spring cloud——01(注册中心、负载均衡)
目录标题
-
- 一、spring cloud 面试题
- 二、什么是微服务
- 三、微服务架构的优缺点
-
- 1、优点
- 2、缺点
- 四、spring cloud微服务技术栈
- 五、导入spring cloud 公共配置
- 六、注册中心
-
- 1、eureka注册中心
-
- 1.1、单机版——两步
- 1.2、集群版——两步(相比单机版只需要修改yml里面的配置即可)
- 1.3、服务提供者(注册到注册中心提供服务)
- 1.4、服务消费者
- 1.5、获取eureka驻注册中心的信息
- 1.6、eureka的自我保护机制
- 1.7、eureka心跳
- 2、zookeeper注册中心
-
- 2.1、将服务提供者注册到zookeeper
- 2.2、服务消费者
- 七、CAP
- 八、负载均衡
-
- 1、Ribben
-
- 1)、 导入pom
- 2)、配置yml
- 3)、 使用默认的轮询算法
- 4)、轮询算法实现原理
- 5)、轮询算法源码解析。
- 6)、修改默认的轮询算法(指定负载均衡算法)
- 7)、 自定义轮询算法
- 8)、其他负载均衡实现原理
- 2、feign与openfeign
-
- 2.1、导入pom
- 2.2、配置yml
- 2.3、开启openfeign
- 2.4、配置opnefeign调用接口
- 2.5、使用
- 2.6、消费端调用超时设置
- 2.7、日志
- 2.8、使用自定义的负载均衡算法
一、spring cloud 面试题
- 什么是微服务
微服务就是将整个应用划分为一小个个组件,
微服务化的核心就是将传统的一站式应用,根据业务拆分成一个一个的服务,彻底地去耦合,每一个微服务提供单个业务功能的服务,一个服务做一件事。
从技术角度看就是一种小而独立的处理过程,类似进程概念,能够自行单独启动或销毁,拥有自己独立的数据库。
- 微服务之间是如何独立通讯的
Dubbo通过rpc、spring cloud 通过restful(http)
RPC与HTTP的区别
既然两种方式都可以实现远程调用,我们该如何选择呢?
-
速度来看,RPC要比http更快,虽然底层都是TCP,但是http协议的信息往往比较臃肿
-
难度来看,RPC实现较为复杂,http相对比较简单
-
灵活性来看,http更胜一筹,因为它不关心实现细节,跨平台、跨语言。
因此,两者都有不同的使用场景: -
如果对效率要求更高,并且开发过程使用统一的技术栈,那么用RPC还是不错的。
-
如果需要更加灵活,跨语言、跨平台,显然http更合适
那么我们该怎么选择呢?
微服务,更加强调的是独立、自治、灵活。而RPC方式的限制较多,因此微服务框架中,一般都会采用基于Http的Rest风格服务。
-
spring cloud 与 Dubbo有那些区别
-
spring boot 和spring cloud,谈谈你的理解
-
什么是服务熔断?什么是服务降级
-
微服务的优缺点分别是什么?说一下你在项目开发中碰到的坑
-
微服务技术栈有哪些?
