数据结构与算法之二叉树大全
目录
- 二叉树的定义
- 二叉树的性质(特性)
- 满二叉树与完全二叉树
- 链式存储的二叉树
- 顺序存储的二叉树
- 线索二叉树(Threaded BinaryTree)
- 二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree)
- 平衡二叉树( Balanced Binary Tree)
-
- 为什么使用平衡二叉树?
- 如何判断平衡二叉树?
- 相关概念
- 旋转方式
- 实例
- 代码实现
二叉树的定义
任何一个节点的子节点数量不超过 2,那就是二叉树;二叉树的子节点分为左节点和右节点,不能颠倒位置
二叉树的性质(特性)
性质1:在二叉树的第i层上至多有2^(i-1)个结点(i>0)
性质2:深度为k的二叉树至多有2^k - 1个结点(k>0)
性质3:对于任意一棵二叉树,如果其叶结点数为N0,而度数为2的结点总数为N2,则N0=N2+1;
性质4:具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度必为 log2(n+1)
性质5:对完全二叉树,若从上至下、从左至右编号,则编号为i 的结点,其左孩子编号必为2i,其右孩子编号必为2i+1;其双亲的编号必为i/2(i=1 时为根,除外)
满二叉树与完全二叉树
满二叉树: 所有叶子结点都集中在二叉树的最下面一层上,而且结点总数为:2^n-1 (n为层数 / 高度)
完全二叉树: 所有的叶子节点都在最后一层或者倒数第二层,且最后一层叶子节点在左边连续,倒数第二层在右边连续(满二叉树也是属于完全二叉树)(从上往下,从左往右能挨着数满)
![]()
链式存储的二叉树
创建二叉树:首先需要一个树的类,还需要另一个类用来存放节点,设置节点;将节点放入树中,就形成了二叉树;(节点中需要权值,左子树,右子树,并且都能对他们的值进行设置)。
树的遍历:
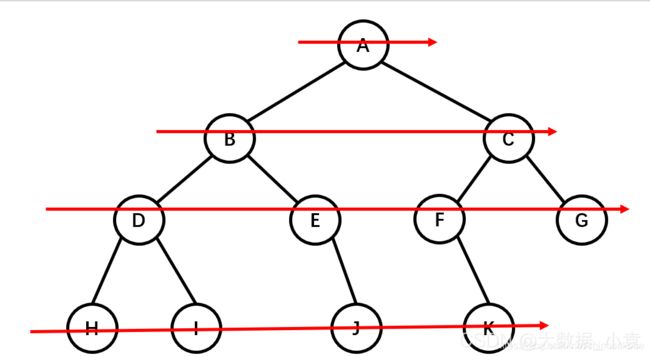
- 先序遍历:根节点,左节点,右节点(如果节点有子树,先从左往右遍历子树,再遍历兄弟节点)
先序遍历结果为:A B D H I E J C F K G
![]()
- 中序遍历:左节点,根节点,右节点(中序遍历可以看成,二叉树每个节点,垂直方向投影下来(可以理解为每个节点从最左边开始垂直掉到地上),然后从左往右数)
中遍历结果为:H D I B E J A F K C G
![]()
- 后序遍历:左节点,右节点,根节点
后序遍历结果:H I D J E B K F G C A
- 层次遍历:从上往下,从左往右
层次遍历结果:A B C D E F G H I J K
查找节点:先对树进行一次遍历,然后找出要找的那个数;因为有三种排序方法,所以查找节点也分为先序查找,中序查找,后序查找;
删除节点:由于链式存储,不能找到要删的数直接删除,需要找到他的父节点,然后将指向该数设置为null;所以需要一个变量来指向父节点,找到数后,再断开连接。
代码实现:
![]()
- 树类
public class BinaryTree {
TreeNode root;
//设置根节点
public void setRoot(TreeNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
//获取根节点
public TreeNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
//先序遍历
public void frontShow() {
if (root != null) {
root.frontShow();
}
}
//中序遍历
public void middleShow() {
if (root != null) {
root.middleShow();
}
}
//后序遍历
public void afterShow() {
if (root != null) {
root.afterShow();
}
}
//先序查找
public TreeNode frontSearch(int i) {
return root.frontSearch(i);
}
//删除一个子树
public void delete(int i) {
if (root.value == i) {
root = null;
} else {
root.delete(i);
}
}
}
- 节点类
public class TreeNode {
//节点的权
int value;
//左儿子
TreeNode leftNode;
//右儿子
TreeNode rightNode;
public TreeNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
//设置左儿子
public void setLeftNode(TreeNode leftNode) {
this.leftNode = leftNode;
}
//设置右儿子
public void setRightNode(TreeNode rightNode) {
this.rightNode = rightNode;
}
//先序遍历
public void frontShow() {
//先遍历当前节点的值
System.out.print(value + " ");
//左节点
if (leftNode != null) {
leftNode.frontShow(); //递归思想
}
//右节点
if (rightNode != null) {
rightNode.frontShow();
}
}
//中序遍历
public void middleShow() {
//左节点
if (leftNode != null) {
leftNode.middleShow(); //递归思想
}
//先遍历当前节点的值
System.out.print(value + " ");
//右节点
if (rightNode != null) {
rightNode.middleShow();
}
}
//后续遍历
public void afterShow() {
//左节点
if (leftNode != null) {
leftNode.afterShow(); //递归思想
}
//右节点
if (rightNode != null) {
rightNode.afterShow();
}
//先遍历当前节点的值
