Java异常你还没有了解吗?
♀️♀️♀️ 今天和大家一起学习一下Java中的异常!
清风的CSDN博客个人主页
c/java领域新星创作者
欢迎点赞✍评论❤️收藏
希望我的文章能对你有所帮助,有不足的地方还请各位看官多多指教,大家一起学习交流!
动动你们发财的小手,点点关注点点赞!在此谢过啦!哈哈哈!
目录
一、异常的概念与体系结构
1.1异常的概念
1.1.1算术异常
1.1.2数组越界异常
1.1.3空指针异常
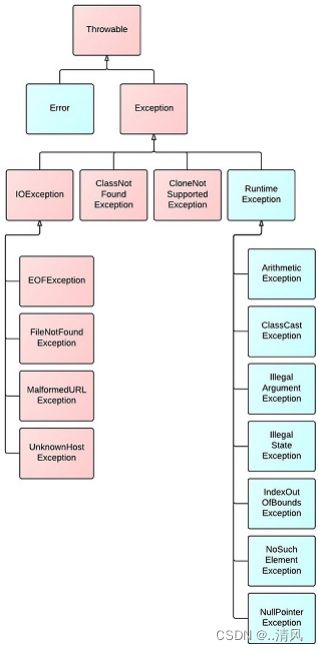
1.2异常的体系结构
1.3异常的分类
1.3.1编译时异常
1.3.2运行时异常
二、异常的处理
2.1防御式编程
2.1.1 LBYL事前防御型
2.1.2EAFP:事后认错型
2.2异常的抛出
2.3异常的捕获
2.3.1异常声明throws
2.3.2try-catch捕获并处理
一、异常的概念与体系结构
1.1异常的概念
在Java中,将程序执行过程中发生的不正常行为称为异常。比如下面的代码:
1.1.1算术异常
System.out.println(10 / 0);
// 执行结果
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero1.1.2数组越界异常
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(arr[100]);
// 执行结果
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 1001.1.3空指针异常
int[] arr = null;
System.out.println(arr.length);
// 执行结果
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException1.2异常的体系结构
1.3异常的分类
1.3.1编译时异常
public class Person {
private String name;
private String gender;
int age;
// 想要让该类支持深拷贝,覆写Object类的clone方法即可
@Override
public Person clone() {
return (Person)super.clone();
}
}
编译时报错:
Error:(17, 35) java: 未报告的异常错误java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException; 必须对其进行捕获或声明以便抛出因为在定义Person类时,并没有实现克隆接口,因此会抛出不支持克隆异常。
1.3.2运行时异常
- 注意:编译时出现的语法性错误,不能称之为异常。例如将 System.out.println 拼写错了, 写成了system.out.println.。此时编译过程中就会出错, 这是 "编译期" 出错。而运行时指的是程序已经编译通过得到class 文件了, 再由 JVM 执行过程中出现的错误。
二、异常的处理
2.1防御式编程
2.1.1 LBYL事前防御型
boolean ret = false;
ret = 登陆游戏();
if (!ret) {
处理登陆游戏错误;
return;
}
ret = 开始匹配();
if (!ret) {
处理匹配错误;
return;
}
ret = 游戏确认();
if (!ret) {
处理游戏确认错误;
return;
}
ret = 选择英雄();
if (!ret) {
处理选择英雄错误;
return;
}
ret = 载入游戏画面();
if (!ret) {
处理载入游戏错误;
return;
}
......2.1.2EAFP:事后认错型
try {
登陆游戏();
开始匹配();
游戏确认();
选择英雄();
载入游戏画面();
...
} catch (登陆游戏异常) {
处理登陆游戏异常;
} catch (开始匹配异常) {
处理开始匹配异常;
} catch (游戏确认异常) {
处理游戏确认异常;
} catch (选择英雄异常) {
处理选择英雄异常;
} catch (载入游戏画面异常) {
处理载入游戏画面异常;
}
....2.2异常的抛出
throw new XXXException("异常产生的原因");下面是一个抛出异常的实例代码:
public static int getElement(int[] array, int index){
if(null == array){
throw new NullPointerException("传递的数组为null");
}
if(index < 0 || index >= array.length){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("传递的数组下标越界");
}
return array[index];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {1,2,3};
getElement(array, 3);
}注意事项:
-
throw必须写在方法体内部
-
抛出的对象必须是Exception 或者 Exception 的子类对象
-
如果抛出的是 RunTimeException 或者 RunTimeException 的子类,则可以不用处理,直接交给JVM来处理
-
如果抛出的是编译时异常,用户必须处理,否则无法通过编译
-
异常一旦抛出,其后的代码就不会执行
2.3异常的捕获
2.3.1异常声明throws
语法格式:
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数列表) throws 异常类型1,异常类型2...{
}下面看一个实例代码:
public class Config {
File file;
/*
FileNotFoundException : 编译时异常,表明文件不存在
此处不处理,也没有能力处理,应该将错误信息报告给调用者,让调用者检查文件名字是否给错误了
*/
public void OpenConfig(String filename) throws FileNotFoundException{
if(filename.equals("config.ini")){
throw new FileNotFoundException("配置文件名字不对");
}
// 打开文件
}
public void readConfig(){
}
}注意事项:
-
throws必须跟在方法的参数列表之后
-
声明的异常必须是 Exception 或者 Exception 的子类
-
方法内部如果抛出了多个异常,throws之后必须跟多个异常类型,之间用逗号隔开,如果抛出多个异常类型具有父子关系,直接声明父类即可。
下面是实例代码:
public class Config {
File file;
// public void OpenConfig(String filename) throws IOException,FileNotFoundException{
// FileNotFoundException 继承自 IOException
public void OpenConfig(String filename) throws IOException{
if(filename.endsWith(".ini")){
throw new IOException("文件不是.ini文件");
}
if(filename.equals("config.ini")){
throw new FileNotFoundException("配置文件名字不对");
}
// 打开文件
}
public void readConfig(){
}
}- 调用声明抛出异常的方法时,调用者必须对该异常进行处理,或者继续使用throws抛出