-
eureka和zookerper都可以提供服务注册与发现的功能,他们有什么区别
eurka高可用、zookeeper高性能
二、什么是微服务
微服务就是一个个的个体,每个个体具有自己独立的功能,具有高内聚性。一个大型的应用可以划分为多个微服务。spring boot 用来开发一个个微服务,而spring cloud 是微服务架构的一套解决方案。。在spring cloud中微服务通过http restful api(B/S)进行通讯,Dubbo通过RPC(C/S)/进行通讯。
三、微服务架构的优缺点
1、优点
- 易于开发和维护
- 单个服务启动快
- 技术栈不受限制
- 易扩展
- 高可用
2、缺点
- 部署困难
- 系统理解性难,系统复杂性大
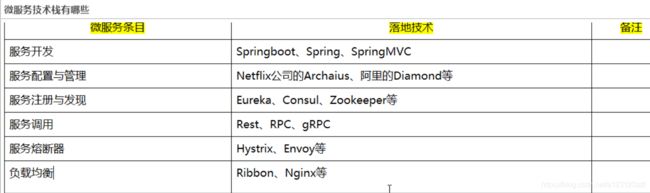
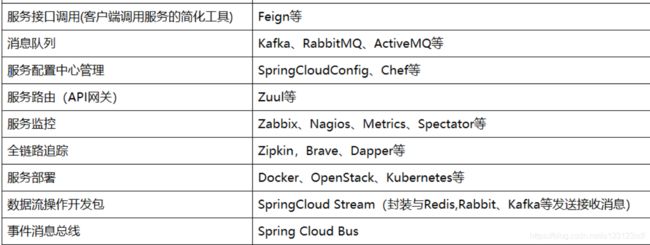
四、spring cloud微服务技术栈
五、导入spring cloud 公共配置
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8maven.compiler.target>
<junit.version>4.12junit.version>
<log4j.version>1.2.17log4j.version>
<lombok.version>1.18.16lombok.version>
<mysql.version>5.1.47mysql.version>
<druid.version>1.1.9druid.version>
<mybatis.spring.boot.version>1.3.0mybatis.spring.boot.version>
properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependenciesartifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASEversion>
<type>pomtype>
<scope>importscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependenciesartifactId>
<version>Hoxton.SR1version>
<type>pomtype>
<scope>importscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependenciesartifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASEversion>
<type>pomtype>
<scope>importscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>${mysql.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>${druid.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>${mybatis.spring.boot.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>${junit.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4jartifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}version>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
dependencies>
dependencyManagement>
六、注册中心
1、eureka注册中心
eureka文章推荐观看讲得很清楚
导入配置:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-serverartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId>
dependency>
1.1、单机版——两步
- 开启Eureka注册中心
package com.lihua.springcloud;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer //开启eureka(服务端的)服务
public class EurekaServerMain03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerMain03.class,args);
}
}
- 配置yml
server:
port: 7001
spring:
application:
name: eureka-service #这个是微服务的名字,如果名字相同那么Eureka注册中心会认为是有相同功能的微服务,把他们组合成一个集群
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost #eureka服务器的ip地址
# lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 3 # 单位是秒,默认30秒。此客户端发送心跳的频率——Atime
# lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 9 #单位是秒,默认90秒,表示eureka server在收到此client上次心跳之后,间隔多久没有收到,就摘除此服务。——Btime
client:
register-with-eureka: false #是否向注册中心注册自己——搭建eureka集群时需要打开(true为打开),不然集群之间不能相互发现
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
# defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:7002/eureka,http://192.168.8.66:7003/eureka #集群版
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka # (单机版)
server:
enable-self-preservation: true #是否关闭自我保护(true开启),(开启后即使检测到微服务短时间内没有心跳,也不会立刻将微服务的注册信息删除。因为eureka会认为可能是发生了网络故障、网络延迟。如果关闭(false)后,检测到没有心跳就会立马剔除改微服务)
eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 2000 #设置自我保护时间(清理失效服务的时间间隔,单位:毫秒)————用于注册中心——————Ctime
# 对于Atime、Btime、Ctime这三个时间,,Atime必须小于Btime
- 直接启动
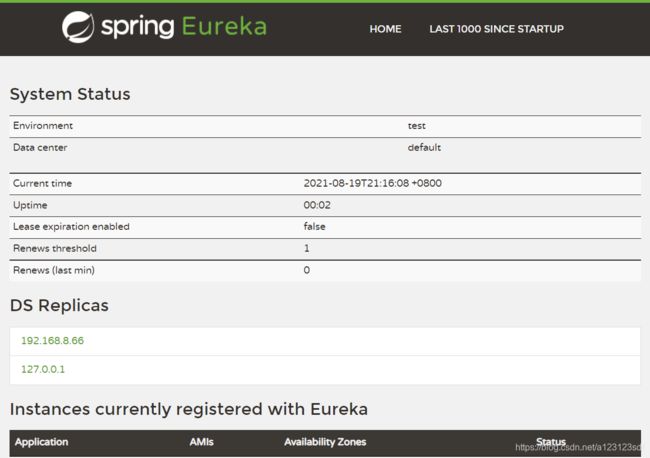
在浏览器输入http://127.0.0.1:7002 即可
