Python实现Labelme的Json标注文件与YOLO格式的TXT标注文件相互转换
Python实现Labelme的Json标注文件与YOLO格式的TXT标注文件相互转换
- 前言
- 前提条件
- 相关介绍
- 实验环境
- Labelme的Json标注文件与YOLO格式的TXT标注文件相互转换
-
- convert_labelme_json_to_txt
-
- jsons/000000000009.json
- 代码实现
- 输出结果
- labels/000000000009.txt
- convert_txt_to_labelme_json
-
- labels/000000000009.txt
- 代码实现
- 输出结果
- jsons/000000000009.json
- 参考
前言
- 由于本人水平有限,难免出现错漏,敬请批评改正。
- 更多精彩内容,可点击进入Python日常小操作专栏、OpenCV-Python小应用专栏、YOLO系列专栏、自然语言处理专栏或我的个人主页查看
- 基于DETR的人脸伪装检测
- YOLOv7训练自己的数据集(口罩检测)
- YOLOv8训练自己的数据集(足球检测)
- YOLOv5:TensorRT加速YOLOv5模型推理
- YOLOv5:IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU、EIoU
- 玩转Jetson Nano(五):TensorRT加速YOLOv5目标检测
- YOLOv5:添加SE、CBAM、CoordAtt、ECA注意力机制
- YOLOv5:yolov5s.yaml配置文件解读、增加小目标检测层
- Python将COCO格式实例分割数据集转换为YOLO格式实例分割数据集
- YOLOv5:使用7.0版本训练自己的实例分割模型(车辆、行人、路标、车道线等实例分割)
- 使用Kaggle GPU资源免费体验Stable Diffusion开源项目
前提条件
- 熟悉Python
相关介绍
- Python是一种跨平台的计算机程序设计语言。是一个高层次的结合了解释性、编译性、互动性和面向对象的脚本语言。最初被设计用于编写自动化脚本(shell),随着版本的不断更新和语言新功能的添加,越多被用于独立的、大型项目的开发。
- PyTorch 是一个深度学习框架,封装好了很多网络和深度学习相关的工具方便我们调用,而不用我们一个个去单独写了。它分为 CPU 和 GPU 版本,其他框架还有 TensorFlow、Caffe 等。PyTorch 是由 Facebook 人工智能研究院(FAIR)基于 Torch 推出的,它是一个基于 Python 的可续计算包,提供两个高级功能:1、具有强大的 GPU 加速的张量计算(如 NumPy);2、构建深度神经网络时的自动微分机制。
- YOLOv5是一种单阶段目标检测算法,该算法在YOLOv4的基础上添加了一些新的改进思路,使其速度与精度都得到了极大的性能提升。它是一个在COCO数据集上预训练的物体检测架构和模型系列,代表了Ultralytics对未来视觉AI方法的开源研究,其中包含了经过数千小时的研究和开发而形成的经验教训和最佳实践。
- YOLO格式标签是目标检测任务中常用的标注格式之一。YOLO格式标注文件由目标框的中心点坐标、宽度和高度组成。具体来说,YOLO格式标注文件的每一行都包含了一个目标的标注信息,其中第一个数字表示目标的类别,后面四个数字分别表示目标框的中心点坐标(x_center, y_center)和宽度w以及高度h,这些值都是相对于图像宽度和高度的比例。
- 例如,下面是一个YOLO格式标注文件的示例:
- 其中,第一行表示一个类别为45的目标,其中心点坐标为图像宽度的0.749891和0.255612,宽度和高度分别为图像宽度和高度的0.477249和0.511224;第二行表示一个类别为50的目标,其中心点坐标为图像宽度的0.64458和0.722577,宽度和高度分别为图像宽度和高度的0.492199和0.513077。
- Labelme是一款图像标注工具,由麻省理工(MIT)的计算机科学和人工智能实验室(CSAIL)研发。它是用Python和PyQT编写的,开源且免费。Labelme支持Windows、Linux和Mac等操作系统。
- 这款工具提供了直观的图形界面,允许用户在图像上标注多种类型的目标,例如矩形框、多边形、线条等,甚至包括更复杂的形状。标注结果以JSON格式保存,便于后续处理和分析。这些标注信息可以用于目标检测、图像分割、图像分类等任务。
- 总的来说,Labelme是一款强大且易用的图像标注工具,可以满足不同的图像处理需求。
实验环境
- Python 3.x (面向对象的高级语言)
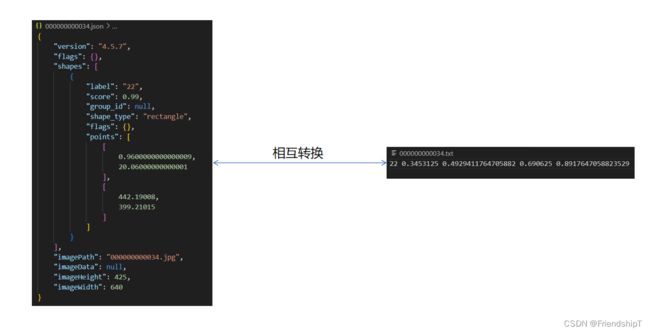
Labelme的Json标注文件与YOLO格式的TXT标注文件相互转换
convert_labelme_json_to_txt
jsons/000000000009.json
{
"version": "4.5.7",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [
{
"label": "45",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
1.0799999999999699,
187.69008
],
[
612.66976,
473.53008
]
]
},
{
"label": "45",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
311.73024,
4.310160000000001
],
[
631.01024,
232.99032
]
]
},
{
"label": "50",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
249.60032000000007,
229.27032
],
[
565.84032,
474.35016
]
]
},
{
"label": "45",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
0.0003200000000092018,
13.510080000000002
],
[
434.48032,
388.63007999999996
]
]
},
{
"label": "49",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
376.2,
40.35996
],
[
451.75007999999997,
86.88996
]
]
},
{
"label": "49",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
465.7797119999999,
38.969952
],
[
523.849728,
85.63996800000001
]
]
},
{
"label": "49",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
385.70016000000004,
73.65983999999999
],
[
469.72,
144.16992
]
]
},
{
"label": "49",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
364.04959999999994,
2.4900960000000016
],
[
458.80992,
73.559856
]
]
}
],
"imagePath": "000000000009.jpg",
"imageData": null,
"imageHeight": 480,
"imageWidth": 640
}
代码实现
import json
import os
import glob
from tqdm import tqdm
def convert_poly_to_rect(coordinateList):
