Netty--ByteBuffer
2. ByteBuffer
有一普通文本文件 data.txt,内容为
1234567890abcd
使用 FileChannel 来读取文件内容
@Slf4j
public class ChannelDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// FileChannel
// 1. 输入输出流, 2. RandomAccessFile
// try (FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel()) {
// // 准备缓冲区
// ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
// while(true) {
// // 从 channel 读取数据,向 buffer 写入
// int len = channel.read(buffer);
// log.debug("读取到的字节数 {}", len);
// if(len == -1) { // 没有内容了
// break;
// }
// // 打印 buffer 的内容
// buffer.flip(); // 切换至读模式
// while(buffer.hasRemaining()) { // 是否还有剩余未读数据
// byte b = buffer.get();
// log.debug("实际字节 {}", (char) b);
// }
// buffer.clear(); // 切换为写模式
// }
// } catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
try (RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("helloword/data.txt", "rw")) {
// 准备缓冲区
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
do {
// 从 channel 读取数据,向 buffer 写入
int len = channel.read(buffer);
log.debug("读到字节数:{}", len);
if (len == -1) {
break;
}
// 打印 buffer 的内容
buffer.flip(); // 切换至读模式
while(buffer.hasRemaining()) { // 是否还有剩余未读数据
log.debug("{}", (char)buffer.get());
}
// 切换 buffer 写模式
buffer.clear();//清空刚刚读取过的数据,如果不清空,会进入死循环,永远读取的都是前10个数据
} while (true);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出
10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 读到字节数:10 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 1 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 2 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 3 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 4 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 5 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 6 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 7 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 8 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 9 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 0 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 读到字节数:4 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - a 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - b 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - c 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - d 10:39:03 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.ChannelDemo1 - 读到字节数:-1
2.1 ByteBuffer 正确使用姿势
- 向 buffer 写入数据,例如调用 channel.read(buffer)
- 调用 flip() 切换至读模式
- 从 buffer 读取数据,例如调用 buffer.get()
- 调用 clear() 或 compact() 切换至写模式
- 重复 1~4 步骤
2.2 ByteBuffer 结构
ByteBuffer 有以下重要属性
- capacity
- position
- limit
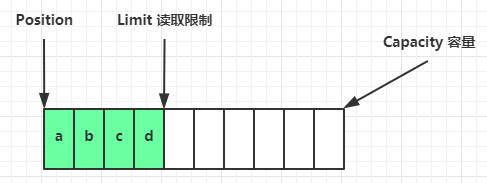
一开始
写模式下,position 是写入位置,limit 等于容量,下图表示写入了 4 个字节后的状态
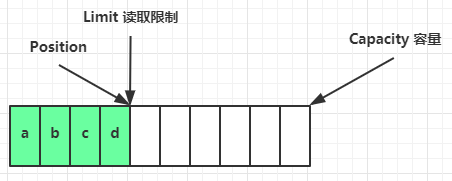
flip 动作发生后,position 切换为读取位置(开头),limit 切换为读取限制(写入的字节总数)
读取 4 个字节后,状态
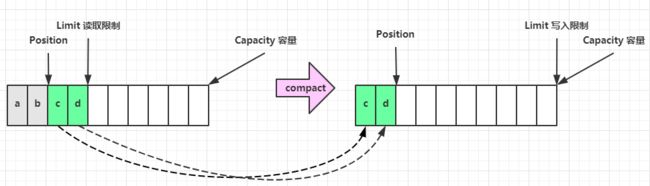
clear 动作发生后,状态
compact 方法,是把未读完的部分向前压缩,然后切换至写模式(让position变为剩余未读的字节数,limit变为buffer的容量)
调试工具类
public class ByteBufferUtil {
private static final char[] BYTE2CHAR = new char[256];
private static final char[] HEXDUMP_TABLE = new char[256 * 4];
private static final String[] HEXPADDING = new String[16];
private static final String[] HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES = new String[65536 >>> 4];
private static final String[] BYTE2HEX = new String[256];
private static final String[] BYTEPADDING = new String[16];
static {
final char[] DIGITS = "0123456789abcdef".toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
HEXDUMP_TABLE[i << 1] = DIGITS[i >>> 4 & 0x0F];
HEXDUMP_TABLE[(i << 1) + 1] = DIGITS[i & 0x0F];
}
int i;
// Generate the lookup table for hex dump paddings
for (i = 0; i < HEXPADDING.length; i++) {
int padding = HEXPADDING.length - i;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding * 3);
for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {
buf.append(" ");
}
HEXPADDING[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for the start-offset header in each row (up to 64KiB).
