第八章 Spring MVC源码分析笔记
一、基础概念
Spring Web MVC是一种基于Java的实现了Web MVC设计模式的请求驱动类型的轻量级Web框架,即使用了MVC架构模式的思想,将web层进行职责解耦,基于请求驱动指的就是使用请求-响应模型,框架的目的就是帮助我们简化开发,Spring Web MVC也是要简化我们日常Web开发的。 另外还有一种基于组件的、事件驱动的Web框架在此就不介绍了,如Tapestry、JSF等。
Spring Web MVC也是服务到工作者模式的实现,但进行可优化。前端控制器是DispatcherServlet,应用控制器其实拆为处理器映射器(Handler Mapping)进行处理器管理和视图解析器(View Resolver)进行视图管理;页面控制器/动作/处理器为Controller接口(仅包含ModelAndView handleRequest(request, response) 方法)的实现(也可以是任何的POJO类);支持本地化(Locale)解析、主题(Theme)解析及文件上传等;提供了非常灵活的数据验证、格式化和数据绑定机制;提供了强大的约定大于配置(惯例优先原则)的契约式编程支持。
Springmvc是基于servlet规范来完成的一个请求响应模块,也是spring中比较大的一个模块,现在基本上都是零xml配置了,采用的是约定大于配置的方式,所以我们的springmvc也是采用这种零xml配置的方式。要完成这种过程,要解决两个问题:1)取代 web.xml 配置,2)取代springmvc.xml配置。
1、接口介绍:
1.1、HandlerMapping接口—处理请求的映射,它的实现类包括:
- SimpleUrlHandlerMapping通过配置文件,把一个URL映射到Controller
- DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping通过注解,把一个URL映射到Controller类上
1.2、HandlerAdapter接口——处理器适配器
AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter类,通过注解,把一个URL映射到Controller类的方法上
1.3、ViewResolver接口的实现类
- UrlBasedViewResolver类 通过配置文件,把一个视图名交给到一个View来处理
- InternalResourceViewResolver类,比上面的类,加入了JSTL的支持
- HandlerExceptionResolver接口 --异常处理
- SimpleMappingExceptionResolver实现类
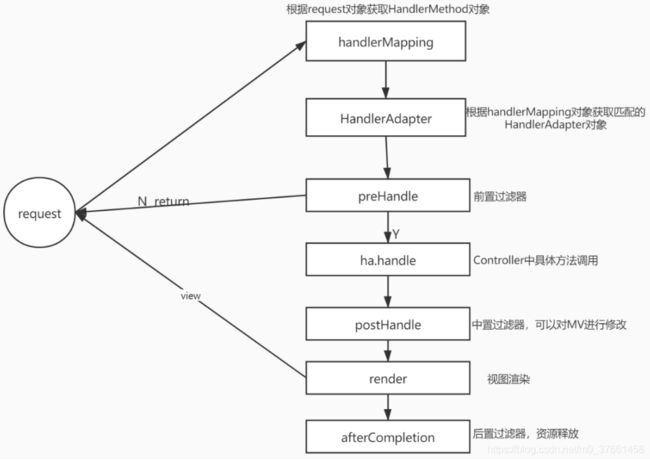
2、Spring Web MVC处理请求的流程
2.1、具体执行步骤如下:
1)首先用户发送请求—>前端控制器,前端控制器根据请求信息(如URL)来决定选择哪一个页面控制器进行处理并把请求委托给它,即以前的控制器的控制逻辑部分。
2)页面控制器接收到请求后,进行功能处理,首先需要收集和绑定请求参数到一个对象,这个对象在Spring Web MVC中叫命令对象,并进行验证,然后将命令对象委托给业务对象进行处理;处理完毕后返回一个ModelAndView(模型数据和逻辑视图名)
3)前端控制器收回控制权,然后根据返回的逻辑视图名,选择相应的视图进行渲染,并把模型数据传入以便视图渲染。
4)前端控制器再次收回控制权,将响应返回给用户,至此整个结束。
