Java实现:利用前序遍历和中序遍历构造二叉树,并从上往下打印每个节点
题目:
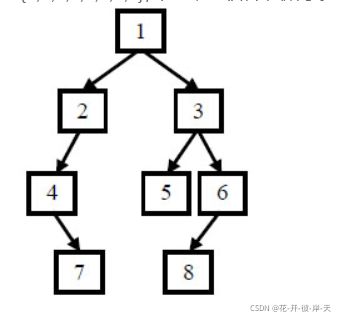
给定 二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历结果,请重建出该二叉树并按照从上往下的顺序打印每个节点。
前序遍历:[1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8]
中序遍历:[4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6]
打印输出:1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8
注:
代码写的很潦草,打印出的二叉树很简单,观赏性不强
代码
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int var) {
this.val = var;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int []pre={1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8};
int in[]={4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6};
//得到构建的二叉树的根节点
TreeNode data=getRealTree(pre,in);
ArrayList<Integer> treeList=getTree(data);
for(Integer a:treeList){
System.out.print(a+" ");
}
}
//根据前序和中序构建二叉树,并返回其根节点
public static TreeNode getRealTree(int pre[],int in[]){
//结束方法的条件
if(pre==null||pre.length==0){
return null;
}
//确定根节点,注意:前序遍历的第一个节点就是树的根节点
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(pre[0]);
//找到根节点在中序遍历中的位置
int index=findIndex(pre,in);
/**
* 构建左子树:左子树=(左子树的前序数组,左子树的中序数组)
* 构建右子树:右子树=(右子树的前序数组,右子树的中序数组)
*
* 中序遍历:
* 因为前序遍历的第一个节点就是树的根节点;
* 找到根节点在中序遍历中的位置,其前面的就是左子树的中序遍历,后面的就是右子树的中序遍历
* 前序遍历:
* 根据中序遍历,可以找到根节点的左右子树的个数
*/
root.left=getRealTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,1,index+1),Arrays.copyOfRange(in,0,index));
root.right=getRealTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,index+1,pre.length),Arrays.copyOfRange(in,index+1,in.length));
return root;
}
//返回中序遍历中与pre[0]相等的节点的索引
public static int findIndex(int []pre,int []in){
for(int i=0;i<in.length;i++){
if(pre[0]==in[i]){
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
/**
* 从上往下打印二叉树:
* 每一次打印一个节点的时候,若是有子节点,则将其子节点放在队列的末尾;接下来队列的头部拿出最早入队的节点,重复之前的过程,直到所有节点被打印
*/
public static ArrayList<Integer> getTree(TreeNode head){
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();
//传入的根节点放入队列,以进行下面的循环
queue.offer(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
//队列不为空,则队首是本次遍历的头节点,遍历后,本次队首会被移除
TreeNode root=queue.poll();
//本次打印是从上往下,从左往右依次进行,所以左节点先入队
if(root.left!=null){
queue.offer(root.left);
}
//节点入队
if(root.right!=null){
queue.offer(root.right);
}
//把本次循环中的队首放入list集合
list.add(root.val);
}
return list;
}
}