【Python】Anaconda软件的conda.exe基本使用
1.为什么还需要 Anaconda?有以下3个原因:
1)Anaconda 附带了一大批常用数据科学包,它附带了 conda、Python 和 150 多个科学包及其依赖项。因此你可以立即开始处理数据。
2)管理包
Anaconda 是在 conda(一个包管理器和环境管理器)上发展出来的。
在数据分析中,你会用到很多第三方的包,而conda(包管理器)可以很好的帮助你在计算机上安装和管理这些包,包括安装、卸载和更新包。
3)管理环境
为什么需要管理环境呢?
比如你在A项目中用了 Python 2,而新的项目B老大要求使用Python 3,而同时安装两个Python版本可能会造成许多混乱和错误。这时候 conda就可以帮助你为不同的项目建立不同的运行环境。
还有很多项目使用的包版本不同,比如不同的pandas版本,不可能同时安装两个 Numpy 版本,你要做的应该是,为每个 Numpy 版本创建一个环境,然后项目的对应环境中工作。这时候conda就可以帮你做到。
(https://www.zhihu.com/question/58033789/answer/254673663)
2.Anaconda的安装教程:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38628350/article/details/79045640
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36015370/article/details/79484455/
https://www.zhihu.com/question/58033789
后面再补充百度云资源
anaconda官网:https://www.anaconda.com/download/
3.conda的基本使用:
conda.exe在“D:\Users\Leon_PC\Anaconda3\Scripts”下可以找到,
打开windows控制台(win+r,输入cmd,回车)
如果之前没有配置好环境,那么定位到“D:\Users\Leon_PC\Anaconda3\Scripts”
cd /d D:\Users\Leon_PC\Anaconda3\Scripts
(1)conda下载的操作,关于下载速度的问题
-
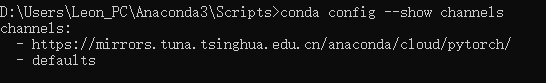
查看conda的下载源
conda config --show channels
-
从channel中安装包时显示channel的url,这样就可以知道包的安装来源了
conda config --set show_channel_urls yes
-
添加清华下载源
conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/pytorch/
-
删除某个下载源
conda config --remove channels
比如:
conda config --remove channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/pytorch/
一些不太能用但是网上基本都有的源:
$ conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/free/
$ conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main/
## Conda Forge
$ conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/conda-forge/
## msys2
$ conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/msys2/
## bioconda
$ conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/bioconda/
## menpo
$ conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/menpo/
(2)conda创建虚拟环境等系列管理环境的操作
-
查看存在哪些虚拟环境
conda env list 或 conda info -e
-
创建新的虚拟环境:tensorflow_gpu是虚拟环境的名称,可以任意设置,其中 -n参数表示环境的名称
conda create -n tensorflow_gpu python=3.6
查看conda create有哪些option参数
conda create -h
usage: conda-script.py create [-h] [--clone ENV] [-n ENVIRONMENT | -p PATH]
[-c CHANNEL] [--use-local] [--override-channels]
[--repodata-fn REPODATA_FNS]
[--strict-channel-priority]
[--no-channel-priority]
[--no-deps | --only-deps] [--no-pin] [--copy]
[--no-shortcuts] [-C] [-k] [--offline] [-d]
[--json] [-q] [-v] [-y] [--download-only]
[--show-channel-urls] [--file FILE]
[--no-default-packages] [--dev]
[package_spec [package_spec ...]]Create a new conda environment from a list of specified packages. To use the created environment, use 'conda activate envname' look in that directory first. This command requires either the -n NAME or -p PREFIX option.
Options:
positional arguments:
package_spec Packages to install or update in the conda
environment.optional arguments:
-h, --help Show this help message and exit.
--clone ENV Path to (or name of) existing local environment.
--file FILE Read package versions from the given file. Repeated
file specifications can be passed (e.g. --file=file1
--file=file2).
--dev Use `sys.executable -m conda` in wrapper scripts
instead of CONDA_EXE. This is mainly for use during
tests where we test new conda source against old
Python versions.Target Environment Specification:
-n ENVIRONMENT, --name ENVIRONMENT
Name of environment.
-p PATH, --prefix PATH
Full path to environment location (i.e. prefix).Channel Customization:
-c CHANNEL, --channel CHANNEL
Additional channel to search for packages. These are
URLs searched in the order they are given (including
local directories using the 'file://' syntax or simply
a path like '/home/conda/mychan' or '../mychan').