X = [int(coordinateList[2 * i]) for i in range(int(len(coordinateList) / 2))]
Y = [int(coordinateList[2 * i + 1]) for i in range(int(len(coordinateList) / 2))]
Xmax = max(X)
Xmin = min(X)
Ymax = max(Y)
Ymin = min(Y)
flag = False
if (Xmax - Xmin) == 0 or (Ymax - Ymin) == 0:
flag = True
return [Xmin, Ymin, Xmax - Xmin, Ymax - Ymin], flag
def convert_labelme_json_to_txt(json_path,img_path,out_txt_path):
json_list = glob.glob(json_path + '/*.json')
num = len(json_list)
for json_path in tqdm(json_list):
with open(json_path, "r")as f_json:
json_data = json.loads(f_json.read())
infos = json_data['shapes']
if len(infos) ==0:
continue
img_w = json_data['imageWidth']
img_h = json_data['imageHeight']
image_name = json_data['imagePath']
image_path = os.path.join(img_path, image_name)
if not os.path.exists(img_path):
print(img_path, 'is None!')
continue
txt_name = os.path.basename(json_path).split('.')[0] + '.txt'
txt_path = os.path.join(out_txt_path, txt_name)
f = open(txt_path, 'w')
for label in infos:
points = label['points']
if len(points) < 2:
continue
if len(points) == 2:
x1 = points[0][0]
y1 = points[0][1]
x2 = points[1][0]
y2 = points[1][1]
points = [[x1, y1], [x2, y1], [x2, y2], [x1, y2]]
else:
if len(points) < 4:
continue
segmentation = []
for p in points:
segmentation.append(int(p[0]))
segmentation.append(int(p[1]))
bbox, flag = convert_poly_to_rect(list(segmentation))
x1, y1, w, h = bbox
if flag:
continue
x_center = x1 + w/2
y_center = y1 + h/2
norm_x = x_center / img_w
norm_y = y_center / img_h
norm_w = w / img_w
norm_h = h / img_h
obj_cls = label['label']
line = [obj_cls, norm_x, norm_y, norm_w, norm_h]
line = [str(ll) for ll in line]
line = ' '.join(line) + '\n'
f.write(line)
f.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
img_path = 'images'
json_path = 'jsons'
out_txt_path = 'labels'
if not os.path.exists(out_txt_path):
os.makedirs(out_txt_path)
convert_labelme_json_to_txt(json_path,img_path,out_txt_path)
输出结果
labels/000000000009.txt
45 0.47890625 0.6875 0.9546875 0.5958333333333333
45 0.7359375 0.24583333333333332 0.5 0.475
50 0.6359375 0.7322916666666667 0.49375 0.5104166666666666
45 0.3390625 0.41770833333333335 0.678125 0.78125
49 0.64609375 0.13125 0.1171875 0.09583333333333334
49 0.771875 0.128125 0.090625 0.09791666666666667
49 0.6671875 0.22604166666666667 0.13125 0.14791666666666667
49 0.6421875 0.078125 0.146875 0.14791666666666667
convert_txt_to_labelme_json
labels/000000000009.txt
45 0.47890625 0.6875 0.9546875 0.595833
45 0.7359375 0.24583333333333332 0.5 0.475
50 0.6359375 0.7322916666666667 0.49375 0.5104166
45 0.3390625 0.41770833333333335 0.678125 0.78125
49 0.64609375 0.13125 0.1171875 0.095833
49 0.771875 0.128125 0.090625 0.0979166
49 0.6671875 0.22604166666666667 0.13125 0.1479166
49 0.6421875 0.078125 0.146875 0.1479166
代码实现
import os
import cv2
import json
import glob
import numpy as np
def convert_txt_to_labelme_json(txt_path, image_path, output_dir, image_fmt='.jpg'):
# txt 转labelme json
# 将yolo的txt转labelme json
txts = glob.glob(os.path.join(txt_path, "*.txt"))
for txt in txts:
labelme_json = {
'version': '4.5.7',
'flags': {},
'shapes': [],
'imagePath': None,
'imageData': None,
'imageHeight': None,
'imageWidth': None,
}
txt_name = os.path.basename(txt)
image_name = txt_name.split(".")[0] + image_fmt
labelme_json['imagePath'] = image_name
image_name = os.path.join(image_path, image_name)
if not os.path.exists(image_name):
raise Exception('txt 文件={},找不到对应的图像={}'.format(txt, image_name))
image = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(image_name, dtype=np.uint8), cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
