力扣刷题篇之链表2
系列文章目录
目录
系列文章目录
前言
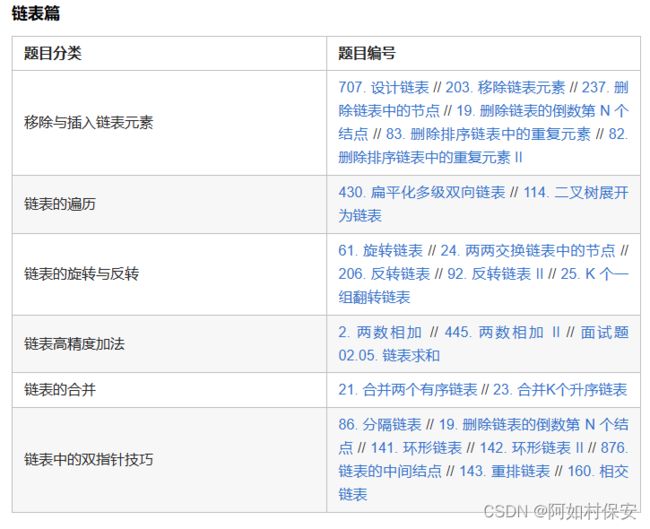
一、链表高精度加法
二、链表的合并
三、链表中的双指针技巧
总结
前言
本系列是个人力扣刷题,本文是链表。刷题顺序按照[力扣刷题攻略] Re:从零开始的力扣刷题生活 - 力扣(LeetCode)
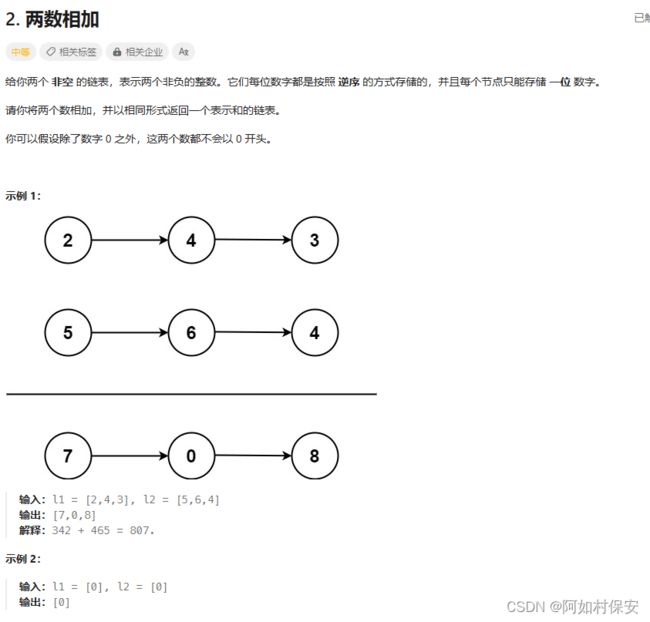
一、链表高精度加法
用carry记录进位。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode root=new ListNode(0);
ListNode cursor=root;
int carry=0;
while(l1!=null||l2!=null||carry!=0){
int l1Val=l1!=null? l1.val:0;
int l2Val=l2!=null? l2.val:0;
int sumVal=l1Val+l2Val+carry;
carry=sumVal/10;
ListNode sumNode=new ListNode(sumVal%10);
cursor.next=sumNode;
cursor=sumNode;
if(l1!=null) l1=l1.next;
if(l2!=null) l2=l2.next;
}
if(carry!=0)cursor.next=new ListNode(carry);
return root.next;
}
}这个跟上一题不一样的是,这个向前进位,上一个向后进位,那么我们先把两个反转,相加后再反转。反转链表的函数要敲熟,这里是写的以头进,整个链表反转,我记得之前有个题写了左边和右边界之间的部分反转。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1==null)return l2;
if(l2==null)return l1;
ListNode head1=reverseNode(l1);
ListNode head2=reverseNode(l2);
ListNode res=new ListNode();
ListNode temp=res;
int val1=0,val2=0;
int carry=0;
while(head1!=null||head2!=null){
val1=head1==null?0:head1.val;
val2=head2==null?0:head2.val;
res.next=new ListNode( (val1+val2+carry)%10 );
carry=(val1+val2+carry)/10;
res=res.next;
head1=head1==null?null:head1.next;
head2=head2==null?null:head2.next;
}
if(carry!=0)res.next=new ListNode(carry);
return reverseNode(temp.next);
}
public ListNode reverseNode(ListNode node){
if(node.next==null) return node;
ListNode prev=null;
ListNode cur=node;
ListNode curBehind=null;
while(cur!=null){
curBehind=cur.next;
cur.next=prev;
prev=cur;
cur=curBehind;
}
return prev;
}
}就是第一题
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
int carry = 0;
ListNode ans = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = ans;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int num1 = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val;
int num2 = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val;
int num = num1 + num2 + carry;
carry = num / 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(num % 10);
l1 = l1 == null ? null : l1.next;
l2 = l2 == null ? null : l2.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
if (carry == 1)
cur.next = new ListNode(carry);
return ans.next;
}
}二、链表的合并
很简单的题,注释的代码之所以不行是因为直接用res.next不够准确,要使用一个额外的指针 current 来正确跟踪新链表的尾部。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
// ListNode node1=list1;
// ListNode node2=list2;
// ListNode res=new ListNode(0);
// if(node1!=null && node2!=null){
// if(node1.val < node2.val){
// res.next= node1;
// node1=node1.next;
// }else{
// res.next=node2;
// node2=node2.next;
