【数据结构与算法】快速排序算法、归并排序算法的介绍和程序实现
目录
- 1. 快速排序算法
-
- 1.1 快速排序的介绍
- 1.2 快速排序的程序实现
- 2. 归并排序算法
-
- 2.1 归并排序的介绍
- 2.2 归并排序的程序实现
1. 快速排序算法
1.1 快速排序的介绍
快速排序(Quicksort)是对冒泡排序的一种改进
基本思想是:通过一趟排序将要排序的数据分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分的所有数据都比另外一部分的所有数据都要小,然后再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序,整个排序过程可以递归进行,以此达到整个数据变成有序序列
1.2 快速排序的程序实现
需求:有一组无序的数据{-9,78,0,23,-567,70, -1,900, 4561}; ,请用快速排序算法实现从小到大排列
程序如下:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {-9, 78, 0, 23, -567, 70, -1, 900, 4561};
// left和right分别是此次快速排序递归的开始index和结束index
quickSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
System.out.println("array = " + Arrays.toString(array));
}
// array是多次递归共用的,left和right分别是此次快速排序递归的开始index和结束index
public static void quickSort(int[] array, int left, int right) {
int tmpLeft = left;
int tmpRight = right;
// 临时的中轴值。注意tmpPivot的值随着交换,其对应的index会不断的发生变化
// 但是最终的目的是让其index右边的值比tmpPivot大,左边的值比tmpPivot小
int tmpPivot = array[(left + right) / 2];
// 交换时的临时变量
int tmp = 0;
// 不断进行遍历,让tmpPivot对应的index的右边的值比tmpPivot大,左边的值比tmpPivot小
// 只有当tmpLeft小于tmpRight才有必要进行值交换
while (tmpLeft < tmpRight) {
// 不断的进行查找,直到在tmpPivot对应index左边的值比tmpPivot大的值,则退出,等待值交换
// tmpLeft不会大于tmpPivot所在index
while (array[tmpLeft] < tmpPivot) {
tmpLeft += 1;
}
// 不断的进行查找,直到在在tmpPivot对应index右边的值比tmpPivot小的值,则退出,等待值交换
// tmpRight不会小于tmpPivot所在index
while (array[tmpRight] > tmpPivot) {
tmpRight -= 1;
}
// 如果l == r说明tmpPivot对应index的左边的值都比tmpPivot小,右边的值都比tmpPivot大
// 直接进行退出,不用再进行值交换
if (tmpLeft == tmpRight) {
break;
}
// 进行左右两边的值交换。可能会将tmpPivot的值也进行交换
tmp = array[tmpLeft];
array[tmpLeft] = array[tmpRight];
array[tmpRight] = tmp;
// 当tmpLeft所在index的值比tmpPivot(tmpRight所在index的值)大
// 进行值交换后,此时tmpRight所在index的值比tmpPivot所在index的值大,tmpRight所在index不用再参与这一轮比较
// 所以需要将tmpRight前移,以便后续的值交换
if (array[tmpLeft] == tmpPivot) {
tmpRight -= 1;
}
// 当tmpRight所在index的值比tmpPivot(tmpLeft所在index的值)小
// 进行值交换后,此时tmpLeft所在index的值比tmpPivot所在index的值小,tmpLeft所在index不用再参与这一轮比较
// 所以需要将tmpLeft后移,以便后续的值交换
if (array[tmpRight] == tmpPivot) {
tmpLeft += 1;
}
}
// 如果tmpLeft == tmpRight, 将tmpLeft后移,tmpRight前移,使后续的递归调用index不重叠
if (tmpLeft == tmpRight) {
tmpLeft += 1;
tmpRight -= 1;
}
// 向左递归
if (left < tmpRight) {
quickSort(array, left, tmpRight);
}
// 向右递归
if (right > tmpLeft) {
quickSort(array, tmpLeft, right);
}
}
}
运行程序,结果如下:
array = [-567, -9, -1, 0, 23, 70, 78, 900, 4561]
2. 归并排序算法
2.1 归并排序的介绍