Then, the defaults or channels from .condarc are
searched (unless --override-channels is given). You
can use 'defaults' to get the default packages for
conda. You can also use any name and the .condarc
channel_alias value will be prepended. The default
channel_alias is http://conda.anaconda.org/.
--use-local Use locally built packages. Identical to '-c local'.
--override-channels Do not search default or .condarc channels. Requires
--channel.
--repodata-fn REPODATA_FNS
Specify name of repodata on remote server. Conda will
try whatever you specify, but will ultimately fall
back to repodata.json if your specs are not
satisfiable with what you specify here. This is used
to employ repodata that is reduced in time scope. You
may pass this flag more than once. Leftmost entries
are tried first, and the fallback to repodata.json is
added for you automatically.Solver Mode Modifiers:
--strict-channel-priority
Packages in lower priority channels are not considered
if a package with the same name appears in a higher
priority channel.
--no-channel-priority
Package version takes precedence over channel
priority. Overrides the value given by `conda config
--show channel_priority`.
--no-deps Do not install, update, remove, or change
dependencies. This WILL lead to broken environments
and inconsistent behavior. Use at your own risk.
--only-deps Only install dependencies.
--no-pin Ignore pinned file.
--no-default-packages
Ignore create_default_packages in the .condarc file.Package Linking and Install-time Options:
--copy Install all packages using copies instead of hard- or
soft-linking.
--no-shortcuts Don't install start menu shortcutsNetworking Options:
-C, --use-index-cache
Use cache of channel index files, even if it has
expired.
-k, --insecure Allow conda to perform "insecure" SSL connections and
transfers. Equivalent to setting 'ssl_verify' to
'false'.
--offline Offline mode. Don't connect to the Internet.Output, Prompt, and Flow Control Options:
-d, --dry-run Only display what would have been done.
--json Report all output as json. Suitable for using conda
programmatically.
-q, --quiet Do not display progress bar.
-v, --verbose Can be used multiple times. Once for INFO, twice for
DEBUG, three times for TRACE.
-y, --yes Do not ask for confirmation.
--download-only Solve an environment and ensure package caches are
populated, but exit prior to unlinking and linking
packages into the prefix.
--show-channel-urls Show channel urls. Overrides the value given by `conda
config --show show_channel_urls`.Examples:
conda create -n myenv sqlite
-
激活环境(进入到虚拟环境中)
activate tensorflow_gpu
-
退出虚拟环境
conda deactivate
-
删除某个虚拟环境
conda remove -n tensorflow_gpu --all
conda remove -h
usage: conda-script.py remove [-h] [-n ENVIRONMENT | -p PATH] [-c CHANNEL]
[--use-local] [--override-channels]
[--repodata-fn REPODATA_FNS] [--all]
[--features] [--force-remove] [--no-pin] [-C]
[-k] [--offline] [-d] [--json] [-q] [-v] [-y]
[--dev]
[package_name [package_name ...]]Remove a list of packages from a specified conda environment.
This command will also remove any package that depends on any of the
specified packages as well---unless a replacement can be found without
that dependency. If you wish to skip this dependency checking and remove
just the requested packages, add the '--force' option. Note however that
this may result in a broken environment, so use this with caution.Options:
positional arguments:
package_name Package names to remove from the environment.optional arguments:
-h, --help Show this help message and exit.
--dev Use `sys.executable -m conda` in wrapper scripts
instead of CONDA_EXE. This is mainly for use during
tests where we test new conda source against old
Python versions.Target Environment Specification:
-n ENVIRONMENT, --name ENVIRONMENT
Name of environment.
-p PATH, --prefix PATH
Full path to environment location (i.e. prefix).Channel Customization:
-c CHANNEL, --channel CHANNEL
Additional channel to search for packages. These are
URLs searched in the order they are given (including
local directories using the 'file://' syntax or simply
a path like '/home/conda/mychan' or '../mychan').
Then, the defaults or channels from .condarc are
searched (unless --override-channels is given). You
can use 'defaults' to get the default packages for
conda. You can also use any name and the .condarc
channel_alias value will be prepended. The default
channel_alias is http://conda.anaconda.org/.
--use-local Use locally built packages. Identical to '-c local'.
--override-channels Do not search default or .condarc channels. Requires
--channel.