1.2、集群版——两步(相比单机版只需要修改yml里面的配置即可)
- 开启Eureka注册中心
package com.lihua.springcloud;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer //开启eureka(服务端的)服务
public class EurekaServerMain03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerMain03.class,args);
}
}
- 配置yml
server:
port: 7001
spring:
application:
name: eureka-service #这个是微服务的名字,如果名字相同那么Eureka注册中心会认为是有相同功能的微服务,把他们组合成一个集群
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost #eureka服务器的ip地址
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 3 # 单位是秒,默认30秒。此客户端发送心跳的频率——Atime
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 9 #单位是秒,默认90秒,表示eureka server在收到此client上次心跳之后,间隔多久没有收到,就摘除此服务。——Btime
client:
register-with-eureka: true #是否向注册中心注册自己——搭建eureka集群时需要打开(true为打开),不然集群之间不能相互发现
fetch-registry: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:7002/eureka,http://192.168.8.66:7003/eureka #集群版,相互加入对方的地址
# defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka # (单机版)
server:
enable-self-preservation: true #是否关闭自我保护(true开启),(检测微服务心跳,当微服务不可用(指定时间没有心跳)就从注册中心
eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 2000 #设置自我保护时间(清理失效服务的时间间隔,单位:毫秒)————用于注册中心——————Ctime
# 对于Atime、Btime、Ctime这三个时间,,Atime必须小于Btime
- 直接启动
在浏览器输入http://127.0.0.1:7002 即可
1.3、服务提供者(注册到注册中心提供服务)
- 导入配置
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId>
dependency>
- 开启eureka客户中心
package com.lihua.springcloud;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
/*
* springboot启动类*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient //开启eureka Client端,向注册中心注册自己,并提供服务
@EnableDiscoveryClient //使用EnableDiscoverClient,对任何注册中心都适用。而EnableEurekaClient是为eureka服务的。
public class PaymentMain8001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain8001.class,args);
}
}
- 配置yml
server:
port: 8001
spring:
application:
name: cloud-payment-service #这个是微服务的名字,如果名字相同那么Eureka注册中心会认为是有相同功能的微服务,把他们组合成一个集群
eureka:
client:
#表示是否将自己注册进Eurekaserver默认为true。
register-with-eureka: true
#是否从EurekaServer抓取已有的注册信息,默认为true。单节点无所谓,集群必须设置为true才能配合ribbon使用负载均衡
fetchRegistry: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka,http://127.0.0.1:7002/eureka,http://192.168.8.66:7003/eureka #向那个注册中心进行注册
instance:
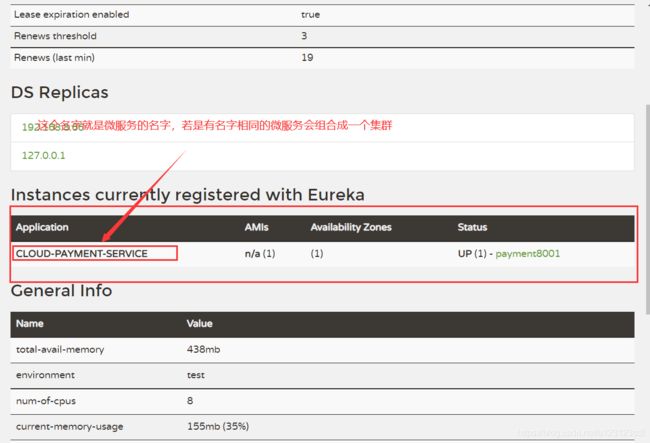
instance-id: payment8001 # 给EurekaUI界面的服务ip起一个别名
prefer-ip-address: true #鼠标停留时是否在左下角显示ip
lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 3 # 单位是秒,默认30秒。此客户端发送心跳的频率——Atime
lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 9 #单位是秒,默认90秒,表示eureka server在收到此client上次心跳之后,间隔多久没有收到,就摘除此服务。——Btime
1.4、服务消费者
服务消费者通过注册中心提供的统一API(如果是集群会根据负载均衡决定调用哪个哪个主机上的微服务)调用(使用)服务提供者提供的功能。
-
注册到eureka
将服务消费者注册到eureka的方式与服务提供者相识。不同的是服务消费者没有数据层(因为数据来说服务提供者) -
服务消费者如何通过注册中心调用服务提供者
- 单机版
对于单机版的其实不使用eureka也能实现。也就相当于前端直接调用后端的url。可以使用各种工具,通过http请求此接口
public static final String PAYMENT_URL = "http://localhost:8001"; 单机版
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/create")
public CommonResult<Payment> create(Payment payment){
return restTemplate.postForObject(PAYMENT_URL+"/payment/create",payment,CommonResult.class);
}
- 集群版
集群版需要负载均衡。因此我们需要eureka的注册中心帮我们选择请求具体哪个节点。
注意:这里还需要配置负载均衡。
// public static final String PAYMENT_URL = "http://localhost:8001"; 单机版
public static final String PAYMENT_URL = "http://CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE"; //集群版,注意:CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE 这个是微服务集群的名字。也就是在配置yml时指定的名字。