2.2、核心架构的具体流程步骤如下:
1) 首先用户发送请求——>DispatcherServlet,前端控制器收到请求后自己不进行处理,而是委托给其他的解析器进行处理,作为统一访问点,进行全局的流程控制。
2)DispatcherServlet——>HandlerMapping,HandlerMapping将会把请求映射HandlerExecutionChain对象(包含一个Handler处理器(页面控制器)对象、多个HandlerInterceptor拦截器)对象,通过这种策略模式,很容易添加新的映射策略。
3)DispatcherServlet——>HandlerAdapter,HandlerAdapter将会把处理器包装为适配器,从而支持多种类型的处理器,即适配器设计模式的应用,从而很容易支持很多类型的处理器。
4)HandlerAdapter——>处理器功能处理方法的调用,HandlerAdapter将会根据适配的结果调用真正的处理器的功能处理方法,完成功能处理;并返回一个ModelAndView对象(包含模型数据、逻辑视图名)。
5)ModelAndView的逻辑视图名——> ViewResolver, ViewResolver将把逻辑视图名解析为具体的View,通过这种策略模式,很容易更换其他视图技术;
6)View——>渲染,View会根据传进来的Model模型数据进行渲染,此处的Model实际是一个Map数据结构,因此很容易支持其他视图技术。
7)返回控制权给DispatcherServlet,由DispatcherServlet返回响应给用户,到此一个流程结束。此处我们只是讲了核心流程,没有考虑拦截器、本地解析、文件上传解析等,后边再细述。
到此,再来看我们前边提出的问题:
1)请求如何给前端控制器?这个应该在web.xml中进行部署描述,在HelloWorld中细讲解。
2)前端控制器如何根据请求信息选择页面控制器进行功能处理? 我们需要配置HandlerMapping进行映射。
3)如何支持多种页面控制器呢?配置HandlerAdapter从而支持多种类型的页面控制器
4)如何页面控制器如何使用业务对象?可以预料到,肯定利用Spring IoC容器的依赖注入功能。
5)页面控制器如何返回模型数据?使用ModelAndView返回。
6)前端控制器如何根据页面控制器返回的逻辑视图名选择具体的视图进行渲染? 使用ViewResolver进行解析。
7)不同的视图技术如何使用相应的模型数据? 因为Model是一个Map数据结构,很容易支持其他视图技术。
2.3、在此我们可以看出具体的核心开发步骤:
1)DispatcherServlet在web.xml中的部署描述,从而拦截请求到Spring Web MVC
接受请求,响应结果,相当于转发器,中央处理器。
2)处理器映射器HandlerMapping的配置:
根据请求的URL查找Handler,从而将请求映射到处理器。
3)处理器适配器HandlerAdapter:
按照特定规则(HandlerAdapter要求的规则)去执行Handler,从而支持多种类型的处理器。
4)处理器Handler(需要自己开发)
编写Handler时按照HandlerAdapter的要求去做,这样适配器才可以正确的执行Handler。
5)视图解析器ViewResolver的配置,从而将逻辑视图名解析为具体视图技术
进行视图解析,根据逻辑视图解析成正真的视图。
6)视图View(需要自己开发jsp)
View是一个接口,实现类支持不同的View类型(jsp、freemarker、pdf..)
