Rasa NLU 组件解析
Rasa 组件 pipeline
文章目录
- Rasa 组件 pipeline
-
- **1. 语言组件**
-
- MitieNLP
- SpacyNLP
- **2. 分词器组件**
-
- WhitespaceTokenizer
- JiebaTokenizer
- MitieTokenizer
- SpacyTokenizer
- ConveRTTokenizer
- LanguageModelTokenizer
- 自定义分词器
- 总结
- **3. 特征提取器组件**
-
- MitieFeaturizer
- SpacyFeaturizer
- ConveRTFeaturizer
- LanguageModelFeaturizer
- RegexFeaturizer
- CountVectorsFeaturizer
- LexicalSyntacticFeaturizer
- 总结
- **4. 意图分类组件**
-
- MitieIntentClassifier
- SklearnIntentClassifier
- KeywordIntentClassifier
- DIETClassifier
- FallbackClassifier
- **5. 实体抽取组件**
-
- MitieEntityExtractor
- SpacyEntityExtractor
- CRFEntityExtractor
- DucklingEntityExtractor
- DIETClassifier
- RegexEntityExtractor
- EntitySynonymMapper
- **6. 响应选择器组件**
-
- 概述
- 输入输出
- 输出示例
- 示例
- **7. 自定义组件**
NLU模块也是一个可细分pipeline结构,过程是Tokenize->Featurize->NER Extract->Intent Classify。熟悉Word2Vec的知友知道,如果要获取句子的word2vec特征,首先要有个分词器,然后要有个word2vec模型。同理,如果Rasa NLU里面引用预训练的语言模型,那就需要提前加载,如果Tokenize使用空格分词或者结巴分词,特征向量使用One-hot编码或者 CountVectorsFeaturizer编码,那就不在需要语言模型了。
1. 语言组件
如果您想在管道中使用预训练的词向量,以下组件会加载所需的预训练模型。
MitieNLP
mitie 基于dlib库开发,dlib是一个c++高性能机器学习库。所以对性能有要求的信息抽取场景,可以考虑使用mitie。mitie现有的资料比较少,github最近更新也是五六年前了。
从mitie代码中看到它的NER使用structural_sequence_labeling_trainer.实现的细节见
https://www.aaai.org/Papers/ICML/2003/ICML03-004.pdf
文中指出,MITIE的NER是HMM 和SVM相结合做的。相比单纯的HMM,这种方法是基于最大margin 标准。这相比纯CRF或者最大熵的HMM有很多优势:
1)可以通过核函数学习非线性的判断关系
2)可以处理overlapping features.
但毕竟是基于传统机器学习的方式,相对于BERT这种海量语料预训练模型来说,效果还是稍差一点,这个可以使用RASA的NLU评估工具跑分试一下[NLU pipelines评估]。但MITIE有无可比拟的速度优势,在算力敏感的情况下自己权衡选择,RASA已经不做官方推荐了
-
使用前先下载mitie模型
https://github.com/mit-nlp/MITI
-
RASA配置使用MITIENLP
pipeline:
- name: "MitieNLP"
# 需要加载的语言模型
model: "data/total_word_feature_extractor.dat"
另外,MITIE没有预训练的中文模型,如果想开发中文机器人,需要自己训练语言模型。具体参考用Rasa NLU构建自己的中文NLU系统。
SpacyNLP
spaCy是一个用Python和Cython编写的高级自然语言处理的库。它跟踪最新的研究成果,并将其应用到实际产品。spaCy带有预训练的统计模型和单词向量,目前支持60多种语言。它用于标记任务,解析任务和命名实体识别任务的卷积神经网络模型,在非常快速的情况下,达到比较好的效果,并且易于在产品中集成应用。在github上接近18k的stars,并且更新比较活跃。最新发布的spaCy3.0也集成了Transformer相关模型。
使用spaCy时,文本字符串的第一步是将其传递给NLP对象。NLP对象本质上是由几个文本预处理操作组成的管道,输入文本字符串通过管道后,最终输出文档,完成各种功能。
上图示意了这个过程,在nlp对象中,要引入预训练spacy的语言模型。
下表显示了SpaCy在各个任务中的得分
该组件所需要的模型需要提前下载到本地,否则会出错
- spacy的中文模型的下载地址:
https://github.com/explosion/spacy-models
- 也可以在命令行中输入:
python -m spacy download zh_core_web_sm
- RASA中模型加载方式
pipeline:
- name: "SpacyNLP"
# 要加载的语言模型
model: "zh_core_web_sm"
# 检索词向量时,这将决定大小写是否
# 这个词是相关的。例如 `hello` 和 `Hello` 将
# 检索相同的向量,如果设置为 `False`。对于一些
# 区分应用程序和模型是有意义的
# 在这两个词之间,因此将其设置为 `True`
case_sensitive: False
以前还有一个HFTransformersNLP,里面主要包含一些BERT,GTP等比较新的Transformer模型,现在已经在LanguageModelFeaturizer中实现了,不在需要在pipeline里面配置HFTransformersNLP语言模型。
2. 分词器组件
分词器将输入文本分成一个一个token,然后传给Featurizer,形成特征向量。
- intent_tokenization_flag和intent_split_symbol是在nlu返回多意图的时候使用。
intent_tokenization_flag指示是否标记意图标签。将其设置为True,以便对意图标签进行标记。intent_split_symbol设置分隔符字符串以分割意图标签,默认为下划线 (_)。
- **intent_tokenization_flag设置为False,nlu只返回一个置信度最高的意图。**但有些时候,一句话包含多个意图,例如:
## intent: affirm+ask_transport
- Yes. How do I get there?
- Sounds good. Do you know how I could get there from home?
用户的回答包含2层意思,首先是同意我的建议,另外是询问怎么去。这时候,需要将intent_tokenization_flag设置为True,然后在训练数据里面编写多意图对应的话术,多个意图中间用intent_split_symbol去分割。在运行的时候,用户说“Sounds good. Do you know how I could get there from home?”,Rasa nlu就会返回affirm+ask_transport这个意图。
- token_pattern是一个正则表达式,是对分词后的结果做后处理:过程是这样:先对一句话进行分词,生成一个序列,然后将序列中每个token再应用到token_pattern处理一次,将新生成的词也放在最终分词列表里面。
WhitespaceTokenizer
空格分词器,每个空格间隔的文本,都将分为一个token,典型的英文句子的分词。该分词器不支持中文分词。
配置方式如下:
pipeline:
- name: "WhitespaceTokenizer"
# 标记以检查是否拆分意图
"intent_tokenization_flag": False
# 意图应该被分割的符号
"intent_split_symbol": "_"
# 检测标记的正则表达式
"token_pattern": None
JiebaTokenizer
jieba分词器,仅可以在中文分词使用,支持自定义词库分词。
要使用JiebaTokenizer您需要安装 Jieba 与pip3 install jieba.
