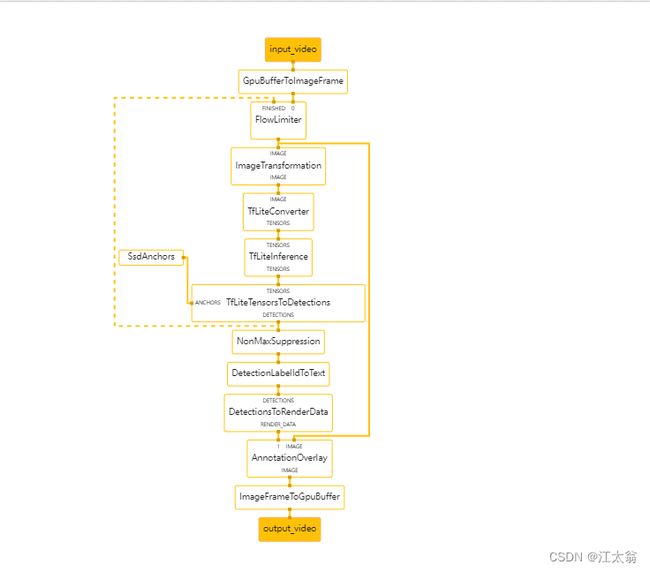
mediapipe流水线分析 二
目标检测 Graph
一 流水线上游输入处理
1 TfLiteConverterCalculator
将输入的数据转换成tensorflow api 支持的Tensor TfLiteTensor 并初始化相关输入输出节点 ,该类的业务主要通过 interpreter std::unique_ptrtflite::Interpreter interpreter_ = nullptr; 实现类 完成 数据在cpu/gpu 上的推理
1.1 TfLiteTensor /Tensor
Tensorflow
在TensorFlow Lite中,TfLiteTensor和Tensor是不同的概念。
Tensor是TensorFlow中的基本数据结构,用于表示多维数组。在TensorFlow Lite中,Tensor被用于输入和输出数据,以及在模型中表示变量和权重。
TfLiteTensor是TensorFlow Lite中特有的数据结构,它是对Tensor的封装,具有一些额外的属性和方法,用于支持TensorFlow Lite特定的功能和操作。例如,TfLiteTensor可以包含额外的信息,如quantization参数(用于量化)和维度(用于调整输入/输出的形状)。\
// A tensor in the interpreter system which is a wrapper around a buffer of
// data including a dimensionality (or NULL if not currently defined).
#ifndef TF_LITE_STATIC_MEMORY
typedef struct TfLiteTensor {
// The data type specification for data stored in `data`. This affects
// what member of `data` union should be used.
TfLiteType type;
// A union of data pointers. The appropriate type should be used for a typed
// tensor based on `type`.
TfLitePtrUnion data;
// A pointer to a structure representing the dimensionality interpretation
// that the buffer should have. NOTE: the product of elements of `dims`
// and the element datatype size should be equal to `bytes` below.
TfLiteIntArray* dims;
// Quantization information.
TfLiteQuantizationParams params;
// How memory is mapped
// kTfLiteMmapRo: Memory mapped read only.
// i.e. weights
// kTfLiteArenaRw: Arena allocated read write memory
// (i.e. temporaries, outputs).
TfLiteAllocationType allocation_type;
// The number of bytes required to store the data of this Tensor. I.e.
// (bytes of each element) * dims[0] * ... * dims[n-1]. For example, if
// type is kTfLiteFloat32 and dims = {3, 2} then
// bytes = sizeof(float) * 3 * 2 = 4 * 3 * 2 = 24.
size_t bytes;
// An opaque pointer to a tflite::MMapAllocation
const void* allocation;
// Null-terminated name of this tensor.
const char* name;
// The delegate which knows how to handle `buffer_handle`.
// WARNING: This is an experimental interface that is subject to change.
struct TfLiteDelegate* delegate;
// An integer buffer handle that can be handled by `delegate`.
// The value is valid only when delegate is not null.
// WARNING: This is an experimental interface that is subject to change.
TfLiteBufferHandle buffer_handle;
// If the delegate uses its own buffer (e.g. GPU memory), the delegate is
// responsible to set data_is_stale to true.
// `delegate->CopyFromBufferHandle` can be called to copy the data from
// delegate buffer.
// WARNING: This is an // experimental interface that is subject to change.
bool data_is_stale;
// True if the tensor is a variable.
bool is_variable;
// Quantization information. Replaces params field above.
TfLiteQuantization quantization;
// Parameters used to encode a sparse tensor.
// This is optional. The field is NULL if a tensor is dense.
// WARNING: This is an experimental interface that is subject to change.
TfLiteSparsity* sparsity;
// Optional. Encodes shapes with unknown dimensions with -1. This field is
// only populated when unknown dimensions exist in a read-write tensor (i.e.
