spring之IoC注解(三)负责注入的注解
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、@Value注解
-
- Product类
- spring配置文件
- 测试程序
- 运行结果
- 二、@Autowired与@Qualifier注解
-
- 1.创建OrderDao接口
- 2.创建OrderDao接口实现类
- 3.创建OrderService类
- 4.配置文件
- 5.测试程序
- 6.运行结果
- 三、@Resource注解(重要)
-
- 1、创建StudentDao接口
- 2、创建接口实现类
- 3、创建StudentService类
- 4、测试程序
- 5、运行结果
- 四、全注解式开发
前言
IoC是控制反转,指的是①、把创建对象的权利交出去,让别人创建,②、创建之后两个对象之间关系的维护也不管了,交给Spring去管理。spring去依赖注入。
@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository
这四个注解是用来声明Bean的,声明后这些Bean将被实例化。如何给Bean的属性赋值?
一、@Value注解
当属性的类型是简单类型时。可以使用@Value注解进行注入,用这个注解的前提是先声明Bean,交给Spring容器来管理。
Product类
使用@Value注解的注入的话,可以用在属性上,并且可以不提供setter方法
@Component
public class Product {
@Value("亲亲虾条")
private String name;
@Value("3")
private int price;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
spring配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.powernode.bean3">context:component-scan>
beans>
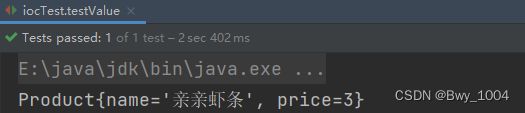
测试程序
@Test
public void testValue(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-Di.xml");
Product product = (Product) context.getBean("product");
System.out.println(product);
}
运行结果
@Value注解也可以用在set方法上
@Component
public class Product {
private String name;
private int price;
@Value("盼盼虾条")
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Value("5")
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
@Component
public class Product {
private String name;
private int price;
public Product(@Value("达利园虾条") String name, @Value("4") int price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
二、@Autowired与@Qualifier注解
@Autowired注解可以用来注入非简单类型
单独使用@Autowire注解,默认根据类型类型装配
1.创建OrderDao接口
public interface OrderDao {
void insert();
}
2.创建OrderDao接口实现类
@Repository
public class OrderDaoImpl implements OrderDao {
@Override
public void insert() {
System.out.println("正在保存订单信息");
}
}
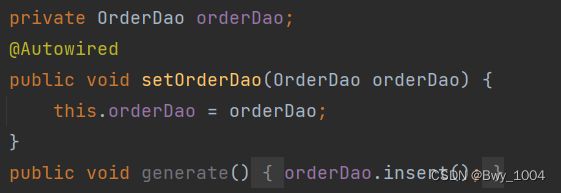
3.创建OrderService类
OrderService类中有OrderDao 属性
在属性上添加@Autowired注解
不需要指定任何属性,直接使用这个注解即可
这个注解的作用的根据类型byType进行自动装配
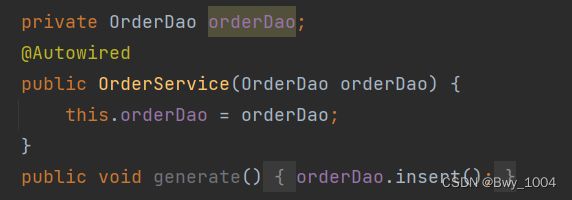
给带有参数的构造方法的参数上添加@Autowired注解也是可以的
只有一个构造方法,并且构造方法的一个参数要和属性对应上,这种情况下@Autowired可以省略
@Service
public class OrderService {
//不需要指定任何属性,直接使用这个注解即可
//这个注解的作用的根据类型byType进行自动装配
@Autowired
private OrderDao orderDao;
public void generate(){
orderDao.insert();
}
}
4.配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="org.powernode">context:component-scan>
beans>
5.测试程序
@Test
public void testAutowired(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-autowired.xml");
OrderService orderService = context.getBean("orderService", OrderService.class);
orderService.generate();
}
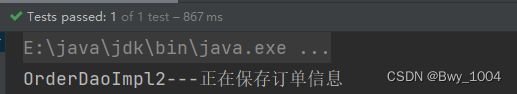
6.运行结果

但是当impl包下有两个实现类时,只靠@Autowired注解完成不了给属性赋值的操作

如果使用@Autowired注解,一定是根据类型进行装配的
如果想解决以上问题,只能根据名字进行装配。
@Autowired和@Qualifier联合使用就可解决以上问题
@Autowired
@Qualifier(“orderDaoImpl2”)
指定是哪个Bean
@Service
public class OrderService {
//不需要指定任何属性,直接使用这个注解即可
//这个注解的作用的根据类型byType进行自动装配
@Autowired
@Qualifier("orderDaoImpl2")
private OrderDao orderDao;
public void generate(){
orderDao.insert();
}
}
三、@Resource注解(重要)
@Resource注解也可以完成非简单类型的注入,那它和@Autowired注解有什么区别?