配置方法如下:
pipeline:
- name: "JiebaTokenizer"
dictionary_path: "path/to/custom/dictionary/dir"
# 标记以检查是否拆分意图
"intent_tokenization_flag": False
# 意图应该被分割的符号
"intent_split_symbol": "_"
# 检测标记的正则表达式
"token_pattern": None
用户的自定义字典文件可以通过指定文件的目录路径来自动加载
dictionary_path。如果dictionary_path是None(默认值),则不会使用自定义字典。
MitieTokenizer
使用MitieNLP进行分词,依赖:需要配置Mitie语言模型。一般在使用全套MiteNLP的时候使用。
配置方法如下:
pipeline:
- name: "MitieTokenizer"
# 标记以检查是否拆分意图
"intent_tokenization_flag": False
# 意图应该被分割的符号
"intent_split_symbol": "_"
# 检测标记的正则表达式
"token_pattern": None
SpacyTokenizer
使用SpacyNLP进行分词,依赖:需要配置Spacy语言模型。
配置方法如下:
pipeline:
- name: "SpacyTokenizer"
# 标记以检查是否拆分意图
"intent_tokenization_flag": False
# 意图应该被分割的符号
"intent_split_symbol": "_"
# 检测标记的正则表达式
"token_pattern": None
ConveRTTokenizer
ConveRTTokenizer分词器已经不再使用了,ConveRTFeaturize实现了ConveRTTokenizer的功能,输入的token可以是任意值,都可以使用ConveRTFeaturizer去生成特征向量。
- 但是,如果使用ConveRTFeaturize,Tokenizer还是要配置的,只是可以配置任意分词器,比如Jieba,对结果没有影响。如果不配置分词器会提示错误:The pipeline configuration contains errors. The component ‘ConveRTFeaturize’ requires ‘Tokenizer’。
LanguageModelTokenizer
LanguageModelTokenizer也不在需要了,LanguageModelFeaturizer实现了诸如BERT,GPT等预训练模型,直接只用即可。
- 但是如果使用LanguageModelFeaturizer,**pipeline里面至少要配置一个分词器,**比如JIeba,空格分词器都行。否则训练的时候会报错。
自定义分词器
如果上述分词器不满足要求,可以自定义分词器。要实现自定义分词器,需要继承Tokenizer和Component类,需要重载的函数有:init,train,tokenize,具体模板如下:
class CustomTokenizer(Tokenizer, Component):
provides = [MESSAGE_TOKENS_NAMES[attribute] for attribute in MESSAGE_ATTRIBUTES]
def train(
self, training_data: TrainingData, config: RasaNLUModelConfig, **kwargs: Any
) -> None:
for example in training_data.training_examples:
for attribute in MESSAGE_ATTRIBUTES:
if example.get(attribute) is not None:
example.set(
MESSAGE_TOKENS_NAMES[attribute],
self.tokenize(example.get(attribute), attribute),
)
# 主要是要实现对应的tokenize
def tokenize(self, text: Text) -> List[Token]:
pass
总结
需要加载语言模型的分词器有Mitie,SpaCy,其中Mitie没有中文预训练模型,如果实现中文对话系统,需要自行准备语料训练Mitie语言模型。SpaCy有中文模型。ConveRTTokenizer,LanguageModelTokenizer已经废弃了,使用ConveRTFeaturize,LanguageModelFeaturizer可以使用任意分词器。
3. 特征提取器组件
RASA Featurizer分为两类:稀疏向量如One-hot和稠密向量如Bert。稀疏特征化器是返回具有大量缺失值(例如零)的特征向量的特征化器。由于这些特征向量通常会占用大量内存,因此我们将它们存储为稀疏特征。稀疏特征仅存储非零值及其在向量中的位置。因此,我们节省了大量内存并能够在更大的数据集上进行训练。
所有Featurizer都可以返回两种不同的特征:序列特征和句子特征。序列特征是(number-of-tokens x feature-dimension)维度的矩阵,矩阵包含了句子中每个Token的特征向量,我们用这个特征去训练序列模型,如实体识别。句子特征由(1 x feature-dimension)大小矩阵表示,它包含完整对话的特征向量,可以用于意图分类等。句子特征可以在任何词袋模型中使用。具体在系统中使用哪种类型的特征值由使用的分类器决定。
RASA支持的特征生成器:
MitieFeaturizer
输出为稠密向量,可以被其他意图分类器使用。需要在pipeline中引入MitieNLP语言模型。但是有意思的是,该特征器并没有被MitieIntentClassifier使用,因为MitieIntentClassifier里面实现了所有分词,特征提取功能,但可以由管道中稍后使用dense_features.。
MitieFeaturizer是对每个Token输出一个feature-dimension维度的向量,那么生成句子向量的做法是通过pooling技术,这里可以选择max pooling和mean pooling,这个参数可以在配置文件中指定。最终会生成一个1 x feature-dimension的句子向量。max pooling算法就是取每个token中相同维度,最大的值作为句子向量的这个维度的值,那么mean pooling就好理解了,句子向量是每个token的均值。
配置方法如下:
pipeline:
- name: "MitieNLP"
model: "data/total_word_feature_extractor.dat"
- name: "MitieTokenizer"
# 标记以检查是否拆分意图
"intent_tokenization_flag": False
# 意图应该被分割的符号
"intent_split_symbol": "_"
# 检测标记的正则表达式
"token_pattern": None
- name: "MitieFeaturizer"
# 指定应该使用什么池操作来计算的向量
# 完整的话语。可用选项:“mean”和“max”。
"pooling": "mean"
SpacyFeaturizer
同Mitie类似,Spacy也输出稠密向量,可以被其他意图分类器使用。SpacyFeaturizer需要在pipeline中引入SpacyNLP语言模型。
因为SpacyFeaturizer也是对每个Token输出一个feature-dimension维度的向量,那么生成句子向量的做法是通过pooling技术,这里可以选择max pooling和mean pooling,可以在配置文件中指定。最终会生成一个1 x feature-dimension的句子向量。
配置方法如下:
pipeline:
- name:"SpacyNLP"
model:"en_core_web_md"
- name: "SpacyTokenizer"
"intent_tokenization_flag": False
"intent_split_symbol": "_"
"token_pattern": None
- name: "SpacyFeaturizer"
# 指定应该使用什么池化操作来计算向量
# 完整的话语。可用选项:“平均”和“最大”。
"pooling": "mean"
ConveRTFeaturizer
使用ConveRT模型生成句子的特征表示。输出为稠密变量。因为ConveRT模型只有英文模型,因此中文对话机器人不能使用ConveRTFeaturizer,除非你想自己训练一个ConveRT模型。使用该Featurizer的时候,需要使用model_url参数配置模型文件的路径,否则训练的时候会报错。ConveRTFeaturizer已经实现了ConveRTTokenizer的功能,所以Pipeline可以配置任意的Tokenizer。从代码里面看ConveRTTokenizer,LanguageModelTokenizer都是继承WhitespaceTokenizer,并没有做特殊处理,而用WhitespaceTokenizer在中文的时候,会提示不支持中文错误,所以可选的分词器并不多,只有MitieTokenizer和SpcayTokenizer。
要使用ConveRTFeaturizer,请使用pip3 install rasa[convert]
简单介绍下ConveRT模型,下面是论文连接:
ConveRT: Efficient and accurate conversational representations from transformersarxiv.org/abs/1911.03688
配置方法如下:
pipeline:
- name: "ConveRTFeaturizer"
# 模型文件的远程URL/本地目录(必需)
"model_url": None
LanguageModelFeaturizer
这就是著名的BERT模型了,输入为用户消息,响应消息等,输出为稠密变量。使用LanguageModelFeaturizer,首先要根据机器人的是中文的还是英文的,选择预训练模型。下表是目前支持的预训练模型。因为LanguageModelFeaturizer里面已经实现了分词功能,因为pipeline里面可以配置任意Tokenizer,但注意要是稠密向量。所以不能配置WhitespaceTokenizer和JiebaTokenizer。而LanguageModelTokenizer又不支持中文,所以只有MitieTokenizer和SpcayTokenizer。这里配置什么分词器并不影响最终结果。
注:这里可以从Tokenizer类自定义个空分词器NullTokenizer,里面什么都不做,然后LanguageModelFeaturizer这类不需要分词器的,pipeline里面都配置NullTokenizer。其实LanguageModelTokenizer和ConveRTTokenizer就什么都没有做,只是继承与WhitespaceTokenizer,而WhitespaceTokenizer有句话not_supported_language_list = [“zh”, “ja”, “th”],所以LanguageModelFeaturizer就不支持中文了。
LanguageModelFeaturizer支持的预训练模型有:
+----------------+--------------+-------------------------+
| Language Model | Parameter | Default value for |
| | "model_name" | "model_weights" |
+----------------+--------------+-------------------------+
| BERT | bert | rasa/LaBSE |
+----------------+--------------+-------------------------+
| GPT | gpt | openai-gpt |
+----------------+--------------+-------------------------+
| GPT-2 | gpt2 | gpt2 |
+----------------+--------------+-------------------------+
| XLNet | xlnet | xlnet-base-cased |
+----------------+--------------+-------------------------+
| DistilBERT | distilbert | distilbert-base-uncased |
+----------------+--------------+-------------------------+
| RoBERTa | roberta | roberta-base |
+----------------+--------------+-------------------------+
其中预训练模型的名称使用model_weights参数配置:
BERT模型,model_weights可选参数有:
bert-base-uncased
bert-large-uncased
bert-base-cased
bert-large-cased
bert-base-multilingual-uncased
bert-base-multilingual-cased
# 中文预训练模型
bert-base-chinese
bert-base-german-cased
bert-large-uncased-whole-word-masking
bert-large-cased-whole-word-masking
bert-large-uncased-whole-word-masking-finetuned-squad
bert-large-cased-whole-word-masking-finetuned-squad
bert-base-cased-finetuned-mrpc
bert-base-german-dbmdz-cased
bert-base-german-dbmdz-uncased
TurkuNLP/bert-base-finnish-cased-v1
TurkuNLP/bert-base-finnish-uncased-v1
wietsedv/bert-base-dutch-cased
roberta模型的model_weights参数可以选
roberta-base
roberta-large
roberta-large-mnli
distilroberta-base
roberta-base-openai-detector
roberta-large-openai-detector
xlnet模型的model_weights参数可选
xlnet-base-cased
xlnet-large-cased
配置方法如下:
比如我训练的中文机器人
# Configuration for Rasa NLU.
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/nlu/components/
language: zh
pipeline:
- name: JiebaTokenizer
- name: RegexFeaturizer
- name: LexicalSyntacticFeaturizer
- name: LanguageModelFeaturizer
model_name: bert # BERT模型
model_weights: bert-base-chinese # 中文预训练模型
- name: DIETClassifier
epochs: 100
- name: EntitySynonymMapper
- name: ResponseSelector
epochs: 100
- name: FallbackClassifier
threshold: 0.3
ambiguity_threshold: 0.1
policies:
- name: MemoizationPolicy
- name: TEDPolicy
max_history: 5
epochs: 100
- name: RulePolicyPolicies# Configuration for Rasa NLU.