// an input or output tensor). (e.g. `dims` contains [1, 1, 1, 3] and
// `dims_signature` contains [1, -1, -1, 3]). Note that this field only
// exists when TF_LITE_STATIC_MEMORY is not defined.
const TfLiteIntArray* dims_signature;
} TfLiteTensor;
在TensorFlow Lite中,通过interpreter_->tensor(index)方法获取TfLiteTensor对象,其中index是>输入或输出张量的索引。
例如,以下是使用TensorFlow Lite C API获取输入张量的示例代码:
const int tensor_index = interpreter_->inputs()[0];
TfLiteTensor* tensor = interpreter_->tensor(tensor_index);
通过interpreter_->ResizeInputTensor(index, shape)方法可以调整输入张量的形状,其中index是输入张量的索引,shape是新的形状。例如,以下是使用TensorFlow Lite C API调整输入张量形状的示例代码:
const int tensor_index = interpreter_->inputs()[0];
interpreter_->ResizeInputTensor(tensor_index, {height, width, channels});
1.2 Tensor
Tensor是TensorFlow中的基本数据结构,用于表示多维数组。在TensorFlow Lite中,Tensor被用于输入和输出数据,以及在模型中表示变量和权重。
在 TensorFlow 中,张量可以通过多种方式创建和操作,例如使用 Python 列表或 NumPy 数组创建张量,或者通过 TensorFlow 提供的各种操作来创建和操作张量。张量的形状可以是任意维度的,例如一维、二维、三维等等。用于各种深度学习任务,例如图像识别、语音识别、自然语言处理等等。TensorFlow 还支持各种不同的硬件和操作系统,可以在各种平台上运行,包括 CPU、GPU、TPU 等等
Tensor的数据结构包括以下方面:
- 张量的形状:张量的形状定义了它的大小和维度,例如一个三维张量的形状可以是(10, 20, 30),表示它有10个长度为20的数组,每个数组包含30个元素。
- 张量的数据类型:张量的数据类型定义了它存储的数据类型,例如float32、int32等。
- 张量的值:张量的值存储在连续的内存中,可以通过索引来访问和修改。
/* Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
==============================================================================*/
#ifndef TENSORFLOW_CORE_FRAMEWORK_TENSOR_H_
#define TENSORFLOW_CORE_FRAMEWORK_TENSOR_H_
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "unsupported/Eigen/CXX11/Tensor" // from @eigen_archive
#include "tensorflow/core/framework/allocator.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/framework/tensor_shape.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/framework/tensor_types.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/framework/types.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/framework/types.pb.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/core/refcount.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/core/status.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/core/stringpiece.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/gtl/inlined_vector.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/platform/mem.h"
#include "tensorflow/core/platform/types.h"
namespace tensorflow {
// Forward declarations. In particular, we forward declare protos so that their
// symbols can be removed from .so exports.
class AllocationDescription;
class OpKernelContext;
class Tensor;
class TensorBuffer;
class TensorCApi;
class TensorInterface;
class TensorCord;
class TensorDescription;
class TensorProto;
class Var;
namespace batch_util {
Status CopyElementToSlice(Tensor element, Tensor* parent, int64_t index);
Status CopySliceToElement(const Tensor& parent, Tensor* element, int64_t index);
Status MaybeMoveSliceToElement(Tensor* parent, Tensor* element, int64_t index);
Status CopyContiguousSlices(const Tensor& src, int64_t src_offset,
int64_t dst_offset, int64_t num_slices,
Tensor* dst);
} // namespace batch_util
/// @ingroup core
/// Interface to access the raw ref-counted data buffer.
class TensorBuffer : public core::RefCounted {
public:
explicit TensorBuffer(void* data_ptr) : data_(data_ptr) {}
~TensorBuffer() override {}
/// \brief data() points to a memory region of size() bytes.
///
/// NOTE(mrry): The `data()` method is not virtual for performance reasons.
/// It can be called multiple times when the contents of a `Tensor` are
/// accessed, and so making it non-virtual allows the body to be inlined.
void* data() const { return data_; }
/// \brief Size (in bytes) of the buffer.
virtual size_t size() const = 0;
/// \brief If this TensorBuffer is sub-buffer of another TensorBuffer,
/// returns that TensorBuffer. Otherwise, returns this.
virtual TensorBuffer* root_buffer() = 0;
/// \brief Fills metadata about the allocation into the proto.
virtual void FillAllocationDescription(
AllocationDescription* proto) const = 0;
virtual bool GetAllocatedBytes(size_t* out_bytes) const;
/// \brief Helper method to reinterpret the buffer as an array of `T`.
template
T* base() const {
return reinterpret_cast(data());
}
/// \brief Whether this TensorBuffer owns the underlying memory.
virtual bool OwnsMemory() const { return true; }
/// \brief The type of the underlying memory.
virtual AllocatorMemoryType GetMemoryType() const {
return AllocatorMemoryType::kUnknown;
}
private:
void* const data_;
};
/// Represents an n-dimensional array of values.
class Tensor {
public:
/// \brief Creates a 1-dimensional, 0-element float tensor.
