM_TRANS = db.lookupIntConstant("_thread_in_vm_trans").intValue();
IN_JAVA = db.lookupIntConstant("_thread_in_Java").intValue();
IN_JAVA_TRANS = db.lookupIntConstant("_thread_in_Java_trans").intValue();
BLOCKED = db.lookupIntConstant("_thread_blocked").intValue();
BLOCKED_TRANS = db.lookupIntConstant("_thread_blocked_trans").intValue();
}
public JavaThread(Address addr) {
super(addr);
}
void setThreadPDAccess(JavaThreadPDAccess access) {
this.access = access;
}
public JavaThread next() {
Address threadAddr = nextField.getValue(addr);
if (threadAddr == null) {
return null;
}
return VM.getVM().getThreads().createJavaThreadWrapper(threadAddr);
}
/** NOTE: for convenience, this differs in definition from the
underlying VM. Only "pure" JavaThreads return true;
CompilerThreads and JVMDIDebuggerThreads return false. FIXME:
consider encapsulating platform-specific functionality in an
object instead of using inheritance (which is the primary reason
we can't traverse CompilerThreads, etc; didn't want to have, for
example, "SolarisSPARCCompilerThread".) */
public boolean isJavaThread() { return true; }
public static AddressField getAnchorField() { return anchorField; }
/** Get the last Java stack pointer */
public Address getLastJavaSP() {
Address sp = lastJavaSPField.getValue(addr.addOffsetTo(anchorField.getOffset()));
return sp;
}
public Address getLastJavaPC() {
Address pc = lastJavaPCField.getValue(addr.addOffsetTo(anchorField.getOffset()));
return pc;
}
/** Abstract accessor to last Java frame pointer, implemented by
OS/CPU-specific JavaThread implementation. May return null if
there is no frame pointer or if it is not necessary on this
platform. */
public Address getLastJavaFP(){
return access.getLastJavaFP(addr);
}
/** Abstract accessor to last Java pc, implemented by
OS/CPU-specific JavaThread implementation. May return null if
there is no frame pointer or if it is not necessary on this
platform. */
/*
public Address getLastJavaPC(){
return access.getLastJavaPC(addr);
}
*/
// FIXME: not yet implementable
// public abstract void setLastJavaFP(Address fp);
/** A stack pointer older than any java frame stack pointer. Only
needed on some platforms; for example, see
thread_solaris_sparc.hpp. */
public Address getBaseOfStackPointer(){
return access.getBaseOfStackPointer(addr);
}
// FIXME: not yet implementable
// public abstract void setBaseOfStackPointer(Address fp);
/** Tells whether the last Java frame is set */
public boolean hasLastJavaFrame() {
return (getLastJavaSP() != null);
}
/** Accessing frames */
public Frame getLastFrame() {
// FIXME: would need to implement runtime routine
// "cacheStatePD(boolean)" for reflective system to be able to
// flush register windows on SPARC
return cookLastFrame(getLastFramePD());
}
/** Internal routine implemented by platform-dependent subclasses */
protected Frame getLastFramePD(){
return access.getLastFramePD(this, addr);
}
/** Accessing frames. Returns the last Java VFrame or null if none
was present. (NOTE that this is mostly unusable in a debugging
system; see getLastJavaVFrameDbg, below, which provides very
different functionality.) */
public JavaVFrame getLastJavaVFrame(RegisterMap regMap) {
if (Assert.ASSERTS_ENABLED) {
Assert.that(regMap != null, "a map must be given");
}
Frame f = getLastFrame();
if (f == null) {
return null;
}
for (VFrame vf = VFrame.newVFrame(f, regMap, this); vf != null; vf = vf.sender()) {
if (vf.isJavaFrame()) {
return (JavaVFrame) vf;
}
}
return null;
}
/** This should only be used by a debugger. Uses the current frame
guess to attempt to get the topmost JavaVFrame.
