你有必要了解一下Flink底层RPC使用的框架和原理
1. 前言
对于Flink中各个组件(JobMaster、TaskManager、Dispatcher等),其底层RPC框架基于Akka实现,本文着重分析Flink中的Rpc框架实现机制及梳理其通信流程。
2. Akka介绍
由于Flink底层Rpc是基于Akka实现,我们先了解下Akka的基本使用。
Akka是一个开发并发、容错和可伸缩应用的框架。它是Actor Model的一个实现,和Erlang的并发模型很像。在Actor模型中,所有的实体被认为是独立的actors。actors和其他actors通过发送异步消息通信。Actor模型的强大来自于异步。它也可以显式等待响应,这使得可以执行同步操作。但是,强烈不建议同步消息,因为它们限制了系统的伸缩性。每个actor有一个邮箱(mailbox),它收到的消息存储在里面。另外,每一个actor维护自身单独的状态。一个Actors网络如下所示:
每个actor是一个单一的线程,它不断地从其邮箱中poll(拉取)消息,并且连续不断地处理。对于已经处理过的消息的结果,actor可以改变它自身的内部状态或者发送一个新消息或者孵化一个新的actor。尽管单个的actor是自然有序的,但一个包含若干个actor的系统却是高度并发的并且极具扩展性的。因为那些处理线程是所有actor之间共享的。这也是我们为什么不该在actor线程里调用可能导致阻塞的“调用”。因为这样的调用可能会阻塞该线程使得他们无法替其他actor处理消息。
2.1. 创建Akka系统
Akka系统的核心ActorSystem和Actor,若需构建一个Akka系统,首先需要创建ActorSystem,创建完ActorSystem后,可通过其创建Actor(注意:Akka不允许直接new一个Actor,只能通过 Akka 提供的某些 API 才能创建或查找 Actor,一般会通过 ActorSystem#actorOf和ActorContext#actorOf来创建 Actor),另外,我们只能通过ActorRef(Actor的引用, 其对原生的 Actor 实例做了良好的封装,外界不能随意修改其内部状态)来与Actor进行通信。如下代码展示了如何配置一个Akka系统。
// 1. 构建ActorSystem
// 使用缺省配置
ActorSystem system = ActorSystem.create("sys");
// 也可显示指定appsys配置
// ActorSystem system1 = ActorSystem.create("helloakka", ConfigFactory.load("appsys"));
// 2. 构建Actor,获取该Actor的引用,即ActorRef
ActorRef helloActor = system.actorOf(Props.create(HelloActor.class), "helloActor");
// 3. 给helloActor发送消息
helloActor.tell("hello helloActor", ActorRef.noSender());
// 4. 关闭ActorSystem
system.terminate();在Akka中,创建的每个Actor都有自己的路径,该路径遵循 ActorSystem 的层级结构,大致如下:
本地:akka://sys/user/helloActor
远程:akka.tcp://[email protected]:2020/user/remoteActor其中本地路径含义如下:
sys,创建的ActorSystem的名字;
user,通过ActorSystem#actorOf和ActorContext#actorOf 方法创建的 Actor 都属于/user下,与/user对应的是/system, 其是系统层面创建的,与系统整体行为有关,在开发阶段并不需要对其过多关注
helloActor,我们创建的HelloActor
其中远程部分路径含义如下:
akka.tcp,远程通信方式为tcp;
[email protected]:2020,ActorSystem名字及远程主机ip和端口号。
2.2. 根据path获取Actor
若提供了Actor的路径,可以通过路径获取到ActorRef,然后与之通信,代码如下所示:
ActorSystem system = ActorSystem.create("sys");