///
/// The returned Tensor is not a scalar (shape {}), but is instead
/// an empty one-dimensional Tensor (shape {0}, NumElements() ==
/// 0). Since it has no elements, it does not need to be assigned a
/// value and is initialized by default (IsInitialized() is
/// true). If this is undesirable, consider creating a one-element
/// scalar which does require initialization:
///
/// ```c++
///
/// Tensor(DT_FLOAT, TensorShape({}))
///
/// ```
Tensor();
/// \brief Creates a Tensor of the given `type` and `shape`. If
/// LogMemory::IsEnabled() the allocation is logged as coming from
/// an unknown kernel and step. Calling the Tensor constructor
/// directly from within an Op is deprecated: use the
/// OpKernelConstruction/OpKernelContext allocate_* methods to
/// allocate a new tensor, which record the kernel and step.
///
/// The underlying buffer is allocated using a `CPUAllocator`.
Tensor(DataType type, const TensorShape& shape);
/// \brief Creates a tensor with the input `type` and `shape`, using
/// the allocator `a` to allocate the underlying buffer. If
/// LogMemory::IsEnabled() the allocation is logged as coming from
/// an unknown kernel and step. Calling the Tensor constructor
/// directly from within an Op is deprecated: use the
/// OpKernelConstruction/OpKernelContext allocate_* methods to
/// allocate a new tensor, which record the kernel and step.
///
/// `a` must outlive the lifetime of this Tensor.
Tensor(Allocator* a, DataType type, const TensorShape& shape);
/// \brief Creates a tensor with the input `type` and `shape`, using
/// the allocator `a` and the specified "allocation_attr" to
/// allocate the underlying buffer. If the kernel and step are known
/// allocation_attr.allocation_will_be_logged should be set to true
/// and LogMemory::RecordTensorAllocation should be called after the
/// tensor is constructed. Calling the Tensor constructor directly
/// from within an Op is deprecated: use the
/// OpKernelConstruction/OpKernelContext allocate_* methods to
/// allocate a new tensor, which record the kernel and step.
///
/// `a` must outlive the lifetime of this Tensor.
Tensor(Allocator* a, DataType type, const TensorShape& shape,
const AllocationAttributes& allocation_attr);
/// \brief Creates a tensor with the input datatype, shape and buf.
///
/// Acquires a ref on buf that belongs to this Tensor.
Tensor(DataType type, const TensorShape& shape, TensorBuffer* buf);
/// \brief Creates a tensor with the input datatype, shape and buf.
///
/// Takes an ownership of the bufffer from the reference counted pointer.
Tensor(DataType type, TensorShape shape, core::RefCountPtr buf);
/// \brief Creates an empty Tensor of the given data type.
///
/// Like Tensor(), returns a 1-dimensional, 0-element Tensor with
/// IsInitialized() returning True. See the Tensor() documentation
/// for details.
explicit Tensor(DataType type);
/// \brief Initializes a tensor with the input `type` and `shape`, or returns
/// an error and leaves `out_tensor` unmodified. This factory method should be
/// used instead of the corresponding constructor if calling code cannot
/// validate that the `DataType` is valid and supported.
///
/// The underlying buffer is allocated using a `CPUAllocator`.
static Status BuildTensor(DataType type, const TensorShape& shape,
Tensor* out_tensor);
private:
// A tag type for selecting the `Tensor` constructor overload that creates a
// scalar tensor in host memory.
struct host_scalar_tag {};
class HostScalarTensorBufferBase;
template
struct ValueAndTensorBuffer;
// Creates a tensor with the given scalar `value` in CPU memory.
template
Tensor(T value, host_scalar_tag tag);
public:
// A series of specialized constructors for scalar tensors in host memory.
//
// NOTE: The `Variant` host-scalar constructor is not defined, because Variant
// is implicitly constructible from many different types, and this causes
// ambiguities with some compilers.
explicit Tensor(float scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(double scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(int32_t scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(uint32 scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(uint16 scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(uint8 scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(int16_t scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(int8_t scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(tstring scalar_value)
: Tensor(std::move(scalar_value), host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(complex64 scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(complex128 scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(int64_t scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(uint64 scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(bool scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(qint8 scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(quint8 scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(qint16 scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(quint16 scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(qint32 scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(bfloat16 scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(Eigen::half scalar_value)
: Tensor(scalar_value, host_scalar_tag{}) {}
explicit Tensor(ResourceHandle scalar_value)
: Tensor(std::move(scalar_value), host_scalar_tag{}) {}
// NOTE: The `const char*` host-scalar constructor is provided as a
// convenience because otherwise passing a string literal would surprisingly
// construct a DT_BOOL tensor.
explicit Tensor(const char* scalar_value)
: Tensor(tstring(scalar_value), host_scalar_tag{}) {}
/// Copy constructor.
Tensor(const Tensor& other);
/// \brief Move constructor. After this call, is safely destructible
/// can be assigned to, and IsInitialized() can be called and will return
/// false. Other calls on (e.g. shape manipulation) are not valid.