--repodata-fn REPODATA_FNS
Specify name of repodata on remote server. Conda will
try whatever you specify, but will ultimately fall
back to repodata.json if your specs are not
satisfiable with what you specify here. This is used
to employ repodata that is reduced in time scope. You
may pass this flag more than once. Leftmost entries
are tried first, and the fallback to repodata.json is
added for you automatically.Solver Mode Modifiers:
--all Remove all packages, i.e., the entire environment.
--features Remove features (instead of packages).
--force-remove, --force
Forces removal of a package without removing packages
that depend on it. Using this option will usually
leave your environment in a broken and inconsistent
state.
--no-pin Ignore pinned file.Networking Options:
-C, --use-index-cache
Use cache of channel index files, even if it has
expired.
-k, --insecure Allow conda to perform "insecure" SSL connections and
transfers. Equivalent to setting 'ssl_verify' to
'false'.
--offline Offline mode. Don't connect to the Internet.Output, Prompt, and Flow Control Options:
-d, --dry-run Only display what would have been done.
--json Report all output as json. Suitable for using conda
programmatically.
-q, --quiet Do not display progress bar.
-v, --verbose Can be used multiple times. Once for INFO, twice for
DEBUG, three times for TRACE.
-y, --yes Do not ask for confirmation.Examples:
conda remove -n myenv scipy
-
虚拟环境重命名
conda 其实没有重命名指令,实现重命名是通过 clone 完成的,分两步:
- 先 clone 一份 new name 的环境
- 删除 old name 的环境
conda create -n new_env --clone tensorflow_gpu
conda remove -n tensorflow_gpu --all
-
查看虚拟环境中通过conda install安装了哪些包
conda list
conda list -h
usage: conda-script.py list [-h] [-n ENVIRONMENT | -p PATH] [--json] [-v] [-q]
[--show-channel-urls] [-c] [-f] [--explicit]
[--md5] [-e] [-r] [--no-pip]
[regex]List linked packages in a conda environment.
Options:
positional arguments:
regex List only packages matching this regular expression.optional arguments:
-h, --help Show this help message and exit.
--show-channel-urls Show channel urls. Overrides the value given by `conda
config --show show_channel_urls`.
-c, --canonical Output canonical names of packages only. Implies --no-
pip.
-f, --full-name Only search for full names, i.e., ^$.
--explicit List explicitly all installed conda packaged with URL
(output may be used by conda create --file).
--md5 Add MD5 hashsum when using --explicit
-e, --export Output requirement string only (output may be used by
conda create --file).
-r, --revisions List the revision history and exit.
--no-pip Do not include pip-only installed packages.Target Environment Specification:
-n ENVIRONMENT, --name ENVIRONMENT
Name of environment.
-p PATH, --prefix PATH
Full path to environment location (i.e. prefix).Output, Prompt, and Flow Control Options:
--json Report all output as json. Suitable for using conda
programmatically.
-v, --verbose Use once for info, twice for debug, three times for
trace.
-q, --quiet Do not display progress bar.Examples:
List all packages in the current environment:
conda list
List all packages installed into the environment 'myenv':
conda list -n myenv
Save packages for future use:
conda list --export > package-list.txt
Reinstall packages from an export file:
conda create -n myenv --file package-list.txt
-
查看虚拟环境中通过pip install安装了哪些包
pip list
-
查看虚拟环境中的python版本(activate env先进入虚拟环境)
python --version
-
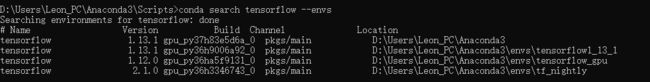
查找conda源中存在的安装包
conda search tensorflow
conda search -h
usage: conda-script.py search [-h] [--envs] [-i] [--subdir SUBDIR]
[-c CHANNEL] [--use-local] [--override-channels]
[--repodata-fn REPODATA_FNS] [-C] [-k]
[--offline] [--json] [-v] [-q]Search for packages and display associated information.
The input is a MatchSpec, a query language for conda packages.
See examples below.Options:
optional arguments:
-h, --help Show this help message and exit.
--envs Search all of the current user's environments. If run
as Administrator (on Windows) or UID 0 (on unix),
search all known environments on the system.
-i, --info Provide detailed information about each package.
--subdir SUBDIR, --platform SUBDIR
Search the given subdir. Should be formatted like
'osx-64', 'linux-32', 'win-64', and so on. The default
is to search the current platform.Channel Customization:
-c CHANNEL, --channel CHANNEL
Additional channel to search for packages. These are
URLs searched in the order they are given (including
local directories using the 'file://' syntax or simply
a path like '/home/conda/mychan' or '../mychan').