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
//先序查找
public TreeNode frontSearch(int i) {
TreeNode target = null;
//对比当前节点的值
if (this.value == i) {
return this;
//当前节点不是要查找的节点
} else {
//查找左儿子
if (leftNode != null) {
//查找的话t赋值给target,查不到target还是null
target = leftNode.frontSearch(i);
}
//如果target不为空,说明在左儿子中已经找到
if (target != null) {
return target;
}
//如果左儿子没有查到,再查找右儿子
if (rightNode != null) {
target = rightNode.frontSearch(i);
}
}
return target;
}
//删除一个子树
public void delete(int i) {
TreeNode parent = this;
//判断左儿子
if (parent.leftNode != null && parent.leftNode.value == i) {
parent.leftNode = null;
return;
}
//判断右儿子
if (parent.rightNode != null && parent.rightNode.value == i) {
parent.rightNode = null;
return;
}
//如果都不是,递归检查并删除左儿子
parent = leftNode;
if (parent != null) {
parent.delete(i);
}
//递归检查并删除右儿子
parent = rightNode;
if (parent != null) {
parent.delete(i);
}
}
}
- 测试类
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一棵树
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
//创建一个根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
//把根节点赋给树
binaryTree.setRoot(root);
//创建左,右节点
TreeNode rootLeft = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode rootRight = new TreeNode(3);
//把新建的节点设置为根节点的子节点
root.setLeftNode(rootLeft);
root.setRightNode(rootRight);
//为第二层的左节点创建两个子节点
rootLeft.setLeftNode(new TreeNode(4));
rootLeft.setRightNode(new TreeNode(5));
//为第二层的右节点创建两个子节点
rootRight.setLeftNode(new TreeNode(6));
rootRight.setRightNode(new TreeNode(7));
//先序遍历
binaryTree.frontShow(); //1 2 4 5 3 6 7
System.out.println();
//中序遍历
binaryTree.middleShow(); //4 2 5 1 6 3 7
System.out.println();
//后序遍历
binaryTree.afterShow(); //4 5 2 6 7 3 1
System.out.println();
//先序查找
TreeNode result = binaryTree.frontSearch(5);
System.out.println(result); //binarytree.TreeNode@1b6d3586
//删除一个子树
binaryTree.delete(2);
binaryTree.frontShow(); //1 3 6 7 ,2和他的子节点被删除了
}
}
顺序存储的二叉树
![]()
概述:顺序存储使用数组的形式实现;由于非完全二叉树会导致数组中出现空缺,有的位置不能填上数字,所以顺序存储二叉树通常情况下只考虑完全二叉树
原理: 顺序存储在数组中是按照第一层第二层一次往下存储的,遍历方式也有先序遍历、中序遍历、后续遍历
性质:
- 第n个元素的左子节点是:2*n+1;
- 第n个元素的右子节点是:2*n+2;
- 第n个元素的父节点是:(n-1)/2
代码实现:
- 树类
public class ArrayBinaryTree {
int[] data;
public ArrayBinaryTree(int[] data) {
this.data = data;
}
//重载先序遍历方法,不用每次传参数了,保证每次从头开始
public void frontShow() {
frontShow(0);
}
//先序遍历
public void frontShow(int index) {
if (data == null || data.length == 0) {
return;
}
//先遍历当前节点的内容
System.out.print(data[index] + " ");
//处理左子树:2*index+1
if (2 * index + 1 < data.length) {
frontShow(2 * index + 1);
}
//处理右子树:2*index+2
if (2 * index + 2 < data.length) {
frontShow(2 * index + 2);
}
}
}
- 测试类
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] data = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
ArrayBinaryTree tree = new ArrayBinaryTree(data);
//先序遍历
tree.frontShow(); //1 2 4 5 3 6 7
}
}
线索二叉树(Threaded BinaryTree)
为什么使用线索二叉树?
