详解Java操作Redis
前言
在Redis官网中提供了各种语言的客户端,地址:https://redis.io/docs/clients/
官方比较推荐的Java操作Redis的客户端
标记为❤的就是推荐使用的java客户端,包括:
-
Jedis和Lettuce:这两个主要是提供了Redis命令对应的API,方便我们操作Redis,而SpringDataRedis又对这两种做了抽象和封装,因此我们后期会直接以SpringDataRedis来学习。
-
Redisson:是在Redis基础上实现了分布式的可伸缩的java数据结构,例如Map.Queue等,而且支持跨进程的同步机制:Lock.Semaphore等待,比较适合用来实现特殊的功能需求。
Jedis快速入门
创建一个Maven项目。
导入依赖坐标
redis.clients
jedis
3.7.0
org.junit.jupiter
junit-jupiter
5.7.0
test
编写测试类
【init】 对Jedis进行 进行初始化,定义了redis的ip地址,端口号密码等等。
【testJ】里面Jedis对redis进行操作,其函数都与redis类似;
Redis常用数据结构详解_abc123mma的博客-CSDN博客
【end】对Jedis进行释放
package cn.itheima;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
public class TestJedis {
private Jedis jedis;
@BeforeEach
public void init() {
jedis = new Jedis("xxx.xxx.xxx.x",6379);
// jedis = TestJedisPool.getJedisPool();
jedis.auth("*****");
jedis.select(0);
System.out.println("连接建立成功");
}
@Test
public void testJ() {
String result = jedis.set("name", "张三");
System.out.println("result :" + result);
String name = jedis.get("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
@AfterEach
public void end() {
if (jedis != null) {
jedis.close();
}
}
}
【利用连接池创建Jedis】
Jedis本身是线程不安全的,并且频繁的创建和销毁连接会有性能损耗,因此我们推荐大家使用Jedis连接池代替Jedis的直连方式
有关池化思想,并不仅仅是这里会使用,很多地方都有,比如说我们的数据库连接池,比如我们tomcat中的线程池,这些都是池化思想的体现。
package cn.itheima;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
public class TestJedisPool {
private static final JedisPool jedisPool;
static {
// 配置连接池
JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig();
// 最大连接数
config.setMaxTotal(8);
// 最大空闲数---没有人访问也能有空闲连接等待连接
config.setMaxIdle(8);
// 最小空闲数
config.setMinIdle(0);
jedisPool = new JedisPool(config,
"xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx",6379,1000,"*******");
}
public static Jedis getJedisPool() {
return jedisPool.getResource();
}
}
【采用springboot整合的Redis】
SpringData是Spring中数据操作的模块,包含对各种数据库的集成,其中对Redis的集成模块就叫做SpringDataRedis,官网地址:Spring Data Redis
-
提供了对不同Redis客户端的整合(Lettuce和Jedis)
-
提供了RedisTemplate统一API来操作Redis
-
支持Redis的发布订阅模型
-
支持Redis哨兵和Redis集群
-
支持基于Lettuce的响应式编程
-
支持基于JDK.JSON.字符串.Spring对象的数据序列化及反序列化
-
支持基于Redis的JDKCollection实现
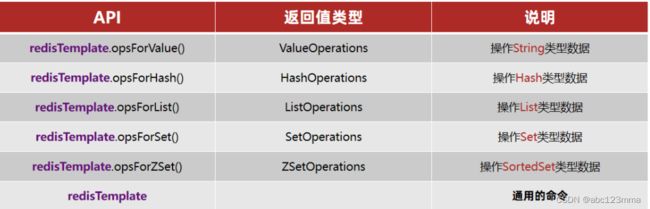
SpringDataRedis中提供了RedisTemplate工具类,其中封装了各种对Redis的操作。并且将不同数据类型的操作API封装到了不同的类型中:
SpringBoot已经提供了对SpringDataRedis的支持,使用非常简单:
导入依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
org.apache.commons
commons-pool2
com.fasterxml.jackson.core
jackson-databind
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
编写配置文件
spring:
redis:
host: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
port: 6379
password: *****
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 8 #最大连接
max-idle: 8 #最大空闲连接
min-idle: 0 #最小空闲连接
max-wait: 100ms #连接等待时间【测试代码】
@SpringBootTest
class RedisDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void testString() {
// 写入一条String数据
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("name", "虎哥");
// 获取string数据
Object name = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("name");
System.out.println("name = " + name);
}
} 提示:SpringDataJpa使用起来非常简单,记住如下几个步骤即可
SpringDataRedis的使用步骤:
引入spring-boot-starter-data-redis依赖
在application.yml配置Redis信息
注入RedisTemplate
插入的结果如下:
【缺点】需要重新定义序列化工具
因此需要引入StringRedisTemplate
StringRedisTemplate
StringRedisTemplate帮我定义了Key-Value的序列化方式,因此我们需要自己定义关于对象的序列化方式
package com.heima;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.heima.redis.pojo.User;
import net.bytebuddy.implementation.bind.annotation.RuntimeType;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
@SpringBootTest
class RedeisDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate template;
// 序列化工具,jackson的序列化工具
private static ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Test
void testString() throws JsonProcessingException {
ValueOperations String = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
String.set("name","zhangsan");
String name = (String) String.get("name");
System.out.println(name);
User user = new User("zhangsan",20);
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(user);
template.opsForValue().set("user:100",json);
java.lang.String val = template.opsForValue().get("user:100");
User user1 = mapper.readValue(val, User.class);
System.out.println("user1 = " + user1);
}
/* @Test
void contextLoads() {
}*/
}
【测试结果】