(getLastJavaVFrame, as a port of the VM's routine, assumes the
VM is at a safepoint.) */
public JavaVFrame getLastJavaVFrameDbg() {
RegisterMap regMap = newRegisterMap(true);
sun.jvm.hotspot.runtime.Frame f = getCurrentFrameGuess();
if (f == null) return null;
boolean imprecise = true;
if (f.isInterpretedFrame() && !f.isInterpretedFrameValid()) {
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println("Correcting for invalid interpreter frame");
}
f = f.sender(regMap);
imprecise = false;
}
VFrame vf = VFrame.newVFrame(f, regMap, this, true, imprecise);
if (vf == null) {
if (DEBUG) {
System.out.println(" (Unable to create vframe for topmost frame guess)");
}
return null;
}
return vf.isJavaFrame() ? (JavaVFrame)vf : vf.javaSender();
}
/** In this system, a JavaThread is the top-level factory for a
RegisterMap, since the JavaThread implementation is already
platform-specific and RegisterMap is also necessarily
platform-specific. The updateMap argument indicates whether the
register map needs to be updated, for example during stack
traversal -- see frame.hpp. */
public RegisterMap newRegisterMap(boolean updateMap){
return access.newRegisterMap(this, updateMap);
}
/** This is only designed to be used by the debugging system.
Returns a "best guess" of the topmost frame on the stack. This
guess should be as "raw" as possible. For example, if the
topmost frame is an interpreter frame (the return PC is in the
interpreter) but is not a valid frame (i.e., the BCI has not yet
been set up) this should still return the topmost frame and not
the sender. Validity checks are done at higher levels. */
public Frame getCurrentFrameGuess(){
return access.getCurrentFrameGuess(this, addr);
}
/** Also only intended for use by the debugging system. Provides the
same effect of OSThread::print(); that is, prints a value which
allows the user to intuitively understand which native OS thread
maps to this Java thread. Does not print a newline or leading or
trailing spaces. */
public void printThreadIDOn(PrintStream tty) {
access.printThreadIDOn(addr,tty);
}
public void printThreadID() {
printThreadIDOn(System.out);
}
public ThreadProxy getThreadProxy() {
return access.getThreadProxy(addr);
}
//
// Safepoint support
//
public JavaThreadState getThreadState() {
int val = (int) threadStateField.getValue(addr);
if (val == UNINITIALIZED) {
return JavaThreadState.UNINITIALIZED;
} else if (val == NEW) {
return JavaThreadState.NEW;
} else if (val == NEW_TRANS) {
return JavaThreadState.NEW_TRANS;
} else if (val == IN_NATIVE) {
return JavaThreadState.IN_NATIVE;
} else if (val == IN_NATIVE_TRANS) {
return JavaThreadState.IN_NATIVE_TRANS;
} else if (val == IN_VM) {
return JavaThreadState.IN_VM;
} else if (val == IN_VM_TRANS) {
return JavaThreadState.IN_VM_TRANS;
} else if (val == IN_JAVA) {
return JavaThreadState.IN_JAVA;
} else if (val == IN_JAVA_TRANS) {
return JavaThreadState.IN_JAVA_TRANS;
} else if (val == BLOCKED) {
return JavaThreadState.BLOCKED;
} else if (val == BLOCKED_TRANS) {
return JavaThreadState.BLOCKED_TRANS;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Illegal thread state " + val);
}
}
// FIXME: not yet implementable
// public void setThreadState(JavaThreadState s);
//
// Miscellaneous operations
//
public OSThread getOSThread() {
return (OSThread) VMObjectFactory.newObject(OSThread.class, osThreadField.getValue(addr));
}
public Address getStackBase() {
return stackBaseField.getValue(addr);
}
public long getStackBaseValue() {
return VM.getVM().getAddressValue(getStackBase());
}
public long getStackSize() {
return stackSizeField.getValue(addr);
}
/** Gets the Java-side thread object for this JavaThread */
public Oop getThreadObj() {
Oop obj = null;
try {
obj = VM.getVM().getObjectHeap().newOop(threadObjField.getValue(addr));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}
/** Get the Java-side name of this thread */
public String getThreadName() {
Oop threadObj = getThreadObj();
if (threadObj == null) {
return "" ;
}
return OopUtilities.threadOopGetName(threadObj);
}
//
// Oop traversal
//
public void oopsDo(AddressVisitor oopVisitor) {
super.oopsDo(oopVisitor);
// FIXME: add in the rest of the routine from the VM
// Traverse the execution stack
for(StackFrameStream fst = new StackFrameStream(this); !fst.isDone(); fst.next()) {
fst.getCurrent().oopsDo(oopVisitor, fst.getRegisterMap());
}
}
public boolean isInStack(Address a) {
if (Assert.ASSERTS_ENABLED) {
Assert.that(VM.getVM().isDebugging(), "Not yet implemented for non-debugging system");
}
Address sp = lastSPDbg();
Address stackBase = getStackBase();
// Be robust
if (sp == null) return false;
return stackBase.greaterThanOrEqual(a) && sp.lessThanOrEqual(a);
}
public boolean isLockOwned(Address a) {
Address stackBase = getStackBase();
Address stackLimit = stackBase.addOffsetTo(-getStackSize());
return stackBase.greaterThanOrEqual(a) && stackLimit.lessThanOrEqual(a);
// FIXME: should traverse MonitorArray/MonitorChunks as in VM
}
public Oop getCurrentParkBlocker() {
Oop threadObj = getThreadObj();
if (threadObj != null) {
return OopUtilities.threadOopGetParkBlocker(threadObj);
}
return null;
}
public void printInfoOn(PrintStream tty) {
tty.println("State: " + getThreadState().toString());
// Attempt to figure out the addresses covered by Java frames.