ActorSelection as = system.actorSelection("/path/to/actor");
Timeout timeout = new Timeout(Duration.create(2, "seconds"));
Future fu = as.resolveOne(timeout);
fu.onSuccess(new OnSuccess() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(ActorRef actor) {
System.out.println("actor:" + actor);
actor.tell("hello actor", ActorRef.noSender());
}
}, system.dispatcher());
fu.onFailure(new OnFailure() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable failure) {
System.out.println("failure:" + failure);
}
}, system.dispatcher()); 由上面可知,若需要与远端Actor通信,路径中必须提供ip:port。
2.3. 与Actor通信
2.3.1. tell方式
当使用tell方式时,表示仅仅使用异步方式给某个Actor发送消息,无需等待Actor的响应结果,并且也不会阻塞后续代码的运行,如:
helloActor.tell("hello helloActor", ActorRef.noSender());
其中:第一个参数为消息,它可以是任何可序列化的数据或对象,第二个参数表示发送者,通常来讲是另外一个 Actor 的引用, ActorRef.noSender()表示无发送者((实际上是一个 叫做deadLetters的Actor)。
2.3.2. ask方式
当我们需要从Actor获取响应结果时,可使用ask方法,ask方法会将返回结果包装在scala.concurrent.Future中,然后通过异步回调获取返回结果。如调用方:
// 异步发送消息给Actor,并获取响应结果
FutureHelloActor处理消息方法的代码大致如下:
private void handleMessage(Object object) {
if (object instanceof String) {
String str = (String) object;
log.info("[HelloActor] message is {}, sender is {}", str, getSender().path().toString());
// 给发送者发送消息
getSender().tell(str, getSelf());
}
}
上面主要介绍了Akka中的ActorSystem、Actor,及与Actor的通信;Flink借此构建了其底层通信系统。
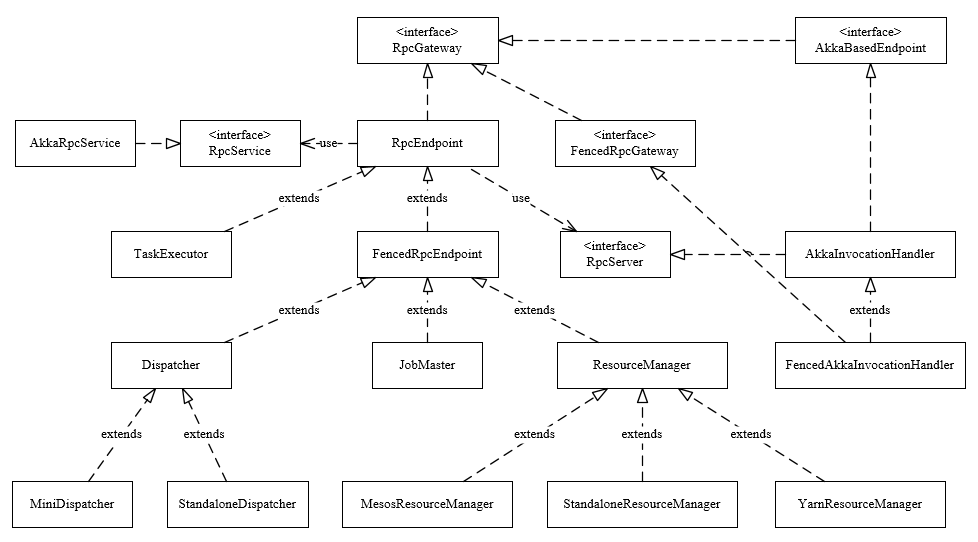
3. RPC类图结构
下图展示了Flink中RPC框架中涉及的主要类。
3.1. RpcGateway
Flink的RPC协议通过RpcGateway来定义;由前面可知,若想与远端Actor通信,则必须提供地址(ip和port),如在Flink-on-Yarn模式下,JobMaster会先启动ActorSystem,此时TaskExecutor的Container还未分配,后面与TaskExecutor通信时,必须让其提供对应地址,从类继承图可以看到基本上所有组件都实现了RpcGateway接口,其代码如下:
public interface RpcGateway {
/**
* Returns the fully qualified address under which the associated rpc endpoint is reachable.
*
* @return Fully qualified (RPC) address under which the associated rpc endpoint is reachable
*/
String getAddress();
/**
* Returns the fully qualified hostname under which the associated rpc endpoint is reachable.