RegexFeaturizer
使用正则表达式创建一个消息表示,注意输入只能是用户消息,这个和其他几个Featurizer不同,输出的内容是一个稀疏向量。
在训练阶段,根据配置会生成一个符合输入句子的正则表达式列表,当运行阶段,针对用户消息,会对每一个正则表达式都匹配一次,如果匹配这个正则表达式就会创建一个特征,然后所有这些特征形成一个列表,输出到分类器和提取器里面。那么分类器和实体提取器会根据这个特征指示知道已经找到分类标签或者实体了,然后会直接使用分类标签和实体。
注意:目前只有CRFEntityExtractor和DIETClassifier这两个才支持RegexFeaturizer。
配置方法如下:
RegexFeaturizer的配置在nlu的pipeline里面配置。
-
case_sensitive: False通过添加选项 使特征化器不区分大小写,默认值为case_sensitive: True. -
要正确处理诸如中文等不使用空格进行分词的语言,用户需要添加
use_word_boundaries: False选项,默认为use_word_boundaries: True.
pipeline:
- name: "RegexFeaturizer"
# 文本将以区分大小写作为默认值进行处理
"case_sensitive": True
# 使用匹配词边界查找表
"use_word_boundaries": True
具体正则表达式的配置在训练数据里面配置:
##Regex的配置方式
nlu:
- regex: account_number
examples: |
- \d{10,12}
配置增量训练
为确保在增量训练sparse_features期间具有固定大小 ,应配置组件以考虑将来可能添加到训练数据中的其他模式。为此,请 在从头开始训练基本模型时配置参数:number_additional_patterns
pipeline:
- name: "RegexFeaturizer"
number_additional_patterns: 10
如果用户未配置,该组件将使用训练数据中当前存在的模式数量的两倍(包括查找表和正则表达式模式)作为number_additional_patterns. 这个数字至少保持在 10,以避免在增量训练期间过于频繁地用完新模式的额外插槽。一旦组件用完额外的模式槽,新模式就会被丢弃,并且在特征化过程中不会考虑。此时,建议从头开始重新训练新模型。
CountVectorsFeaturizer
把用户消息,意图,响应消息创建一个词袋模型表示。输出也是稀疏矩阵。
CountVectorizer生成算法是使用sklearn 的 CountVectorizer创建用户消息、意图和响应的词袋表示 。所有仅由数字组成的标记(例如 123 和 99 但不包括 a123d)将分配给相同的功能。
有关配置参数的详细说明,请参阅sklearn 的 CountVectorizer 文档 。
下面将几个关键参数做个解释:
- analyzer,min-ngram,max-ngram:
analyzer可选值为word,char,char_wb。这个参数指定是用word的n-grams还是char的n-grams。例如,对于“中国北京“这个词,如果analyzer是word,那特征有“中国”,“北京”;如果analyzer配置为char,特征就有“中”,“国”,“北”,“京”四个token。如果min-ngram为1,max-ngram为2,依旧对于中国北京“这个词,如果analyzer是word,特征有“中国”,“北京”,“中国北京”;如果analyzer配置问char,特征就有“中”,“国”,“北”,“京”,“中国”,“国北”,“北京”。char_wb和char区别在于边界处理上,当analyzer为char_wb,单词边缘的n-gram用空格填充,例如,当min-ngram为1,max-ngram为2时,“中国北京”具有的特征有“中”,“国”,“北”,“京”,“中国”,“国北”,“北京”,“京 ”。
- ·use_lemma:
可选值为True和False,主要对于英文语言提取特征,因为英文有时态和语态问题,同一个单词有不同的表现方式,因此当use_lemma为True时候,use和used是一个特征。目前只有SpacyTokenizer支持,可以通过设置use_lemma为False来关闭。
需要注意的是,所有的纯数字都会编码为同一个特征向量。
- OOV_token,OOV_words:
由于训练数据是有限的词汇表,因此不能保证在预测过程中算法遇到所有词都在训练数据中心出现,为了教算法如何处理这些集外词,这里提供了两个配置参数OOV_token和OOV_words。
OOV_token是一个字符串,例如"oov",在预测期间,所有未知单词都将被视为OOV_token对应的那个单词。我们可以在训练数据中编写一个intent,例如叫 intent _out_of_scope,包含一定数量的OOV_token和其他单词,这样在预测期间,算法将将含有未知单词的消息归类为这个意图。
OOV_words是一个单词列表,所有训练数据在此列表中的词,都被认为是OOV_token。这个东西有什么用途呢?假如,有一个词,不是很关键,我们想吧他设为集外词,那么我们要找训练数据,一条一条的找,把这个词改成_oov_,那么,有了OOV_words这个工具,我们只需要吧这个词添加到OOV_words配置里面就可以了。如果配置OOV_words,首先需要配置OOV_token。
需要注意的是,CountVectorsFeaturizer是通过计算词频来创建一个词袋表示的,因此对句子中OOV_token的数量很敏感。
-
**use_shared_vocab:**如果要在用户消息和意图之间共享词汇表,则需要将选项use_shared_vocab设置为True。
例如:
pipeline: - name: "CountVectorsFeaturizer" # 要使用的分析器,可以是“word”、“char”或“char_wb” analyzer: "word" # 设置n-gram的上下限 min_ngram: 1 max_ngram: 1 # 设置词汇表外标记 OOV_token: "_oov_" # 是否使用共享的词汇表 use_shared_vocab: False
配置增量训练
为了确保在增量训练sparse_features期间它们的大小是固定的 ,该组件应配置为考虑将来可能作为新训练示例的一部分添加的额外词汇标记。为此,请在从头开始训练基本模型时配置参数:additional_vocabulary_size
additional_vocabulary_size:稠密特征是固定长度,但是稀疏特征的长度是变的,比如新编写的训练数据多了一个新词,那么向量就变长了,为了能固定稀疏特征的长度,引入additional_vocabulary_size配置参数。 本质上就是为新词填充一些槽位,在没有新词的时候,这些槽位就填占位符,有新词就用新词替换占位符。
例如:
pipeline:
- name: "CountVectorsFeaturizer"
additional_vocabulary_size:
text: 1000
response: 1000
action_text: 1000
在上面的示例中,为文本(用户消息)、响应(ResponseSelector使用的bot响应)和操作文本(ResponseSelector未使用的bot响应)中的每一类定义额外的词汇表大小。如果use_shared_vocab=True,只需定义text属性一个值。如果用户未配置任何属性,additional_vocabulary_size的默认值是当前词汇表的一半。为了避免在增量训练中过于频繁地用完额外的词汇表,这个数字至少保持在1000。一旦组件用完了额外的词汇表槽,新的词汇表标记就会被丢弃,这时候就需要从头开始训练模型了,不能增量训练了。
CountVectorsFeaturizer的配置示例如下:
pipeline:
- name: "CountVectorsFeaturizer"
additional_vocabulary_size:
text: 1000
response: 1000
action_text: 1000
# 要使用的分析器,可以是“word”、“char”或“char_wb”'
analyzer: "word"
# 设置n-gram的上下限
min_ngram: 1
max_ngram: 1
# 设置词汇表外标记
OOV_token: "_oov_"
OOV_words: []
# 是否使用共享的词汇表
"use_shared_vocab": False
参数列表参考下文:
Parameter | Default Value | Description |
+===================+======================+==============================================================+
| use_shared_vocab | False | If set to 'True' a common vocabulary is used for labels |
| | | and user message. |
+-------------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| analyzer | word | Whether the features should be made of word n-gram or |
| | | character n-grams. Option 'char_wb' creates character |
| | | n-grams only from text inside word boundaries; |
| | | n-grams at the edges of words are padded with space. |
| | | Valid values: 'word', 'char', 'char_wb'. |
+-------------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| strip_accents | None | Remove accents during the pre-processing step. |
| | | Valid values: 'ascii', 'unicode', 'None'. |
+-------------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| stop_words | None | A list of stop words to use. |
| | | Valid values: 'english' (uses an internal list of |
| | | English stop words), a list of custom stop words, or |
| | | 'None'. |
+--------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| min_df | 1 | When building the vocabulary ignore terms that have a |
| | | document frequency strictly lower than the given threshold. |
+--------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| max_df | 1 | When building the vocabulary ignore terms that have a |
| | | document frequency strictly higher than the given threshold |
| | | (corpus-specific stop words). |
+--------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| min_ngram | 1 | The lower boundary of the range of n-values for different |
| | | word n-grams or char n-grams to be extracted. |
+--------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| max_ngram | 1 | The upper boundary of the range of n-values for different |
| | | word n-grams or char n-grams to be extracted. |
+--------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| max_features | None | If not 'None', build a vocabulary that only consider the top |
| | | max_features ordered by term frequency across the corpus. |
+--------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| lowercase | True | Convert all characters to lowercase before tokenizing. |
+--------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| OOV_token | None | Keyword for unseen words. |
+--------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| OOV_words | [] | List of words to be treated as 'OOV_token' during training. |
+--------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| alias | CountVectorFeaturizer| Alias name of featurizer. |
+--------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| use_lemma | True | Use the lemma of words for featurization. |
+--------------+----------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
LexicalSyntacticFeaturizer
将输入的消息创建词法和语法特征,用于后续的实体识别。输入是用户输入消息,输出是稀疏向量。
============== ==========================================================================================
Feature Name Description
============== ==========================================================================================
BOS Checks if the token is at the beginning of the sentence.