当用二叉链表作为二叉树的存储结构时,可以很方便的找到某个结点的左右孩子;但一般情况下,无法直接找到该结点在某种遍历序列中的前驱和后继结点
原理:n个结点的二叉链表中含有n+1(2n-(n-1)=n+1个空指针域。利用二叉链表中的空指针域,存放指向结点在某种遍历次序下的前驱和后继结点的指针。
例如:某个结点的左孩子为空,则将空的左孩子指针域改为指向其前驱;如果某个结点的右孩子为空,则将空的右孩子指针域改为指向其后继(这种附加的指针称为"线索")
![]()
代码实现:
- 树类
public class ThreadedBinaryTree {
ThreadedNode root;
//用于临时存储前驱节点
ThreadedNode pre = null;
//设置根节点
public void setRoot(ThreadedNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
//中序线索化二叉树
public void threadNodes() {
threadNodes(root);
}
public void threadNodes(ThreadedNode node) {
//当前节点如果为null,直接返回
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//处理左子树
threadNodes(node.leftNode);
//处理前驱节点
if (node.leftNode == null) {
//让当前节点的左指针指向前驱节点
node.leftNode = pre;
//改变当前节点左指针类型
node.leftType = 1;
}
//处理前驱的右指针,如果前驱节点的右指针是null(没有右子树)
if (pre != null && pre.rightNode == null) {
//让前驱节点的右指针指向当前节点
pre.rightNode = node;
//改变前驱节点的右指针类型
pre.rightType = 1;
}
//每处理一个节点,当前节点是下一个节点的前驱节点
pre = node;
//处理右子树
threadNodes(node.rightNode);
}
//遍历线索二叉树
public void threadIterate() {
//用于临时存储当前遍历节点
ThreadedNode node = root;
while (node != null) {
//循环找到最开始的节点
while (node.leftType == 0) {
node = node.leftNode;
}
//打印当前节点的值
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
//如果当前节点的右指针指向的是后继节点,可能后继节点还有后继节点
while (node.rightType == 1) {
node = node.rightNode;
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
}
//替换遍历的节点
node = node.rightNode;
}
}
//获取根节点
public ThreadedNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
//先序遍历
public void frontShow() {
if (root != null) {
root.frontShow();
}
}
//中序遍历
public void middleShow() {
if (root != null) {
root.middleShow();
}
}
//后序遍历
public void afterShow() {
if (root != null) {
root.afterShow();
}
}
//先序查找
public ThreadedNode frontSearch(int i) {
return root.frontSearch(i);
}
//删除一个子树
public void delete(int i) {
if (root.value == i) {
root = null;
} else {
root.delete(i);
}
}
}
- 节点类
public class ThreadedNode {
//节点的权
int value;
//左儿子
ThreadedNode leftNode;
//右儿子
ThreadedNode rightNode;
//标识指针类型,1表示指向上一个节点,0
int leftType;
int rightType;
public ThreadedNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
//设置左儿子
public void setLeftNode(ThreadedNode leftNode) {
this.leftNode = leftNode;
}
//设置右儿子
public void setRightNode(ThreadedNode rightNode) {
this.rightNode = rightNode;
}
//先序遍历
public void frontShow() {
//先遍历当前节点的值
System.out.print(value + " ");
//左节点
if (leftNode != null) {
leftNode.frontShow(); //递归思想
}
//右节点
if (rightNode != null) {
rightNode.frontShow();
}
}
//中序遍历
public void middleShow() {
//左节点
if (leftNode != null) {
leftNode.middleShow(); //递归思想
}
//先遍历当前节点的值
System.out.print(value + " ");
//右节点
if (rightNode != null) {
rightNode.middleShow();
}
}
//后续遍历
public void afterShow() {
//左节点
if (leftNode != null) {
leftNode.afterShow(); //递归思想
}
//右节点
if (rightNode != null) {
rightNode.afterShow();
}
//先遍历当前节点的值
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
//先序查找
public ThreadedNode frontSearch(int i) {
ThreadedNode target = null;
//对比当前节点的值
if (this.value == i) {
return this;
//当前节点不是要查找的节点
} else {
//查找左儿子
if (leftNode != null) {
//查找的话t赋值给target,查不到target还是null