Tensor(Tensor&& other);
// Explicitly delete constructor that take a pointer (except char*)
// so that the pointer doesn't get implicitly cast to bool.
template ::value,
T>::type* = nullptr>
explicit Tensor(T* t) = delete;
~Tensor();
// I/O operators.
friend std::ostream& // NOLINT: iosfwd
operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Tensor& tensor);
/// Returns the data type.
DataType dtype() const { return shape_.data_type(); }
/// Returns the shape of the tensor.
const TensorShape& shape() const { return shape_; }
/// \brief Convenience accessor for the tensor shape.
///
/// For all shape accessors, see comments for relevant methods of
/// `TensorShape` in `tensor_shape.h`.
int dims() const { return shape().dims(); }
/// Convenience accessor for the tensor shape.
int64_t dim_size(int d) const { return shape().dim_size(d); }
/// Convenience accessor for the tensor shape.
int64_t NumElements() const { return shape().num_elements(); }
bool IsSameSize(const Tensor& b) const {
return shape().IsSameSize(b.shape());
}
// True iff the two tensors use the same underlying refcounted storage
bool SharesBufferWith(const Tensor& b) const;
/// \brief If necessary, has this Tensor been initialized?
///
/// Zero-element Tensors are always considered initialized, even if they
/// have never been assigned to and do not have any memory allocated.
bool IsInitialized() const;
/// Returns the estimated memory usage of this tensor.
size_t TotalBytes() const;
// Returns the size of allocated memory for this tensor.
size_t AllocatedBytes() const;
/// Returns true iff this tensor is aligned.
bool IsAligned() const {
#if EIGEN_MAX_ALIGN_BYTES == 0
return true;
#else
void* ptr = base();
return dtype() == DT_STRING || NumElements() == 0 ||
(reinterpret_cast(ptr) % EIGEN_MAX_ALIGN_BYTES == 0);
#endif
}
/// Assign operator. This tensor shares other's underlying storage.
Tensor& operator=(const Tensor& other) {
CopyFromInternal(other, other.shape());
return *this;
}
/// Move operator. See move constructor for details.
Tensor& operator=(Tensor&& other);
/// \brief Copy the other tensor into this tensor and reshape it.
///
/// This tensor shares other's underlying storage. Returns `true`
/// iff `other.shape()` has the same number of elements of the given
/// `shape`.
bool CopyFrom(const Tensor& other,
const TensorShape& shape) TF_MUST_USE_RESULT {
if (other.NumElements() != shape.num_elements()) return false;
CopyFromInternal(other, shape);
return true;
}
/// \brief Slice this tensor along the 1st dimension.
/// I.e., the returned tensor satisfies
/// returned[i, ...] == this[dim0_start + i, ...].
/// The returned tensor shares the underlying tensor buffer with this
/// tensor.
///
/// NOTE: The returned tensor may not satisfy the same alignment
/// requirement as this tensor depending on the shape. The caller
/// must check the returned tensor's alignment before calling certain
/// methods that have alignment requirement (e.g., `flat()`, `tensor()`).
///
/// NOTE: When fed with an N-dimensional tensor, this method returns a tensor
/// also with N dimensions. If you want to select a sub tensor, see SubSlice.
///
/// REQUIRES: `dims()` >= 1
/// REQUIRES: `0 <= dim0_start <= dim0_limit <= dim_size(0)`
Tensor Slice(int64_t dim0_start, int64_t dim0_limit) const;
/// \brief Select a subslice from this tensor along the 1st dimension.
///
/// When fed with an N-dimensional tensor, this method returns a tensor with
/// N-1 dimensions, where the returned tensor is a subslice of the input
/// tensor along the first dimension. The N-1 dimensions of the returned
/// tensor are the last N-1 dimensions of the input tensor.
///
/// NOTE: The returned tensor may not satisfy the same alignment
/// requirement as this tensor depending on the shape. The caller
/// must check the returned tensor's alignment before calling certain
/// methods that have alignment requirement (e.g., `flat()`, `tensor()`).
///
/// REQUIRES: `dims()` >= 1
/// REQUIRES: `0 <= index < dim_size(0)`
Tensor SubSlice(int64_t index) const;
/// \brief Parse `other` and construct the tensor.
/// Returns `true` iff the parsing succeeds. If the parsing fails,
/// the state of `*this` is unchanged.
bool FromProto(const TensorProto& other) TF_MUST_USE_RESULT;
bool FromProto(Allocator* a, const TensorProto& other) TF_MUST_USE_RESULT;
/// \brief Fills in `proto` with `*this` tensor's content.
///
/// `AsProtoField()` fills in the repeated field for `proto.dtype()`, while
/// `AsProtoTensorContent()` encodes the content in `proto.tensor_content()`
/// in a compact form.
void AsProtoField(TensorProto* proto) const;
void AsProtoTensorContent(TensorProto* proto) const;
/// \brief Return the tensor data as an `Eigen::Tensor` with the type and
/// sizes of this `Tensor`.
