小白也能学,从0到部署yolov5教程,Windows Linux PC arm Jeston全平台部署-(上)
注意!本篇首发于GiantPandaCV公众号,未经允许,不得转载!
需要的repo: 欢迎star
https://github.com/msnh2012/MsnhnetModelZoo
https://github.com/msnh2012/Msnhnet
https://github.com/msnh2012/CasiaLabeler
准备工作
1. 安装配置Cuda, Cudnn, Pytorch
该部分不进行详细介绍, 具体过程请百度.此处小编使用Pytorch1.9.
2. 制作自己的数据集
- 这里小编给大家准备了一个人体检测的数据集,供大家测试使用.
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1lpyNNdYqdKj8R-RCQwwCWg 提取码:6agk - 数据集准备工作.
(1) 层级关系
yolov5数据集所需的文件夹结构,以小编提供的数据集为例.
- people文件夹下包含两个子文件夹images(用于存放图片)和labels(用于存放标签文件).
- images文件夹下包含train和val两个文件夹,分别存放训练集的图片和验证集的图片.
- labels文件夹下包含train和val两个文件夹,分别存放训练集的标签和验证集的标签.

(2) 下载标注软件
这里小编自己编写了一款标注软件,直接支持导出yolov5格式。
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1AI5f5BYbboK0KYpHf7v4-A 提取码:19o1

(3) 准备需要标注的数据(注意本软件单次只能标注1000张,建议单次500张以下)
这里我简单准备了6张猫狗数据的。
(4) 准备标签文件
新建一个labels.txt文件(名字任意).将类名按照自己需要的顺序进行输入(注意,这里的顺序关系到最后导出yolov5 labels文件的标签顺序)

- 开始标注.
(1) 导入图片和标签文件
打开CasiaLabeler软件.点击 标注>打开 导入图片.
点击 标注>添加标签导入标签. 选择之前创建的标签文件,导入后如图.

(2) 开始标注并指定标签
初步框选标注对象。

在标注信息栏,修改对象的标签。
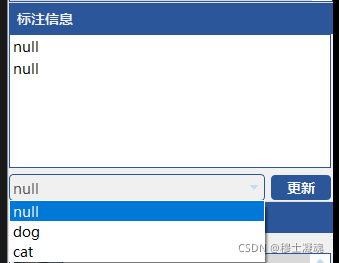
在属性窗口可以修改标注框的颜色。

完成之后。(PS.标注框可以通过Ctrl+C和Ctrl+V进行复制粘贴)

(3) 导出标注结果
点击 标注>导出标注结果>yolov5 ,并指定一个空文件夹.

(4) 整理数据集层级结构

PS.
-
1.标注过程请及时保存工程文件
-
3.标注完成后,可以自动切换下一张预览标注结果。点击 视图>预览 即可自动切换标注场景,切换间隔使劲按可以点击 帮助>设置 设置预览间隔时间.

-
5.丢失解决方法,点击 帮助>设置.在图片路径修改处,选择需要修改的工程,并指定图片新的路径,点击 转换 即可完成工程文件修复。再次打开工程即可。

3. 准备Yolov5代码
1 Clone代码
git clone https://github.com/msnh2012/MsnhnetModelZoo.git
(注意!必须Clone小编为msnhnet定制的代码!)
2 安装依赖
pip install requirements.txt(可以手动安装)
4. 准备Yolov5预训练模型
(1) 这里小编已经给大家准备好了预训练模型(yolov5_pred文件夹中)
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1lpyNNdYqdKj8R-RCQwwCWg 提取码:6agk
(2) 将下载好的预训练模型文件拷贝至yolov5ForMsnhnet/yolov5/weights文件夹下
模型训练
1. 准备工作
(1) 数据集准备(这里以people数据集为例)
- 将标注好的数据集放置在datas文件夹下。
- 在datas文件夹下创建一个people.yaml文件,用于配置数据集信息
- train: 训练集图片位置
- val: 验证集图片位置
- nc: 类别数量
- names: 所有类的名称