3、SpringMVC搭建环境
3.1、配置文件说明
第一步:加入架包、注意添加comments-logging.jar与jstl.jar文件
第二步:配置文件web.xml
web.xml配置DispatcherServlet容器
<servlet>
<servlet-name>spring-dispatcherservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-dispatcher.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
<load-on-startup>0load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>spring-dispatcherservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
第三步:Spring配置文件(*-servlet.xml)
<context:component-scan base-package="com.chj" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
context:component-scan>
InternalResourceViewResolver:用于支持Servlet、JSP视图解析。
viewClass:JstlView表示JSP模板页面需要使用JSTL标签库,classpath中必须包含jstl的相关jar包。
prefix和suffix:查找视图页面的前缀和后缀(前缀[逻辑视图名]后缀),比如传进来的逻辑视图名为hello,则该该jsp视图页面应该存放在“WEB-INF/jsp/hello.jsp”。
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="viewClass" value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView"/>
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
bean>
3.2、请求如何映射到具体的Action中的方法?HandlerMaping映射
方案一:
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping:表示将请求的URL和Bean名字映射,如URL为 “上下文/hello”,
则Spring配置文件必须有一个名字为“/hello”的Bean,上下文默认忽略。
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter:表示所有实现了Controller接口的Bean可以作为Spring Web MVC中的处理器。
如果需要其他类型的处理器,可以通过实现HadlerAdapter来解决。
方式1:处理器将bean的name作为URL进行查找
需要在配置Handler时指定bean name就是URL(/hello.do)
方式2:简单的URL映射 --多个映射器可以并存
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping">
<property name="mappings">
<props>
<prop key="/test.do">helloActionprop>
<prop key="/list.do">helloActionprop>
props>
property>
bean>
处理器适配器HadlerAdapter 两种方式:
需要编写的Handler类,实现Controller接口。
需要编写的Handler类,实现HttpRequestHandler接口。
方案二:
基于注解映射,可以使用DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping
方案三:
采用注解方式(spring3.0不能这样写)
3.3、参数传值
1)页面传值到控制器
获取页面参数@RequestParam("username")String username,如果URL后面不跟参数则会报错404,因为这种方式spring会默认参数作为路劲的一部分,也可以去掉@RequestParam,直接写String username也会获取页面参数。
2)从控制器将值传递到页面(可以直接通过一个model对象或者ModelAndView视图对象进行传值)其中model对象只能一个个传值,当需要传递很多参数值得时候就要使用ModelAndView对象来传值
public String welcome(String username,Model model) {
System.out.println(username);
//当使用一个参数的时候默认方式为:
//key参数类型、value值==model.addAttribute("String",username)或者("user",new User())
model.addAttribute("message",username);
model.addAttribute(new User());
return "hello";
}
3.4、RESUT风格路劲参数传递
JSP页面:user/xx/edit,列如:修改
控制器:方法中路劲映射通过加参数来实现/{id}/edit,参数值通过注解@PathVariable String id来实现
@RequestMapping(value="/{id}/edit",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String edit(@PathVariable String id,User user) {
usernamp.put(id,user);
return "redirect:/user/users";
}
补充:服务器端验证(通过bean-validated实现校验)
1.加入bean-validated.jar包
2、在实体bean中通过注解添加验证信息
3、在控制器中注解(@Validated User user,BindingResult br) 添加验证对象
4、前台页面获取校验信息
4、异常处理:
4.1、局部异常处理
1)新建一个类继承RuntimeException接口实现父类中的几个默认方法
2)控制器中通过判断对于错误信息跑出异常,并将异常结果放到request对象中跳转到错误页面throw new UserExcption("用户名不存在!");
//局部异常处理——仅仅只能处理这个控制器中的异常
@ExceptionHandler(value={UserExcption.class})
public String haddleExcption(UserExcption e,HttpServletRequest req){
req.setAttribute("e", e);
return "error";
}
3)在error页面直接通过${e.message} 取出异常结果
4.2、全局异常
注意使用全局异常时,针对局部异常要做相应调整,在spring配置文件中添加异常配置代码
<bean id="exceptionResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver">
<property name="defaultErrorView" value="error">property>
<property name="exceptionAttribute" value="ex">property>
<property name="exceptionMappings">
<props>
<prop key="com.chj.test.UserExcption">errorprop>
<prop key="IOException">error/ioexpprop>
<prop key="java.sql.SQLException">error/sqlexpprop>
props>
property>
bean>
5、文件上传处理
1)首先加入所需架包(commons-fileupload.jar、commons-io-2.4.jar)然后在spring配置文件中增加文件上传配置代码:
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="5000000">property>
bean>
2)在控制器中通过MultipartFile attachs对象来获取页面上传的文件
注意:页面使用上传标签是form表单的提交类型也要做修改,增加enctype="multipart/form-data"
String realPath = req.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("upload");
File f = new File(realPath+"/"+attachs.getOriginalFilename());
if(attachs.isEmpty()){
}else{
FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(attachs.getInputStream(), f);
}
6、整合hibernate4.2+spring3.1+springMVC
6.1、Hibernate整合
jar包:核心包,必须包:hibernate-distribution-3.6.0.Final\lib\required\
Jpa,c3p0(数据库连接池、提高效率),jdbc(驱动)
配置文件:hibernate-distribution-3.6.0.Final\project\etc\
Hibernate.cfg.xml,*.hbm.xml
6.2、spring2.5整合
jar包:核心包,aop相关包:
- 动态代理aspectj两个
- 子类代理cglib三个,日志
applicationContext.xml
二、取代web.xml配置
在servlet中有一个规范,就是当servlet容器启动的时候会根据spi规范加META-INF/services文件夹下面的javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer文件,该文件下面的类会实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口。代码如下:
