从零开始搭建微服务:资源服务器
为了演示认证服务器和资源服务器在分离的模式下,如何进行资源保护和资源获取,我们来搭建两个微服务提供者:elsa-server-system和elsa-server-demo资源服务器。
因为存在多个资源服务器,因此,我们为这些微服务提供一个父模块,来统一管理。
elsa-server 父模块
创建elsa-server 父模块项目
File==>新建==>Other==>搜索Maven,选择Maven Module,然后Next
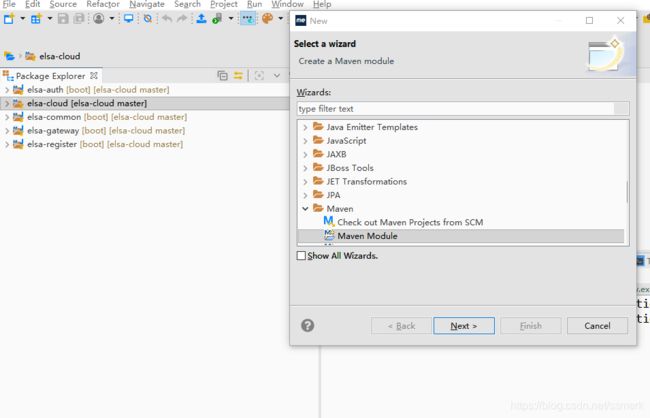
填写Module Name:elsa-server,点击Next

一直Next至FInish为止,创建完成,删除不必要的文件,仅保留pom.xml文件,项目结构如下
配置elsa-server依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>com.elsagroupId>
<artifactId>elsa-cloudartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
parent>
<artifactId>elsa-serverartifactId>
<packaging>pompackaging>
<name>elsa-servername>
<description>Elsa-Server资源服务提供模块description>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.elsagroupId>
<artifactId>elsa-commonartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
值得注意的是:
pom ,因为此项目是作为所有微服务的父项目,所以这里指定为pom- 因为是微服务,同样的需要各种依赖,所以引入elsa-common
elsa-server-system 系统模块
创建elsa-server-system系统模块
在项目elsa-server上右键==>新建==>Other==>搜索Maven,选择Maven Module,然后Next
填写Module Name:elsa-server-system,点击Next

一直Next至FInish为止,创建完成,添加资源目录resources,项目结构如下
引入系统模块依赖
<project
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>com.elsagroupId>
<artifactId>elsa-serverartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
parent>
<artifactId>elsa-server-systemartifactId>
<name>elsa-server-systemname>
<description>Elsa-Server-System微服务系统模块description>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
创建系统模块入口类
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) //表示开启Spring Cloud Security权限注解
public class ElsaServerSystemApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ElsaServerSystemApp.class, args);
}
}
- @EnableDiscoveryClient 开启服务注册与发现
- @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) 表示开启Spring Cloud Security权限注解
系统模块application.yml配置
server:
port: 8201
spring:
application:
name: Elsa-Server-System
eureka:
instance:
# 向Eureka 服务端发送心跳的间隔时间,单位为秒,用于服务续约。这里配置为20秒,即每隔20秒向febs-register发送心跳,表明当前服务没有宕机
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 20
client:
# 为true时表示将当前服务注册到Eureak服务端
register-with-eureka: true
# 为true时表示从Eureka 服务端获取注册的服务信息
fetch-registry: true