for (i = 0; i < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length; i++) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(12);
buf.append(NEWLINE);
buf.append(Long.toHexString(i << 4 & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));
buf.setCharAt(buf.length() - 9, '|');
buf.append('|');
HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-hex-dump conversion
for (i = 0; i < BYTE2HEX.length; i++) {
BYTE2HEX[i] = ' ' + StringUtil.byteToHexStringPadded(i);
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte dump paddings
for (i = 0; i < BYTEPADDING.length; i++) {
int padding = BYTEPADDING.length - i;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding);
for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {
buf.append(' ');
}
BYTEPADDING[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-char conversion
for (i = 0; i < BYTE2CHAR.length; i++) {
if (i <= 0x1f || i >= 0x7f) {
BYTE2CHAR[i] = '.';
} else {
BYTE2CHAR[i] = (char) i;
}
}
}
/**
* 打印所有内容
* @param buffer
*/
public static void debugAll(ByteBuffer buffer) {
int oldlimit = buffer.limit();
buffer.limit(buffer.capacity());
StringBuilder origin = new StringBuilder(256);
appendPrettyHexDump(origin, buffer, 0, buffer.capacity());
System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+");
System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), oldlimit);
System.out.println(origin);
buffer.limit(oldlimit);
}
/**
* 打印可读取内容
* @param buffer
*/
public static void debugRead(ByteBuffer buffer) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(256);
appendPrettyHexDump(builder, buffer, buffer.position(), buffer.limit() - buffer.position());
System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- read -----------------------+----------------+");
System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), buffer.limit());
System.out.println(builder);
}
private static void appendPrettyHexDump(StringBuilder dump, ByteBuffer buf, int offset, int length) {
if (isOutOfBounds(offset, length, buf.capacity())) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"expected: " + "0 <= offset(" + offset + ") <= offset + length(" + length
+ ") <= " + "buf.capacity(" + buf.capacity() + ')');
}
if (length == 0) {
return;
}
dump.append(
" +-------------------------------------------------+" +
NEWLINE + " | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |" +
NEWLINE + "+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");
final int startIndex = offset;
final int fullRows = length >>> 4;
final int remainder = length & 0xF;
// Dump the rows which have 16 bytes.
for (int row = 0; row < fullRows; row++) {
int rowStartIndex = (row << 4) + startIndex;
// Per-row prefix.
appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, row, rowStartIndex);
// Hex dump
int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + 16;
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(" |");
// ASCII dump
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append('|');
}
// Dump the last row which has less than 16 bytes.
if (remainder != 0) {
int rowStartIndex = (fullRows << 4) + startIndex;
appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, fullRows, rowStartIndex);
// Hex dump
int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + remainder;
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(HEXPADDING[remainder]);
dump.append(" |");
// Ascii dump
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(BYTEPADDING[remainder]);
dump.append('|');
}
dump.append(NEWLINE +
"+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");
}
private static void appendHexDumpRowPrefix(StringBuilder dump, int row, int rowStartIndex) {
if (row < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length) {
dump.append(HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[row]);
} else {
dump.append(NEWLINE);
dump.append(Long.toHexString(rowStartIndex & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));
dump.setCharAt(dump.length() - 9, '|');
dump.append('|');
}
}
public static short getUnsignedByte(ByteBuffer buffer, int index) {
return (short) (buffer.get(index) & 0xFF);
}
}
2.3 ByteBuffer 常见方法
分配空间
可以使用 allocate 方法为 ByteBuffer 分配空间,其它 buffer 类也有该方法
Bytebuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
向 buffer 写入数据
有两种办法
- 调用 channel 的 read 方法
- 调用 buffer 自己的 put 方法
int readBytes = channel.read(buf);
和
buf.put((byte)127);
从 buffer 读取数据
同样有两种办法
- 调用 channel 的 write 方法
- 调用 buffer 自己的 get 方法