EOS Checks if the token is at the end of the sentence.
low Checks if the token is lower case.
upper Checks if the token is upper case.
title Checks if the token starts with an uppercase character and all remaining characters are
lowercased.
digit Checks if the token contains just digits.
prefix5 Take the first five characters of the token.
prefix2 Take the first two characters of the token.
suffix5 Take the last five characters of the token.
suffix3 Take the last three characters of the token.
suffix2 Take the last two characters of the token.
suffix1 Take the last character of the token.
pos Take the Part-of-Speech tag of the token (``SpacyTokenizer`` required).
pos2 Take the first two characters of the Part-of-Speech tag of the token
(``SpacyTokenizer`` required).
============== ==========================================================================================
特征提取器是后续计算的基础,信息越多越有利于后面的计算,所以常常都是几种办法组合使用。尤其RegexFeaturizer是最常用的。LexicalSyntacticFeaturizer也会提供一些有益的信息。值得注意的是,在后续说到的分类器会对特征有要求,是稀疏向量还是稠密向量。
总结
可以对接多个Featurizer来完成特征提取,最常见的是RegexFeaturizer,再加上一个稠密特征器。
4. 意图分类组件
RASA的逻辑是根据用户本轮说话的意图做分类,然后结合历史上下文,给出一个action。意图分类是后续策略选择的基础。
RASA支持的意图分类器有:
MitieIntentClassifier
使用MitieNLP的分类器,需要Tokenizer都使用MitieNLP,但是MitieIntentClassifier分类器里面已经自带Featurizer功能,所以不是必须配置的。简单来说,是基于稀疏线性核的一个多分类线性SVM。
具体算法参考:
https://github.com/mit-nlp/MITIEgithub.com/mit-nlp/MITIE
描述
该分类器使用 MITIE 来执行意图分类。底层分类器使用具有稀疏线性内核的多类线性 SVM
(请参阅MITIE 训练器代码train_text_categorizer_classifier中的函数 )。
**输入:**是用户的消息
**输出:**是intent
输出示例:
{
"intent": {"name": "greet", "confidence": 0.98343}
}
配置方法如下:
pipeline:
- name: "MitieNLP"
model: "data/total_word_feature_extractor.dat"
- name: "MitieTokenizer"
"intent_tokenization_flag": False
"intent_split_symbol": "_"
"token_pattern": None
- name: "MitieFeaturizer"
"pooling": "mean"
- name: "MitieIntentClassifier"
SklearnIntentClassifier
使用Sklearn去做意图识别。sklearn也是通过SVM做意图识别,只是sklearn的SVM是通过grid search方法优化的。
描述
sklearn 意图分类器训练一个线性 SVM,该 SVM 使用网格搜索进行优化。它还提供了没有“获胜”的标签的排名。需要在管道中使用SklearnIntentClassifier密集的特征化器。这个密集的特征化器创建了用于分类的特征。有关算法本身的更多信息,请查看 GridSearchCV 文档。
输入:dense_features用于用户消息
输出:intent和intent_ranking
输出示例:
{
"intent": {"name": "greet", "confidence": 0.78343},
"intent_ranking": [
{
"confidence": 0.1485910906220309,
"name": "goodbye"
},
{
"confidence": 0.08161531595656784,
"name": "restaurant_search"
}
]
}
配置:
SklearnIntentClassifier使用时候需要将SVM的超参数配置上。
pipeline:
- name: "SklearnIntentClassifier"
# 指定要执行的正则化值列表
# 交叉验证C-SVM。
# 这与GridSearchCV中的 “kernel” 超参数一起使用。
C: [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 100]
# 指定与C-SVM一起使用的内核。
# 这与GridSearchCV中的“`C``超参数一起使用。
kernels: ["linear"]
# C-SVM的Gamma参数。
"gamma": [0.1]
# 我们试图找到一个很好的交叉折叠使用期间
# 意图训练,这指定了最大折叠数。
"max_cross_validation_folds": 5
# 用于评估超参数的评分函数。
# 这可以是名称或函数。
"scoring_function": "f1_weighted"
KeywordIntentClassifier
简单的关键字匹配意图分类,适用于小型项目,意图比较少的情况。当意图很多,相关性又很大的时候,关键词分类器无法区分。
关键字的匹配方式是,训练数据的整句话都作为关键字,去搜索用户说的话。因此写配置数据的时候,仔细设计那个训练数据很重要,关键字不能太长,这容易匹配不上意图,也不能太短,缺少意图的区分度。
描述
该分类器通过在消息中搜索关键字来工作。默认情况下,匹配区分大小写,仅搜索用户消息中关键字字符串的完全匹配。意图的关键字是 NLU 训练数据中该意图的示例。这意味着整个示例都是关键字,而不是示例中的单个单词。
输出
intent
输入
没有
输出示例
{
"intent": {"name": "greet", "confidence": 1.0}
}
配置方法如下:
pipeline:
- name: "KeywordIntentClassifier"
case_sensitive: True
DIETClassifier
DIET模型是(Dual Intent and Entity Transformer)的简称, 解决了对话理解问题中的2个问题,意图分类和实体识别。DIET使用的是纯监督的方式,没有任何预训练的情况下,无须大规模预训练是关键,性能好于fine-tuning Bert, 但是训练速度是bert的6倍。输入是用户消息和可选意图的稠密或者稀疏向量。输出是实体,意图和评分。
描述
DIET体系结构基于两个任务共享的Transformer。实体标签序列通过Transformer后,输出序列进入顶层条件随机场(CRF)标记层 预测,输出每个Token成为BIOE的概率。完整话语和意图标签经过Transformer输出到单个语义向量空间中。利用点积损失最大化与 目标标签的相似度,最小化与负样本的相似度。
输出
entities,intent和intent_ranking
需要
dense_features和/或sparse_features用于用户消息和可选的意图
输出示例
{
"intent": {"name": "greet", "confidence": 0.8343},
"intent_ranking": [
{
"confidence": 0.385910906220309,
"name": "goodbye"
},
{
"confidence": 0.28161531595656784,
"name": "restaurant_search"
}
],
"entities": [{
"end": 53,
"entity": "time",
"start": 48,
"value": "2017-04-10T00:00:00.000+02:00",
"confidence": 1.0,
"extractor": "DIETClassifier"
}]
}
参数配置
如果您想使用DIETClassifierjust for intent 分类,请设置entity_recognition为False. 如果您只想进行实体识别,请设置intent_classification为False。默认情况下DIETClassifier两者都执行,即entity_recognition和intent_classification设置为 True。
您可以定义许多超参数来调整模型。如果要调整模型,请首先修改以下参数:
epochs:此参数设置算法将看到训练数据的次数(默认值:300)。一个epoch等于所有训练示例的一个前向传递和一个后向传递。有时模型需要更多的 epoch 才能正确学习。有时更多的时期不会影响性能。时期数越少,模型训练得越快。hidden_layers_sizes:此参数允许您定义用户消息和意图的前馈层数及其输出维度(默认值:text: [], label: [])。列表中的每个条目都对应一个前馈层。例如,如果您设置text: [256, 128],我们将在变压器前面添加两个前馈层。输入标记的向量(来自用户消息)将被传递到这些层。第一层的输出维度为 256,第二层的输出维度为 128。如果使用空列表(默认行为),则不会添加前馈层。确保仅使用正整数值。通常,使用 2 的幂数。此外,通常的做法是在列表中具有递减的值:下一个值小于或等于之前的值。embedding_dimension:此参数定义模型内部使用的嵌入层的输出维度(默认值:20)。我们在模型架构中使用了多个嵌入层。例如,完整话语和意图的向量在比较之前被传递到嵌入层并计算损失。number_of_transformer_layers:此参数设置要使用的转换器层数(默认值:2)。转换器层的数量对应于模型使用的转换器块。transformer_size:此参数设置变压器中的单元数(默认值:256)。从变压器出来的向量将具有给定的transformer_size.connection_density:此参数定义模型中所有前馈层设置为非零值的内核权重的比例(默认值:0.2)。该值应介于 0 和 1 之间。如果设置connection_density为 1,则不会将内核权重设置为 0,该层充当标准前馈层。您不应设置connection_density为 0,因为这将导致所有内核权重为 0,即模型无法学习。constrain_similarities:此参数设置为True对所有相似项应用 sigmoid 交叉熵损失。这有助于将输入标签和负标签之间的相似性保持为较小的值。这应该有助于将模型更好地推广到现实世界的测试集。model_confidence:此参数允许用户配置在推理过程中如何计算置信度。它只能采用一个值作为输入,即softmax. 在softmax,置信度在范围内[0, 1]。计算出的相似度用softmax激活函数进行归一化。
上述配置参数是您应该配置的参数,以使您的模型适合您的数据。但是,存在可以调整的附加参数。
更多可配置参数:
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| Parameter | Default Value | Description |
+=================================+==================+==============================================================+
| hidden_layers_sizes | text: [] | Hidden layer sizes for layers before the embedding layers |
| | label: [] | for user messages and labels. The number of hidden layers is |
| | | equal to the length of the corresponding list. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| share_hidden_layers | False | Whether to share the hidden layer weights between user |
| | | messages and labels. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| transformer_size | 256 | Number of units in transformer. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| number_of_transformer_layers | 2 | Number of transformer layers. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| number_of_attention_heads | 4 | Number of attention heads in transformer. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| use_key_relative_attention | False | If 'True' use key relative embeddings in attention. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| use_value_relative_attention | False | If 'True' use value relative embeddings in attention. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| max_relative_position | None | Maximum position for relative embeddings. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| unidirectional_encoder | False | Use a unidirectional or bidirectional encoder. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| batch_size | [64, 256] | Initial and final value for batch sizes. |
| | | Batch size will be linearly increased for each epoch. |
| | | If constant `batch_size` is required, pass an int, e.g. `8`. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| batch_strategy | "balanced" | Strategy used when creating batches. |