# 新实例信息的变化到Eureka服务端的间隔时间,单位为秒
instance-info-replication-interval-seconds: 30
# 默认值为30秒,即每30秒去Eureka服务端上获取服务并缓存,这里指定为3秒的原因是方便开发时测试,实际可以指定为默认值即可;
registry-fetch-interval-seconds: 3
serviceUrl:
# 指定Eureka服务端地址
defaultZone: http://elsa:123456@localhost:8001/register/eureka/
# oauth2相关配置
security:
oauth2:
resource:
id: ${spring.application.name}
user-info-uri: http://localhost:8301/auth/user
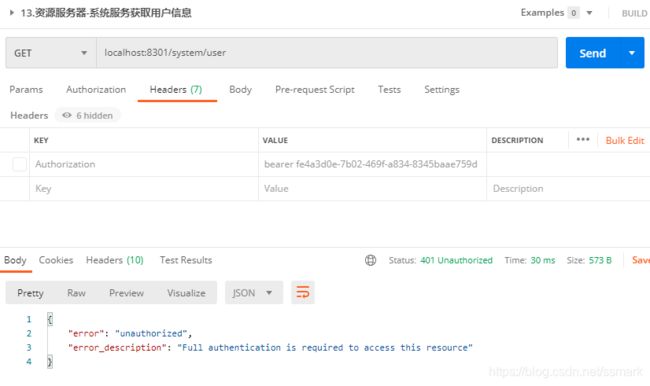
配置里内容基本上前面章节中有重复,就不作过多介绍。这里主要说明下:user-info-uri,它的原理是在授权服务器认证后将认证信息Principal通过形参绑定到URL的方式,获取用户信息。
ElsaServerSystemResourceServerConfigure Web安全配置类
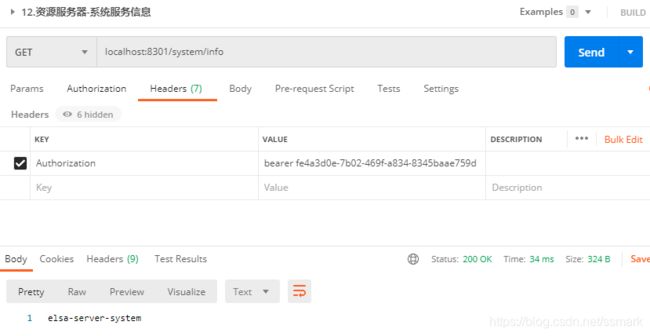
配置所有访问elsa-server-system的请求都需要认证,只有通过认证服务器发放的令牌才能进行访问。
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ElsaServerSystemResourceServerConfigure extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.requestMatchers().antMatchers("/**")
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/**").authenticated();
}
}
TestController
创建一个Controller,对外提供一些REST服务。在com.elsa.server.system路径下新建controller包,然后在该包下新增TestController:
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("info")
public String test() {
return "elsa-server-system";
}
@GetMapping("user")
public Principal currentUser(Principal principal) {
return principal;
}
}
elsa-server-demo Demo模块
参照elsa-server-system系统模块创建过程,创建elsa-server子项目,并且引入依赖,创建入口类,配置application.yml,Web安全配置类,过程无差异,可参照源码。唯一不同的是测试controller稍作调整。
DemoController
@RestController
public class DemoController {
@GetMapping("demo1")
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('user:add')")
public String demo1() {
return "拥有'user:add'权限";
}
@GetMapping("demo2")
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyAuthority('user:update')")
public String demo2() {
return "拥有'user:update'权限";
}
@GetMapping("user")
public Principal currentUser(Principal principal) {
return principal;
}
}
- demo1方法测试拥有权限user:add的情况。
- demo2方法测试没有权限user:update的情况。
- user方法测试获取用户信息,此处主要是针对user-info-uri。
网关服务器配置
到这里,elsa-server-system和elsa-server-demo资源服务器微服务创建完成,下面需要在网关服务器elsa-gateway配置网关访问以上两个资源服务器的路由网关。
zuul:
routes:
system:
path: /system/**
serviceId: Elsa-Server-System