h, w = image.shape[:2]
labelme_json['imageHeight'] = h
labelme_json['imageWidth'] = w
with open(txt, 'r') as t:
lines = t.readlines()
for line in lines:
content = line.split(' ')
label = content[0]
object_width = float(content[3])
object_height = float(content[4])
top_left_x = (float(content[1]) - object_width / 2) * w
top_left_y = (float(content[2]) - object_height / 2) * h
bottom_right_x = (float(content[1]) + object_width / 2) * w
bottom_right_y = (float(content[2]) + object_height / 2) * h
try:
shape = {
'label': str(label),
'score':float(content[5]),
'group_id': None,
'shape_type': 'rectangle',
'flags': {},
'points': [
[float(top_left_x), float(top_left_y)],
[float(bottom_right_x), float(bottom_right_y)]
]
}
except Exception as e:
# print(e)
shape = {
'label': str(label),
'score':float(0.99),
'group_id': None,
'shape_type': 'rectangle',
'flags': {},
'points': [
[float(top_left_x), float(top_left_y)],
[float(bottom_right_x), float(bottom_right_y)]
]
}
labelme_json['shapes'].append(shape)
json_name = txt_name.split('.')[0] + '.json'
json_name_path = os.path.join(output_dir, json_name)
fd = open(json_name_path, 'w')
json.dump(labelme_json, fd, indent=4)
fd.close()
print("save json={}".format(json_name_path))
if __name__=="__main__":
in_imgs_dir = 'images'
in_label_txt_dir = 'labels'
out_labelme_json_dir = 'jsons'
if not os.path.exists(out_labelme_json_dir):
os.mkdir(out_labelme_json_dir)
convert_txt_to_labelme_json(in_label_txt_dir,in_imgs_dir,out_labelme_json_dir,image_fmt='.jpg')
输出结果
jsons/000000000009.json
{
"version": "4.5.7",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [
{
"label": "45",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
1.0799999999999699,
187.69008
],
[
612.66976,
473.53008
]
]
},
{
"label": "45",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
311.73024,
4.310160000000001
],
[
631.01024,
232.99032
]
]
},
{
"label": "50",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
249.60032000000007,
229.27032
],
[
565.84032,
474.35016
]
]
},
{
"label": "45",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
0.0003200000000092018,
13.510080000000002
],
[
434.48032,
388.63007999999996
]
]
},
{
"label": "49",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
376.2,
40.35996
],
[
451.75007999999997,
86.88996
]
]
},
{
"label": "49",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
465.7797119999999,
38.969952
],
[
523.849728,
85.63996800000001
]
]
},
{
"label": "49",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
385.70016000000004,
73.65983999999999
],
[
469.72,
144.16992
]
]
},
{
"label": "49",
"score": 0.99,
"group_id": null,
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"points": [
[
364.04959999999994,
2.4900960000000016
],
[
458.80992,
73.559856
]
]
}
],
"imagePath": "000000000009.jpg",
"imageData": null,
"imageHeight": 480,
"imageWidth": 640
}
参考
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/lucky404/article/details/132156805
[2] https://blog.csdn.net/h609232722/article/details/130710032
- 由于本人水平有限,难免出现错漏,敬请批评改正。
- 更多精彩内容,可点击进入Python日常小操作专栏、OpenCV-Python小应用专栏、YOLO系列专栏、自然语言处理专栏或我的个人主页查看
- 基于DETR的人脸伪装检测
- YOLOv7训练自己的数据集(口罩检测)
- YOLOv8训练自己的数据集(足球检测)
- YOLOv5:TensorRT加速YOLOv5模型推理
- YOLOv5:IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU、EIoU
- 玩转Jetson Nano(五):TensorRT加速YOLOv5目标检测
- YOLOv5:添加SE、CBAM、CoordAtt、ECA注意力机制
- YOLOv5:yolov5s.yaml配置文件解读、增加小目标检测层
- Python将COCO格式实例分割数据集转换为YOLO格式实例分割数据集
- YOLOv5:使用7.0版本训练自己的实例分割模型(车辆、行人、路标、车道线等实例分割)
- 使用Kaggle GPU资源免费体验Stable Diffusion开源项目