target = leftNode.frontSearch(i);
}
//如果target不为空,说明在左儿子中已经找到
if (target != null) {
return target;
}
//如果左儿子没有查到,再查找右儿子
if (rightNode != null) {
target = rightNode.frontSearch(i);
}
}
return target;
}
//删除一个子树
public void delete(int i) {
ThreadedNode parent = this;
//判断左儿子
if (parent.leftNode != null && parent.leftNode.value == i) {
parent.leftNode = null;
return;
}
//判断右儿子
if (parent.rightNode != null && parent.rightNode.value == i) {
parent.rightNode = null;
return;
}
//如果都不是,递归检查并删除左儿子
parent = leftNode;
if (parent != null) {
parent.delete(i);
}
//递归检查并删除右儿子
parent = rightNode;
if (parent != null) {
parent.delete(i);
}
}
}
- 测试类
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一棵树
ThreadedBinaryTree binaryTree = new ThreadedBinaryTree();
//创建一个根节点
ThreadedNode root = new ThreadedNode(1);
//把根节点赋给树
binaryTree.setRoot(root);
//创建左,右节点
ThreadedNode rootLeft = new ThreadedNode(2);
ThreadedNode rootRight = new ThreadedNode(3);
//把新建的节点设置为根节点的子节点
root.setLeftNode(rootLeft);
root.setRightNode(rootRight);
//为第二层的左节点创建两个子节点
rootLeft.setLeftNode(new ThreadedNode(4));
ThreadedNode fiveNode = new ThreadedNode(5);
rootLeft.setRightNode(fiveNode);
//为第二层的右节点创建两个子节点
rootRight.setLeftNode(new ThreadedNode(6));
rootRight.setRightNode(new ThreadedNode(7));
//中序遍历
binaryTree.middleShow(); //4 2 5 1 6 3 7
System.out.println();
//中序线索化二叉树
binaryTree.threadNodes();
// //获取5的后继节点
// ThreadedNode afterFive = fiveNode.rightNode;
// System.out.println(afterFive.value); //1
binaryTree.threadIterate(); //4 2 5 1 6 3 7
}
}
二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree)
无序序列:
![]() 二叉排序树图解:
二叉排序树图解:
![]()
概述:二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree)也叫二叉查找树或者是一颗空树,对于二叉树中的任何一个非叶子节点,要求左子节点比当前节点值小,右子节点比当前节点值大
特点:
- 查找性能与插入删除性能都适中还不错
- 中序遍历的结果刚好是从大到小
创建二叉排序树原理:其实就是不断地插入节点,然后进行比较。
删除节点
- 删除叶子节点,只需要找到父节点,将父节点与他的连接断开即可
- 删除有一个子节点的就需要将他的子节点换到他现在的位置
- 删除有两个子节点的节点,需要使用他的前驱节点或者后继节点进行替换,就是左子树最右下方的数(最大的那个)或右子树最左边的树(最小的数);即离节点值最接近的值;(还要注解要去判断这个值有没有右节点,有就要将右节点移上来)
代码实现:
- 树类
public class BinarySortTree {
Node root;
//添加节点
public void add(Node node) {
//如果是一颗空树
if (root == null) {
root = node;
} else {
root.add(node);
}
}
//中序遍历
public void middleShow() {
if (root != null) {
root.middleShow(root);
}
}
//查找节点
public Node search(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
return root.search(value);
}
//查找父节点
public Node searchParent(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
return root.searchParent(value);
}
//删除节点
public void delete(int value) {
if (root == null) {
return;
} else {
//找到这个节点
Node target = search(value);
//如果没有这个节点
if (target == null) {
return;
}
//找到他的父节点
Node parent = searchParent(value);
//要删除的节点是叶子节点
if (target.left == null && target.left == null) {
//要删除的节点是父节点的左子节点
if (parent.left.value == value) {
parent.left = null;
}
//要删除的节点是父节点的右子节点
else {
parent.right = null;
}
}
//要删除的节点有两个子节点的情况
else if (target.left != null && target.right != null) {
//删除右子树中值最小的节点,并且获取到值
int min = deletMin(target.right);
//替换目标节点中的值
target.value = min;
}
//要删除的节点有一个左子节点或右子节点
else {
//有左子节点
if (target.left != null) {
//要删除的节点是父节点的左子节点