sensitiveHeaders: "*"
demo:
path: /demo/**
serviceId: Elsa-Server-Demo
sensitiveHeaders: "*"
网关服务器完整配置文件application.xml
server:
port: 8301
spring:
application:
name: Elsa-Gateway
zuul:
routes:
auth:
# 以/auth开头的请求都会被转发到名称为Elsa-Auth的服务上
path: /auth/**
# 服务名
serviceId: Elsa-Auth
# 由于我们需要在请求头中携带令牌,所以sensitiveHeaders设置为*,表示不过滤请求头信息,即请求的请求头信息将原封不动的转发出去
sensitiveHeaders: "*"
system:
path: /system/**
serviceId: Elsa-Server-System
sensitiveHeaders: "*"
demo:
path: /demo/**
serviceId: Elsa-Server-Demo
sensitiveHeaders: "*"
# 设置为true时,表示开启重试机制;
retryable: true
# Zuul配合Eureka后会有一套默认的配置规则,这里我们只想请求根据我们显示配置的路由规则走,所以设置为*,表示关闭所有默认路由配置规则;
ignored-services: "*"
ribbon:
eager-load:
# Zuul内部通过Ribbon按照一定的负载均衡算法来获取服务,Ribbon进行客户端负载均衡的Client并不是在服务启动的时候就初始化好的,而是在调用的时候才会去创建相应的Client,所以第一次调用的耗时不仅仅包含发送HTTP请求的时间,还包含了创建RibbonClient的时间,这样一来如果创建时间速度较慢,同时设置的超时时间又比较短的话,第一次请求很容易出现超时的情况。设置为true的时候表示开启Ribbon的饥饿加载模式,即在应用启动的时候就去获取相应的Client备用。
enabled: true
ribbon:
# 设置请求超时时间,单位为毫秒;
ReadTimeout: 3000
eureka:
instance:
# 向Eureka 服务端发送心跳的间隔时间,单位为秒,用于服务续约。这里配置为20秒,即每隔20秒向febs-register发送心跳,表明当前服务没有宕机
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 20
client:
# 为true时表示将当前服务注册到Eureak服务端
register-with-eureka: true
# 为true时表示从Eureka 服务端获取注册的服务信息
fetch-registry: true
# 新实例信息的变化到Eureka服务端的间隔时间,单位为秒
instance-info-replication-interval-seconds: 30
# 默认值为30秒,即每30秒去Eureka服务端上获取服务并缓存,这里指定为3秒的原因是方便开发时测试,实际可以指定为默认值即可;
registry-fetch-interval-seconds: 3
serviceUrl:
# 指定Eureka服务端地址
defaultZone: http://elsa:123456@localhost:8001/register/eureka/
PostMan测试
分别启动应用
1.Redis
2.ElsaRegesterApp
3.ElsaAuthApp
4.ElsaGatewayApp
5.ElsaServerSystemApp
6.ElsaServerDemoApp
资源服务器-认证
资源服务器-系统服务获取用户信息
资源服务器-Demo模块服务有权限

我们在elsa-auth模块的ElsaUserDetailService类loadUserByUsername方法模拟用户拥有user:add权限,所以可以正常访问。
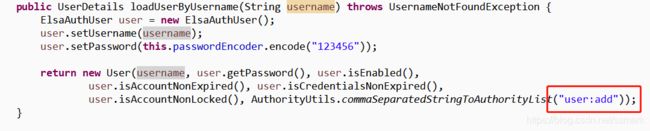
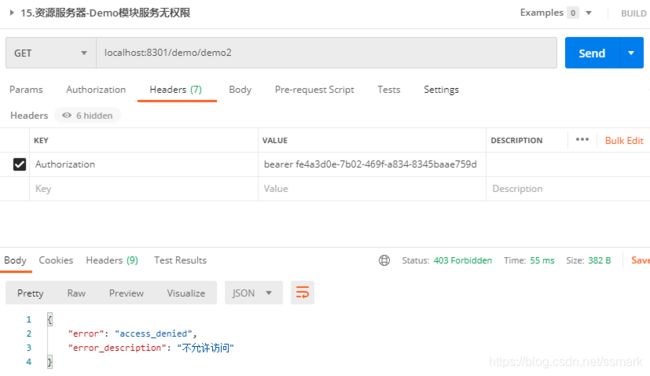
而下面的demo2没有user:update权限,所以无法访问。
资源服务器-Demo模块服务无权限
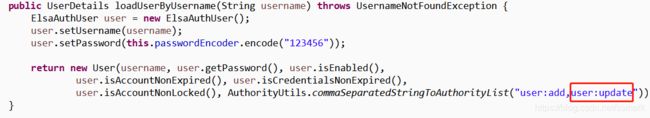
当我们在ElsaUserDetailService类loadUserByUsername方法中增加user:update时,重启ElsaAuthApp。
再测试此URL时,拥有user:update权限
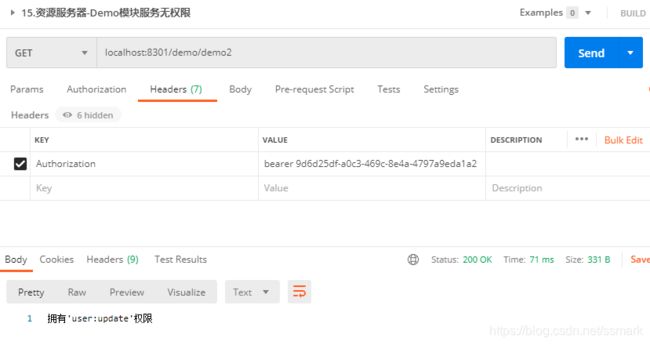
资源服务器-Demo模块服务获取用户信息
源码下载
源码地址:资源服务器