| | | Can be either 'sequence' or 'balanced'. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| epochs | 300 | Number of epochs to train. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| random_seed | None | Set random seed to any 'int' to get reproducible results. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| learning_rate | 0.001 | Initial learning rate for the optimizer. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| embedding_dimension | 20 | Dimension size of embedding vectors. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| dense_dimension | text: 128 | Dense dimension for sparse features to use. |
| | label: 20 | |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| concat_dimension | text: 128 | Concat dimension for sequence and sentence features. |
| | label: 20 | |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| number_of_negative_examples | 20 | The number of incorrect labels. The algorithm will minimize |
| | | their similarity to the user input during training. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| similarity_type | "auto" | Type of similarity measure to use, either 'auto' or 'cosine' |
| | | or 'inner'. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| loss_type | "cross_entropy" | The type of the loss function, either 'cross_entropy' |
| | | or 'margin'. Type 'margin' is only compatible with |
| | | "model_confidence=cosine", |
| | | which is deprecated (see changelog for 2.3.4). |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| ranking_length | 10 | Number of top intents to report. Set to 0 to report all |
| | | intents. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| renormalize_confidences | False | Normalize the reported top intents. Applicable only with loss|
| | | type 'cross_entropy' and 'softmax' confidences. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| maximum_positive_similarity | 0.8 | Indicates how similar the algorithm should try to make |
| | | embedding vectors for correct labels. |
| | | Should be 0.0 < ... < 1.0 for 'cosine' similarity type. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| maximum_negative_similarity | -0.4 | Maximum negative similarity for incorrect labels. |
| | | Should be -1.0 < ... < 1.0 for 'cosine' similarity type. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| use_maximum_negative_similarity | True | If 'True' the algorithm only minimizes maximum similarity |
| | | over incorrect intent labels, used only if 'loss_type' is |
| | | set to 'margin'. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| scale_loss | False | Scale loss inverse proportionally to confidence of correct |
| | | prediction. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| regularization_constant | 0.002 | The scale of regularization. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| negative_margin_scale | 0.8 | The scale of how important it is to minimize the maximum |
| | | similarity between embeddings of different labels. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| connection_density | 0.2 | Connection density of the weights in dense layers. |
| | | Value should be between 0 and 1. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| drop_rate | 0.2 | Dropout rate for encoder. Value should be between 0 and 1. |
| | | The higher the value the higher the regularization effect. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| drop_rate_attention | 0.0 | Dropout rate for attention. Value should be between 0 and 1. |
| | | The higher the value the higher the regularization effect. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| use_sparse_input_dropout | True | If 'True' apply dropout to sparse input tensors. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| use_dense_input_dropout | True | If 'True' apply dropout to dense input tensors. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| evaluate_every_number_of_epochs | 20 | How often to calculate validation accuracy. |
| | | Set to '-1' to evaluate just once at the end of training. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| evaluate_on_number_of_examples | 0 | How many examples to use for hold out validation set. |
| | | Large values may hurt performance, e.g. model accuracy. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| intent_classification | True | If 'True' intent classification is trained and intents are |
| | | predicted. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| entity_recognition | True | If 'True' entity recognition is trained and entities are |
| | | extracted. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| use_masked_language_model | False | If 'True' random tokens of the input message will be masked |
| | | and the model has to predict those tokens. It acts like a |
| | | regularizer and should help to learn a better contextual |
| | | representation of the input. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| tensorboard_log_directory | None | If you want to use tensorboard to visualize training |
| | | metrics, set this option to a valid output directory. You |
| | | can view the training metrics after training in tensorboard |
| | | via 'tensorboard --logdir ' . |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| tensorboard_log_level | "epoch" | Define when training metrics for tensorboard should be |
| | | logged. Either after every epoch ('epoch') or for every |
| | | training step ('batch'). |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| featurizers | [] | List of featurizer names (alias names). Only features |
| | | coming from the listed names are used. If list is empty |
| | | all available features are used. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| checkpoint_model | False | Save the best performing model during training. Models are |
| | | stored to the location specified by `--out`. Only the one |
| | | best model will be saved. |
| | | Requires `evaluate_on_number_of_examples > 0` and |
| | | `evaluate_every_number_of_epochs > 0` |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| split_entities_by_comma | True | Splits a list of extracted entities by comma to treat each |
| | | one of them as a single entity. Can either be `True`/`False` |
| | | globally, or set per entity type, such as: |
| | | ``` |
| | | ... |
| | | - name: DIETClassifier |
| | | split_entities_by_comma: |
| | | address: True |
| | | ... |
| | | ... |
| | | ``` |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| constrain_similarities | False | If `True`, applies sigmoid on all similarity terms and adds |
| | | it to the loss function to ensure that similarity values are |
| | | approximately bounded. Used only if `loss_type=cross_entropy`|
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
| model_confidence | "softmax" | Affects how model's confidence for each intent |
| | | is computed. Currently, only one value is supported: |
| | | 1. `softmax` - Similarities between input and intent |
| | | embeddings are post-processed with a softmax function, |
| | | as a result of which confidence for all intents sum up to 1. |
| | | This parameter does not affect the confidence for entity |
| | | prediction. |
+---------------------------------+------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------+
配置示例如下:
# Configuration for Rasa NLU.
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/nlu/components/
language: zh
pipeline:
- name: JiebaTokenizer
- name: RegexFeaturizer
- name: LexicalSyntacticFeaturizer
- name: LanguageModelFeaturizer
model_name: bert # BERT模型
model_weights: bert-base-chinese # 中文预训练模型
- name: DIETClassifier
epochs: 100
- name: EntitySynonymMapper
- name: ResponseSelector
epochs: 100
- name: FallbackClassifier
threshold: 0.3
ambiguity_threshold: 0.1
FallbackClassifier
当意图识别的得分比较低时,使用该分类器决定是否给出nlu_fallback意图。
注意,这个FallbackClassifier总是跟在其他意图分类器之后,对前一个意图分类提给出的意图及置信度进行判定。如果前一个意图分类器给出的意图预测置信度低于threshold,或者两个排名最高的意图的置信度得分接近时,FallbackClassifier实施回退操作。
描述
如果先前的 意图分类器无法以大于或等于的置信度对意图进行分类,则使用 意图FallbackClassifier对用户消息进行分类。它还可以在排名靠前的两个意图的置信度分数比 .nlu_fallback``threshold``FallbackClassifier``ambiguity_threshold
您可以使用FallbackClassifier来实现 处理具有不确定 NLU 预测的消息的后备操作。
rules:
- rule: Ask the user to rephrase in case of low NLU confidence
steps:
- intent: nlu_fallback
- action: utter_please_rephrase
输出
entities,intent和intent_ranking
需要
intent并intent_ranking从先前的意图分类器输出
输出示例
{
"intent": {"name": "nlu_fallback", "confidence": 0.7183846840434321},
"intent_ranking": [
{
"confidence": 0.7183846840434321,
"name": "nlu_fallback"
},
{
"confidence": 0.28161531595656784,
"name": "restaurant_search"
}
],
"entities": [{
"end": 53,
"entity": "time",
"start": 48,
"value": "2017-04-10T00:00:00.000+02:00",
"confidence": 1.0,
"extractor": "DIETClassifier"
}]
}
配置
只有在没有其他意图预测的置信度大于或等于 的情况下,才会添加其对意图 的FallbackClassifier预测。nlu_fallback``threshold
threshold:此参数设置预测nlu_fallback意图的阈值。如果先前的意图分类器预测的意图没有大于或等于的置信度水平threshold,FallbackClassifier则将添加具有nlu_fallback置信度的意图预测1.0。ambiguity_threshold:如果你配置了一个ambiguity_threshold, 如果两个最高排名的意图的置信度分数的差异小于,FallbackClassifier也会预测意图。nlu_fallback``ambiguity_threshold
配置示例如下:
# Configuration for Rasa NLU.
# https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/nlu/components/
language: zh
pipeline:
- name: JiebaTokenizer
- name: RegexFeaturizer
- name: LexicalSyntacticFeaturizer
- name: LanguageModelFeaturizer
model_name: bert # BERT模型
model_weights: bert-base-chinese # 中文预训练模型
- name: DIETClassifier
epochs: 100
- name: EntitySynonymMapper
- name: ResponseSelector
epochs: 100
- name: FallbackClassifier
threshold: 0.3
ambiguity_threshold: 0.1
5. 实体抽取组件
一个对话机器人,除了理解用户的语义以外,还需要从用户获取必要的信息,用于信息检索的变量,我们简称为slot(槽),而填槽的内容大部分来自于用户对话中的命名实体,极个别也有用户的意图作为slot。举例来说,用户意图为订火车票,那机器人必须知道是从哪里出发目的地是哪里,这个信息就需要从用户对话中提取地名这个命名实体。RASA的实体提取器完成这一功能。
如果您使用多个实体提取器,我们建议每个提取器都针对一组专有的实体类型。例如,使用[Duckling](https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/components#ducklingentityextractor)提取日期和时间, 使用[DIETClassifier](https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/components#dietclassifier-1)提取人名。否则,如果多个提取器针对相同的实体类型,则很可能会多次提取实体。
例如,如果您使用两个或更多通用提取器,如[MitieEntityExtractor](https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/components#mitieentityextractor)、 [DIETClassifier](https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/components#dietclassifier-1)或[CRFEntityExtractor](https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/components#crfentityextractor),则所有这些都将找到并提取训练数据中的实体类型。如果您使用实体类型填充的[插槽](https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/domain#slots)`text`是 type ,那么管道中的最后一个提取器将获胜。如果槽的类型为`list`,则所有结果都将添加到列表中,包括重复项。
即使提取器专注于不同的实体类型,也可能发生另一个不太明显的重复/重叠提取情况。想象一个送餐机器人和一个用户消息,如`I would like to order the Monday special`. 假设,如果您的时间提取器的性能不是很好,它可能会`Monday`在这里提取作为订单的时间,而您的其他提取器可能会提取`Monday special`为餐点。如果您遇到此类重叠的实体,添加额外的训练数据以改进您的提取器可能是有意义的。如果这还不够,您可以添加一个 [自定义组件](https://rasa.com/docs/rasa/components#custom-components),根据您自己的逻辑解决实体提取中的冲突。
目前RASA支持的实体提取器有:
MitieEntityExtractor
使用MitieNLP提取命名实体。需要引入MitieNLP语言模型, 虽然在pipeline里面也需要配置MitieTokenizer,MitieFeaturizer,但实际上在MitieEntityExtractor执行的时候,它会自己重新生成Feature。
描述
MitieEntityExtractor使用 MITIE 实体提取来查找消息中的实体。底层分类器使用具有稀疏线性内核和自定义特征的多类线性 SVM。MITIE 组件不提供实体置信度值。
输出示例
{
"entities": [{
"value": "New York City",
"start": 20,
"end": 33,
"confidence": null,
"entity": "city",
"extractor": "MitieEntityExtractor"
}]
}
配置
pipeline:
- name: "MitieEntityExtractor"
SpacyEntityExtractor
使用SpacyNLP提取命名实体。需要引入SpacyNLP语言模型, SpacyTokenizer,SpacyFeaturizer。
描述
该组件使用 spaCy 预测消息的实体。spaCy 使用统计 BILOU 转换模型。截至目前,该组件只能使用 spaCy 内置的实体提取模型,不能重新训练。此提取器不提供任何置信度分数。
您可以在此交互式演示中测试 spaCy 的实体提取模型。请注意,某些 spaCy 模型高度区分大小写。
提取器SpacyEntityExtractor不提供confidence级别,并且将始终返回null。
输出
entities
需要
SpacyNLP
输出示例
{
"entities": [{
"value": "New York City",
"start": 20,
"end": 33,
"confidence": null,
"entity": "city",
"extractor": "SpacyEntityExtractor"
}]
}
配置
配置 spaCy 组件应该提取的维度,即实体类型。可以在spaCy 文档中找到可用维度的完整列表。未指定维度选项将提取所有可用维度。
pipeline:
- name: "SpacyEntityExtractor"
# 要提取的维度
dimensions: ["PERSON", "LOC", "ORG", "PRODUCT"]
CRFEntityExtractor
条件随机场实体提取器,目前最常用的NER工具,跟LSTM组合,或者和BERT组合能取到非常好的效果。
描述
该组件实现了一个条件随机字段 (CRF) 来进行命名实体识别。CRF 可以被认为是一个无向马尔可夫链,其中时间步长是单词,状态是实体类。单词的特征(大写、POS 标记等)给出了某些实体类的概率,相邻实体标签之间的转换也是如此:然后计算并返回最可能的标签集。
如果您想将自定义特征(例如预训练的词嵌入)传递给CRFEntityExtractor,您可以在 之前将任何密集特征化器添加到管道中,然后通过添加到其特征配置 中CRFEntityExtractor进行配置 CRFEntityExtractor以使用密集特征。自动找到额外的密集特征并检查密集特征是否是 的可迭代的,其中每个条目都是一个向量。如果检查失败,将显示警告。但是,将在没有额外自定义功能的情况下继续训练。如果存在密集特征,则将密集特征传递给 并使用它们进行训练。"text_dense_feature"``CRFEntityExtractor``len(tokens)``CRFEntityExtractor``CRFEntityExtractor``sklearn_crfsuite
配置
CRFEntityExtractor有一个要使用的默认功能列表。但是,您可以覆盖默认配置。可以使用以下功能:
=================== ==========================================================================================
Feature Name Description
=================== ==========================================================================================
low Checks if the token is lower case.