*
* @return Fully qualified hostname under which the associated rpc endpoint is reachable
*/
String getHostname();
}3.2. RpcEndpoint
每个RpcEndpoint对应了一个路径(endpointId和actorSystem共同确定),每个路径对应一个Actor,其实现了RpcGateway接口,其构造函数如下:
protected RpcEndpoint(final RpcService rpcService, final String endpointId) {
// 保存rpcService和endpointId
this.rpcService = checkNotNull(rpcService, "rpcService");
this.endpointId = checkNotNull(endpointId, "endpointId");
// 通过RpcService启动RpcServer
this.rpcServer = rpcService.startServer(this);
// 主线程执行器,所有调用在主线程中串行执行
this.mainThreadExecutor = new MainThreadExecutor(rpcServer, this::validateRunsInMainThread);
}在RpcEndpoint中还定义了一些方法如runAsync(Runnable)、callAsync(Callable, Time)方法来执行Rpc调用,值得注意的是在Flink的设计中,对于同一个Endpoint,所有的调用都运行在主线程,因此不会有并发问题,当启动RpcEndpoint/进行Rpc调用时,其会委托RcpServer进行处理。
3.3. RpcService
Rpc服务的接口,其主要作用如下:
根据提供的RpcEndpoint来启动RpcServer(Actor);
根据提供的地址连接到RpcServer,并返回一个RpcGateway;
延迟/立刻调度Runnable、Callable;
停止RpcServer(Actor)或自身服务;
在Flink中其实现类为AkkaRpcService。
3.3.1. AkkaRpcService
AkkaRpcService中封装了ActorSystem,并保存了ActorRef到RpcEndpoint的映射关系,在构造RpcEndpoint时会启动指定rpcEndpoint上的RpcServer,其会根据Endpoint类型(FencedRpcEndpoint或其他)来创建不同的Actor(FencedAkkaRpcActor或AkkaRpcActor),并将RpcEndpoint和Actor对应的ActorRef保存起来,然后使用动态代理创建RpcServer,具体代码如下:
public RpcServer startServer(C rpcEndpoint) {
checkNotNull(rpcEndpoint, "rpc endpoint");
CompletableFuture terminationFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
final Props akkaRpcActorProps;
// 根据RpcEndpoint类型创建不同类型的Props
if (rpcEndpoint instanceof FencedRpcEndpoint) {
akkaRpcActorProps = Props.create(
FencedAkkaRpcActor.class,
rpcEndpoint,
terminationFuture,
getVersion(),
configuration.getMaximumFramesize());
} else {
akkaRpcActorProps = Props.create(
AkkaRpcActor.class,
rpcEndpoint,
terminationFuture,
getVersion(),
configuration.getMaximumFramesize());
}
ActorRef actorRef;
// 同步块,创建Actor,并获取对应的ActorRef
synchronized (lock) {
checkState(!stopped, "RpcService is stopped");
actorRef = actorSystem.actorOf(akkaRpcActorProps, rpcEndpoint.getEndpointId());
actors.put(actorRef, rpcEndpoint);
}
LOG.info("Starting RPC endpoint for {} at {} .", rpcEndpoint.getClass().getName(), actorRef.path());
// 获取Actor的路径
final String akkaAddress = AkkaUtils.getAkkaURL(actorSystem, actorRef);
final String hostname;
Option host = actorRef.path().address().host();
if (host.isEmpty()) {
hostname = "localhost";
} else {
hostname = host.get();
}
// 解析该RpcEndpoint实现的所有RpcGateway接口
Set> implementedRpcGateways = new HashSet<>(RpcUtils.extractImplementedRpcGateways(rpcEndpoint.getClass()));
// 额外添加RpcServer和AkkaBasedEnpoint类
implementedRpcGateways.add(RpcServer.class);
implementedRpcGateways.add(AkkaBasedEndpoint.class);
final InvocationHandler akkaInvocationHandler;
// 根据不同类型动态创建代理对象
if (rpcEndpoint instanceof FencedRpcEndpoint) {
// a FencedRpcEndpoint needs a FencedAkkaInvocationHandler
akkaInvocationHandler = new FencedAkkaInvocationHandler<>(
akkaAddress,
hostname,
actorRef,
configuration.getTimeout(),
configuration.getMaximumFramesize(),
terminationFuture,
((FencedRpcEndpoint) rpcEndpoint)::getFencingToken);
implementedRpcGateways.add(FencedMainThreadExecutable.class);
} else {
