Linux 字符设备驱动结构(二)—— 自动创建设备节点
Linux 字符设备驱动结构(二)—— 自动创建设备节点。
第一种是使用mknod手工创建:mknod filename type major minor
第二种是自动创建设备节点:利用udev(mdev)来实现设备文件的自动创建,首先应保证支持udev(mdev),由busybox配置。
具体udev相关知识这里不详细阐述,可以移步Linux 文件系统与设备文件系统 :udev 设备文件系统,这里主要讲使用方法。
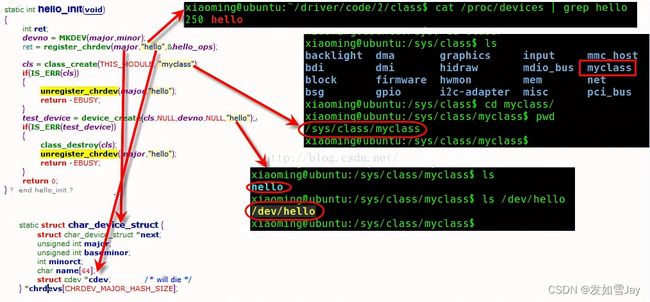
在驱动用加入对udev 的支持主要做的就是:在驱动初始化的代码里调用class_create(...)为该设备创建一个class,再为每个设备调用device_create(...)创建对应的设备。
内核中定义的struct class结构体,顾名思义,一个struct class结构体类型变量对应一个类,内核同时提供了class_create(…)函数,可以用它来创建一个类,这个类存放于sysfs下面,一旦创建好了这个类,再调用 device_create(…)函数来在/dev目录下创建相应的设备节点。
这样,加载模块的时候,用户空间中的udev会自动响应device_create()函数,去/sysfs下寻找对应的类从而创建设备节点。
下面是两个函数的解析:
1. class_create(…) 函与class_destroy
其实该函数是一个宏
原型:
/* This is a #define to keep the compiler from merging different
* instances of the __key variable */
#define class_create(owner, name) \
({ \
static struct lock_class_key __key; \
__class_create(owner, name, &__key); \
})
/*
功能:创建一个类
参数:
owner THIS_MODULE
name 类名字
返回值
可以定义一个struct class的指针变量cls接受返回值,然后通过IS_ERR(cls)判断
是否失败,如果成功这个宏返回0,失败返回非9值(可以通过PTR_ERR(cls)来获得
失败返回的错误码)
*/
__class_create(owner, name, &__key)源代码如下:
struct class *__class_create(struct module *owner, const char *name,
struct lock_class_key *key)
{
struct class *cls;
int retval;
cls = kzalloc(sizeof(*cls), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cls) {
retval = -ENOMEM;
goto error;
}
cls->name = name;
cls->owner = owner;
cls->class_release = class_create_release;
retval = __class_register(cls, key);
if (retval)
goto error;
return cls;
error:
kfree(cls);
return ERR_PTR(retval);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__class_create);
class_destroy函数:
void class_destroy(struct class *cls){
if ((cls == NULL) || (IS_ERR(cls)))
return;
class_unregister(cls);
}
2. device_create(…) 函数
原型:
struct device *device_create(struct class *class, struct device *parent,
dev_t devt, void *drvdata, const char *fmt, ...)
/*
功能:创建一个字符设备文件
参数:
class :指向该设备应注册到的结构类的指针
parent:指向这个新设备的父结构设备的指针(如果有的话),一般设为NULL
devt:设备号
drvdata:null
fmt:设备名称的字符串
返回值:
成功时返回&struct设备指针,错误时返回ERR_PTR()。
*/
下面是源码解析:
struct device *device_create(struct class *class, struct device *parent,
dev_t devt, void *drvdata, const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list vargs;
struct device *dev;
va_start(vargs, fmt);
dev = device_create_vargs(class, parent, devt, drvdata, fmt, vargs);
va_end(vargs);
return dev;
}
device_create_vargs(class, parent, devt, drvdata, fmt, vargs)解析如下:
struct device *device_create_vargs(struct class *class, struct device *parent,
dev_t devt, void *drvdata, const char *fmt,
va_list args)
{
return device_create_groups_vargs(class, parent, devt, drvdata, NULL,
fmt, args);
}
3. 一个实例
hello.c:
#include test.c:
#include makefile:
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m:=hello.o
$(info "2nd")
else
KDIR := /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD:=$(shell pwd)
all:
$(info "1st")
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
rm -f *.ko *.o *.symvers *.mod.c *.mod.o *.order
endif