upper Checks if the token is upper case.
title Checks if the token starts with an uppercase character and all remaining characters are
lowercased.
digit Checks if the token contains just digits.
prefix5 Take the first five characters of the token.
prefix2 Take the first two characters of the token.
suffix5 Take the last five characters of the token.
suffix3 Take the last three characters of the token.
suffix2 Take the last two characters of the token.
suffix1 Take the last character of the token.
pos Take the Part-of-Speech tag of the token (``SpacyTokenizer`` required).
pos2 Take the first two characters of the Part-of-Speech tag of the token
(``SpacyTokenizer`` required).
pattern Take the patterns defined by ``RegexFeaturizer``.
bias Add an additional "bias" feature to the list of features.
text_dense_features Adds additional features from a dense featurizer.
=================== ==========================================================================================
当特征化器在带有滑动窗口的用户消息中的标记上移动时,您可以在滑动窗口中定义先前标记、当前标记和下一个标记的特征。您将特征定义为[before, token, after]数组。
另外,您可以设置一个标志来确定是否使用 BILOU 标记模式。
BILOU_flag确定是否使用 BILOU 标记。默认True。
pipeline:
- name: "CRFEntityExtractor"
# BILOU_标志决定是否使用BILOU标签。
"BILOU_flag": True
# 要在滑动窗口中提取的特征
"features": [
["low", "title", "upper"],
[
"bias",
"low",
"prefix5",
"prefix2",
"suffix5",
"suffix3",
"suffix2",
"upper",
"title",
"digit",
"pattern",
],
["low", "title", "upper"],
["text_dense_features"]
]
# 优化算法的最大迭代次数。
"max_iterations": 50
# L1正则化的权重
"L1_c": 0.1
# L2正则化的权重
"L2_c": 0.1
# 要使用的密集特性器的名称。
# 如果列表为空,则使用所有可用的密集特性。
"featurizers": []
# 指示是否应将提取的实体列表分割为给定实体类型的单个实体
"split_entities_by_comma":
address: False
email: True
如果使用 POS 功能(
pos或pos2),您需要SpacyTokenizer在您的管道中使用。如果
pattern使用功能,您需要RegexFeaturizer在您的管道中使用。如果使用特征,你需要在你的管道
text_dense_features中有一个密集的特征化器(例如)。LanguageModelFeaturizer
DucklingEntityExtractor
这个组件允许Rasa调用一个远程http服务来提前命名实体,成为Duckling服务器。
描述
要使用这个组件,您需要运行一个Duckling服务器。
最简单的选择是使用 docker run -p 8000:8000 rasa/duckling.
或者,可以直接安装Duckling,然后启动服务器。
Duckling 允许识别日期、数字、距离和其他结构化实体并将它们标准化。请注意,duckling 会尝试在不提供排名的情况下提取尽可能多的实体类型。例如,如果您同时为小鸭组件指定number和time作为维度,则该组件将提取两个实体:10作为数字和 in 10 minutes作为来自文本的时间I will be there in 10 minutes。在这种情况下,您的应用程序必须决定哪种实体类型是正确的。提取器将始终返回 1.0 作为置信度,因为它是基于规则的系统。
可以在 Duckling GitHub 存储库中找到支持的语言列表。
配置
配置小鸭组件应该提取哪些维度,即实体类型。可以在Ducking中找到可用尺寸的完整列表。未指定维度选项将提取所有可用维度。
pipeline:
- name: "DucklingEntityExtractor"
# 正在运行的duckling服务器的url
url: "http://localhost:8000"
# 要提取的维度
dimensions: ["time", "number", "amount-of-money", "distance"]
# 允许您配置语言环境,默认情况下语言为
# 使用
locale: "de_DE"
# 如果不设置,将使用Duckling的默认时区
# 需要从相对表达式(如“明天”)计算日期
timezone: "Europe/Berlin"
# 从运行中的duckling服务器的http url接收响应的超时时间
# 如果不设置,默认的duckling HTTP url超时时间设置为3秒。
timeout : 3
DIETClassifier
-
Dual Intent Entity Transformer (DIET) 用于意图分类和实体提取
-
描述
您可以在 Intent Classifiers 部分找到DIETClassifier的详细说明。
RegexEntityExtractor
该组件使用在训练数据中定义的查找表和正则表达式提取实体。该组件检查用户消息是否包含某个查找表的条目或与某个正则表达式匹配。如果找到匹配项,则将该值提取为实体。
描述
该组件使用训练数据中定义的查找表和正则表达式提取实体。该组件检查用户消息是否包含查找表之一的条目或匹配正则表达式之一。如果找到匹配项,则将该值提取为实体。
此组件仅使用名称与训练数据中定义的实体之一相同的那些正则表达式特征。确保为每个实体至少注释一个示例。
当您将此提取器与MitieEntityExtractor、 CRFEntityExtractor或DIETClassifier结合使用时,它可能会导致实体的多次提取。特别是如果许多训练句子具有实体类型的实体注释,而您也为其定义了正则表达式。有关多重提取的更多信息,请参阅实体提取器部分开头的大信息框 。
如果您似乎需要此 RegexEntityExtractor 和另一个上述统计提取器,我们建议您考虑以下两个选项之一。
当您对每种类型的提取器都有专有实体类型时,建议使用选项 1。为了确保提取器不会相互干扰,只为每个正则表达式/查找实体类型注释一个例句,而不是更多。
当您想使用正则表达式匹配作为统计提取器的附加信号时,选项 2 很有用,但您没有单独的实体类型。在这种情况下,您需要 1)在管道中的提取器之前添加 RegexFeaturizer 2)在训练数据中注释所有实体示例,以及 3)从管道中删除 RegexEntityExtractor。这样,您的统计提取器将收到有关存在正则表达式匹配的附加信号,并且将能够统计确定何时依赖这些匹配以及何时不依赖这些匹配。
配置
通过添加选项使实体提取器区分大小写case_sensitive: True,默认值为 case_sensitive: False.
要正确处理诸如中文等不使用空格进行分词的语言,用户需要添加use_word_boundaries: False选项,
默认为use_word_boundaries: True.
pipeline:
- name: RegexEntityExtractor
# 文本将被处理为默认不区分大小写
case_sensitive: False
# 使用查找表提取实体
use_lookup_tables: True
# 使用正则表达式提取实体
use_regexes: True
# 为查找表使用匹配词边界
"use_word_boundaries": True
EntitySynonymMapper
实体同义词映射,这个组件功能主要是将其他Extractor提取到的实体,使用**同义词表,归一化到同一种说法,**为后续处理提供方便。
描述
如果训练数据包含定义的同义词,该组件将确保检测到的实体值将映射到相同的值。例如,如果您的训练数据包含以下示例:
[
{
"text": "I moved to New York City",
"intent": "inform_relocation",
"entities": [{
"value": "nyc",
"start": 11,
"end": 24,
"entity": "city",
}]
},
{
"text": "I got a new flat in NYC.",
"intent": "inform_relocation",
"entities": [{
"value": "nyc",
"start": 20,
"end": 23,
"entity": "city",
}]
}
]
该组件将允许您将实体映射New York City到. 即使消息包含,实体提取也会返回。当此组件更改现有实体时,它会将自身附加到此实体的处理器列表中。NYC``nyc``nyc``NYC
配置:
pipeline:
- name: "EntitySynonymMapper"
当
EntitySynonymMapper作为 NLU 管道的一部分使用时,需要将其放置在配置文件中的任何实体提取器下方。
6. 响应选择器组件
概述
响应选择器组件可用于构建响应检索模型,以直接从一组候选响应中预测机器人响应。对话管理器使用该模型的预测来发出预测的响应。它将用户输入和响应标签嵌入到相同的空间中,并遵循与DIETClassifier完全相同的神经网络架构和优化。
要使用此组件,您的训练数据应包含检索意图。要定义这些,请查看有关 NLU 训练示例的 文档和有关为检索意图定义响应话语的文档。
输入输出
选择器的输入是用户信息和响应消息的稀疏或者稠密特征。输出是一个字典,其中键作为响应选择器的检索意图,其值包含预测的响应模板、置信度和检索意图下的响应键。
输出示例
NLU 的解析输出将具有一个名为的属性response_selector ,其中包含每个响应选择器组件的输出。每个响应选择器由该响应选择器的参数标识retrieval_intent并存储两个属性:
response:对应检索意图下的预测响应键,预测的置信度和相关响应。ranking:使用前 10 个候选响应键的置信度进行排名。
例如:
{
"response_selector": {
"faq": {
"response": {
"id": 1388783286124361986,
"confidence": 0.7,
"intent_response_key": "chitchat/ask_weather",
"response_templates": [
{
"text": "It's sunny in Berlin today",
"image": "https://i.imgur.com/nGF1K8f.jpg"
},
{
"text": "I think it's about to rain."