akkaInvocationHandler = new AkkaInvocationHandler(
akkaAddress,
hostname,
actorRef,
configuration.getTimeout(),
configuration.getMaximumFramesize(),
terminationFuture);
}
// Rather than using the System ClassLoader directly, we derive the ClassLoader
// from this class . That works better in cases where Flink runs embedded and all Flink
// code is loaded dynamically (for example from an OSGI bundle) through a custom ClassLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = getClass().getClassLoader();
// 生成RpcServer对象,而后对该server的调用都会进入Handler的invoke方法处理,handler实现了多个接口的方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
RpcServer server = (RpcServer) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
classLoader,
implementedRpcGateways.toArray(new Class[implementedRpcGateways.size()]),
akkaInvocationHandler);
return server;
} 当启动RpcServer后,即创建了相应的Actor(注意此时Actor的处于停止状态)和动态代理对象,需要调用RpcEndpoint#start启动启动Actor,此时启动RpcEndpoint流程如下(以非FencedRpcEndpoint为例):
调用RpcEndpoint#start;
委托给RpcServer#start;
调用动态代理的AkkaInvocationHandler#invoke;发现调用的是StartStoppable#start方法,则直接进行本地方法调用;invoke方法的代码如下:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Class declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
Object result;
// 先匹配指定类型(handler已实现接口的方法),若匹配成功则直接进行本地方法调用;若匹配为FencedRpcGateway类型,则抛出异常(应该在FencedAkkaInvocationHandler中处理);其他则进行Rpc调用
if (declaringClass.equals(AkkaBasedEndpoint.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(Object.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(RpcGateway.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(StartStoppable.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(MainThreadExecutable.class) ||
declaringClass.equals(RpcServer.class)) {
result = method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (declaringClass.equals(FencedRpcGateway.class)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("AkkaInvocationHandler does not support the call FencedRpcGateway#" +
method.getName() + ". This indicates that you retrieved a FencedRpcGateway without specifying a " +
"fencing token. Please use RpcService#connect(RpcService, F, Time) with F being the fencing token to " +
"retrieve a properly FencedRpcGateway.");
} else {
result = invokeRpc(method, args);
}
return result;
}调用AkkaInvocationHandler#start;
通过ActorRef#tell给对应的Actor发送消息rpcEndpoint.tell(ControlMessages.START, ActorRef.noSender());;
调用AkkaRpcActor#handleControlMessage处理控制类型消息;
在主线程中将自身状态变更为Started状态;
经过上述步骤就完成了Actor的启动过程,Actor启动后便可与Acto通信让其执行代码(如runSync/callSync等)和处理Rpc请求了。下面分别介绍处理执行代码和处理Rpc请求;
3.3.1.1. 执行代码
与Actor通信,通过调用runSync/callSync等方法其直接执行代码。
下面以scheduleRunAsync方法为例分析请求Actor执行代码流程,方法代码如下:
public void scheduleRunAsync(Runnable runnable, long delayMillis) {
checkNotNull(runnable, "runnable");
checkArgument(delayMillis >= 0, "delay must be zero or greater");
// 判断是否为本地Actor
if (isLocal) {
long atTimeNanos = delayMillis == 0 ? 0 : System.nanoTime() + (delayMillis * 1_000_000);
// 向Actor发送消息runnable
tell(new RunAsync(runnable, atTimeNanos));
} else {
// 抛出异常,不支持远程发送Runnable消息
throw new RuntimeException("Trying to send a Runnable to a remote actor at " +
rpcEndpoint.path() + ". This is not supported.");
}