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/create")
public CommonResult<Payment> create(Payment payment){
return restTemplate.postForObject(PAYMENT_URL+"/payment/create",payment,CommonResult.class);
}
1.5、获取eureka驻注册中心的信息
开启自动获取注册信息
@EnableDiscoveryClient //开启注册中心,获取具体服务信息的功能
public class PaymentMain8001 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain8001.class,args);
}
}
//等价于@Autowired、获取注册中心里面服务的基本信息 ,(注意不要导错包)
@Resource
private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
@GetMapping("/discoveryClient")
public Object discovery(){
//获取eureka注册表的主机
List<String> services = discoveryClient.getServices();
for (String service : services) {
log.info("****service****"+service);
}
List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE");
for (ServiceInstance instance : instances) {
log.info("*****instance*****"+instance.getInstanceId()+"\t"+instance.getHost()+"\t"+instance.getServiceId());
}
return this.discoveryClient;
}
1.6、eureka的自我保护机制
此之外,Eureka还有一种自我保护机制|如果在15分钟内超过85%的节点都没有正常的心跳,那么Eureka就认为客户端与注册中心出现了网络故障。
eureka.client.healthcheck.enabled=true #是否关闭自我保护(true开启)
开启后即使检测到微服务短时间内没有心跳,也不会立刻将微服务的注册信息删除。因为eureka会认为可能是发生了网络故障、网络延迟。如果关闭(false)后,检测到没有心跳就会立马剔除改微服务。
关闭保护模式后,一般需要在服务端和客户端设置下面的属性(当然他们都有默认值)
server 服务端
# 设为false,关闭自我保护。默认是打开的。
eureka.server.enable-self-preservation=false
# 清理间隔(单位毫秒,默认是60*1000)
eureka.server.eviction-interval-timer-in-ms=4000
client 客户端
# 开启健康检查,默认是开启的
eureka.client.healthcheck.enabled=true
# 单位是秒,默认30秒。此客户端发送心跳的频率
eureka.instance.lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds=30
# 单位是秒,默认90秒,表示eureka server在收到此client上次心跳之后,间隔多久没有收到,就摘除此服务。
eureka.instance.lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds=10
1.7、eureka心跳
eureka心跳心跳是检测,微服务是否可用的标志。
# 单位是秒,默认30秒。此客户端发送心跳的频率
eureka.instance.lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds=30
# 单位是秒,默认90秒,表示eureka server在收到此client上次心跳之后,间隔多久没有收到,就摘除此服务。
eureka.instance.lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds=10
2、zookeeper注册中心
安装启动zookerper服务
2.1、将服务提供者注册到zookeeper
- 导入pom
<dependencies>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zookeeper-discoveryartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
- 配置yml
server:
port: 8003
spring:
application:
name: zk-payment #这个名称就是注册进eureka注册中心的服务名字(Application)
cloud:
zookeeper:
connect-string: 39.96.52.225:2181
- 开启注册中心客户端
/**
* spring boot 启动类
* @author 15594
*/
@SpringBootApplication
//开启注册中心客户端
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class ZKMain8003 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ZKMain8003.class,args);
}
}
- 编写test代码
/**
* @author 15594
*/
@RestController
public class HelloZkController {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String serverPort;
@GetMapping("/helloZk")
public String helloZk() {
return "zookeeper注册中心"+serverPort;
}
}
注意:启动时可能会发生jar包冲突报错。spring-cloud-starter-zookeeper-discovery 里面的 org.apache.zookeeper:zookeeper:3.5.3-beta jar包与zookeeper自带的jar包冲突
解决:移除spring-cloud-starter-zookeeper-discovery 自带的jar包,导入与zookeeper版本一样的jar包版本
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zookeeper-discoveryartifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeepergroupId>
