ES6-promise简单理解
文章目录
-
- promise是什么
- promise的三种状态
- promise的特点
- promise的链式调用
- promise之return
- promise.all(处理并发请求)
- promsie.allSettled(批量处理请求)
- promise.race
- promise.resolve和reject
- 手写简单的promise
promise是什么
Promise 是异步编程的一种解决方案,也是为了解决回调函数层层嵌套的地狱而生
promise的三种状态
**1. pending (等待)
- fulfilled(成功的)
- reject(失败的)**
promise的特点
- 对象的状态不受外界影响。
- 一旦从等待状态变成为其他状态就永远不能更改状态了。
- 一旦新建Promise就会立即执行,无法中途取消
- 不设置回调函数callback,Promise内部抛出的错误,就不会反应到外部
- 当处于pending状态时,无法得知目前进展到哪一个阶段
promise的链式调用
- 传统的回调地狱,代码少还可以,多了简直无法看了
// 模拟发送请求
let req = function(callback) {
setTimeout(() =>{
let data = 123;
callback(data)
},500)
}
// 嵌套函数的回调地狱
req((data) =>{
console.log("1",data); // 1 123
req((data)=>{
console.log("2",data); // 2 123
req((data)=>{
console.log("3",data); // 3 123
req((data)=>{
console.log("4",data); // 4 123
req((data)=>{
console.log("5",data); // 5 123
})
})
})
})
})
- promise的写法,相对于回调来说就简介优雅一些
let p1 = new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(1)
},100)
})
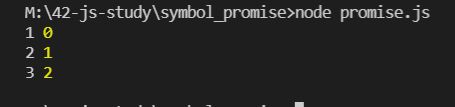
p1.then(res =>{
console.log("res",res); // 1
return res
}).then(res=>{
console.log("1",res); // 1
return res
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res); // 1
})
promise之return
- return 一个promise对象
let i = 0;
let fn = function() {
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(i++)
},100)
})
}
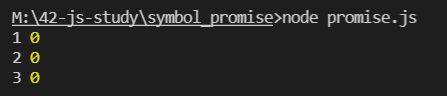
fn().then(res =>{
console.log("1",res);
return fn() // 每次是会返回一个新的promise 0
}).then(res =>{
console.log("2",res);
return fn() // 每次都返回新的promsie 1
}).then(res =>{
console.log("3",res); 2
})
- promise之return 一个值
let i = 0;
let fn = function() {
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(i++)
},100)
})
}
fn().then(res =>{
console.log("1",res);
return res
}).then(res =>{
console.log("2",res);
return res
}).then(res =>{
console.log("3",res); // 返回最初的值 0
})
promise.all(处理并发请求)
- promise.all的普通写法
let p1 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(111)},300)
})
let p2 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res("000")},300)
})
let p3 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(222)},300)
})
let p4 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(333)},300)
})
let p5 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(444)},300)
})
let arr = [p1,p2,p3,p4,p5]
Promise.all(arr).then(res=>{
console.log('all====res'+res)
}).catch(err=>{
console.log('err===='+err)
})
- promise.all异常会怎样.,我们把p2对象rej一个错误值
let p1 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(111)},300)
})
let p2 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ rej("000")},300)
})
let p3 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(222)},300)
})
let p4 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(333)},300)
})
let p5 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(444)},300)
})
let arr = [p1,p2,p3,p4,p5]
Promise.all(arr).then(res=>{
console.log('all====res'+res)
}).catch(err=>{
console.log('err===='+err)
})
可以看出只执行了错误的值,这在实际开发中,显然不是我们想要的结果值,我们想要的是失败的或者成功的都显示出来

- promise.all,处理异常,我们把p2和p4对象分别返回一个错误值
let p1 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(111)},300)
}).then(res=>{
console.log("res-111",res);
}).catch(err=>{
console.log("err-111",err);
})
let p2 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ rej("000")},300)
}).then(res=>{
console.log("res-000",res);
}).catch(err=>{
console.log("err-000",err);
})
let p3 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(222)},300)
}).then(res=>{
console.log("res-222",res);
}).catch(err=>{
console.log("err-222",err);
})
let p4 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(333)},300)
}).then(res=>{
console.log("res-333",res);
}).catch(err=>{
console.log("err-333",err);
})
let p5 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(444)},300)
}).then(res=>{
console.log("res-444",res);
}).catch(err=>{
console.log("err-444",err);
})
let arr = [p1,p2,p3,p4,p5]
Promise.all(arr).then(res=>{
console.log('all====res'+res)
}).catch(err=>{
console.log('all====err'+err)
})
显然这种结果是我们想要的,但是如果有几十条几百条,这样写是不是太费手了
- promise.all,批量处理异常
let p1 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(111)},300)
})
let p2 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ rej("000")},300)
})
let p3 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(222)},300)
})
let p4 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ rej(333)},300)
})
let p5 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(444)},300)
})
// watchPromiseError 统一处理成功或者错误的
async function watchPromiseError(p) {
try {
console.log("p",p);
const data = await p;
return {
err:0,
res: data
}
} catch (error) {
return {
err: 1,
res:error
}
}
}
let arr = [p1,p2,p3,p4,p5]
Promise.all(arr.map(item => watchPromiseError(item))).then(res=>{
console.log("promiseAll-res",res);
}).catch(err=>{
console.log("promiseAll-err",err);
})
可以看出这样也能拿到所有的结果值,还有一种promsie.allSettled也可以解决