归并排序(merge-sort)是利用归并的思想实现的排序方法,该算法采用经典的分治(divide-and-conquer)策略(分治法将问题分(divide)成一些小的问题然后递归求解,而治(conquer)的阶段则将分的阶段得到的各答案"修补"在一起,即分而治之)
归并排序的思想如下所示:
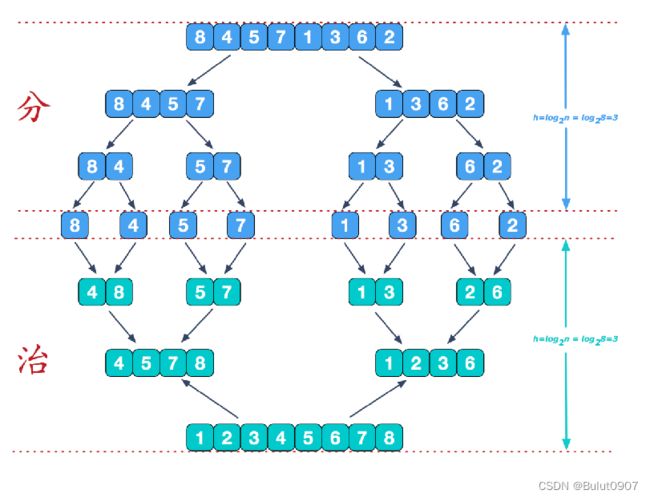
归并排序我们采用递归去实现(也可采用迭代的方式去实现)。分阶段可以理解为就是递归拆分子序列的过程。而治阶段,需要将两个已经内部有序外部无序的子序列合并成一个有序序列
2.2 归并排序的程序实现
需求:有一组无序的数据{8, 4, 5, 7, 1, 3, 6, 2},请用归并排序算法实现从小到大排列
程序如下:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {8, 4, 5, 7, 1, 3, 6, 2};
// 用来保存合并后的有序序列的临时数组, 供每次合并使用,大小和原始数组一样大
int[] tmpArray = new int[array.length];
mergeSort(array, 0, array.length - 1, tmpArray);
System.out.println("归并排序后 = " + Arrays.toString(array));
}
// 归并排序实现。先进行拆分,再进行合并
public static void mergeSort(int[] array, int left, int right, int[] tmpArray) {
// 当拆分后只有一个元素时,left == right,就不再进行拆分,拆分完成
if (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
// 向左递归进行拆分
mergeSort(array, left, mid, tmpArray);
// 向右递归进行拆分
mergeSort(array, mid + 1, right, tmpArray);
// 等左右都拆分完成。开始对左右进行合并
// 合并前左边的是有序的,右边的也是有序的,但左右无序,合并后的数据是有序的
// 然后不断的进行回溯
merge(array, left, mid, right, tmpArray);
}
}
/* 各参数含义:
array:原始的数组
left:合并前的左边有序序列的开始index
right:合并前左右有序序列的中间index
right:合并前右边有序序列的结束index
tmpArray:用来保存合并后的有序序列的临时数组
*/
public static void merge(int[] array, int left, int mid, int right, int[] tmpArray) {
// 左边有序序列的第一个index
int tmpLeft = left;
// 右边有序序列的第一个index
int tmpRight = mid + 1;
int tmpArrayIndex = 0;
// 同时遍历左边有序序列,和右边有序序列
while (tmpLeft <= mid && tmpRight <= right) {
// 如果左边有序序列的值小,则将左边有序序列的值保存到tmpArray,然后将左边有序序列的index后移
// tmpArray保存的是左右两个有序序列的较小值
if (array[tmpLeft] <= array[tmpRight]) {
tmpArray[tmpArrayIndex] = array[tmpLeft];
tmpArrayIndex += 1;
tmpLeft += 1;
} else {
// 如果右边有序序列的值小,则将右边有序序列的值保存到tmpArray,然后将右边有序序列的index后移
// tmpArray保存的是左右两个有序序列的较小值
tmpArray[tmpArrayIndex] = array[tmpRight];
tmpArrayIndex += 1;
tmpRight += 1;
}
}
// 当右边的有序序列都保存到tmpArray中,将左边有序序列的剩余元素依次保存到tmpArray
while (tmpLeft <= mid) {
tmpArray[tmpArrayIndex] = array[tmpLeft];
tmpArrayIndex += 1;
tmpLeft += 1;
}
// 当左边的有序序列都保存到tmpArray中,将右边有序序列的剩余元素依次保存到tmpArray
while (tmpRight <= right) {
tmpArray[tmpArrayIndex] = array[tmpRight];
tmpArrayIndex += 1;
tmpRight += 1;
}
// 将tmpArray此次保存的数据,重新赋值给array对应index范围
// 使array对应index范围的数据,由无序序列变成一个有序序列,便于后续的合并
tmpArrayIndex = 0;
int copy2ArrayLeft = left;
while (copy2ArrayLeft <= right) {
array[copy2ArrayLeft] = tmpArray[tmpArrayIndex];
tmpArrayIndex += 1;
copy2ArrayLeft += 1;
}
}
}
运行程序,结果如下:
归并排序后 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]