1、ServletContainerInitializer代码入口
META-INF\services\javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer
com.chj.tomcat.MyServletContainerInitializer
@HandlesTypes(LoadServlet.class)
public class MyServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(Set
Iterator var4;
if (set != null) {
var4 = set.iterator();
while (var4.hasNext()) {
Class clazz = (Class) var4.next();
if (!clazz.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(clazz.getModifiers()) && LoadServlet.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
try {
((LoadServlet) clazz.newInstance()).loadOnstarp(servletContext);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
该类在启动的时候会被servlet容器实例化,然后调用onStartup方法,并且servlet容器会收集实现了@HandlesTypes注解里面的接口的类,并且做为入参传入到onStartup方法中,我们拿到set容器中的类就可以反射调用接口里面的方法了,这是servlet规范,该规范就能保证servlet容器在启动的时候就会完成这些操作。Springmvc就借助这一点完成了取代web.xml 的工作。
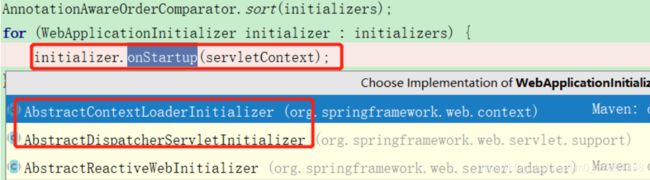
在springmvc中,spring-web jar包下面也会有一个javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer文件,如图:
org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
Tomcat就会加载这个类,调用其onStartup方法。
@HandlesTypes({WebApplicationInitializer.class})
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
public SpringServletContainerInitializer() { }
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set
List
Iterator var4;
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
var4 = webAppInitializerClasses.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
Class waiClass = (Class)var4.next();
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) && WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass, new Class[0]).newInstance());
} catch (Throwable var7) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", var7);
}
}
}
}
收集的是实现了WebApplicationInitializer接口的类,在springmvc工程中我们自己写了这么一个类:
com.chj.mvc.WebAppInitializer
public class WebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
//父容器
@Override
protected Class[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringContainer.class};
}
//SpringMVC配置子容器
@Override
protected Class[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{MvcContainer.class};
}
//获取DispatcherServlet的映射信息
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
MyFilter myFilter = new MyFilter();
return new Filter[]{myFilter};
}
}
该类的父类最终会实现WebApplicationInitializer接口,所以该类的父类必定会有一个onStartup方法。其父类如下:
org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer
public abstract class AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer extends AbstractContextLoaderInitializer {
public static final String DEFAULT_SERVLET_NAME = "dispatcher";
public AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer() {
}
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
//1、注册ContextLoaderListener
super.onStartup(servletContext);
//2、注册DispatcherServlet
this.registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext);
}
2、super.onStartup完成了实例化listener的工作
org.springframework.web.context.AbstractContextLoaderInitializer#registerContextLoaderListener
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
this.registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext);
}
protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = this.createRootApplicationContext();
if (rootAppContext != null) {
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(this.getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
servletContext.addListener(listener);
} else {
this.logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}
这些代码功能就类似于在web.xml配置了ContextLoaderListener,做了几个事情,1 创建了上下文对象,如下:
org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer#createRootApplicationContext
public abstract class AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
public AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer() {
}
@Nullable
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
Class[] configClasses = this.getRootConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.register(configClasses);
return context;
} else {
return null;
}
}
这个上下文对象就是基于注解扫描的上下文对象,所以用这个上下文是需要注册一个类进去,这个类就是用钩子方法调用到了自己写的方法。
com.chj.mvc.WebAppInitializer#getRootConfigClasses
public class WebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
//父容器
@Override
protected Class[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringContainer.class};
}
在钩子方法中获取到的类springContainer就会去扫描基本包,有@ComponentScan注解,如图:
com.chj.mvc.SpringContainer
//不扫描有@Controller注解的类
@ComponentScan(value = "com.chj",excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})
})
public class SpringContainer {
}
通过钩子方法获取到扫描类后,注册到了上下文对象中,然后把spring的上下文对象设置到了ContextLoaderListener监听器对象中,最后把监听器对象设置到了servletContext中。这里上下文对象还没有调用refresh方法完成spring的启动。
