c++标准模板(STL)(std::list)(六)
定义于头文件
template< class T, class Allocator = std::allocator > class list; (1)
namespace pmr { template
using list = std::list>;} (2) (C++17 起) std::list 是支持常数时间从容器任何位置插入和移除元素的容器。不支持快速随机访问。它通常实现为双向链表。与 std::forward_list 相比,此容器提供双向迭代但在空间上效率稍低。
在 list 内或在数个 list 间添加、移除和移动元素不会非法化迭代器或引用。迭代器仅在对应元素被删除时非法化。
std::list 满足容器 (Container) 、具分配器容器 (AllocatorAwareContainer) 、序列容器 (SequenceContainer) 及可逆容器 (ReversibleContainer) 的要求。
插入元素
std::list::insert | iterator insert( iterator pos, const T& value ); |
(1) | (C++11 前) | |
| iterator insert( const_iterator pos, const T& value ); |
(C++11 起) | ||
| iterator insert( const_iterator pos, T&& value ); |
(2) | (C++11 起) | |
| void insert( iterator pos, size_type count, const T& value ); |
(C++11 前) | ||
| iterator insert( const_iterator pos, size_type count, const T& value ); |
(C++11 起) | ||
| template< class InputIt > |
(4) | (C++11 前) | |
| template< class InputIt > |
(C++11 起) | ||
| iterator insert( const_iterator pos, std::initializer_list |
(5) | (C++11 起) | |
插入元素到容器中的指定位置。
1-2) 在 pos 前插入 value 。
3) 在 pos 前插入 value 的 count 个副本。
4) 在 pos 前插入来自范围 [first, last) 的元素。
若 InputIt 为整数类型,则此重载与重载 (3) 拥有相同效果。 |
(C++11 前) |
此重载仅若 InputIt 足以为遗留输入迭代器 (LegacyInputIterator) 才参与重载决议,以避免与重载 (3) 有歧义。 |
(C++11 起) |
若 first 和 last 是指向 *this 中的迭代器,则行为未定义。
5) 在 pos 前插入来自 initializer_list ilist 的元素。
没有引用和迭代器被非法化。
参数
| pos | - | 将内容插入到其前的迭代器。 pos 可为 end() 迭代器 |
| value | - | 要插入的元素值 |
| first, last | - | 要插入的元素范围,不能是指向调用 insert 所用的容器中的迭代器 |
| ilist | - | 要插入的值来源的 initializer_list |
| 类型要求 | ||
- 为使用重载 (1) , T 必须满足可复制插入 (CopyInsertable) 的要求。 |
||
- 为使用重载 (2) , T 必须满足可移动插入 (MoveInsertable) 的要求。 |
||
- 为使用重载 (3) , T 必须满足可复制赋值 (CopyAssignable) 和 可复制插入 (CopyInsertable) 的要求。 |
||
- 为使用重载 (4,5) , T 必须满足可就位构造 (EmplaceConstructible) 的要求。 |
||
返回值
1-2) 指向被插入 value 的迭代器。
3) 指向首个被插入元素的迭代器,或若 count==0 则为 pos 。
4) 指向首个被插入元素的迭代器,或若 first==last 则为 pos 。
5) 指向首个被插入元素的迭代器,或若 ilist 为空则为 pos 。
复杂度
1-2) 常数。
3) 与 count 成线性。
4) 与 std::distance(first, last) 成线性。
5) 与 ilist.size() 成线性。
异常
若抛出异常,则无效果(强异常保证)。
调用示例
#include
#include
#include
#include
template
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& s, const std::list& v)
{
s.put('[');
char comma[3] = {'\0', ' ', '\0'};
for (const auto& e : v)
{
s << comma << e;
comma[0] = ',';
}
return s << ']';
}
int main()
{
// c++11 初始化器列表语法:
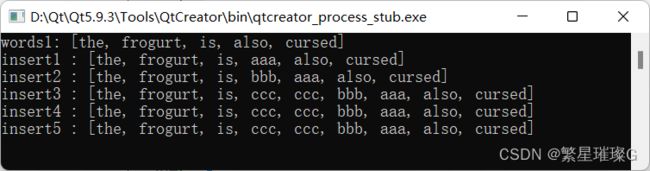
std::list words1 {"the", "frogurt", "is", "also", "cursed"};
std::cout << "words1: " << words1 << '\n';
//在 pos 前插入 value
std::list::iterator itf = std::find(words1.begin(), words1.end(), std::string("also"));
words1.insert(itf, "aaa");
std::cout << "insert1 : " << words1 << '\n';
//在 pos 前插入 value, 移动语义
itf = std::find(words1.begin(), words1.end(), std::string("aaa"));
words1.insert(itf, std::move(std::string("bbb")));
std::cout << "insert2 : " << words1 << '\n';
//在 pos 前插入 value 的 count 个副本。
itf = std::find(words1.begin(), words1.end(), std::string("bbb"));
words1.insert(itf, 2, std::move(std::string("ccc")));
std::cout << "insert3 : " << words1 << '\n';
//在 pos 前插入来自范围 [first, last) 的元素。
std::list words2;
words2.insert(words2.end(), words1.begin(), words1.end());
std::cout << "insert4 : " << words2 << '\n';
//在 pos 前插入来自 initializer_list ilist 的元素。
std::list words3;
words3.insert(words3.end(), {"the", "frogurt", "is", "also", "cursed"});
std::cout << "insert5 : " << words2 << '\n';
}
输出
原位构造元素
std::list::emplace | template< class... Args > |
(C++11 起) |
直接于 pos 前插入元素到容器中。通过 std::allocator_traits::construct 构造元素,它典型地用布置 new 在容器所提供的位置原位构造元素。将参数 args... 作为 std::forward
没有引用和迭代器被非法化。
参数
| pos | - | 将构造新元素到其前的迭代器 |
| args | - | 转发给元素构造函数的参数 |
| 类型要求 | ||
- T (容器元素类型) 必须满足可就位构造 (EmplaceConstructible) 的要求。 |
||
返回值
指向被安置的元素的迭代器。
复杂度
常数。
异常
若抛异常(例如由构造函数),则保留容器不修改,如同未曾调用过此函数(强异常保证)。
调用示例
#include
#include
#include
#include
class Ctest
{
public:
Ctest() {}
Ctest(int a, int b)
{
A = a;
B = b;
}
void printf() const
{
std::cout << "{" << A << "," << B << "}";
}
bool operator ==(const Ctest &t)
{
return A == t.A && B == t.B;
}
private:
int A;
int B;
};
void print(const std::string &name, const std::list &tlist)
{
std::cout << name << " : ";
for (auto &test : tlist)
{
test.printf();
std::cout << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
int main()
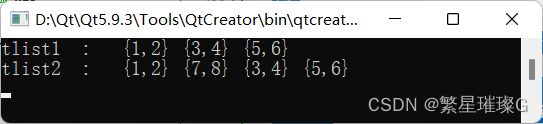
{
std::list tlist{{1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6}};
print("tlist1", tlist);
auto itf = std::find(tlist.begin(), tlist.end(), Ctest(3, 4));
tlist.emplace(itf, 7, 8);
print("tlist2", tlist);
return 0;
}
输出