flutter绘制指南04-路径的操作方法
本节目标:
[1]. 了解路径的封闭、重置、偏移操作
[2]. 了解路径的[矩形边距]和检测点是否在路径中
[3]. 了解路径的[路径变换]和[路径联合]
[4]. 了解路劲测量的用法和作用
一. 路径操作
路径操作时路径使用中的重要一环。很多路径的
特效和复杂路径的拼合都会使用他们
1. close、reset和shift
path#close: 用于将路径的尾点和起点,进行路径封闭
path#reset: 用于将路径进行重置,清除路径内容
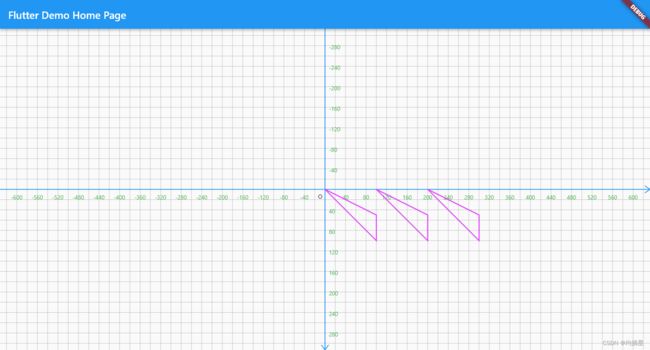
path#shift: 指定点Offset将路径进行平移,返回一条新的路径.
void drawPathShift(Canvas canvas){
Path path=Path();
Paint paint=Paint();
paint
..color=Colors.purpleAccent
..strokeWidth=2
..style=PaintingStyle.stroke;
path
..lineTo(100, 100)
..relativeLineTo(0, -50)
..close();
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
canvas.drawPath(path.shift(Offset(100, 0)), paint);
canvas.drawPath(path.shift(Offset(200, 0)), paint);
}
2. contains和getBounds
Paint和#contains可以判断点Offset在不在路径之内。
这是一个非常好用的方法。可以更具这个方法做一些触点判断或者简单的碰撞检测
Paint#getBounds可以获取当前路径所在的矩形区域
void drawContainsAndGetBounds(Canvas canvas) {
Path path = Path();
Paint paint = Paint()
..color = Colors.purple
..style = PaintingStyle.fill;
path
..relativeMoveTo(0, 0)
..relativeLineTo(-30, 120)
..relativeLineTo(30, -30)
..relativeLineTo(30, 30)
..close();
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
print(path.contains(Offset(20, 20)));
print(path.contains(Offset(0, 20)));
Rect bounds = path.getBounds();
canvas.drawRect(
bounds,
Paint()
..color = Colors.orange
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke
..strokeWidth = 1);
}
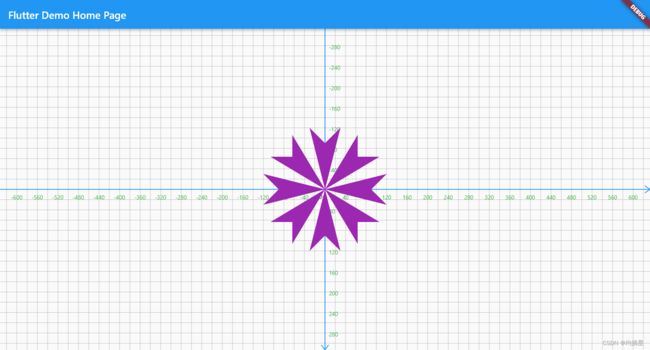
3.Path#transform:路径变换
可以用于对称图形,当已经有一部分单体路径,可以更具一个4*4的路径进行变换
可以使用Matrix4对象 进行生成辅助举证。就能够很方便的进行缩放、平移、旋转、斜切等变换效果
void drawPathTransForm(Canvas canvas){
Path path=Path();
Paint paint=Paint();
paint..color=Colors.purple
..style=PaintingStyle.fill;
path..relativeMoveTo(0, 0)
..relativeLineTo(-30, 120)
..relativeLineTo(30, -30)
..relativeLineTo(30, 30);
for(int i=0;i<8;i++){
canvas.drawPath(path.transform(Matrix4.rotationZ(i*pi/4).storage), paint);
}
}
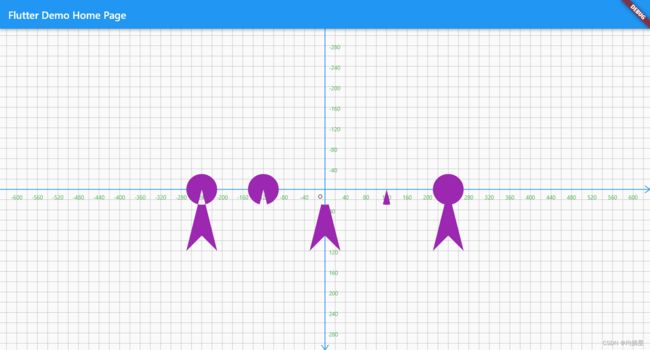
4.combine:路径联合
Path#combine用于结合两个路径,并且生成新的路径,可以用于生成复杂的路径.
一共有以下五种联合方式,效果如下图
void drawPathCombine(Canvas canvas){
Paint paint=Paint();
Path path=Path();
paint
..color=Colors.purple
..style=PaintingStyle.fill;
path
..relativeMoveTo(0, 0)
..relativeLineTo(-30, 120)
..relativeLineTo(30, -30)
..relativeLineTo(30, 30)
..close();