// NOTE: we should make this a method and let the Stackwalk panel use the result too.
//
sun.jvm.hotspot.runtime.Frame tmpFrame = getCurrentFrameGuess();
if (tmpFrame != null ) {
Address sp = tmpFrame.getSP();
Address maxSP = sp;
Address minSP = sp;
RegisterMap tmpMap = newRegisterMap(false);
while ((tmpFrame != null) && (!tmpFrame.isFirstFrame())) {
tmpFrame = tmpFrame.sender(tmpMap);
if (tmpFrame != null) {
sp = tmpFrame.getSP();
maxSP = AddressOps.max(maxSP, sp);
minSP = AddressOps.min(minSP, sp);
}
}
tty.println("Stack in use by Java: " + minSP + " .. " + maxSP);
} else {
tty.println("No Java frames present");
}
tty.println("Base of Stack: " + getBaseOfStackPointer());
tty.println("Last_Java_SP: " + getLastJavaSP());
tty.println("Last_Java_FP: " + getLastJavaFP());
tty.println("Last_Java_PC: " + getLastJavaPC());
// More stuff like saved_execption_pc, safepoint_state, ...
access.printInfoOn(addr, tty);
}
///
// //
// FIXME: add more accessors //
// //
///
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Internals only below this point
//
private Frame cookLastFrame(Frame fr) {
if (fr == null) {
return null;
}
Address pc = fr.getPC();
if (Assert.ASSERTS_ENABLED) {
if (pc == null) {
Assert.that(VM.getVM().isDebugging(), "must have PC");
}
}
return fr;
}
private Address lastSPDbg() {
return access.getLastSP(addr);
}
}
在父类中有一个osThread
// allocated data structures
set_osthread(NULL);
这个OsThread可以理解为把面向过程的创建线程封装成了面向对象的也就是osThread
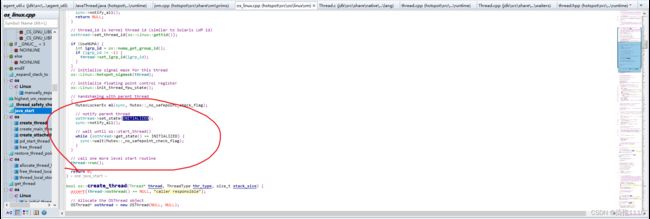
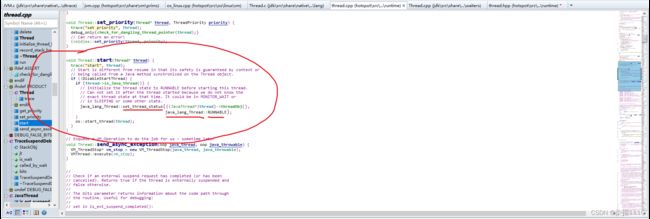
JavaThread的构造方法
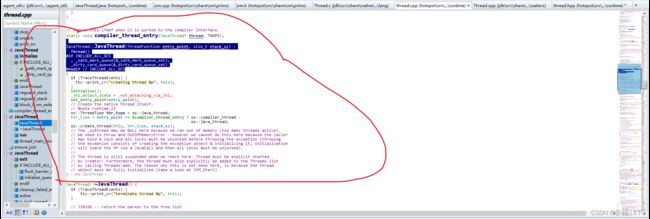
下图可以看到在JavaThread的构造函数中创建了线程但是线程执行的方法不是我们java中的run方法
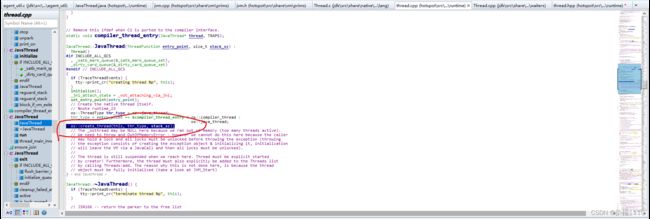
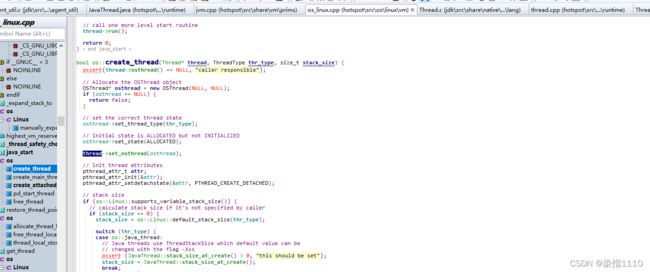
在create_thread中创建了osthread并且osthread与javathread做了绑定
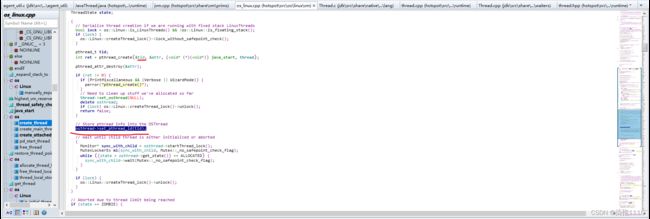