- @Resource注解是JDK扩展包中的,也就是说属于JDK的一部分。所以该注解是标准注解,更加具有通用性
- @Autowired注解是spring框架自己的
- @Resource注解默认根据名称来装配byName,未指定name时,使用属性名作为name,通过name找不到的话会自动启动通过类型byType装配
- @Autowired注解默认根据类型装配byType,如果想根据名称装配,需要配合@Qualifier注解一起用
- @Resource注解用在属性上、setter方法上
- @Autowirede注解用在属性上、setter方法上、构造方法上、构造方法参数上。
1、创建StudentDao接口
public interface StudentDao {
void deleteById();
}
2、创建接口实现类
StudentDaoImpl:
@Repository
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
@Override
public void deleteById() {
System.out.println("mysql数据库正在删除学生信息");
}
}
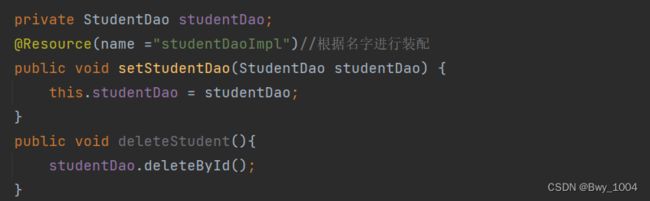
3、创建StudentService类
使用@Resource注解
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Resource(name ="studentDaoImpl")//根据名字进行装配
private StudentDao studentDao;
public void deleteStudent(){
studentDao.deleteById();
}
}
4、测试程序
@Test
public void testResource(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-resource.xml");
StudentService service = context.getBean("studentService", StudentService.class);
service.deleteStudent();
}
5、运行结果
@Resource注解默认根据名称来装配byName,未指定name时,使用属性名作为name,通过name找不到的话会自动启动通过类型byType装配
未指定name时,使用属性名作为name
Resource注解没有指定name属性的值时,就默认将当前的属性名(studentDao)作为name的值进行查找,此时需要对StudentDaoImpl类中的@Repository注解name值也得为属性值才行(@Repository(“studentDao”)):
StudentService:
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Resource//根据名字进行装配
private StudentDao studentDao;
public void deleteStudent(){
studentDao.deleteById();
}
}
StudentDaoImpl:
@Repository("studentDao")
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
@Override
public void deleteById() {
System.out.println("mysql数据库正在删除学生信息");
}
}
四、全注解式开发
所谓全注解式开发就是不再使用spring配置文件了。写一个配置类来代替配置文件。
编写一个类代替spring框架的配置文件
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"cn.powernode.dao","cn.powernode.service"})
public class SpringConfig {
}
测试程序:
注意:测试程序中不能再写
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“spring-resource.xml”);
应该如下:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);