promsie.allSettled(批量处理请求)
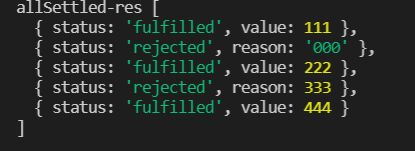
- allSettled和all类似,不同的是,allSettled可以返回成功和失败的结果,不会再失败后被中断
let p1 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(111)},300)
})
let p2 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ rej("000")},300)
})
let p3 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(222)},300)
})
let p4 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ rej(333)},300)
})
let p5 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(444)},300)
})
// watchPromiseError 统一处理成功或者错误的
async function watchPromiseError(p) {
try {
console.log("p",p);
const data = await p;
return {
err:0,
res: data
}
} catch (error) {
return {
err: 1,
res:error
}
}
}
let arr = [p1,p2,p3,p4,p5]
Promise.allSettled(arr).then(res=>{
console.log("allSettled-res",res);
}).catch(err=>{
console.log("allSettled-err",err);
})
promise.race
- 普通写法
let p1 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(111)},500)
})
let p2 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res("000")},300)
})
let p3 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(222)},300)
})
let p4 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(333)},300)
})
let p5 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(444)},300)
})
let arr = [p1,p2,p3,p4,p5];
Promise.race([p1,p2,p3,p4,p5]).then(res=>{
console.log(res); // 111
})
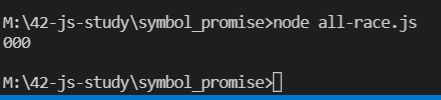
- race异常是怎样的呢,我们把p2改为rej看下
let p1 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(111)},500)
})
let p2 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ rej("000")},300)
})
let p3 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(222)},300)
})
let p4 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(333)},300)
})
let p5 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(444)},300)
})
let arr = [p1,p2,p3,p4,p5];
Promise.race([p1,p2,p3,p4,p5]).then(res=>{
console.log(res); // 111
})
可以看出报错了,被reject拒绝了,值是000,吧啦吧啦的,反正就这个报错意思吧

- 处理异常
let p1 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(111)},500)
})
let p2 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ rej("000")},300)
})
let p3 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(222)},300)
})
let p4 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(333)},300)
})
let p5 = new Promise((res,rej) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ res(444)},300)
})
let arr = [p1,p2,p3,p4,p5];
async function watchPromiseError(p) {
try {
const data = await p;
return {
err:0,
res: data
}
} catch (error) {
return {
err: 1,
res:error
}
}
}
Promise.race(arr.map(item=>watchPromiseError(item))).then(res=>{
console.log(res); // 111
})
看出就算出错,也是只返回最先请求的那个方法,正如race本身字面来说,就是赛跑的意思,谁跑的快就是谁

promise.resolve和reject
let p2 = new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{
setTimeout(()=>{ reject("000")},300)
})
p2.then(res=>{
console.log(res);
}).catch(err=>{
return Promise.resolve(err) // 相当于 resolve了
}).then(res=>{
console.log("res",res); // 000
return Promise.reject(res) // 相当于reject了
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res);
}).catch(err=>{
console.log("err",err); // 000
})
手写简单的promise
class MyPromise {
constructor(executor) {
// 规定状态
this.state = "pending"
// 保存 `resolve(res)` 的res值
this.value = undefined
// 保存 `reject(err)` 的err值
this.reason = undefined
// 成功存放的数组
this.successCB = []
// 失败存放的数组
this.failCB = []
let resolve = (value) => {
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.state = "fulfilled"
this.value = value
this.successCB.forEach(f => f())
}
}
let reject = (reason) => {
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.state = "rejected"
this.value = value
this.failCB.forEach(f => f())
}
}
try {
// 执行
executor(resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
// 若出错,直接调用reject
reject(error)
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this.state === "fulfilled") {
onFulfilled(this.value)
}
if (this.state === "rejected") {
onRejected(this.value)
}
if (this.state === "pending") {
this.successCB.push(() => { onFulfilled(this.value) })
this.failCB.push(() => { onRejected(this.reason) })
}
}
}