int writeBytes = channel.write(buf);
和
byte b = buf.get();
get 方法会让 position 读指针向后走,如果想重复读取数据
- 可以调用 rewind 方法将 position 重新置为 0
- 或者调用 get(int i) 方法获取索引 i 的内容,它不会移动读指针
mark 和 reset
mark 是在读取时,做一个标记,即使 position 改变,只要调用 reset 就能回到 mark 的位置
注意
rewind 和 flip 都会清除 mark 位置
字符串与 ByteBuffer 互转
// 1. 字符串转为 ByteBuffer,不会转为读模式
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
buffer1.put("hello".getBytes());
debugAll(buffer1);
// 2. Charset,直接转为读模式
ByteBuffer buffer2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
debugAll(buffer2);
// 3. wrap,直接转为读模式
ByteBuffer buffer3 = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes());
debugAll(buffer3);
// 4. 转为字符串
String str1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer2).toString();
System.out.println(str1);
buffer1.flip();//此处要转为读模式
String str2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer1).toString();
System.out.println(str2);
输出
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| e4 bd a0 e5 a5 bd |...... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| e4 bd a0 e5 a5 bd |...... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
class java.nio.HeapCharBuffer
你好
⚠️ Buffer 的线程安全
Buffer 是非线程安全的
2.4 Scattering Reads
分散读取,有一个文本文件 3parts.txt
onetwothree
使用如下方式读取,可以将数据填充至多个 buffer
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("3parts.txt", "r").getChannel()) {
ByteBuffer b1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b3 = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
channel.read(new ByteBuffer[]{b1, b2, b3});
b1.flip();
b2.flip();
b3.flip();
debugAll(b1);
debugAll(b2);
debugAll(b3);
} catch (IOException e) {
}
结果
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 6f 6e 65 |one |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 74 77 6f |two |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 74 68 72 65 65 |three |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
2.5 Gathering Writes
使用如下方式写入,可以将多个 buffer 的数据填充至 channel
// try (RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("helloword/3parts.txt", "rw")) {
// FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();
// ByteBuffer d = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
// ByteBuffer e = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
// channel.position(11);
// d.put(new byte[]{'f', 'o', 'u', 'r'});
// e.put(new byte[]{'f', 'i', 'v', 'e'});
// d.flip();
// e.flip();
// debugAll(d);
// debugAll(e);
// channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{d, e});
// } catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
ByteBuffer b1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
ByteBuffer b2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("world");
ByteBuffer b3 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("你好");
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("words2.txt", "rw").getChannel()) {
channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{b1, b2, b3});
} catch (IOException e) {
}
输出
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 66 6f 75 72 |four |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 66 69 76 65 |five |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
文件内容
onetwothreefourfive
2.6 练习(黏包、半包)
网络上有多条数据发送给服务端,数据之间使用 \n 进行分隔 但由于某种原因这些数据在接收时,被进行了重新组合,例如原始数据有3条为
- Hello,world\n
- I'm zhangsan\n
- How are you?\n
变成了下面的两个 byteBuffer (黏包(效率上的算法问题),半包(读取的空间问题))
- Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo
- w are you?\n
现在要求你编写程序,将错乱的数据恢复成原始的按 \n 分隔的数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
网络上有多条数据发送给服务端,数据之间使用 \n 进行分隔
但由于某种原因这些数据在接收时,被进行了重新组合,例如原始数据有3条为
Hello,world\n
I'm zhangsan\n
How are you?\n
变成了下面的两个 byteBuffer (黏包,半包)
Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo
w are you?\n
现在要求你编写程序,将错乱的数据恢复成原始的按 \n 分隔的数据
*/
ByteBuffer source = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
source.put("Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo".getBytes());
split(source);
source.put("w are you?\n".getBytes());
split(source);
}
private static void split(ByteBuffer source) {
source.flip();
for (int i = 0; i < source.limit(); i++) {
// 找到一条完整消息
if (source.get(i) == '\n') {
int length = i + 1 - source.position();
// 把这条完整消息存入新的 ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer target = ByteBuffer.allocate(length);
// 从 source 读,向 target 写
for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {
target.put(source.get());
}
debugAll(target);
}
}
source.compact();
}