Then, the defaults or channels from .condarc are
searched (unless --override-channels is given). You
can use 'defaults' to get the default packages for
conda. You can also use any name and the .condarc
channel_alias value will be prepended. The default
channel_alias is http://conda.anaconda.org/.
--use-local Use locally built packages. Identical to '-c local'.
--override-channels Do not search default or .condarc channels. Requires
--channel.
--repodata-fn REPODATA_FNS
Specify name of repodata on remote server. Conda will
try whatever you specify, but will ultimately fall
back to repodata.json if your specs are not
satisfiable with what you specify here. This is used
to employ repodata that is reduced in time scope. You
may pass this flag more than once. Leftmost entries
are tried first, and the fallback to repodata.json is
added for you automatically.Networking Options:
-C, --use-index-cache
Use cache of channel index files, even if it has
expired.
-k, --insecure Allow conda to perform "insecure" SSL connections and
transfers. Equivalent to setting 'ssl_verify' to
'false'.
--offline Offline mode. Don't connect to the Internet.Output, Prompt, and Flow Control Options:
--json Report all output as json. Suitable for using conda
programmatically.
-v, --verbose Use once for info, twice for debug, three times for
trace.
-q, --quiet Do not display progress bar.Examples:
Search for a specific package named 'scikit-learn':
conda search scikit-learn
Search for packages containing 'scikit' in the package name:
conda search *scikit*
Note that your shell may expand '*' before handing the command over to conda.
Therefore it is sometimes necessary to use single or double quotes around the query.conda search '*scikit'
conda search "*scikit*"Search for packages for 64-bit Linux (by default, packages for your current
platform are shown):conda search numpy[subdir=linux-64]
Search for a specific version of a package:
conda search 'numpy>=1.12'
Search for a package on a specific channel
conda search conda-forge::numpy
conda search 'numpy[channel=conda-forge, subdir=osx-64]'
-
查找当前电脑中所有虚拟环境中的某个包,比如tensorflow(在本机内查找包)
conda search tensorflow --envs
列出所有虚拟环境中关于tensorflow的安装包信息
-
更新包
conda update xxx (更新某一个包)
conda update --all(更新所有包)
-
卸载包
conda remove 或 conda uninstall
(3)新建完虚拟环境之后安装spyder
-
激活虚拟环境
activate tensorflow_gpu
-
安装spyder
conda install spyder
会安装一个专门配对虚拟环境的spyder,这样你就可以在spyder里面import 虚拟环境中的tensorflow,而不需要用到pycharm去设置python源什么的,当然那样也是可以的,但是我比较常用spyder作为IDE
(4)安装tensorflow要注意的问题
-
通过conda install不要用pip,不然可能不能正常import
conda install tensorflow-gpu==1.13.1
conda 安装将自动安装 GPU 支持所需的 CUDA 和 CuDNN 库。pip 安装则需要手动安装这些库。人人喜欢一步到位,尤其是在下载与安装库这方面。
使用 pip 安装 TensorFlow 时,GPU 支持所需的 CUDA 和 CuDNN 库必须单独手动安装,增加了大量负担。而使用 conda 安装 GPU 加速版本的 TensorFlow 时,只需使用命令 conda install tensorflow-gpu,这些库就会自动安装成功,且版本与 tensorflow-gpu 包兼容。此外,conda 安装这些库的位置不会与通过其他方法安装的库的其他实例产生冲突。不管使用 pip 还是 conda 安装 GPU 支持的 TensorFlow,NVIDIA 驱动程序都必须单独安装。
对于 TensorFlow 的多个版本,conda 包可使用多种 CUDA 版本。例如,对于 TensorFlow 1.10.0 版本,conda 包支持可用的 CUDA 8.0、9.0 和 9.2 库。而 pip 包仅支持 CUDA 9.0 库。在不支持 CUDA 库最新版本的系统上运行时,这非常重要。最后,由于这些库是通过 conda 自动安装的,用户可轻松创建多个环境,并对比不同 CUDA 版本的性能。
(https://blog.csdn.net/abc13526222160/article/details/84673109)
(5)安装opencv要注意的问题
-
要用pip安装opencv-python,然后用conda安装opencv
https://blog.csdn.net/lyq_12/article/details/84783220
pip install opencv-python
conda install opencv