3、registerDispatcherServlet(servletContext)完成了实例化DispatcherServlet
org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer#registerDispatcherServlet
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
String servletName = this.getServletName();
Assert.hasLength(servletName, "getServletName() must not return null or empty");
WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = this.createServletApplicationContext();
Assert.notNull(servletAppContext, "createServletApplicationContext() must not return null");
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = this.createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
Assert.notNull(dispatcherServlet, "createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext) must not return null");
dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(this.getServletApplicationContextInitializers());
Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, dispatcherServlet);
if (registration == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to register servlet with name '" + servletName + "'. Check if there is another servlet registered under the same name.");
} else {
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping(this.getServletMappings());
registration.setAsyncSupported(this.isAsyncSupported());
Filter[] filters = this.getServletFilters();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(filters)) {
Filter[] var7 = filters;
int var8 = filters.length;
for(int var9 = 0; var9 < var8; ++var9) {
Filter filter = var7[var9];
this.registerServletFilter(servletContext, filter);
}
}
this.customizeRegistration(registration);
}
}
步骤跟创建监听器差不多,创建上下文对象,跟上面差不多,创建dispatcherServlet对象,把servlet对象加入到servletContext上下文中。把上下文对象设置到了dispatcherServlet对象中了,这里上下文对象还没有调用refresh方法,没有启动spring容器。
4、启动spring容器
注意:通过listener启动加载的是父容器,容器初始化就是将spring容器放入到listener里面;通过DispatcherServlet启动加载的是子容器,就是将spring容器放入到DispatcherServlet里面。由于DispatcherServlet实现了HttpServlet接口,所以DispatcherServlet初始化的时候必定会调用init方法。
最后会通过onRefresh方法,调用搜spring的refresh方法完成时spring的初始化。
4.1、ContextLoaderListener监听器的启动
Web.xml配置文件中配置ContextLoaderListener
<listener>
listener>
org.springframework.web.context.AbstractContextLoaderInitializer#onStartup
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext);
}
protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
//创建spring上下文,注册了SpringContainer
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext();
if (rootAppContext != null) {
//创建监听器,形如这种配置
*
* */
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
servletContext.addListener(listener);
} else {
logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as " +
"createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener#contextInitialized
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
其实没什么特别的,就是会拿到上下文对象调用refresh方法,需要特殊记忆的就是,会把上下文对象设置到servletContext中。
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
// 把上下文对象设置到servletContext中
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
} catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
4.2、DispatcherServlet的启动
因为这个是一个servlet,servlet要完成spring容器的启动,就只能在init方法里面做。
<servlet>
<servlet-name>spring-dispatcherservlet-name>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-dispatcher.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
<load-on-startup>0load-on-startup>
servlet>
org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean#init
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initServletBean
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
} catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
}
这里也没什么特别的,也是拿到上下文对象调用了refresh方法完成spring容器的启动。
4.3、初始化容器加载
需要注意的是这里:
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initWebApplicationContext
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//这里会从servletContext中获取到父容器,就是通过监听器加载的容器
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//容器加载
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
会从servletContext中获取父容器
//这里会从servletContext中获取到父容器,就是通过监听器加载的容器
WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
就是由listener负责启动的容器,然后把父容器设置到了自己的上下文对象中,所以这里监听器启动的容器是父容器,dispatcherServlet启动的容器是子容器,两者是父子关系。这里就用servlet规范完成了取代web.xml的工作,并启动了容器。
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#onRefresh
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
4.4、创建web容器
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#createWebApplicationContext(WebApplicationContext)
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable WebApplicationContext parent) {
return createWebApplicationContext((ApplicationContext) parent);
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
Class contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
4.5、配置刷新容器