}AkkaInvocationHandler#invoke -> AkkaInvocation#scheduleRunAsync;
AkkaRpcActor#handleMessage->AkkaRpcActor#handleRpcMessage,其中handleRpcMessage方法如下:
protected void handleRpcMessage(Object message) {
// 根据消息类型不同进行不同的处理
if (message instanceof RunAsync) {
handleRunAsync((RunAsync) message);
} else if (message instanceof CallAsync) {
handleCallAsync((CallAsync) message);
} else if (message instanceof RpcInvocation) {
handleRpcInvocation((RpcInvocation) message);
} else {
log.warn(
"Received message of unknown type {} with value {}. Dropping this message!",
message.getClass().getName(),
message);
sendErrorIfSender(new AkkaUnknownMessageException("Received unknown message " + message +
" of type " + message.getClass().getSimpleName() + '.'));
}
}
AkkaRpcActor#handleRunAsync,其代码如下:
private void handleRunAsync(RunAsync runAsync) {
// 获取延迟调度时间
final long timeToRun = runAsync.getTimeNanos();
final long delayNanos;
// 若为0或已经到了调度时间,则立刻进行调度
if (timeToRun == 0 || (delayNanos = timeToRun - System.nanoTime()) <= 0) {
// run immediately
try {
runAsync.getRunnable().run();
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("Caught exception while executing runnable in main thread.", t);
ExceptionUtils.rethrowIfFatalErrorOrOOM(t);
}
}
else {
// schedule for later. send a new message after the delay, which will then be immediately executed
// 计算出延迟时间
FiniteDuration delay = new FiniteDuration(delayNanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
// 重新封装消息
RunAsync message = new RunAsync(runAsync.getRunnable(), timeToRun);
final Object envelopedSelfMessage = envelopeSelfMessage(message);
// 等待指定延迟时间后给自己再发送一个消息
getContext().system().scheduler().scheduleOnce(delay, getSelf(), envelopedSelfMessage,
getContext().dispatcher(), ActorRef.noSender());
}
}注意:当还未到调度时间时,该Actor会延迟一段时间后再次给自己发送消息;
3.3.1.2. 处理Rpc请求
当调用非AkkaInvocationHandler实现的方法时,则进行Rpc请求。
下面分析处理Rpc调用的流程。
AkkaInvocationHandler#invokeRpc,其方法如下:
private Object invokeRpc(Method method, Object[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取方法相应的信息
String methodName = method.getName();
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
Time futureTimeout = extractRpcTimeout(parameterAnnotations, args, timeout);
// 创建RpcInvocationMessage(可分为LocalRpcInvocation/RemoteRpcInvocation)
final RpcInvocation rpcInvocation = createRpcInvocationMessage(methodName, parameterTypes, args);
Class returnType = method.getReturnType();
final Object result;
// 无返回,则使用tell方法
if (Objects.equals(returnType, Void.TYPE)) {
tell(rpcInvocation);
result = null;
} else {
// execute an asynchronous call
// 有返回,则使用ask方法
CompletableFuture resultFuture = ask(rpcInvocation, futureTimeout);
CompletableFuture completableFuture = resultFuture.thenApply((Object o) -> {
// 调用返回后进行反序列化
if (o instanceof SerializedValue) {
try {
return ((SerializedValue) o).deserializeValue(getClass().getClassLoader());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new CompletionException(
new RpcException("Could not deserialize the serialized payload of RPC method : "
+ methodName, e));
}
} else {
// 直接返回
return o;
}
});
// 若返回类型为CompletableFuture则直接赋值
if (Objects.equals(returnType, CompletableFuture.class)) {