var pathOval=Path()..addOval(Rect.fromCenter(center: Offset(0,0), width: 60, height: 60));
canvas.drawPath(Path.combine(PathOperation.difference, path, pathOval),paint);
canvas.translate(120,0);
canvas.drawPath(Path.combine(PathOperation.intersect, path, pathOval),paint);
canvas.translate(120,0);
canvas.drawPath(Path.combine(PathOperation.union, path, pathOval),paint);
canvas.translate(-120*3,0);
canvas.drawPath(Path.combine(PathOperation.reverseDifference, path, pathOval),paint);
canvas.translate(-120,0);
canvas.drawPath(Path.combine(PathOperation.xor, path, pathOval),paint);
}
二. 路径测量的使用
computeMetrics是路径中一个非常实用的操作,可以更具这个方法获得很多有价值的信息。比如路径上某点在路径上的位置、角度、路径长度等。通过这些与动画结合,可以做出环路径运动.路径绘制动画等效果。
1.认识Path#computeMetrics
通过path.computeMetrics(),可以获取一个课迭代的PathMetrics类对象。它迭代出的是PathMetric对象。也就是每个路径的测量信息。也就是说通过path.computeMetrics()你可以获取一组路径的测量信息。主义。如下
path.addOval之后,PathMetrics对象中元素变为两个。
Path path=Path();
path
..relativeMoveTo(0,0)
..relativeLineTo(-30,120)
..relativeLineTo(30,-30)
..relativeLineTo(30,30)
..close();
path.addOval(Rect.fromCenter(center:Offset.zero,width:50,height:50));
通过
PathMetrics对象可以获得路径长度length、路径索引contourIndex以及isClosed路径是否闭合。
PathMetrics pms=path.computeMetrics();
Tangent t;
pms.forEach((pm){
print("---length;-${pm.contourIndex};-${pm.contourIndex}----isClosed:-${pm.isClosed}----")
})
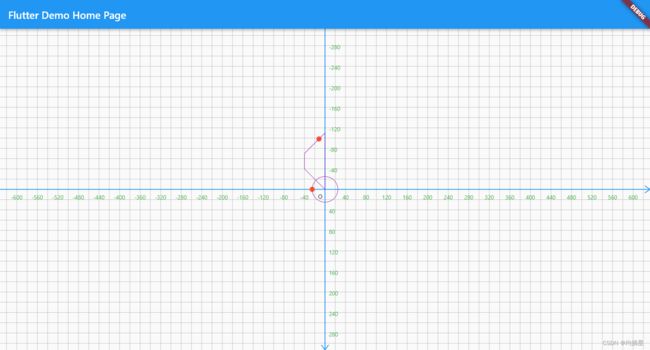
2. 路径测量获取路径某个位置的信息
比如我想要在路径一半的地方绘制一个小球,如果通过自己计算的话。非常的困难
幸运的是我是通过路径进行计算的,实现起来就非常的方便。甚至还能得到改点的角度、速度信息。
下面通过pm.length*0.5表示在路径长度为50%时候的点的信息。
void drawPmsCenterPoints(Canvas canvas){
Paint paint=new Paint();
Path path=new Path();
paint
..style=PaintingStyle.stroke
..color=Colors.purple;
path
..relativeMoveTo(0, 0)
..relativeLineTo(-40, -40)
..relativeLineTo(0, -30)
..relativeLineTo(40,-40)
..close();
path.addOval(Rect.fromCenter(center: Offset.zero,width: 50,height: 50));
PathMetrics pms=path.computeMetrics();
pms.forEach((pm){
Tangent? tangent=pm.getTangentForOffset(pm.length*0.5);
if(tangent==null)return;
canvas.drawCircle(tangent.position, 5, Paint()..color=Colors.deepOrange);
});
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
}
3.路径测量和动画相结合
下面将小球沿着路径进行动画,使用动画控制器让数字在3秒内从0到达1.达到动画效果。
import 'dart:math';
import 'dart:ui';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