if (parent.left.value == value) {
parent.left = target.left;
}
//要删除的节点是父节点的右子节点
else {
parent.right = target.left;
}
}
//有右子节点
else {
//要删除的节点是父节点的左子节点
if (parent.left.value == value) {
parent.left = target.right;
}
//要删除的节点是父节点的右子节点
else {
parent.right = target.right;
}
}
}
}
}
//删除一棵树中最小的节点
private int deletMin(Node node) {
Node target = node;
//递归向左找最小值
while (target.left != null) {
target = target.left;
}
//删除最小的节点
delete(target.value);
return target.value;
}
}
- 节点类
public class Node {
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
//向子树中添加节点
public void add(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
/*判断传入的节点的值比当前紫薯的根节点的值大还是小*/
//添加的节点比当前节点更小(传给左节点)
if (node.value < this.value) {
//如果左节点为空
if (this.left == null) {
this.left = node;
}
//如果不为空
else {
this.left.add(node);
}
}
//添加的节点比当前节点更大(传给右节点)
else {
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = node;
} else {
this.right.add(node);
}
}
}
//中序遍历二叉排序树,结果刚好是从小到大
public void middleShow(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
middleShow(node.left);
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
middleShow(node.right);
}
//查找节点
public Node search(int value) {
if (this.value == value) {
return this;
} else if (value < this.value) {
if (left == null) {
return null;
}
return left.search(value);
} else {
if (right == null) {
return null;
}
return right.search(value);
}
}
//查找父节点
public Node searchParent(int value) {
if ((this.left != null && this.left.value == value) || (this.right != null && this.right.value == value)) {
return this;
} else {
if (this.value > value && this.left != null) {
return this.left.searchParent(value);
} else if (this.value < value && this.right != null) {
return this.right.searchParent(value);
}
return null;
}
}
}
- 测试类
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {8, 3, 10, 1, 6, 14, 4, 7, 13};
//创建一颗二叉排序树
BinarySortTree bst = new BinarySortTree();
//循环添加
/* for(int i=0;i< arr.length;i++) {
bst.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}*/
for (int i : arr) {
bst.add(new Node(i));
}
//中序遍历
bst.middleShow(); //1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
System.out.println();
//查找节点
Node node = bst.search(10);
System.out.println(node.value);//10
Node node2 = bst.search(20);
System.out.println(node2); //null
//查找父节点
Node node3 = bst.searchParent(1);
Node node4 = bst.searchParent(14);
System.out.println(node3.value); //3
System.out.println(node4.value); //10
//删除叶子节点
// bst.delete(13);
// bst.middleShow(); //1 3 4 6 7 8 10 14
// System.out.println();
// //删除只有一个子节点的节点
// bst.delete(10);
// bst.middleShow(); //1 3 4 6 7 8 ;10和14都没了
//删除有两个子节点的节点
bst.delete(3);
bst.middleShow(); //1 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
}
}
平衡二叉树( Balanced Binary Tree)
为什么使用平衡二叉树?
平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree)又被称为AVL树,且具有以下性质:它是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。这个方案很好的解决了二叉查找树退化成链表的问题,把插入,查找,删除的时间复杂度最好情况和最坏情况都维持在O(logN)。但是频繁旋转会使插入和删除牺牲掉O(logN)左右的时间,不过相对二叉查找树来说,时间上稳定了很多。
二叉排序树插入 {1,2,3,4,5,6} 这种数据结果如下图所示:
![]()
平衡二叉树插入 {1,2,3,4,5,6} 这种数据结果如下图所示:
![]()
如何判断平衡二叉树?