(2) 选择所需训练的模型(这里以yolov5m为例)
(3) 关于anchors
# anchors
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
anchors参数共有三行,每行9个数值;每一行代表不同的特征图;
-
第一行是在最大的特征图上的anchors
-
第二行是在中间的特征图上的anchors
-
第三行是在最小的特征图上的anchors
-
yolov5会在训练最开始自动对anchors进行check(可以修改 train.py中以下代码使用或者不使用自动anchor).
parser.add_argument('--noautoanchor', action='store_true', help='disable autoanchor check')
- 如果标注信息对anchor的最佳召回率>=0.98,则不需要重新计算anchors, 反之则需要从新计算。
check代码如下:
- 参数:
dataset: 数据集
model: 模型
thr: dataset中标注框宽高比最大阈值,参数在超参文件 hyp.scratch.yaml"中"anchor_t"设置。
imgsz: 图片尺寸
def check_anchors(dataset, model, thr=4.0, imgsz=640):
# Check anchor fit to data, recompute if necessary
print('\nAnalyzing anchors... ', end='')
m = model.module.model[-1] if hasattr(model, 'module') else model.model[-1] # Detect()
shapes = imgsz * dataset.shapes / dataset.shapes.max(1, keepdims=True)
scale = np.random.uniform(0.9, 1.1, size=(shapes.shape[0], 1)) # augment scale
wh = torch.tensor(np.concatenate([l[:, 3:5] * s for s, l in zip(shapes * scale, dataset.labels)])).float() # wh
def metric(k): # compute metric
r = wh[:, None] / k[None]
x = torch.min(r, 1. / r).min(2)[0] # ratio metric
best = x.max(1)[0] # best_x
aat = (x > 1. / thr).float().sum(1).mean() # anchors above threshold
bpr = (best > 1. / thr).float().mean() # best possible recall
return bpr, aat
bpr, aat = metric(m.anchor_grid.clone().cpu().view(-1, 2))
print('anchors/target = %.2f, Best Possible Recall (BPR) = %.4f' % (aat, bpr), end='')
if bpr < 0.98: # threshold to recompute
print('. Attempting to generate improved anchors, please wait...' % bpr)
na = m.anchor_grid.numel() // 2 # number of anchors
new_anchors = kmean_anchors(dataset, n=na, img_size=imgsz, thr=thr, gen=1000, verbose=False)
new_bpr = metric(new_anchors.reshape(-1, 2))[0]
if new_bpr > bpr: # replace anchors
new_anchors = torch.tensor(new_anchors, device=m.anchors.device).type_as(m.anchors)
m.anchor_grid[:] = new_anchors.clone().view_as(m.anchor_grid) # for inference
m.anchors[:] = new_anchors.clone().view_as(m.anchors) / m.stride.to(m.anchors.device).view(-1, 1, 1) # loss
check_anchor_order(m)
print('New anchors saved to model. Update model *.yaml to use these anchors in the future.')
else:
print('Original anchors better than new anchors. Proceeding with original anchors.')
print('') # newline
- 聚类anchor代码:
- 参数:
path: 之前创建的people.yaml数据集配置文件路径
n: anchors 组数量 xx,xx为一组
img_size: 图片尺寸
thr: dataset中标注框宽高比最大阈值,参数在超参文件 hyp.scratch.yaml"中"anchor_t"设置。
gen: kmean算法iter次数
verbose: 是否打印结果
def kmean_anchors(path='./data/coco128.yaml', n=9, img_size=640, thr=4.0, gen=1000, verbose=True):
""" Creates kmeans-evolved anchors from training dataset
Arguments:
path: path to dataset *.yaml, or a loaded dataset
n: number of anchors
img_size: image size used for training
thr: anchor-label wh ratio threshold hyperparameter hyp['anchor_t'] used for training, default=4.0
gen: generations to evolve anchors using genetic algorithm
Return:
k: kmeans evolved anchors
Usage:
from utils.general import *; _ = kmean_anchors()
"""
thr = 1. / thr
def metric(k, wh): # compute metrics
r = wh[:, None] / k[None]
x = torch.min(r, 1. / r).min(2)[0] # ratio metric
# x = wh_iou(wh, torch.tensor(k)) # iou metric
return x, x.max(1)[0] # x, best_x
def fitness(k): # mutation fitness
_, best = metric(torch.tensor(k, dtype=torch.float32), wh)
return (best * (best > thr).float()).mean() # fitness
def print_results(k):
k = k[np.argsort(k.prod(1))] # sort small to large
x, best = metric(k, wh0)
bpr, aat = (best > thr).float().mean(), (x > thr).float().mean() * n # best possible recall, anch > thr
print('thr=%.2f: %.4f best possible recall, %.2f anchors past thr' % (thr, bpr, aat))
print('n=%g, img_size=%s, metric_all=%.3f/%.3f-mean/best, past_thr=%.3f-mean: ' %
(n, img_size, x.mean(), best.mean(), x[x > thr].mean()), end='')