result = completableFuture;
} else {
try {
// 从CompletableFuture获取
result = completableFuture.get(futureTimeout.getSize(), futureTimeout.getUnit());
} catch (ExecutionException ee) {
throw new RpcException("Failure while obtaining synchronous RPC result.", ExceptionUtils.stripExecutionException(ee));
}
}
}
return result;
}AkkaRpcActor#handleRpcInvocation,其代码如下:
private void handleRpcInvocation(RpcInvocation rpcInvocation) {
Method rpcMethod = null;
try {
// 获取方法的信息
String methodName = rpcInvocation.getMethodName();
Class[] parameterTypes = rpcInvocation.getParameterTypes();
// 在RpcEndpoint中找指定方法
rpcMethod = lookupRpcMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
log.error("Could not load method arguments.", e);
// 异常处理
RpcConnectionException rpcException = new RpcConnectionException("Could not load method arguments.", e);
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(rpcException), getSelf());
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Could not deserialize rpc invocation message.", e);
// 异常处理
RpcConnectionException rpcException = new RpcConnectionException("Could not deserialize rpc invocation message.", e);
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(rpcException), getSelf());
} catch (final NoSuchMethodException e) {
log.error("Could not find rpc method for rpc invocation.", e);
// 异常处理
RpcConnectionException rpcException = new RpcConnectionException("Could not find rpc method for rpc invocation.", e);
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(rpcException), getSelf());
}
if (rpcMethod != null) {
try {
// this supports declaration of anonymous classes
rpcMethod.setAccessible(true);
// 返回类型为空则直接进行invoke
if (rpcMethod.getReturnType().equals(Void.TYPE)) {
// No return value to send back
rpcMethod.invoke(rpcEndpoint, rpcInvocation.getArgs());
}
else {
final Object result;
try {
result = rpcMethod.invoke(rpcEndpoint, rpcInvocation.getArgs());
}
catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
log.debug("Reporting back error thrown in remote procedure {}", rpcMethod, e);
// tell the sender about the failure
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(e.getTargetException()), getSelf());
return;
}
final String methodName = rpcMethod.getName();
// 方法返回类型为CompletableFuture
if (result instanceof CompletableFuture) {
final CompletableFuture responseFuture = (CompletableFuture) result;
// 发送结果(使用Patterns发送结果给调用者,并会进行序列化并验证结果大小)
sendAsyncResponse(responseFuture, methodName);
} else {
// 类型非CompletableFuture,发送结果(使用Patterns发送结果给调用者,并会进行序列化并验证结果大小)
sendSyncResponse(result, methodName);
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Error while executing remote procedure call {}.", rpcMethod, e);
// tell the sender about the failure
getSender().tell(new Status.Failure(e), getSelf());
}
}
}将结果返回给调用者AkkaInvocationHandler#ask;
经过上述步骤就完成Rpc(本地/远程)调用,可以看到底层也是通过Akka提供的tell/ask方法进行通信;经过上述步骤就完成Rpc(本地/远程)调用,可以看到底层也是通过Akka提供的tell/ask方法进行通信;
4. 总结
RPC框架是Flink任务运行的基础,Flink整个RPC框架基于Akka实现,并对Akka中的ActorSystem、Actor进行了封装和使用,文章主要分析了Flink底层RPC通信框架的实现和相关流程,Flink整个通信框架的组件主要由RpcEndpoint、RpcService、RpcServer、AkkaInvocationHandler、AkkaRpcActor等构成。RpcEndpoint定义了一个Actor的路径;RpcService提供了启动RpcServer、执行代码体等方法;RpcServer/AkkaInvocationHandler提供了与Actor通信的接口;AkkaRpcActor为Flink封装的Actor。