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Config config = new Config();
config.openConfig("config.ini");
}将光标放在抛出异常方法上,alt + Insert 快速 处理:
2.3.2try-catch捕获并处理
语法格式:
try{
// 将可能出现异常的代码放在这里
}catch(要捕获的异常类型 e){
// 如果try中的代码抛出异常了,此处catch捕获时异常类型与try中抛出的异常类型一致时,或者是try中
抛出异常的基类时,就会被捕获到
// 对异常就可以正常处理,处理完成后,跳出try-catch结构,继续执行后序代码
}[catch(异常类型 e){
// 对异常进行处理
}finally{
// 此处代码一定会被执行到
}]
// 后序代码
// 当异常被捕获到时,异常就被处理了,这里的后序代码一定会执行
// 如果捕获了,由于捕获时类型不对,那就没有捕获到,这里的代码就不会被执行
注意:
1. []中表示可选项,可以添加,也可以不用添加
2. try中的代码可能会抛出异常,也可能不会下面是一个实例代码:
public class Config {
File file;
public void openConfig(String filename) throws FileNotFoundException{
if(!filename.equals("config.ini")){
throw new FileNotFoundException("配置文件名字不对");
}
// 打开文件
}
public void readConfig(){
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Config config = new Config();
try {
config.openConfig("config.txt");
System.out.println("文件打开成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
// 异常的处理方式
//System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // 只打印异常信息
//System.out.println(e); // 打印异常类型:异常信息
e.printStackTrace(); // 打印信息最全面
}
// 一旦异常被捕获处理了,此处的代码会执行
System.out.println("异常如果被处理了,这里的代码也可以执行");
}
}关于异常的处理方式:1.异常的种类有很多, 我们要根据不同的业务场景来决定。2.对于比较严重的问题(例如和算钱相关的场景), 应该让程序直接崩溃, 防止造成更严重的后果。3.对于不太严重的问题(大多数场景), 可以记录错误日志, 并通过监控报警程序及时通知程序猿。4.对于可能会恢复的问题(和网络相关的场景), 可以尝试进行重试。5.在我们当前的代码中采取的是经过简化的第二种方式。我们记录的错误日志是出现异常的方法调用信息, 能很快速的让我们找到出现异常的位置.。以后在实际工作中我们会采取更完备的方式来记录异常信息。
注意事项:
-
try块内抛出异常位置之后的代码将不会被执行
-
如果抛出异常类型与catch时异常类型不匹配,即异常不会被成功捕获,也不会被处理,继续往外抛,直到JVM收到中断程序----异常是按照类型来捕获的
比如下面的代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int[] array = {1,2,3};
System.out.println(array[3]); // 此处会抛出数组越界异常
}catch (NullPointerException e){ // 捕获时候捕获的是空指针异常--真正的异常无法被捕获到
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("后序代码");
}
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3 at day20210917.ArrayOperator.main(ArrayOperator.java:24)- try中可能会抛出多个不同的异常对象,则必须用多个catch来捕获----即多种异常,多次捕获
例如:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
try {
System.out.println("before");
// arr = null;
System.out.println(arr[100]);
System.out.println("after");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("这是个数组下标越界异常");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("这是个空指针异常");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("after try catch");
}- 如果多个异常的处理方式是完全相同, 也可以写成这样:
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException | NullPointerException e) {
...
}- 如果异常之间具有父子关系,一定是子类异常在前catch,父类异常在后catch,否则语法错误:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
try {
System.out.println("before");
arr = null;
System.out.println(arr[100]);
System.out.println("after");
} catch (Exception e) { // Exception可以捕获到所有异常
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NullPointerException e){ // 永远都捕获执行到
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("after try catch");
}
Error:(33, 10) java: 已捕获到异常错误java.lang.NullPointerException- 可以通过一个catch捕获所有的异常,即多个异常,一次捕获(不推荐)
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
try {
System.out.println("before");
arr = null;
System.out.println(arr[100]);
System.out.println("after");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("after try catch");
}由于 Exception 类是所有异常类的父类. 因此可以用这个类型表示捕捉所有异常。
注意:catch 进行类型匹配的时候, 不光会匹配相同类型的异常对象, 也会捕捉目标异常类型的子类对象.。如刚才的代码, NullPointerException 和 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 都是 Exception 的子类, 因此都能被捕获到。
好啦,今天的分享就到这里!!
✨创作不易,还希望各位大佬支持一下!
点赞,你的认可是我创作的动力!
⭐收藏,你的青睐是我努力的方向!
✏️评论:你的意见是我进步的财富!