///
/// Use these methods when you know the data type and the number of
/// dimensions of the Tensor and you want an `Eigen::Tensor`
/// automatically sized to the `Tensor` sizes. The implementation check
/// fails if either type or sizes mismatch.
///
/// Example:
///
/// ```c++
///
/// typedef float T;
/// Tensor my_mat(...built with Shape{rows: 3, cols: 5}...);
/// auto mat = my_mat.matrix(); // 2D Eigen::Tensor, 3 x 5.
/// auto mat = my_mat.tensor(); // 2D Eigen::Tensor, 3 x 5.
/// auto vec = my_mat.vec(); // CHECK fails as my_mat is 2D.
/// auto vec = my_mat.tensor(); // CHECK fails as my_mat is 2D.
/// auto mat = my_mat.matrix();// CHECK fails as type mismatch.
///
/// ```
template
typename TTypes::Vec vec() {
return tensor();
}
template
typename TTypes::Matrix matrix() {
return tensor();
}
template
typename TTypes::Tensor tensor() TF_ATTRIBUTE_NOINLINE;
/// \brief Return the tensor data to an `Eigen::Tensor` with the
/// same size but a bitwise cast to the specified dtype `T`.
///
/// Using a bitcast is useful for move and copy operations.
/// NOTE: this is the same as `tensor()` except a bitcast is allowed.
template
typename TTypes::Tensor bit_casted_tensor();
/// \brief Return the tensor data to an `Eigen::Tensor` with the
/// last dimension elements converted into single elements of a larger type.
///
/// For example, this is useful for kernels that can treat NCHW_VECT_C int8
/// tensors as NCHW int32 tensors. The sizeof(T) should equal the size of
/// the original element type * num elements in the original last dimension.
/// NDIMS should be 1 less than the original number of dimensions.
template
typename TTypes::Tensor reinterpret_last_dimension();
/// \brief Return the tensor data as an `Eigen::Tensor` of the data type and a
/// specified shape.
///
/// These methods allow you to access the data with the dimensions
/// and sizes of your choice. You do not need to know the number of
/// dimensions of the Tensor to call them. However, they `CHECK` that
/// the type matches and the dimensions requested creates an
/// `Eigen::Tensor` with the same number of elements as the tensor.
///
/// Example:
///
/// ```c++
///
/// typedef float T;
/// Tensor my_ten(...built with Shape{planes: 4, rows: 3, cols: 5}...);
/// // 1D Eigen::Tensor, size 60:
/// auto flat = my_ten.flat();
/// // 2D Eigen::Tensor 12 x 5:
/// auto inner = my_ten.flat_inner_dims();
/// // 2D Eigen::Tensor 4 x 15:
/// auto outer = my_ten.shaped({4, 15});
/// // CHECK fails, bad num elements:
/// auto outer = my_ten.shaped({4, 8});
/// // 3D Eigen::Tensor 6 x 5 x 2:
/// auto weird = my_ten.shaped({6, 5, 2});
/// // CHECK fails, type mismatch:
/// auto bad = my_ten.flat();
///
/// ```
template
typename TTypes::Flat flat();
template
typename TTypes::UnalignedFlat unaligned_flat() {
return unaligned_shaped({NumElements()});
}
/// Returns the data as an Eigen::Tensor with NDIMS dimensions, collapsing all
/// Tensor dimensions but the last NDIMS-1 into the first dimension of the
/// result. If NDIMS > dims() then leading dimensions of size 1 will be
/// added to make the output rank NDIMS.
template
typename TTypes::Tensor flat_inner_dims();
/// Returns the data as an Eigen::Tensor with NDIMS dimensions, collapsing all
/// Tensor dimensions but the first NDIMS-1 into the last dimension of the
/// result. If NDIMS > dims() then trailing dimensions of size 1 will be
/// added to make the output rank NDIMS.
template
typename TTypes::Tensor flat_outer_dims();
/// Returns the data as an Eigen::Tensor with NDIMS dimensions, collapsing the
/// first 'begin' Tensor dimensions into the first dimension of the result and
/// the Tensor dimensions of the last dims() - 'begin' - NDIMS into the last
/// dimension of the result. If 'begin' < 0 then the |'begin'| leading
/// dimensions of size 1 will be added. If 'begin' + NDIMS > dims() then
/// 'begin' + NDIMS - dims() trailing dimensions of size 1 will be added.
template
typename TTypes::Tensor flat_inner_outer_dims(int64_t begin);
template
typename TTypes::Tensor shaped(gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes);
/// \brief Return the tensor data to an `Eigen::Tensor` with the new
/// shape specified in `new_sizes` and cast to a new dtype `T`.
///
/// Using a bitcast is useful for move and copy operations.
/// The allowed bitcast is the only difference from `shaped()`.
template
typename TTypes::Tensor bit_casted_shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes);
template
typename TTypes::UnalignedTensor unaligned_shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes);
/// \brief Return the Tensor data as a `TensorMap` of fixed size 1:
/// `TensorMap>`.