— THE END —
![]()
猜你喜欢:
◤半年文章精选系列◥
Flink从入门到放弃之源码解析系列
《Flink组件和逻辑计划》
《Flink执行计划生成》
《JobManager中的基本组件(1)》
《JobManager中的基本组件(2)》
《JobManager中的基本组件(3)》
《TaskManager》
《算子》
《网络》
《水印WaterMark》
《CheckPoint》
《任务调度及负载均衡》
《异常处理》
大数据成神之路-基础篇
《HashSet》
《HashMap》
《LinkedList》
《ArrayList/Vector》
《ConcurrentSkipListMap》
《ConcurrentHashMap1.7》
《ConcurrentHashMap1.8 Part1》
《ConcurrentHashMap1.8 Part2》
《CopyOnWriteArrayList》
《CopyOnWriteArraySet》
《ConcurrentLinkedQueue》
《LinkedBlockingDeque》
《LinkedBlockingQueue》
《ArrayBlockingQueue》
《ConcurrentSkipListSet》
大数据成神之路-进阶篇
《JVM&NIO基础入门》
《分布式理论基础和原理》
《分布式中的常见问题解决方案(分布式锁/事务/ID)》
《Zookeeper》
《RPC》
《Netty入门篇》
《Netty源码篇》
《Linux基础》
Flink入门系列
《Flink入门》
《Flink DataSet&DataSteam API》
《Flink集群部署》
《Flink重启策略》
《Flink分布式缓存》
《Flink广播变量》
《Flink中的Time》
《Flink中的窗口》
《时间戳和水印》
《Broadcast广播变量》
《Flink-Kafka-Connector》
《Flink之Table-&-SQL》
《Flink实战项目之实时热销排行》
《Flink-Redis-Sink》
《Flink消费Kafka写入Mysql》
Flink高级进阶
《FaultTolerance》
《流表对偶(duality)性》
《持续查询(ContinuousQueries)》
《DataStream-Connectors之Kafka》
《SQL概览》
《JOIN 算子》
《TableAPI》
《JOIN-LATERAL》
《JOIN-LATERAL-Time Interval(Time-windowed)》
《Temporal-Table-JOIN》
《State》
《FlinkSQL中的回退更新-Retraction》
《Apache Flink结合Apache Kafka实现端到端的一致性语义》
《Flink1.8.0发布!新功能抢先看》
《Flink1.8.0重大更新-Flink中State的自动清除详解》
《Flink在滴滴出行的应用与实践》
《批流统一计算引擎的动力源泉—Flink Shuffle机制的重构与优化》
《HBase分享 | Flink+HBase场景化解决方案》
《腾讯基于Flink的实时流计算平台演进之路》
《Flink进阶-Flink CEP(复杂事件处理)》
《Flink基于EventTime和WaterMark处理乱序事件和晚到的数据》
《Flink 最锋利的武器:Flink SQL 入门和实战》
《Flink Back Pressure》
《使用Flink读取Kafka中的消息》
《Flink on YARN部署快速入门指南》
《Apache Flink状态管理和容错机制介绍》
Hadoop生态圈系列
《Hadoop极简入门》
《MapReduce编程模型和计算框架架构原理》
《分布式文件系统-HDFS》
《YARN》
《Hadoop机架感知》
《HDFS的一个重要知识点-HDFS的数据流》
《Hadoop分布式缓存(DistributedCache)》
《如何从根源上解决 HDFS 小文件问题》(https://dwz.cn/FqDPpRUc)
《Hadoop解决小文件存储思路》(https://dwz.cn/2oCdmCkw)
《Hadoop所支持的几种压缩格式》
《MapReduce Join》
《YARN Capacity Scheduler(容量调度器)》
《hadoop上搭建hive》
《基于Hadoop的数据仓库Hive基础知识》
《Hive使用必知必会系列》
《一个小知识点-Hive行转列实现Pivot》
《面试必备技能-HiveSQL优化》
《HBase和Hive的区别和各自适用的场景》
《一篇文章入门Hbase》
《敲黑板:HBase的RowKey设计》
《HBase读写优化》
《HBase在滴滴出行的应用场景和最佳实践》
《Phoenix=HBase+SQL,让HBase插上了翅膀》
《一个知识点将你拒之门外之Hbase的二级索引》(https://dwz.cn/umfBOZ5l)
《Phoenix重磅 | Phoenix核心功能原理及应用场景介绍》
《DB、DW、DM、ODS、OLAP、OLTP和BI的概念理解》
《Hive/HiveSQL常用优化方法全面总结》
实时计算系列(spark、kafka等)
《Spark Streaming消费Kafka数据的两种方案》
《Apache Kafka简单入门》
《你不得不知道的知识-零拷贝》
《Kafka在字节跳动的实践和灾备方案》
《万字长文干货 | Kafka 事务性之幂等性实现》
《Kafka最佳实践》
《Kafka Exactly-Once 之事务性实现》
《Kafka连接器深度解读之错误处理和死信队列》
《Spark之数据倾斜调优》
《Structured Streaming 实现思路与实现概述》
《Spark内存调优》
《广告点击数实时统计:Spark StructuredStreaming + Redis Streams》
《Spark Shuffle在网易的优化》
《SparkSQL极简入门》
《下一代分布式消息队列Apache Pulsar》
《Pulsar与Kafka消费模型对比》
《Spark SQL重点知识总结》
《Structured Streaming 之状态存储解析》
《周期性清除Spark Streaming流状态的方法》
《Spark Structured Streaming特性介绍》
《Spark Streaming 反压(Back Pressure)机制介绍》
《Spark 从 Kafka 读数设置子并发度问题》
规范和系统设计
《阿里云10 PB+/天的日志系统设计和实现》
《阿里云Redis开发规范》
《Java中多个ifelse语句的替代设计》
《面试系列:十个海量数据处理方法大总结》
杂谈
《作为面试官的一点点感悟,谈谈技术人的成长之路》
《成年人的世界没有容易二字》
《我最近在关注的事》
《真香》
《简单说说学习这件事》
《20多岁做什么,将来才不会后悔》
《2019-05-12最近的总结》
《我军新闻联播气势+9999》
《周末分享 | 高手的战略》
《周末分享 | 快速定位自己的缺点》
《周末分享 | 我见过最高级的聪明是靠谱》