<artifactId>zookeeperartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.zookeepergroupId>
<artifactId>zookeeperartifactId>
<version>3.7.0version>
dependency>
- 测试
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 10] ls /
[services, zookeeper]
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 11] ls /services
[zk-payment]
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 12] ls /services/zk-payment
[92658886-55d9-4c53-85cd-e7529e5e8267]
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 13] ls /services/zk-payment/92658886-55d9-4c53-85cd-e7529e5e8267
[]
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 14] get /services/zk-payment/92658886-55d9-4c53-85cd-e7529e5e8267
{"name":"zk-payment","id":"92658886-55d9-4c53-85cd-e7529e5e8267","address":"LAPTOP-73OST0O0.mshome.net","port":8003,"sslPort":null,"payload":{"@class":"org.springframework.cloud.zookeeper.discovery.ZookeeperInstance","id":"application-1","name":"zk-payment","metadata":{}},"registrationTimeUTC":1629443160158,"serviceType":"DYNAMIC","uriSpec":{"parts":[{"value":"scheme","variable":true},{"value":"://","variable":false},{"value":"address","variable":true},{"value":":","variable":false},{"value":"port","variable":true}]}}
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 15]
2.2、服务消费者
服务消费者的实现方式和服务提供者的实现方式差不多。
七、CAP
c :一致性(节点越多,就越难保证节点间数据一致)
a:可用性(节点多,又要保证数据一致,那么就要话很多时间去实现节点的一致性,这样可用性(延迟、网络故障多)就会降低)
p:分区容错性(节点越多(集群越大)分区容错性越好)
数据存在的节点越多,分区容忍性越高,但要复制更新的数据就越多,一致性就越难保证。为了保证一致性,更新所有节点数据所需要的时间就越长,可用性就会降低。
八、负载均衡
Ribben、Feigen、opnefan、
Nginx
1、Ribben
Ribben 如果有注册中心,那么从注册中心获取到注册到注册中心的注册表,根据负载均衡算法从注册表中获取请求的节点的url。(当然Ribben在没有注册中心时也时可以使用的)。
Ribben一般配合RestTemplate配合使用
1)、 导入pom
org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client:2.2.1.RELEASE 里面已经自带了。

<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-clientartifactId>
dependency>
2)、配置yml
#指示此客户端是否应从 eureka 服务器获取 eureka 注册表信息。
# 使用ribben必须要为true,因为ribben的负载均衡算法是要获取注册中心的注册表
eureka.client.fetch-registry=true
3)、 使用默认的轮询算法
ribben 结合 RestTemplate
- 配置RestTemplate(config)。
package com.lihua.springcloud.config;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@Configuration
public class ApplicationContextConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced //开启负载均衡,让消费者知道调用注册中心的那个服务(这个服务的功能一致,但在不同的服务器上)
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
- 通过RestTemplate调用微服务
package com.lihua.springcloud.controller;
import com.lihua.springcloud.pojo.CommonResult;
import com.lihua.springcloud.pojo.Payment;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RestController
@Slf4j
/**
* 服务的消费者
* 远程调用服务提供者
* */
public class OrderController {
// public static final String PAYMENT_URL = "http://localhost:8001"; 单机版
public static final String PAYMENT_URL = "http://CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE"; //集群版,从注册中心中选取注册表
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/create")
public CommonResult<Payment> create(Payment payment){
return restTemplate.postForObject(PAYMENT_URL+"/payment/create",payment,CommonResult.class);
}
//getForObject():返回对象为响应体中数据转化成的对象,基本上可以理解为Json。
//getForEntity():返回对象为ResponseEntity对象,包含了响应中的一些重要信息,比如响应头、响应状态码、响应体等。
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/get/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