- 1、是二叉排序树
- 2、任何一个节点的左子树或者右子树都是平衡二叉树(左右高度差小于等于 1)
(1)下图不是平衡二叉树,因为它不是二叉排序树违反第 1 条件
![]()
(2)下图不是平衡二叉树,因为有节点子树高度差大于 1 违法第 2 条件(5的左子树为0,右子树为2)
![]()
(3)下图是平衡二叉树,因为符合 1、2 条件
![]()
相关概念
平衡因子 BF
- 定义:左子树和右子树高度差
- 计算:
左子树高度 - 右子树高度的值 - 别名:简称 BF(Balance Factor)
- 一般来说 BF 的绝对值大于 1,,平衡树二叉树就失衡,需要旋转纠正
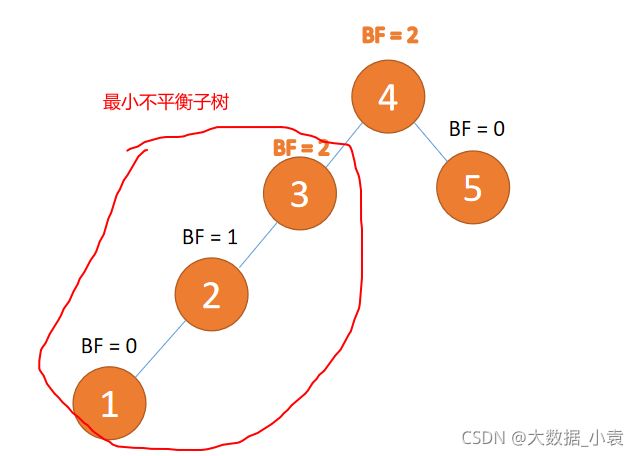
最小不平衡子树
-
距离插入节点最近的,并且 BF 的绝对值大于 1 的节点为根节点的子树。
-
旋转纠正只需要纠正最小不平衡子树即可
-
例子如下图所示:
旋转方式
2 种旋转方式:
左旋 :
- 旧根节点为新根节点的左子树
- 新根节点的左子树(如果存在)为旧根节点的右子树
右旋:
- 旧根节点为新根节点的右子树
- 新根节点的右子树(如果存在)为旧根节点的左子树
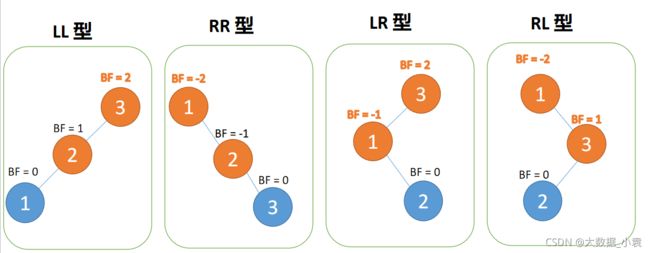
4 种旋转纠正类型:
- 左左型:插入左孩子的左子树,右旋
- 右右型:插入右孩子的右子树,左旋
- 左右型:插入左孩子的右子树,先左旋,再右旋
- 右左型:插入右孩子的左子树,先右旋,再左旋
左左型:
第三个节点(1)插入的时候,BF(3) = 2,BF(2) = 1,右旋,根节点顺时针旋转
![]()
右右型:
第三个节点(3)插入的时候,BF(1)=-2 BF(2)=-1,RR 型失衡,左旋,根节点逆时针旋转
![]()
左右型:
第三个节点(3)插入的 时候,BF(3)=2 BF(1)=-1 LR 型失衡,先 左旋 再 右旋
![]()
![]()
右左型:
第三个节点(1)插入的 时候,BF(1)=-2 BF(3)=1 RL 型失衡,先 右旋 再 左旋
![]()
![]()
实例
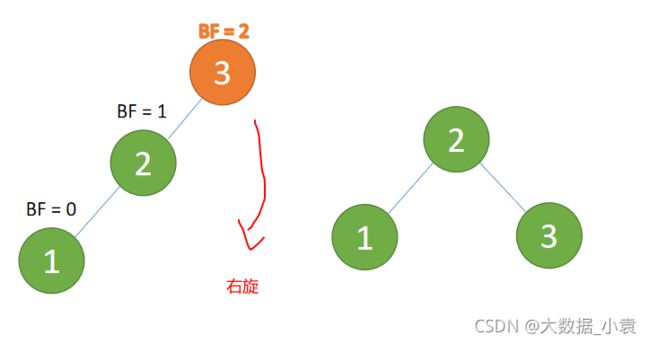
(1)、依次插入 3、2、1 插入第三个点 1 的时候 BF(3)=2 BF(2)=1,LL 型失衡,对最小不平衡树 {3,2,1}进行 右旋
- 旧根节点(节点 3)为新根节点(节点 2)的右子树
- 新根节点(节点 2)的右子树(这里没有右子树)为旧根节点的左子树
(2)依次插入 4 ,5 插入 5 点的时候 BF(3) = -2 BF(4)=-1,RR 型失衡,对最小不平衡树 {3,4,5} 进行左旋
- 旧根节点(节点 3)为新根节点(节点 4)的左子树
- 新根节点(节点 4)的左子树(这里没有左子树)为旧根节点的右子树
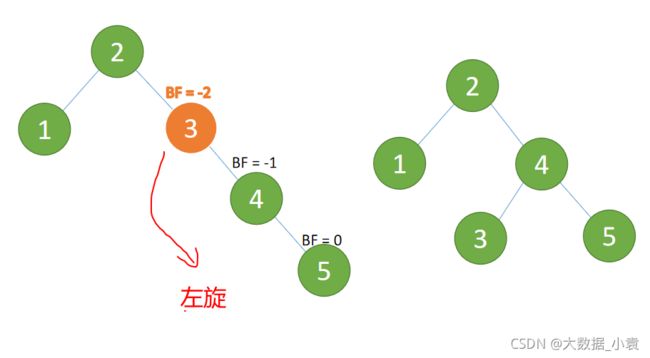
(3)插入 4 ,5 插入 5 点的时候 BF(2)=-2 BF(4)=-1 ,RR 型失衡 对最小不平衡树{1,2,4}进行左旋
- 旧根节点(节点 2)为新根节点(节点 4)的左子树
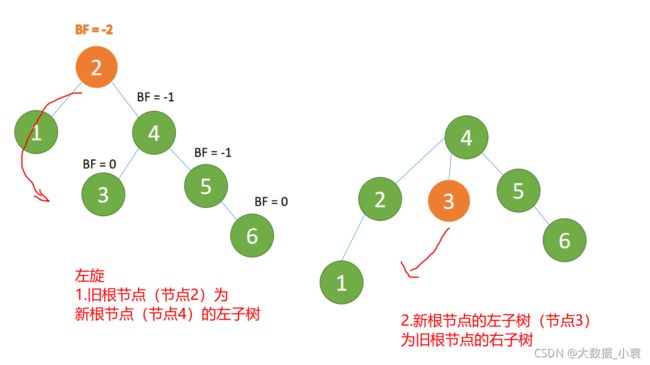
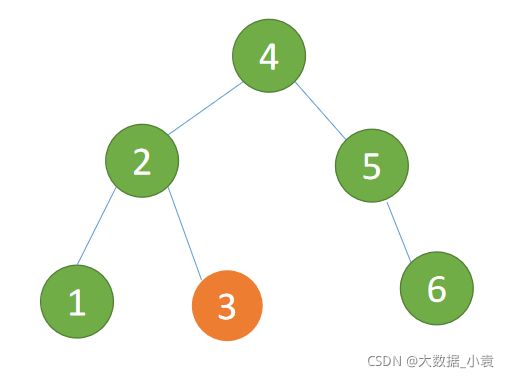
- 新根节点(节点 4)的 左子树(节点 3)为旧根节点的右子树
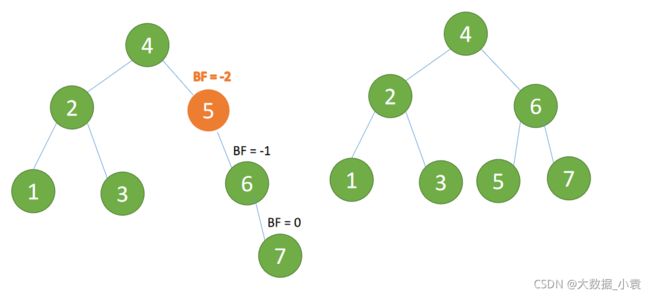
(4)插入 7 节点的时候 BF(5)=-2, BF(6)=-1 ,RR 型失衡,对最小不平衡树 进行左旋
- 旧根节点(节点 5)为新根节点(节点 6)的左子树
- 新根节点的左子树(这里没有)为旧根节点的右子树