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
} else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
wac.refresh();
}
4.6、refresh()方法分析
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//为容器初始化做准备,重要程度:0 Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
org.springframework.web.servlet.ComplexWebApplicationContext#refresh
public class ComplexWebApplicationContext extends StaticWebApplicationContext {
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException {
super.refresh();
org.springframework.web.servlet.SimpleWebApplicationContext#refresh
public class SimpleWebApplicationContext extends StaticWebApplicationContext {
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException {
super.refresh();
然后开始执行spring的refresh方法,以及配置初始化相关配置。
二、取代springmvc.xml配置
1、传统的xml配置方式
<context:component-scan base-package="com.chj" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
context:component-scan>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:config/core/core.properties"/>
<mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:message-converters register-defaults="true">
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes" value = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8" />
bean>
mvc:message-converters>
mvc:annotation-driven>
<bean id="formHttpMessageConverter" class="org.springframework.http.converter.FormHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes">
<list>
<value>application/x-www-form-urlencodedvalue>
<value>multipart/form-datavalue>
list>
property>
bean>
<bean id="stringHttpMessageConverter" class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
bean>
<bean id="byteArrayHttpMessageConverter" class="org.springframework.http.converter.ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter">
<property name="supportedMediaTypes">
<list>
<value>application/octet-streamvalue>
list>
property>
bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
bean>
<bean id="exceptionResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver">
<property name="exceptionMappings">
<props>
<prop key="java.lang.Exception">
error
prop>
props>
property>
bean>
<mvc:cors>
<mvc:mapping path="/**" allowed-origins="*"
allowed-methods="POST, GET, OPTIONS, DELETE, PUT"
allowed-headers="Content-Type, Access-Control-Allow-Headers, Authorization, X-Requested-With" allow-credentials="true"/>
mvc:cors>
beans>
2、通过注解配置方式实现@EnableWebMvc
我们用一个@EnableWebMvc就可以完全取代xml配置,其实两者完成的工作是一样的,都是为了创建必要组件的实例:
2.1、@EnableWebMvc注解配置使用
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class AppConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserInterceptor userInterceptor;
@Override
public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
registry.enableContentNegotiation(new MappingJackson2JsonView());
registry.jsp("/jsp/", ".jsp");
}
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/view/ok").setViewName("ok");
registry.addViewController("/view/index").setViewName("index");
}
@Override
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(userInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/user/**").excludePathPatterns("/user/query/**");
registry.addInterceptor(new UserInterceptor1()).addPathPatterns("/user/**").excludePathPatterns("");
}
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/image/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/img/");
}
@Override
public void configureHandlerExceptionResolvers(List
super.configureHandlerExceptionResolvers(exceptionResolvers);
}
}
这里会导入一个核心类WebMvcConfigurationSupport,在这个类里面会完成很多组件的实例化,比如HandlerMapping,HandlerAdapter等等。
2.2、WebMvcConfigurationSupport里组件实例化
HandlerMapping实例化,代码如下所示:
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping() {
RequestMappingHandlerMapping mapping = createRequestMappingHandlerMapping();
mapping.setOrder(0);
mapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors());
mapping.setContentNegotiationManager(mvcContentNegotiationManager());
mapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());
PathMatchConfigurer configurer = getPathMatchConfigurer();
Boolean useSuffixPatternMatch = configurer.isUseSuffixPatternMatch();
if (useSuffixPatternMatch != null) {
mapping.setUseSuffixPatternMatch(useSuffixPatternMatch);
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport#viewControllerHandlerMapping
@Bean
@Nullable
public HandlerMapping viewControllerHandlerMapping() {
ViewControllerRegistry registry = new ViewControllerRegistry(this.applicationContext);
addViewControllers(registry);
AbstractHandlerMapping handlerMapping = registry.buildHandlerMapping();
if (handlerMapping == null) {
return null;
}
handlerMapping.setPathMatcher(mvcPathMatcher());