/// Using `scalar()` allows the compiler to perform optimizations as
/// the size of the tensor is known at compile time.
template
typename TTypes::Scalar scalar();
/// Const versions of all the methods above.
template
typename TTypes::ConstVec vec() const {
return tensor();
}
template
typename TTypes::ConstMatrix matrix() const {
return tensor();
}
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor tensor() const TF_ATTRIBUTE_NOINLINE;
/// \brief Return the tensor data to an `Eigen::Tensor` with the
/// same size but a bitwise cast to the specified dtype `T`.
///
/// Using a bitcast is useful for move and copy operations.
/// NOTE: this is the same as `tensor()` except a bitcast is allowed.
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor bit_casted_tensor() const;
/// \brief Return the tensor data to an `Eigen::Tensor` with the
/// last dimension elements converted into single elements of a larger type.
///
/// For example, this is useful for kernels that can treat NCHW_VECT_C int8
/// tensors as NCHW int32 tensors. The sizeof(T) should equal the size of
/// the original element type * num elements in the original last dimension.
/// NDIMS should be 1 less than the original number of dimensions.
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor reinterpret_last_dimension() const;
template
typename TTypes::ConstFlat flat() const;
template
typename TTypes::UnalignedConstFlat unaligned_flat() const {
return unaligned_shaped({NumElements()});
}
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes) const;
/// \brief Return the tensor data to an `Eigen::Tensor` with the new
/// shape specified in `new_sizes` and cast to a new dtype `T`.
///
/// Using a bitcast is useful for move and copy operations.
/// The allowed bitcast is the only difference from `shaped()`.
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor bit_casted_shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes) const;
template
typename TTypes::UnalignedConstTensor unaligned_shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes) const;
template
typename TTypes::ConstScalar scalar() const;
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor flat_inner_dims() const;
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor flat_outer_dims() const;
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor flat_inner_outer_dims(
int64_t begin) const;
/// Render the first `max_entries` values in `*this` into a string.
std::string SummarizeValue(int64_t max_entries, bool print_v2 = false) const;
/// A human-readable summary of the tensor suitable for debugging.
// `num_values` is the number of actual data values in the tensor
// included in the message. If the tensor might be resident in
// GPU/TPU memory use DeviceSafeDebugString instead.
std::string DebugString(int num_values) const;
std::string DebugString() const { return DebugString(3); }
// Variant of DebugString() that should be used for possibly non-CPU tensors.
// If the tensor is not resident on CPU, we can't read its values as
// DebugString() does.
std::string DeviceSafeDebugString() const;
/// Fill in the `TensorDescription` proto with metadata about the
/// tensor that is useful for monitoring and debugging.
void FillDescription(TensorDescription* description) const;
/// \brief Returns a `StringPiece` mapping the current tensor's buffer.
///
/// The returned `StringPiece` may point to memory location on devices
/// that the CPU cannot address directly.
///
/// NOTE: The underlying tensor buffer is refcounted, so the lifetime
/// of the contents mapped by the `StringPiece` matches the lifetime of
/// the buffer; callers should arrange to make sure the buffer does
/// not get destroyed while the `StringPiece` is still used.
///
/// REQUIRES: `DataTypeCanUseMemcpy(dtype())`.
StringPiece tensor_data() const;
void* data() const;
/// Copy the other tensor into this tensor, reshape it and reinterpret the
/// buffer's datatype. If an ok Status is returned, the two tensors now share
/// the same underlying storage.
///
/// This call requires that the `other` tensor and the given type and shape
/// are "compatible" (i.e. they occupy the same number of bytes).
///
/// Specifically:
///
/// shape.num_elements() * DataTypeSize(type)
///
/// must equal
///
/// other.num_elements() * DataTypeSize(other.dtype())
///
/// In addition, this function requires:
/// * DataTypeSize(other.dtype()) != 0
/// * DataTypeSize(type) != 0
///
/// If any of the requirements are not met, errors::InvalidArgument is
/// returned.
Status BitcastFrom(const Tensor& other, DataType dtype,
const TensorShape& shape);
/// Like BitcastFrom, but CHECK fails if any preconditions are not met.
///
/// Deprecated. Use BitcastFrom instead and check the returned Status.
void UnsafeCopyFromInternal(const Tensor& other, DataType dtype,
const TensorShape& shape) {
TF_CHECK_OK(BitcastFrom(other, dtype, shape));
}
// Returns true if the refcount on buf_ and any possible underlying root
// buffer is one.
bool RefCountIsOne() const;
// Experimental. Returns the refcount on buf_ if it points to a regular
// TensorBuffer. If buf_ points to a SubBuffer, returns -1.
int RefCount() const;
// Returns the type of the underlying memory.