}
],
"template_name": "utter_chitchat/ask_weather"
},
"ranking": [
{
"id": 1388783286124361986,
"confidence": 0.7,
"intent_response_key": "chitchat/ask_weather"
},
{
"id": 1388783286124361986,
"confidence": 0.3,
"intent_response_key": "chitchat/ask_name"
}
]
}
}
}
如果retrieval_intent特定响应选择器的参数保留为其默认值,则相应的响应选择器将default在返回的输出中标识。
{
"response_selector": {
"default": {
"response": {
"id": 1388783286124361986,
"confidence": 0.7,
"intent_response_key": "chitchat/ask_weather",
"responses": [
{
"text": "It's sunny in Berlin today",
"image": "https://i.imgur.com/nGF1K8f.jpg"
},
{
"text": "I think it's about to rain."
}
],
"utter_action": "utter_chitchat/ask_weather"
},
"ranking": [
{
"id": 1388783286124361986,
"confidence": 0.7,
"intent_response_key": "chitchat/ask_weather"
},
{
"id": 1388783286124361986,
"confidence": 0.3,
"intent_response_key": "chitchat/ask_name"
}
]
}
}
}
配置
该算法几乎包括了DIETClassifier使用的所有超参数。如果要调整模型,请首先修改以下参数:
epochs:此参数设置算法将看到训练数据的次数(默认值:300)。一个epoch等于所有训练示例的一个前向传递和一个后向传递。有时模型需要更多的 epoch 才能正确学习。有时更多的时期不会影响性能。时期数越少,模型训练得越快。hidden_layers_sizes:此参数允许您定义用户消息和意图的前馈层数及其输出维度(默认值:text: [256, 128], label: [256, 128])。列表中的每个条目都对应一个前馈层。例如,如果您设置text: [256, 128],我们将在变压器前面添加两个前馈层。输入标记的向量(来自用户消息)将被传递到这些层。第一层的输出维度为 256,第二层的输出维度为 128。如果使用空列表(默认行为),则不会添加前馈层。确保仅使用正整数值。通常,使用 2 的幂数。此外,通常的做法是在列表中具有递减的值:下一个值小于或等于之前的值。embedding_dimension:此参数定义模型内部使用的嵌入层的输出维度(默认值:20)。我们在模型架构中使用了多个嵌入层。例如,完整话语和意图的向量在比较之前被传递到嵌入层并计算损失。number_of_transformer_layers:此参数设置要使用的转换器层数(默认值:0)。转换器层的数量对应于模型使用的转换器块。transformer_size:此参数设置变压器中的单元数(默认值:None)。从变压器出来的向量将具有给定的transformer_size.connection_density:此参数定义模型中所有前馈层设置为非零值的内核权重的比例(默认值:0.2)。该值应介于 0 和 1 之间。如果设置connection_density为 1,则不会将内核权重设置为 0,该层充当标准前馈层。您不应设置connection_density为 0,因为这将导致所有内核权重为 0,即模型无法学习。constrain_similarities:此参数设置为True对所有相似项应用 sigmoid 交叉熵损失。这有助于将输入标签和负标签之间的相似性保持为较小的值。这应该有助于将模型更好地推广到现实世界的测试集。model_confidence:此参数允许用户配置在推理过程中如何计算置信度。它只能采用一个值作为输入,即softmax. 在softmax,置信度在范围内[0, 1]。计算出的相似度用softmax激活函数进行归一化。
该组件还可以配置为针对特定检索意图训练响应选择器。该参数retrieval_intent设置训练此响应选择器模型的检索意图的名称。默认为None,即模型针对所有检索意图进行了训练。
在其默认配置中,该组件使用带有响应键(例如)的检索意图faq/ask_name作为训练的标签。或者,也可以通过切换use_text_as_label到将其配置为使用响应的文本作为训练标签True。在这种模式下,组件将使用具有文本属性的第一个可用响应进行训练。如果没有找到,则回退到使用检索意图和响应键作为标签。
示例
1、首先要在config.yaml的pipeline里面打开ResponseSelector
language: zh
pipeline:
- name: "JiebaTokenizer"
- name: "CountVectorsFeaturizer"
- name: "DIETClassifier"
entity_recognition: False
epochs: 50
- name: ResponseSelector
epochs: 50
policies:
- name: TEDPolicy
max_history: 5
epochs: 100
- name: MemoizationPolicy
- name: RulePolicy
2、要在data/nlu.yaml里面配置好训练数据
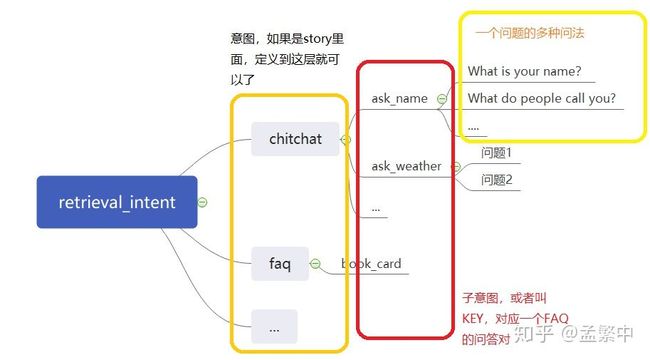
chitchat就是这个检索型机器人的意图了,可以有多个这样的意图,每个意图对应一组faq,前面提到的retrieval_intent就可以指定chitchat这个意图名称,也可以不指定,就是在所有的都生效。ask_name就是键值名称了。相当于chitchat这个意图下,有好多个askname*,*每个askname下面有很多问句。关系如下图。
- intent: chitchat/ask_name
examples: |
- What is your name?
- May I know your name?
- What do people call you?
- Do you have a name for yourself?
- intent: chitchat/ask_weather
examples: |
- What's the weather like today?
- Does it look sunny outside today?
- Oh, do you mind checking the weather for me please?
- I like sunny days in Berlin.
responses:
utter_chitchat/ask_name:
- image: "https://i.imgur.com/zTvA58i.jpeg"
text: hello, my name is retrieval bot.
- text: Oh yeah, I am called the retrieval bot.
utter_chitchat/ask_weather:
- text: Oh, it does look sunny right now in Berlin.
image: "https://i.imgur.com/vwv7aHN.png"
- text: I am not sure of the whole week but I can see the sun is out today.
3、要在data/rules.yaml里面配置好训练数据
配置了1和2以后,还不能响应,因为chitchat这个意图并没有在story.yaml中出现,所以要在rules.yaml里面配置规则。
- rule: Response with a chitchat utterance whenever user indulges in some chitchat
steps:
- intent: chitchat
- action: utter_chitchat
至此,一个检索型机器人已经配置好了。
7. 自定义组件
3.0 中的新功能
Rasa Open Source 3.0 统一了 NLU 组件和策略的实现。这需要更改为早期版本的 Rasa Open Source 编写的自定义组件。有关迁移的分步指南,请参阅 迁移指南。
您可以创建一个自定义组件来执行 NLU 目前不提供的特定任务(例如,情绪分析)。
您可以通过添加模块路径将自定义组件添加到管道中。因此,如果您有一个名为sentiment 包含SentimentAnalyzer类的模块:
管道:
- name: "sentiment.SentimentAnalyzer"
有关自定义组件的完整指南,请参阅自定义图形组件指南。还请务必阅读有关组件生命周期的部分。