代码随想录算法训练营第18天|513. 找树左下角的值 112. 路径总和 113.路径总和ii 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
JAVA代码编写
513. 找树左下角的值
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
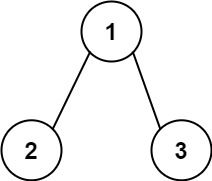
输入: root = [2,1,3]
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
输出: 7
提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是
[1,104] -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
教程:https://programmercarl.com/0513.%E6%89%BE%E6%A0%91%E5%B7%A6%E4%B8%8B%E8%A7%92%E7%9A%84%E5%80%BC.html#%E5%85%B6%E4%BB%96%E8%AF%AD%E8%A8%80%E7%89%88%E6%9C%AC
视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1424y1Z7pn/
方法一:
思路:在树的最后一行找到最左边的值。
-
如何判断是最后一行呢,其实就是深度最大的叶子节点一定是最后一行。
-
那么如何找最左边的呢?可以使用前序遍历(当然中序,后序都可以,因为本题没有 中间节点的处理逻辑,只要左优先就行),保证优先左边搜索,然后记录深度最大的叶子节点,此时就是树的最后一行最左边的值。
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度: O(n), n 是二叉树的节点数。
-
空间复杂度:O(h),h 是二叉树的高度。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int Deep = -1;
private int value = 0;
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
value = root.val;
findleftValue(root,0);
return value;
}
private void findleftValue(TreeNode root, int deep){
if(root==null) return;
if(root.left==null && root.right==null){
if(deep>Deep){
value=root.val;
Deep = deep;
}
}
if(root.left != null)
findleftValue(root.left, deep + 1);
if(root.right != null)
findleftValue(root.right, deep + 1);
}
}
112. 路径总和
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
输出:true
解释:等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
输出:false
解释:树中存在两条根节点到叶子节点的路径:
(1 --> 2): 和为 3
(1 --> 3): 和为 4
不存在 sum = 5 的根节点到叶子节点的路径。
示例 3:
输入:root = [], targetSum = 0
输出:false
解释:由于树是空的,所以不存在根节点到叶子节点的路径。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[0, 5000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
教程:https://programmercarl.com/0112.%E8%B7%AF%E5%BE%84%E6%80%BB%E5%92%8C.html
视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19t4y1L7CR/
方法一:
思路:用目标和-减去遍历的节点值,每次根据条件当前节点没有左右孩子,且该节点的值=目标值。
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n), n 是二叉树的节点数。
- 空间复杂度:O(h),h 是二叉树的高度。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) return false; // 为空退出
// 叶子节点判断是否符合
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root.val == targetSum;
// 求两侧分支的路径和
return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
}
}
113. 路径总和 II
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点总数在范围
[0, 5000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
教程:https://programmercarl.com/0112.%E8%B7%AF%E5%BE%84%E6%80%BB%E5%92%8C.html
方法一:
思路:
在深度优先搜索(DFS)过程中,当我们走完一条路径,需要回退到上一个节点继续搜索其他分支时,就需要执行这个操作。
复杂度分析:
-
时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 为节点数。
-
空间复杂度: O(h),其中 h 为树的高度。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return res; // 非空判断
List<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
preorderdfs(root, targetSum, res, path);
return res;
}
public void preorderdfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path) {
path.add(root.val);
// 遇到了叶子节点
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
// 找到了和为 targetsum 的路径
if (targetSum - root.val == 0) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
return; // 如果和不为 targetsum,返回
}
if (root.left != null) {
preorderdfs(root.left, targetSum - root.val, res, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯,移除最后一个节点
}
if (root.right != null) {
preorderdfs(root.right, targetSum - root.val, res, path);
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯
}
}
}
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
示例 1:
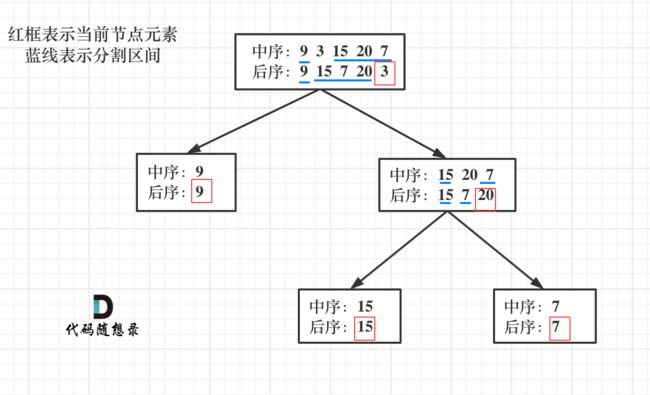
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
输入:inorder = [-1], postorder = [-1]
输出:[-1]
提示:
1 <= inorder.length <= 3000postorder.length == inorder.length-3000 <= inorder[i], postorder[i] <= 3000inorder和postorder都由 不同 的值组成postorder中每一个值都在inorder中inorder保证是树的中序遍历postorder保证是树的后序遍历
教程:https://programmercarl.com/0106.%E4%BB%8E%E4%B8%AD%E5%BA%8F%E4%B8%8E%E5%90%8E%E5%BA%8F%E9%81%8D%E5%8E%86%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E6%9E%84%E9%80%A0%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91.html#%E6%80%9D%E8%B7%AF
视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1vW4y1i7dn/
方法一:
思路:
说到一层一层切割,就应该想到了递归。
中序遍历:LDR,后序遍历LRD
来看一下一共分几步:
- 第一步:如果数组大小为零的话,说明是空节点了。
- 第二步:如果不为空,那么取后序数组最后一个元素作为节点元素。
- 第三步:找到后序数组最后一个元素在中序数组的位置,作为切割点
- 第四步:切割中序数组,切成中序左数组和中序右数组 (顺序别搞反了,一定是先切中序数组)
- 第五步:切割后序数组,切成后序左数组和后序右数组
- 第六步:递归处理左区间和右区间
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 在最坏情况下,树为链状结构,空间复杂度为 O(n);在平衡二叉树的情况下,空间复杂度为 O(logn)
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
public class Solution {
Map<Integer, Integer> map; // 方便根据数值查找位置
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) { // 用map保存中序序列的数值对应位置
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return findNode(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder,0, postorder.length); // 前闭后开
}
public TreeNode findNode(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd) {
//中序遍历:LDR,后序遍历LRD
// 参数里的范围都是前闭后开
if (inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd) { // 不满足左闭右开,说明没有元素,返回空树
return null;
}
int rootIndex = map.get(postorder[postEnd - 1]); // 找到后序遍历的最后一个元素在中序遍历中的位置
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(inorder[rootIndex]); // 构造结点
int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin; // 保存中序左子树个数,用来确定后序数列的个数
root.left = findNode(inorder, inBegin, rootIndex, postorder, postBegin, postBegin + lenOfLeft);
root.right = findNode(inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd, postorder, postBegin + lenOfLeft, postEnd - 1);
return root;
}
}