return restTemplate.getForObject(PAYMENT_URL+"/payment/get/"+id,CommonResult.class);
}
}
- 启动服务测试
4)、轮询算法实现原理
1、从注册中心获取注册表。
2、有了注册表就能获取到同一微服务的主机数(num),主机请求url
3、获取到的主机url会存储在一个list集合里面
4、计算index(集合list的下标),index = 第几次请求(从1开始,客户端每请求一次加一)%num
5、通过index下标获取下一次(轮询到的)请求的主机 。
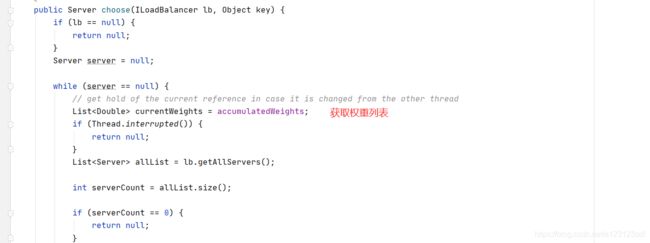
5)、轮询算法源码解析。
总的来所说,轮询算法。第几次请求与主机数取余获得index,取余过程中使用cas和自旋锁,计算出index。
6)、修改默认的轮询算法(指定负载均衡算法)
相比默认的方法,需要添加一步
在主启动类添加注解@RibbonClient(name = “CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE”, configuration = RoundRobinRule.class) //启用Ribbon,并使用自己自定义的负载均衡算法
configuration 可选参数:
- RoundRobinRule 轮询
- RandomRule 随机
- RetryRule (重试)先按照RoundRobinRule的策略获取服务,如果获取服务失败则在指定时间内会进行重
- WeightedResponseTimeRule(根据响应时间权重) 对RoundRobinRule的扩展,响应速度越快的实例选择权重越大,越容易被选择
- BestAvailableRule 会先过滤掉由于多次访问故障而处于断路器跳闸状态的服务,然后选择一个并发量最小的服务
- AvailabilityFilteringRule 先过滤掉故障实例,再选择并发较小的实例
- ZoneAvoidanceRule 复合判断server所在区域的性能和server的可用性选择服务器
7)、 自定义轮询算法
只需要三步:
- 创建配置类
package com.lihua.config;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.IRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.WeightedResponseTimeRule;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/*
* RoundRobinRule 轮询
RandomRule 随机
RetryRule 先按照RoundRobinRule的策略获取服务,如果获取服务失败则在指定时间内会进行重
WeightedResponseTimeRule 对RoundRobinRule的扩展,响应速度越快的实例选择权重越大,越容易被选择
BestAvailableRule 会先过滤掉由于多次访问故障而处于断路器跳闸状态的服务,然后选择一个并发量最小的服务
AvailabilityFilteringRule 先过滤掉故障实例,再选择并发较小的实例
ZoneAvoidanceRule 默认规则,复合判断server所在区域的性能和server的可用性选择服务器
*/
@Configuration
public class MySelfRule {
@Bean
public IRule myRule(){
return new MyRoundRobinRule();//使用自己的负载均衡算法
}
}
- 自定义轮询算法(模仿官方的写就可以了)
package com.lihua.config;
import com.netflix.client.config.IClientConfig;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.AbstractLoadBalancerRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.ILoadBalancer;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.Server;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* 自定义轮询算法
* @author 15594
*/
public class MyRoundRobinRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
private AtomicInteger nextServerCyclicCounter;
public MyRoundRobinRule() {
nextServerCyclicCounter = new AtomicInteger(0);
System.out.println("自定义轮询");
}
public MyRoundRobinRule(ILoadBalancer lb) {
this();
setLoadBalancer(lb);
}
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
System.out.println("没有负载均衡器");
return null;
}
List<Server> allServers1 = lb.getAllServers();
for (Server server : allServers1) {
System.out.println(server.getHostPort());
}
Server server = null;
int count = 0;
while (server == null && count++ < 10) {
//获取可用的服务器列表
List<Server> reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers();
//获取全部服务器列表
List<Server> allServers = lb.getAllServers();
int upCount = reachableServers.size();
int serverCount = allServers.size();
if ((upCount == 0) || (serverCount == 0)) {
System.out.println("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb);
return null;
}
int nextServerIndex = incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount);
server = allServers.get(nextServerIndex);
if (server == null) {
/* Transient. */
Thread.yield();
continue;
}
if (server.isAlive() && (server.isReadyToServe())) {
return (server);
}
// Next.