AllocatorMemoryType GetMemoryType() const { return buf_->GetMemoryType(); }
private:
void CheckType(DataType expected_dtype) const;
void CheckTypeAndIsAligned(DataType expected_dtype) const;
void CheckIsAlignedAndSingleElement() const;
void set_dtype(DataType t) { shape_.set_data_type(t); }
// TensorShape's InlineVector.
static gtl::InlinedVector ComputeFlatInnerDims(
gtl::ArraySlice orig, int64_t num_out_dims);
static gtl::InlinedVector ComputeFlatOuterDims(
gtl::ArraySlice orig, int64_t num_out_dims);
TensorShape shape_;
TensorBuffer* buf_;
friend class DMAHelper; // For access to buf_.
friend class TensorCApi; // For access to buf_.
friend class TensorCord; // For access to buf_.
friend class TensorReference; // For access to buf_.
friend class VariableOp; // For access to set_shape.
friend class AutoReloadVariableOp; // For access to set_shape.
friend class TensorTestHelper; // For access to set_shape.
friend class TensorInterface; // For access to set_shape.
friend class CastOpBase; // For access to set_dtype.
friend class ScopedAllocator; // For access to buf_.
friend class PjRtTensorBufferUtil; // For access to buf_.
friend Status batch_util::CopyElementToSlice(
Tensor element, Tensor* parent,
int64_t index); // For access to base().
friend Status batch_util::CopySliceToElement(
const Tensor& parent, Tensor* element,
int64_t index); // For access to base().
friend Status batch_util::MaybeMoveSliceToElement(
Tensor* parent, Tensor* element,
int64_t index); // For access to base().
friend Status batch_util::CopyContiguousSlices(
const Tensor& src, int64_t src_offset, int64_t dst_offset,
int64_t num_slices,
Tensor* dst); // For access to base().
bool CanUseDMA() const;
// Only needed by variable op to set the shape of an uninitialized
// Tensor.
// TODO: Remove this when we have a better story for detecting
// uninitialized tensors.
void set_shape(const TensorShape& shape) {
DataType dt = dtype();
shape_ = shape;
set_dtype(dt);
}
inline void CopyFromInternal(const Tensor& other, const TensorShape& shape) {
DCHECK_EQ(shape.num_elements(), other.NumElements());
// Data type will be overwritten if this == &other, since dtype is part of
// shape.
DataType other_dtype = other.dtype();
shape_ = shape;
set_dtype(other_dtype);
if (buf_ != other.buf_) {
if (buf_) buf_->Unref();
buf_ = other.buf_;
if (buf_) buf_->Ref();
}
}
template
T* base() const;
template
void FillDimsAndValidateCompatibleShape(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes,
Eigen::array* dims) const;
template
void FillDimsAndValidateCompatibleShape(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes,
Eigen::array* dims) const;
};
// Implementation details
// START_SKIP_DOXYGEN
template
T* Tensor::base() const {
return buf_ == nullptr ? nullptr : buf_->base();
}
// This routine is defined out of line for code-space savings
template
typename TTypes::Tensor Tensor::tensor() {
CheckTypeAndIsAligned(DataTypeToEnum::v());
return typename TTypes::Tensor(base(),
shape().AsEigenDSizes());
}
// This routine is defined out of line for code-space savings
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor Tensor::tensor() const {
CheckTypeAndIsAligned(DataTypeToEnum::v());
return typename TTypes::ConstTensor(base(),
shape().AsEigenDSizes());
}
template
typename TTypes::Tensor Tensor::bit_casted_tensor() {
CHECK(IsAligned());
return typename TTypes::Tensor(base(),
shape().AsEigenDSizes());
}
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor Tensor::bit_casted_tensor() const {
CHECK(IsAligned());
return typename TTypes::ConstTensor(base(),
shape().AsEigenDSizes());
}
template
typename TTypes::Tensor Tensor::reinterpret_last_dimension() {
if (NDIMS == dims()) {
return tensor();
}
CHECK(IsAligned());
CHECK_EQ(static_cast(NDIMS), dims() - 1);
CHECK_EQ(static_cast(sizeof(T)),
shape_.dim_sizes()[NDIMS] * DataTypeSize(dtype()));
Eigen::array dims;
for (int d = 0; d < NDIMS; ++d) {
dims[d] = shape_.dim_sizes()[d];
}
return typename TTypes::Tensor(base(), dims);
}
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor Tensor::reinterpret_last_dimension()
const {
if (NDIMS == dims()) {
return tensor();
}
CHECK(IsAligned());
CHECK_EQ(static_cast(NDIMS), dims() - 1);
CHECK_EQ(static_cast(sizeof(T)),
shape_.dim_sizes()[NDIMS] * DataTypeSize(dtype()));
Eigen::array dims;
for (int d = 0; d < NDIMS; ++d) {
dims[d] = shape_.dim_sizes()[d];
}
return typename TTypes::ConstTensor(base(), dims);
}
template
void Tensor::FillDimsAndValidateCompatibleShape(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes,
Eigen::array* dims) const {
CHECK_EQ(NDIMS, new_sizes.size());
int64_t new_num_elements = 1;
for (size_t d = 0; d < NDIMS; d++) {
new_num_elements *= new_sizes[d];
(*dims)[d] = new_sizes[d];
}
CHECK_EQ(new_num_elements, NumElements());
}
template
void Tensor::FillDimsAndValidateCompatibleShape(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes,
Eigen::array* dims) const {
CHECK_EQ(NDIMS, new_sizes.size());
int64_t new_num_elements = 1;
for (size_t d = 0; d < NDIMS; d++) {
new_num_elements *= new_sizes[d];
(*dims)[d] = new_sizes[d];
}
const int element_size = DataTypeSize(BaseType(dtype()));
if (element_size > 0) {
CHECK_EQ(new_num_elements * static_cast(sizeof(T)),
NumElements() * element_size);
} else {
// DataTypeSize() returns 0 for some data types. In this case, assume that T
// has the same size as the buffer type.