import 'coordinate.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
// This is the theme of your application.
//
// Try running your application with "flutter run". You'll see the
// application has a blue toolbar. Then, without quitting the app, try
// changing the primarySwatch below to Colors.green and then invoke
// "hot reload" (press "r" in the console where you ran "flutter run",
// or simply save your changes to "hot reload" in a Flutter IDE).
// Notice that the counter didn't reset back to zero; the application
// is not restarted.
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: const MyHomePage(title: 'Flutter Demo Home Page'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({Key? key, required this.title}) : super(key: key);
// This widget is the home page of your application. It is stateful, meaning
// that it has a State object (defined below) that contains fields that affect
// how it looks.
// This class is the configuration for the state. It holds the values (in this
// case the title) provided by the parent (in this case the App widget) and
// used by the build method of the State. Fields in a Widget subclass are
// always marked "final".
final String title;
@override
State createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin{
late AnimationController _ctrl;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
// 确定初始化
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
//横屏
SystemChrome.setPreferredOrientations(
[DeviceOrientation.landscapeLeft, DeviceOrientation.landscapeRight]);
//全屏显示
SystemChrome.setEnabledSystemUIOverlays([]);
_ctrl=AnimationController(duration: Duration(seconds: 3),vsync: this)
..forward();
}
@override
void dispose() {
_ctrl.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// This method is rerun every time setState is called, for instance as done
// by the _incrementCounter method above.
//
// The Flutter framework has been optimized to make rerunning build methods
// fast, so that you can just rebuild anything that needs updating rather
// than having to individually change instances of widgets.
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
// Here we take the value from the MyHomePage object that was created by
// the App.build method, and use it to set our appbar title.