server = null;
}
if (count >= 10) {
System.out.println("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: "
+ lb);
}
System.out.println("经过轮询获取到的url为:"+server.getHostPort());
return server;
}
private int incrementAndGetModulo(int modulo) {
for (;;) {
//原子操作,获取nextServerCyclicCounter里面的值,初始值为0,客户端每请求一次就加一
int current = nextServerCyclicCounter.get();
int next = (current + 1) % modulo;
if (nextServerCyclicCounter.compareAndSet(current, next)) {
return next;
}
}
}
@Override
public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig iClientConfig) {
}
@Override
public Server choose(Object key) {
ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = getLoadBalancer();
return choose(getLoadBalancer(),key);
}
}
- 修改主启动类上的@RibbonClient注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient //开启eureka Client端,向注册中心注册自己,并发现使用服务
@RibbonClient(name = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE", configuration = MySelfRule.class) //启用Ribbon,并使用自己自定义的负载均衡算法
public class OrderMain80 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderMain80.class,args);
}
}
8)、其他负载均衡实现原理
- 请求响应时间权重(WeightedResponseTimeRule)
WeightedResponseTimeRule,继承与轮询算法。当权重表没有初始化时,会回退使用轮询算法。
首先时起一个定时任务,定时计算更新权重表。权重表是根据服务器响应时间计算出来的。



2、feign与openfeign
feign与openfeign里面也是有了(集成了)reibben,只是feign与openfeign封装了一些reibben的操作,使得操作更简单。openfeign(升级版)又取代了feign。
2.1、导入pom
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeignartifactId>
dependency>
2.2、配置yml
server:
port: 81
eureka:
client:
#表示是否将自己注册进Eurekaserver默认为true。
register-with-eureka: false
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka,http://127.0.0.1:7002/eureka #向那个注册中心进行注册
#这里不将它注册进注册中心,因为它是消费者
#设置feign客户端超时时间(OpenFeign默认支持ribbon)(单位:毫秒)
ribbon:
#指的是建立连接所用的时间,适用于网络状况正常的情况下,两端连接所用的时间
ReadTimeout: 5000
#指的是建立连接后从服务器读取到可用资源所用的时间
ConnectTimeout: 5000
logging:
level:
# feign日志以什么级别监控哪个接口
com.lihua.springcloud.service.PaymentFeignService: debug
#这些配置可能没有用
#配置ribbon
#stu-provide:
# ribbon:
# NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule #配置规则 随机
# NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RoundRobinRule #配置规则 轮询
# NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.RetryRule #配置规则 重试
# NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.WeightedResponseTimeRule #配置规则 响应时间权重
#NFLoadBalancerRuleClassName: com.netflix.loadbalancer.BestAvailableRule #配置规则 最空闲连接策略
# ConnectTimeout: 5000 #请求连接超时时间
# ReadTimeout: 5000 #请求处理的超时时间
#OkToRetryOnAllOperations: true #对所有请求都进行重试
#MaxAutoRetriesNextServer: 2 #切换实例的重试次数
# MaxAutoRetries: 1 #对当前实例的重试次数
2.3、开启openfeign
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableFeignClients //使用并开启feign
public class OrderFeignMain80 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderFeignMain80.class,args);
}
}
2.4、配置opnefeign调用接口
//opnefeign根mybatis一样会自动生成实现类
@FeignClient(value = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE") //负载均衡策略可以在yml中配置
@Component //没有注入spring可能会报错
public interface PaymentFeignService {
@GetMapping(value = "/payment/get/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
@GetMapping("/payment/feign/timeout")
public String paymentFeignTimeout();
}
2.5、使用
public class OrderFeignController {
@Autowired
private PaymentFeignService paymentFeignService;
@GetMapping("/consumer/payment/get/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
return paymentFeignService.getPaymentById(id);
}
@GetMapping("/payment/feign/timeout")
public String paymentFeignTimeout(){
//openfeign-ribben ,客户端默认等待1秒钟。超过就是请求超时
//当业务时间超过1秒后,需要自己设置约定时间。在yml中设置