for i, x in enumerate(k):
print('%i,%i' % (round(x[0]), round(x[1])), end=', ' if i < len(k) - 1 else '\n') # use in *.cfg
return k
if isinstance(path, str): # *.yaml file
with open(path) as f:
data_dict = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader) # model dict
from utils.datasets import LoadImagesAndLabels
dataset = LoadImagesAndLabels(data_dict['train'], augment=True, rect=True)
else:
dataset = path # dataset
# Get label wh
shapes = img_size * dataset.shapes / dataset.shapes.max(1, keepdims=True)
wh0 = np.concatenate([l[:, 3:5] * s for s, l in zip(shapes, dataset.labels)]) # wh
# Filter
i = (wh0 < 3.0).any(1).sum()
if i:
print('WARNING: Extremely small objects found. '
'%g of %g labels are < 3 pixels in width or height.' % (i, len(wh0)))
wh = wh0[(wh0 >= 2.0).any(1)] # filter > 2 pixels
# Kmeans calculation
print('Running kmeans for %g anchors on %g points...' % (n, len(wh)))
s = wh.std(0) # sigmas for whitening
k, dist = kmeans(wh / s, n, iter=30) # points, mean distance
k *= s
wh = torch.tensor(wh, dtype=torch.float32) # filtered
wh0 = torch.tensor(wh0, dtype=torch.float32) # unflitered
k = print_results(k)
# Plot
# k, d = [None] * 20, [None] * 20
# for i in tqdm(range(1, 21)):
# k[i-1], d[i-1] = kmeans(wh / s, i) # points, mean distance
# fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 7))
# ax = ax.ravel()
# ax[0].plot(np.arange(1, 21), np.array(d) ** 2, marker='.')
# fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 7)) # plot wh
# ax[0].hist(wh[wh[:, 0]<100, 0],400)
# ax[1].hist(wh[wh[:, 1]<100, 1],400)
# fig.tight_layout()
# fig.savefig('wh.png', dpi=200)
# Evolve
npr = np.random
f, sh, mp, s = fitness(k), k.shape, 0.9, 0.1 # fitness, generations, mutation prob, sigma
pbar = tqdm(range(gen), desc='Evolving anchors with Genetic Algorithm') # progress bar
for _ in pbar:
v = np.ones(sh)
while (v == 1).all(): # mutate until a change occurs (prevent duplicates)
v = ((npr.random(sh) < mp) * npr.random() * npr.randn(*sh) * s + 1).clip(0.3, 3.0)
kg = (k.copy() * v).clip(min=2.0)
fg = fitness(kg)
if fg > f:
f, k = fg, kg.copy()
pbar.desc = 'Evolving anchors with Genetic Algorithm: fitness = %.4f' % f
if verbose:
print_results(k)
return print_results(k)
修改opt参数
weights: 加载的权重文件(weights文件夹下yolov5m.pt)
cfg: 模型配置文件,网络结构(model文件夹下yolov5m_people.yaml)
data: 数据集配置文件,数据集路径,类名等(datas文件夹下people.yaml)
hyp: 超参数文件
epochs: 训练总轮次
batch-size: 批次大小
img-size: 输入图片分辨率大小(512*512)
rect: 是否采用矩形训练,默认False
resume: 接着打断训练上次的结果接着训练
nosave: 不保存模型,默认False
notest: 不进行test,默认False
noautoanchor: 不自动调整anchor,默认False
evolve: 是否进行超参数进化,默认False
bucket: 谷歌云盘bucket,一般不会用到
cache-images: 是否提前缓存图片到内存,以加快训练速度,默认False
name: 数据集名字,如果设置:results.txt to results_name.txt,默认无
device: 训练的设备,cpu;0(表示一个gpu设备cuda:0);0,1,2,3(多个gpu设备)
multi-scale: 是否进行多尺度训练,默认False
single-cls: 数据集是否只有一个类别,默认False
adam: 是否使用adam优化器
sync-bn: 是否使用跨卡同步BN,在DDP模式使用
local_rank: gpu编号
logdir: 存放日志的目录
workers: dataloader的最大worker数量(windows需设置为0) 
2. 开始train
python train_people.py

训练过程中,会在yolov5/runs文件夹下生成一个exp文件夹,
- weights包含训练过程中最后一次训练好的模型last.pt和历史最佳模型best.pt。
- events文件可以使用tensorboard查看训练过程。
在exp文件夹中,打开终端,运行
tensorboard --logdir=.
在浏览器中输入
http://localhost:6006/
可查看训练过程与曲线.
- 其它过程文件。
推理测试
- 将runs/exp文件夹下的best.pt文件拷贝到weights文件夹下。
- 在inference/images文件夹下放置几个测试图片。这里放置一张官方的bus.jpg
在yolov5文件夹中打开终端,执行:
python detect --weights weights/best.pt --source inference/images --output inference/output
- 在inference/output文件夹中会生成推理结果。
至此,使用pytorch训练yolov5模型完成,下一篇将介绍如何在CMake(c++),Winform(C#)以及windows(PC),linux(Jetson Nx)中使用Msnhnet部署yolov5.
最后
- 欢迎关注我和Buff及公众号的小伙伴们一块维护的一个深度学习框架Msnhnet:
- https://github.com/msnh2012/Msnhnet


![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-DyuUJUe7-1631755886313)(imgs/model.png)]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/86e7adda1f5c49d1886e8624187455b8.png)