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Container(
width: double.maxFinite,
height: double.maxFinite,
child: CustomPaint(
painter: PaperPainter(progress: _ctrl),
),
));
}
}
class PaperPainter extends CustomPainter {
final Coordinate coordinate = Coordinate();
final Animation progress;
PaperPainter({required this.progress}):super(repaint: progress);
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
coordinate.paint(canvas, size);
canvas.translate(size.width / 2, size.height / 2);
// drawContainsAndGetBounds(canvas);
// drawPathShift(canvas);
// drawPathTransForm(canvas);
// drawPathCombine(canvas);
// drawPmsCenterPoints(canvas);
drawAnimationRectangle(canvas);
}
void drawContainsAndGetBounds(Canvas canvas) {
Path path = Path();
Paint paint = Paint()
..color = Colors.purple
..style = PaintingStyle.fill;
path
..relativeMoveTo(0, 0)
..relativeLineTo(-30, 120)
..relativeLineTo(30, -30)
..relativeLineTo(30, 30)
..close();
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
print(path.contains(Offset(20, 20)));
print(path.contains(Offset(0, 20)));
Rect bounds = path.getBounds();
canvas.drawRect(
bounds,
Paint()
..color = Colors.orange
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke
..strokeWidth = 1);
}
void drawPathShift(Canvas canvas){
Path path=Path();
Paint paint=Paint();
paint
..color=Colors.purpleAccent
..strokeWidth=2
..style=PaintingStyle.stroke;
path
..lineTo(100, 100)
..relativeLineTo(0, -50)
..close();
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
canvas.drawPath(path.shift(Offset(100, 0)), paint);
canvas.drawPath(path.shift(Offset(200, 0)), paint);
}
void drawPathTransForm(Canvas canvas){
Path path=Path();
Paint paint=Paint();
paint..color=Colors.purple
..style=PaintingStyle.fill;
path..relativeMoveTo(0, 0)
..relativeLineTo(-30, 120)
..relativeLineTo(30, -30)
..relativeLineTo(30, 30);
for(int i=0;i<8;i++){
canvas.drawPath(path.transform(Matrix4.rotationZ(i*pi/4).storage), paint);
}
}
void drawPathCombine(Canvas canvas){
Paint paint=Paint();
Path path=Path();
paint
..color=Colors.purple
..style=PaintingStyle.fill;
path
..relativeMoveTo(0, 0)
..relativeLineTo(-30, 120)
..relativeLineTo(30, -30)
..relativeLineTo(30, 30)
..close();
var pathOval=Path()..addOval(Rect.fromCenter(center: Offset(0,0), width: 60, height: 60));
canvas.drawPath(Path.combine(PathOperation.difference, path, pathOval),paint);
canvas.translate(120,0);
canvas.drawPath(Path.combine(PathOperation.intersect, path, pathOval),paint);
canvas.translate(120,0);
canvas.drawPath(Path.combine(PathOperation.union, path, pathOval),paint);
canvas.translate(-120*3,0);
canvas.drawPath(Path.combine(PathOperation.reverseDifference, path, pathOval),paint);
canvas.translate(-120,0);
canvas.drawPath(Path.combine(PathOperation.xor, path, pathOval),paint);
}
void drawPmsCenterPoints(Canvas canvas){
Paint paint=new Paint();
Path path=new Path();
paint
..style=PaintingStyle.stroke
..color=Colors.purple;
path
..relativeMoveTo(0, 0)
..relativeLineTo(-40, -40)
..relativeLineTo(0, -30)
..relativeLineTo(40,-40)
..close();
path.addOval(Rect.fromCenter(center: Offset.zero,width: 50,height: 50));
PathMetrics pms=path.computeMetrics();
pms.forEach((pm){
Tangent? tangent=pm.getTangentForOffset(pm.length*0.5);
if(tangent==null)return;
canvas.drawCircle(tangent.position, 5, Paint()..color=Colors.deepOrange);
});
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
}
void drawAnimationRectangle(Canvas canvas){
Paint paint=Paint()
..color=Colors.purple
..strokeWidth=1
..style=PaintingStyle.stroke;
Path path=Path()
..relativeMoveTo(0, 0)
..relativeLineTo(-30, 120)
..relativeLineTo(30, -30)
..relativeLineTo(30, 30)
..close();
PathMetrics pms=path.computeMetrics();
pms.forEach((element) {
Tangent? tangent=element.getTangentForOffset(element.length*progress.value);
if(tangent==null)return ;
canvas.drawCircle(tangent.position, 5, Paint()..color=Colors.deepOrange);
});
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
}
@override
bool shouldRepaint(CustomPainter oldDelegate) => false;
}