return paymentFeignService.paymentFeignTimeout();
}
}
2.6、消费端调用超时设置
#设置feign客户端超时时间(OpenFeign默认支持ribbon)(单位:毫秒)
ribbon:
#指的是建立连接所用的时间,适用于网络状况正常的情况下,两端连接所用的时间
ReadTimeout: 5000
#指的是建立连接后从服务器读取到可用资源所用的时间
ConnectTimeout: 5000
2.7、日志
Feign提供了日志打印功能,我们可以通过配置来调整日恙级别,从而了解Feign 中 Http请求的细节。
说白了就是对Feign接口的调用情况进行监控和输出
- 配置config
/**
NONE:默认的,不显示任何日志;
BASIC:仅记录请求方法、URL、响应状态码及执行时间;
HEADERS:除了BASIC中定义的信息之外,还有请求和响应的头信息;
FULL:除了HEADERS中定义的信息之外,还有请求和响应的正文及元数据。
* */
@Configuration
public class FeignConfig {
@Bean
Logger.Level feignLoggerLevel()
{
return Logger.Level.FULL;
}
}
- 配置yml(指定要监控哪个类)
logging:
level:
# feign日志以什么级别监控哪个接口
com.lihua.springcloud.service.PaymentFeignService: debug
2.8、使用自定义的负载均衡算法
- 编写好负载均衡算法,与ribben一样
package com.lihua.config;
import com.netflix.client.config.IClientConfig;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.AbstractLoadBalancerRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.ILoadBalancer;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.Server;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* 自定义轮询算法
* @author 15594
*/
public class MyRoundRobinRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
private AtomicInteger nextServerCyclicCounter;
public MyRoundRobinRule() {
nextServerCyclicCounter = new AtomicInteger(0);
System.out.println("自定义轮询");
}
public MyRoundRobinRule(ILoadBalancer lb) {
this();
setLoadBalancer(lb);
}
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
System.out.println("没有负载均衡器");
return null;
}
List<Server> allServers1 = lb.getAllServers();
for (Server server : allServers1) {
System.out.println(server.getHostPort());
}
Server server = null;
int count = 0;
while (server == null && count++ < 10) {
//获取可用的服务器列表
List<Server> reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers();
//获取全部服务器列表
List<Server> allServers = lb.getAllServers();
int upCount = reachableServers.size();
int serverCount = allServers.size();
if ((upCount == 0) || (serverCount == 0)) {
System.out.println("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb);
return null;
}
int nextServerIndex = incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount);
server = allServers.get(nextServerIndex);
if (server == null) {
/* Transient. */
Thread.yield();
continue;
}
if (server.isAlive() && (server.isReadyToServe())) {
return (server);
}
// Next.
server = null;
}
if (count >= 10) {
System.out.println("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: "
+ lb);
}
System.out.println("经过轮询获取到的url为:"+server.getHostPort());
return server;
}
private int incrementAndGetModulo(int modulo) {
for (;;) {
//原子操作,获取nextServerCyclicCounter里面的值,初始值为0,客户端每请求一次就加一
int current = nextServerCyclicCounter.get();
int next = (current + 1) % modulo;
if (nextServerCyclicCounter.compareAndSet(current, next)) {
return next;
}
}
}
@Override
public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig iClientConfig) {
}
@Override
public Server choose(Object key) {
ILoadBalancer loadBalancer = getLoadBalancer();
return choose(getLoadBalancer(),key);
}
}
@Configuration
public class MySelfRule {
@Bean
public IRule myRule(){
return new MyRoundRobinRule();
}
}
- 修改openfeign调用接口的配置
@FeignClient(value = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE",configuration = MySelfRule.class) //负载均衡策略在yml中配置
@Component //没有注入spring可能会报错
public interface PaymentFeignService {
@GetMapping(value = "/payment/get/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> getPaymentById(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
@GetMapping("/payment/feign/timeout")
public String paymentFeignTimeout();
}