python调用google开源求解器OR-Tools求解旅行商问题(TSP)
文章目录
- 1. 安装
- 2. python调用OR-Tools求解TSP
OR-Tools是一款Google旗下的开源优化工具。可以方便的求解 Linear optimization、Constraint optimization、Mixed-integer optimization、Assignment、Scheduling、Packing、Routing、Network flows等类型的问题。
面向不同问题的优化工具套件。OR-Tools集合了各种先进的优化算法,它所包含的接口求解器主要分为 约束规划(Constraint Programming)、线性和混合整数规划(Linear and Mixed-Integer Programming)、车辆路径规划(Vehicle Routing)以及图论算法(Graph Algorithms)这四个基本求解器,能够按照优化问题的类型,提供相对应的不同类和接口。例如:对于最简单的线性规划问题,可以使用Linear Solver来解决。
1. 安装
python -m pip install --upgrade --user ortools
2. python调用OR-Tools求解TSP
代码参考来自OR-Tools官网示例,学习梳理记录一下
- 完整python代码
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
def create_data_model():
data = {}
# 设置节点的位置信息,一行代表一个城市的横坐标及纵坐标
data['locations'] = [[ 94, 99],
[ 66, 67],
[ 14, 78],
[ 95, 56],
[ 68, 9],
[ 26, 20],
[ 51, 67],
[ 39, 39],
[ 5, 55],
[ 12, 33],
[ 55, 85],
[ 98, 46],
[ 36, 39],
[ 65, 100],
[ 57, 89],
[ 88, 24],
[ 53, 96],
[ 91, 41],
[ 32, 69],
[ 38, 38],
[ 38, 39],
[ 85, 100],
[ 7, 37],
[ 85, 96],
[ 89, 48],
[ 85, 35],
[ 32, 29],
[ 31, 25],
[ 20, 17],
[ 75, 21],
[ 74, 29],
[ 6, 32],
[ 20, 81],
[ 62, 1],
[ 11, 48],
[ 1, 69],
[ 99, 70],
[ 20, 27],
[ 25, 42],
[ 6, 31],
[ 78, 24],
[ 42, 39],
[ 83, 30],
[ 94, 10],
[ 90, 37],
[ 76, 73],
[ 9, 56],
[ 39, 33],
[ 74, 15],
[ 77, 14]]
data['num_vehicles'] = 1 # TSP问题车辆数设置为1
data['depot'] = 0 # 设置起点位置
return data
def create_distance_callback(data, manager):
# 创建距离的回调函数
distances_ = {}
index_manager_ = manager
scale = 100
# 计算两个城市的距离,使用欧式距离。注意缩放距离距离(因为or-tools的routing solver适应于整数)
for from_counter, from_node in enumerate(data['locations']):
distances_[from_counter] = {}
for to_counter, to_node in enumerate(data['locations']):
if from_counter == to_counter:
distances_[from_counter][to_counter] = 0
else:
distances_[from_counter][to_counter] = int(math.hypot((from_node[0] - to_node[0]),(from_node[1] - to_node[1])) * scale)
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
# 通过索引获取距离矩阵的距离
from_node = index_manager_.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = index_manager_.IndexToNode(to_index)
return distances_[from_node][to_node]
return distance_callback
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
print('Obj = : {}'.format(solution.ObjectiveValue()))
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = 'Route for vehicle 0:\n'
route_distance = 0
route = [] # 保存结果
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += ' {} ->'.format(manager.IndexToNode(index))
route.append(index)
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += ' {}\n'.format(manager.IndexToNode(index))
print(plan_output)
return route
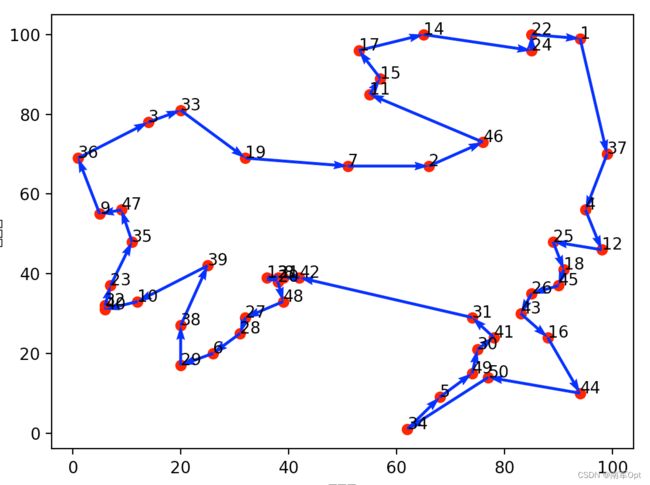
def plot_route(route, city_location):
plt.figure()
# 绘制散点
x = np.array(city_location)[:, 0] # 横坐标
y = np.array(city_location)[:, 1] # 纵坐标
plt.scatter(x, y, color='r')
# 绘制城市编号
for i, txt in enumerate(range(1, len(city_location) + 1)):
plt.annotate(txt, (x[i], y[i]))
# 绘制方向
x0 = x[route]
y0 = y[route]
for i in range(len(city_location) - 1):
plt.quiver(x0[i], y0[i], x0[i + 1] - x0[i], y0[i + 1] - y0[i], color='b', width=0.005, angles='xy', scale=1,
scale_units='xy')
plt.quiver(x0[-1], y0[-1], x0[0] - x0[-1], y0[0] - y0[-1], color='b', width=0.005, angles='xy', scale=1,
scale_units='xy')
plt.xlabel('横坐标')
plt.ylabel('纵坐标')
plt.show()
plt.savefig('TSP.png')
def or_tools_tsp():
# 算例数据设置
data = create_data_model()
# 创建路由索引管理器
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(len(data['locations']), data['num_vehicles'], data['depot'])
# 创建路由模型
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
# 创建和注册距离的回调函数
distance_callback = create_distance_callback(data, manager)
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# 设置目标函数:计算每个'弧'的成本,直接传入距离即位置间的成本就是两者之间的距离
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# 设置参数
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
# 设置初始解的(启发式)搜索策略
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
# 设置时间限制
search_parameters.time_limit.seconds = 30
# 设置日志
search_parameters.log_search = True
# 求解
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# 输出结果并绘制图
if solution:
route = print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
plot_route(route, data['locations'])
if __name__ == '__main__':
or_tools_tsp()