(5)依次插入 10 ,9 。插入 9 点的时候 BF(10) = 1,BF(7) = -2 ,RL 型失衡,对先右旋再左旋,右子树先右旋
- 旧根节点(节点 10)为新根节点(节点 9)的右子树
- 新根节点(节点 9)的右子树(这里没有右子树)为旧根节点的左子树
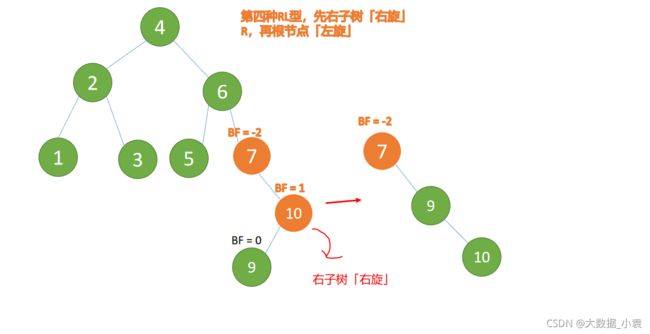
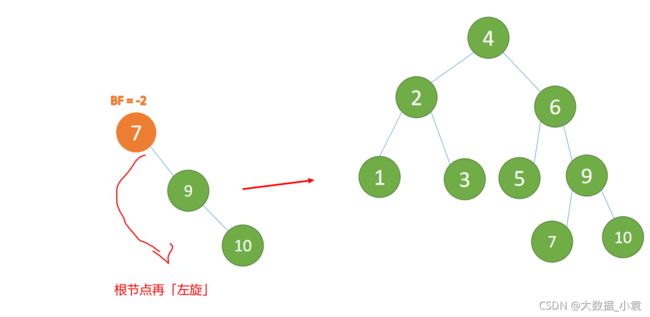
最小不平衡子树再左旋: - 旧根节点(节点 7)为新根节点(节点 9)的左子树
- 新根节点(节点 9)的左子树(这里没有左子树)为旧根节点的右子树
代码实现
![]()
- 节点类
public class Node {
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
//获取当前节点高度
public int height() {
return Math.max(left == null ? 0 : left.height(), right == null ? 0 : right.height()) + 1;
}
//获取左子树高度
public int leftHeight() {
if (left == null) {
return 0;
}
return left.height();
}
//获取右子树高度
public int rightHeight() {
if (right == null) {
return 0;
}
return right.height();
}
//向子树中添加节点
public void add(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
/*判断传入的节点的值比当前紫薯的根节点的值大还是小*/
//添加的节点比当前节点更小(传给左节点)
if (node.value < this.value) {
//如果左节点为空
if (this.left == null) {
this.left = node;
}
//如果不为空
else {
this.left.add(node);
}
}
//添加的节点比当前节点更大(传给右节点)
else {
if (this.right == null) {
this.right = node;
} else {
this.right.add(node);
}
}
//查询是否平衡
//右旋转
if (leftHeight() - rightHeight() >= 2) {
//双旋转,当左子树左边高度小于左子树右边高度时
if (left != null && left.leftHeight() < left.rightHeight()) {
//左子树先进行左旋转
left.leftRotate();
//整体进行右旋转
rightRotate();
}
//单旋转
else {
rightRotate();
}
}
//左旋转
if (leftHeight() - rightHeight() <= -2) {
//双旋转
if (right != null && right.rightHeight() < right.leftHeight()) {
right.rightRotate();
leftRotate();
}
//单旋转
else {
leftRotate();
}
}
}
//右旋转
private void rightRotate() {
//创建一个新的节点,值等于当前节点的值
Node newRight = new Node(value);
//把新节点的右子树设置为当前节点的右子树
newRight.right = right;
//把新节点的左子树设置为当前节点的左子树的右子树