handlerMapping.setUrlPathHelper(mvcUrlPathHelper());
handlerMapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors());
handlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());
return handlerMapping;
}
2.3、MappingHandlerAdapter实例化
org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport#requestMappingHandlerAdapter
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerAdapter requestMappingHandlerAdapter() {
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter adapter = createRequestMappingHandlerAdapter();
adapter.setContentNegotiationManager(mvcContentNegotiationManager());
adapter.setMessageConverters(getMessageConverters());
adapter.setWebBindingInitializer(getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer());
adapter.setCustomArgumentResolvers(getArgumentResolvers());
adapter.setCustomReturnValueHandlers(getReturnValueHandlers());
if (jackson2Present) {
adapter.setRequestBodyAdvice(Collections.singletonList(new JsonViewRequestBodyAdvice()));
adapter.setResponseBodyAdvice(Collections.singletonList(new JsonViewResponseBodyAdvice()));
}
AsyncSupportConfigurer configurer = new AsyncSupportConfigurer();
configureAsyncSupport(configurer);
if (configurer.getTaskExecutor() != null) {
adapter.setTaskExecutor(configurer.getTaskExecutor());
}
if (configurer.getTimeout() != null) {
adapter.setAsyncRequestTimeout(configurer.getTimeout());
}
adapter.setCallableInterceptors(configurer.getCallableInterceptors());
adapter.setDeferredResultInterceptors(configurer.getDeferredResultInterceptors());
return adapter;
}
然后在实例化过程中会涉及到很多钩子方法的调用,而这些钩子方法就是我们需要去实现的,比如获取拦截器的钩子方法,获取静态资源处理的钩子方法等等。代码如下:
com.chj.mvc.AppConfig#addInterceptors
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(userInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/user/**").excludePathPatterns("/user/query/**");
registry.addInterceptor(new UserInterceptor1()).addPathPatterns("/user/**").excludePathPatterns("");
}
3、SpringMVC配置加载分析
3.1、SpringMVC配置标签解析入口
spring-webmvc-5.1.3.RELEASE.jar!/META-INF/spring.handlers
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc=org.springframework.web.servlet.config.MvcNamespaceHandler
org.springframework.web.servlet.config.MvcNamespaceHandler#init
public class MvcNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation-driven", new AnnotationDrivenBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("default-servlet-handler", new DefaultServletHandlerBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("interceptors", new InterceptorsBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("resources", new ResourcesBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("view-controller", new ViewControllerBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("redirect-view-controller", new ViewControllerBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("status-controller", new ViewControllerBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("view-resolvers", new ViewResolversBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("tiles-configurer", new TilesConfigurerBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("freemarker-configurer", new FreeMarkerConfigurerBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("groovy-configurer", new GroovyMarkupConfigurerBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("script-template-configurer", new ScriptTemplateConfigurerBeanDefinitionParser());
registerBeanDefinitionParser("cors", new CorsBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
3.2、spring web容器初始化入口
org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer#onStartup
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
org.springframework.web.context.AbstractContextLoaderInitializer#registerContextLoaderListener
public abstract class AbstractContextLoaderInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
registerContextLoaderListener(servletContext);
}
protected void registerContextLoaderListener(ServletContext servletContext) {
//创建spring上下文,注册了SpringContainer
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = createRootApplicationContext();
if (rootAppContext != null) {
//创建监听器,形如这种配置
*
* */
ContextLoaderListener listener = new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext);
listener.setContextInitializers(getRootApplicationContextInitializers());
servletContext.addListener(listener);
}else {
logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as " +
"createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}
3、请求之前建立映射关系
3.1、请求映射关系图
3.2、HandlerMapping类实例化方法
在HandlerMapping类实例化的时候就会完成url和method的映射关系,要根据一个请求能够唯一到找到一个类和一个方法。
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping() {