// NOTE: If we can be sure that DataTypeSize() does not return 0 for all POD
// types, then we should check DataTypeToEnum::v() == dtype(). Or simply
// check if `element_size > 0` to err when bit cast is attempted on Tensor
// of unknown data type size.
CHECK_EQ(new_num_elements, NumElements());
}
}
template
typename TTypes::Flat Tensor::flat() {
// Equivalent to 'return shaped({NumElements()});'
CheckTypeAndIsAligned(DataTypeToEnum::v());
Eigen::array dims;
dims[0] = NumElements();
return typename TTypes::Tensor(base(), dims);
}
template
typename TTypes::ConstFlat Tensor::flat() const {
// Equuivalent to 'return shaped({NumElements()});'
CheckTypeAndIsAligned(DataTypeToEnum::v());
Eigen::array dims;
dims[0] = NumElements();
return typename TTypes::ConstTensor(base(), dims);
}
template
typename TTypes::Tensor Tensor::shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes) {
CheckTypeAndIsAligned(DataTypeToEnum::v());
Eigen::array dims;
FillDimsAndValidateCompatibleShape(new_sizes, &dims);
return typename TTypes::Tensor(base(), dims);
}
template
typename TTypes::Tensor Tensor::bit_casted_shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes) {
CHECK(IsAligned());
Eigen::array dims;
FillDimsAndValidateCompatibleShape(new_sizes, &dims);
return typename TTypes::Tensor(base(), dims);
}
template
typename TTypes::UnalignedTensor Tensor::unaligned_shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes) {
CheckType(DataTypeToEnum::v());
Eigen::array dims;
FillDimsAndValidateCompatibleShape(new_sizes, &dims);
return typename TTypes::UnalignedTensor(base(), dims);
}
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor Tensor::shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes) const {
CheckType(DataTypeToEnum::v());
CHECK(IsAligned()) << "ptr = " << base();
Eigen::array dims;
FillDimsAndValidateCompatibleShape(new_sizes, &dims);
return typename TTypes::ConstTensor(base(), dims);
}
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor Tensor::bit_casted_shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes) const {
CHECK(IsAligned());
Eigen::array dims;
FillDimsAndValidateCompatibleShape(new_sizes, &dims);
return typename TTypes::ConstTensor(base(), dims);
}
template
typename TTypes::UnalignedConstTensor Tensor::unaligned_shaped(
gtl::ArraySlice new_sizes) const {
CheckType(DataTypeToEnum::v());
Eigen::array dims;
FillDimsAndValidateCompatibleShape(new_sizes, &dims);
return typename TTypes::UnalignedConstTensor(base(), dims);
}
template
typename TTypes::Scalar Tensor::scalar() {
static_assert(
!std::is_same::value,
"std::string is no longer a scalar type, use tensorflow::tstring");
CheckIsAlignedAndSingleElement();
return typename TTypes::Scalar(base());
}
template
typename TTypes::ConstScalar Tensor::scalar() const {
static_assert(
!std::is_same::value,
"std::string is no longer a scalar type, use tensorflow::tstring");
CheckIsAlignedAndSingleElement();
return typename TTypes::ConstScalar(base());
}
template
typename TTypes::Tensor Tensor::flat_inner_dims() {
return shaped(ComputeFlatInnerDims(shape_.dim_sizes(), NDIMS));
}
template
typename TTypes::Tensor Tensor::flat_outer_dims() {
return shaped(ComputeFlatOuterDims(shape_.dim_sizes(), NDIMS));
}
template
typename TTypes::Tensor Tensor::flat_inner_outer_dims(int64_t begin) {
gtl::InlinedVector flat_outer =
ComputeFlatOuterDims(shape_.dim_sizes(), begin + NDIMS);
return shaped(ComputeFlatInnerDims(flat_outer, NDIMS));
}
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor Tensor::flat_inner_dims() const {
return shaped(ComputeFlatInnerDims(shape_.dim_sizes(), NDIMS));
}
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor Tensor::flat_outer_dims() const {
return shaped(ComputeFlatOuterDims(shape_.dim_sizes(), NDIMS));
}
template
typename TTypes::ConstTensor Tensor::flat_inner_outer_dims(
int64_t begin) const {
gtl::InlinedVector