newRight.left = left.right;
//把当前节点的值换位左子节点的值
value = left.value;
//把当前节点的左子树设置为左子树的左子树
left = left.left;
//把当前节点设置为新节点
right = newRight;
}
//左旋转
private void leftRotate() {
//创建一个新的节点,值等于当前节点的值
Node newLeft = new Node(value);
//把新节点的左子树设置为当前节点的左子树
newLeft.left = left;
//把新节点的右子树设置为当前节点的右子树的左子树
newLeft.right = right.left;
//把当前节点的值换位右子节点的值
value = right.value;
//把当前节点的右子树设置为右子树的右子树
right = right.right;
//把当前节点设置为新节点
left = newLeft;
}
//中序遍历二叉排序树,结果刚好是从小到大
public void middleShow(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
middleShow(node.left);
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
middleShow(node.right);
}
//查找节点
public Node search(int value) {
if (this.value == value) {
return this;
} else if (value < this.value) {
if (left == null) {
return null;
}
return left.search(value);
} else {
if (right == null) {
return null;
}
return right.search(value);
}
}
//查找父节点
public Node searchParent(int value) {
if ((this.left != null && this.left.value == value) || (this.right != null && this.right.value == value)) {
return this;
} else {
if (this.value > value && this.left != null) {
return this.left.searchParent(value);
} else if (this.value < value && this.right != null) {
return this.right.searchParent(value);
}
return null;
}
}
}
- 测试类
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6};
//创建一颗二叉排序树
BinarySortTree bst = new BinarySortTree();
//循环添加
for (int i : arr) {
bst.add(new Node(i));
}
//查看高度
System.out.println(bst.root.height()); //3
//查看节点值
System.out.println(bst.root.value); //根节点为4
System.out.println(bst.root.left.value); //左子节点为2
System.out.println(bst.root.right.value); //右子节点为5
}
}