RequestMappingHandlerMapping mapping = createRequestMappingHandlerMapping();
mapping.setOrder(0);
mapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors());
mapping.setContentNegotiationManager(mvcContentNegotiationManager());
mapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());
PathMatchConfigurer configurer = getPathMatchConfigurer();
Boolean useSuffixPatternMatch = configurer.isUseSuffixPatternMatch();
if (useSuffixPatternMatch != null) {
mapping.setUseSuffixPatternMatch(useSuffixPatternMatch);
}
Boolean useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch = configurer.isUseRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch();
if (useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch != null) {
mapping.setUseRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch);
}
这个是RequestMappingHandlerMapping的实例化。在其父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中实现了 InitializingBean接口,所以在RequestMappingHandlerMapping实例化完成以后就会调用到afterPropertiesSet方法。在这个方法里面完成了映射关系的建立。
这里判断类上面是否有@Controller 注解和@RequestMapping 注解,只有这种类才需要建立映射关系
3.3、完成映射关系属性赋值
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping#afterPropertiesSet
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
this.config.setUrlPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper());
this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher());
this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(this.useSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(this.useTrailingSlashMatch);
this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager());
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#afterPropertiesSet
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#processCandidateBean
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
//如果类上面有@Controller注解或者@RequestMapping注解
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
//建立uri和method的映射关系
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
3.4、创建HandlerMethod,建立uri和handlerMethod的映射关系
建立url和RequestMappingInfo映射关系,判断method上是否有CrossOrigin注解,把注解里面的属性封装成CorsConfiguration,这个是做跨域访问控制的。
org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#registerHandlerMethod
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
//创建HandlerMethod对象,其实
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
//检验是否唯一
assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
//建立uri对象和handlerMethod的映射关系
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
List
for (String url : directUrls) {
//建立url和RequestMappingInfo映射关系
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
//判断method上是否有CrossOrigin注解,把注解里面的属性封装成CorsConfiguration,这个是做跨域访问控制的
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
//建立映射关系
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
3.5、构建RequestMappingInfo对象
/*
* consumes: 指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),例如application/json, text/html;
produces: 指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回;
params: 指定request中必须包含某些参数值是,才让该方法处理。
headers: 指定request中必须包含某些指定的header值,才能让该方法处理请求。
media type
* */
@RequestMapping(value = "/getUser",
method = RequestMethod.GET,
params = "username=chj",
consumes = "application/json",
produces = "application/json",
headers = "Referer=http://www.xx.com/")
public @ResponseBody
String getUser(HttpSession session, OutputStream outputStream) {
return "xx";
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping#createRequestMappingInfo(java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement)
@Nullable
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
RequestCondition condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping#createRequestMappingInfo(RequestMapping, RequestCondition)
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition customCondition) {
RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
.methods(requestMapping.method())
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name());
if (customCondition != null) {
builder.customCondition(customCondition);
}
return builder.options(this.config).build();
}
3.6、大体思路
1)循环类里面的所有方法;
2)收集方法上面的@RequestMapping注解,把注解里面的配置信息封装到类里面,该类就是 RequestMappingInfo类,并且跟类上面的@RequestMapping注解封装类RequestMappingInfo合并,比如类上面是/common,方法上面是/queryUser。这两者合并后就是/common/queryUser。这样的url才是我们需要的。合并完就是这样的 url;
3)然后建立method对象和对应的RequestMappingInfo的映射关系,把关系存放到map中;
4)创建HandlerMethod对象,该类型封装了method、beanName、bean方法类型等信息;
5)建立RequestMappingInfo和HandlerMethod的映射关系;
//建立uri对象和handlerMethod的映射关系
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
6)建立url和RequestMappingInfo对象的映射关系;
//建立url和RequestMappingInfo映射关系
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
这样映射关系就已经建立好,这样根据请求url我们就可以唯一的找到一个HandlerMethod对象了,注意这个对象中还不能进行反射调用,还确实参数数组。