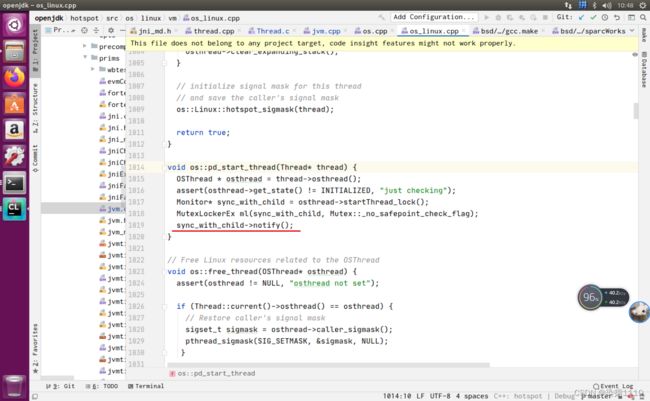
create_thread中真正创建线程的代码然后执行的是java_start函数
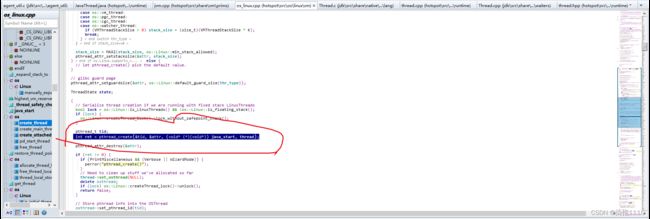
在java_start函数中进行了子线程进行了阻塞
java_start子线程进入了阻塞在这期间main线程也是在运行着的然后再次回到create_thread函数main执行osthread->set_pthread_id(tid);osthread与操作系统的线程做了绑定
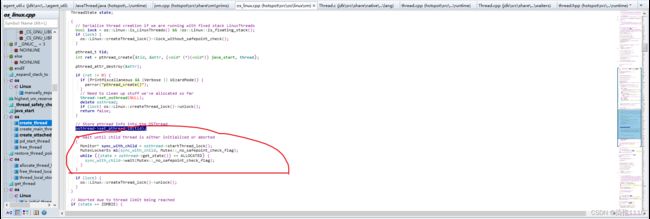
create_thread函数中创建了线程,创建线程是main线程做的然后下面main线程进入了阻塞上面子线程进入阻塞之前调用了notify_all();唤醒了主线程
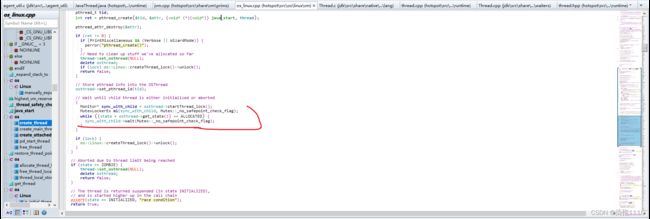
主线程进入阻塞但是在子线程执行java_start函数时进行了唤醒这时main被唤醒了
然后假设子线程被唤醒了然后就会执行run函数
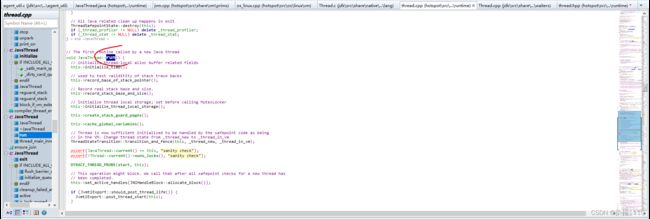
根据上面的图可以看到this->initialize_tlab();tlab在这里初始化了
然后在run方法中的thread_main_inner函数中调用了java的run方法
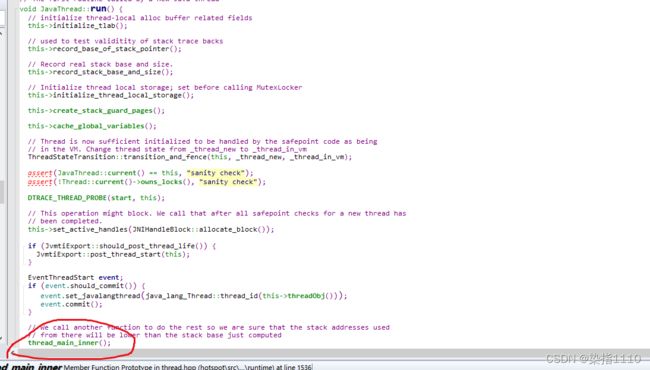
在这调用java的run方法
this->entry_point()(this, this);
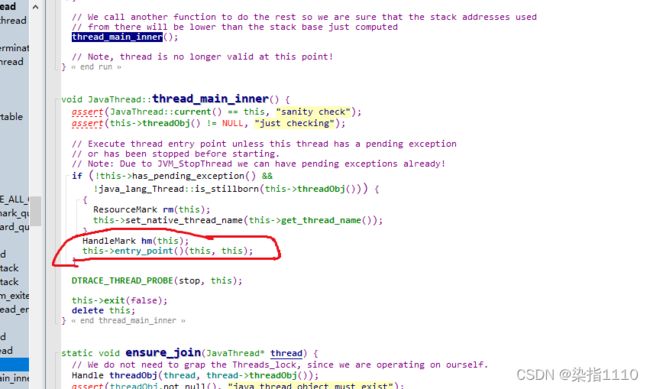
entry_point就是下面的thread_entry,thread_entry最终会调到javaCalls,javaCalls是c访问java的代码的大门
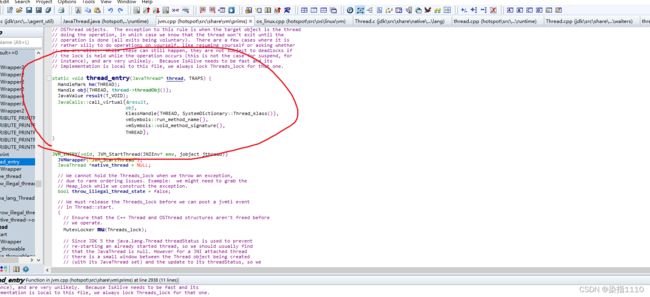
然后主线程被唤醒继续往下走最终会到Thread::start(native_thread);