// }
// res=res.next;
// }
// if(node1!=null){
// res.next=node1;
// // node1=node1.next;
// }
// if(node2!=null){
// res.next=node2;
// // node2=node2.next;
// }
// return res.next;
// }
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); // 创建虚拟头节点
ListNode current = dummy; // 当前节点指针
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
current.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
current.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
current = current.next;
}
// 将剩余的节点连接到结果链表
if (list1 != null) {
current.next = list1;
}
if (list2 != null) {
current.next = list2;
}
return dummy.next; // 返回真正的头节点
}
}利用了分治和递归的方法,将 K 个有序链表分成更小的子问题,然后递归地合并它们。(这题还要再思考下
-
mergeKLists方法是入口方法,接受一个ListNode数组lists作为输入。首先,检查数组的长度,如果为空,直接返回null。否则,调用split方法,将问题分解为更小的子问题。 -
split方法用于分治,将 K 个链表分成两部分,然后递归地调用mergeTwoLists方法来合并它们。它使用递归分割的方式,将 K 个链表不断分成两半,然后合并两半。 -
mergeTwoLists方法用于合并两个有序链表,这个方法在每个分治阶段都会调用。它比较两个链表的头节点的值,选择较小的头节点,然后递归地调用mergeTwoLists来合并剩余的部分,最终返回合并后的链表。
采用了分治的方法,将大问题分解为小问题,并逐步合并这些小问题,最终得到合并后的 K 个有序链表。如果输入的 lists 包含 K 个有序链表,这段代码应该能够正确地合并它们。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 合并两个有序链表
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length == 0) {
return null;
}
return split(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
public ListNode split(ListNode[] lists, int i, int j) {
// System.out.println(i + " " + j);
if (j == i) {
return lists[i];
}
int m = (i + j) >>> 1;
return mergeTwoLists(
split(lists, i, m),
split(lists, m + 1, j)
);
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode p1, ListNode p2) {
if (p2 == null || p1 == null) {
return p2 == null ? p1 : p2;
}
if (p1.val < p2.val) {
p1.next = mergeTwoLists(p1.next, p2);
return p1;
} else {
p2.next = mergeTwoLists(p1, p2.next);
return p2;
}
}
}
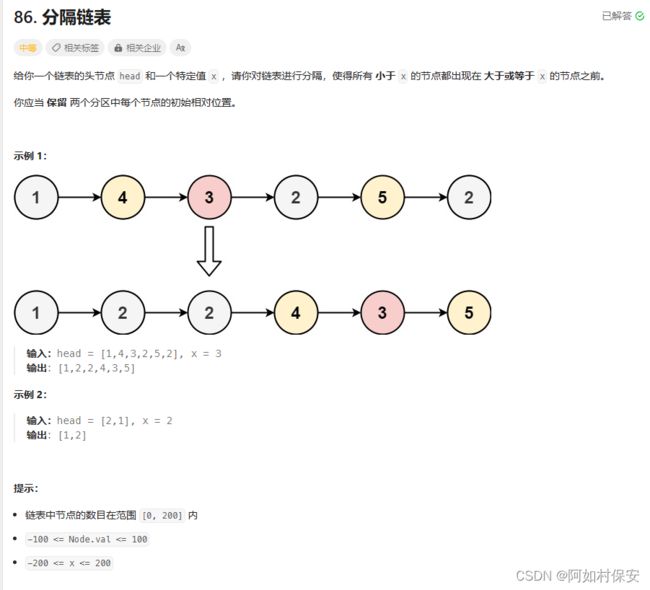
三、链表中的双指针技巧
用bigger指向大于或者等于x的链表,smaller指向小于x的链表,最后small连接big。
这里有个地方要注意就是,一定要把最后的节点指向空,避免出现环路。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode bigger=new ListNode(0);
ListNode smaller=new ListNode(0);
ListNode big=bigger;
ListNode small=smaller;
while(head!=null){
if(head.val之前做过的十九题
这里有个特殊情况,只有两个节点,且删除倒数第二节点情况。
用快慢指针,快指针先走n-1步。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode quick = head;
int count = 0;
while (count < n -1) {
quick = quick.next;
count++;
}
ListNode prev = slow;
boolean notRun = true;
while (quick != null && quick.next != null) {
prev = slow;
quick = quick.next;
slow = slow.next;
notRun = false;
}
if (notRun) { // 处理只有两个节点,且删除倒数第二节点情况
head = head.next;
return head;
}
if (prev != slow) {
prev.next = slow.next;
}
return head;
}
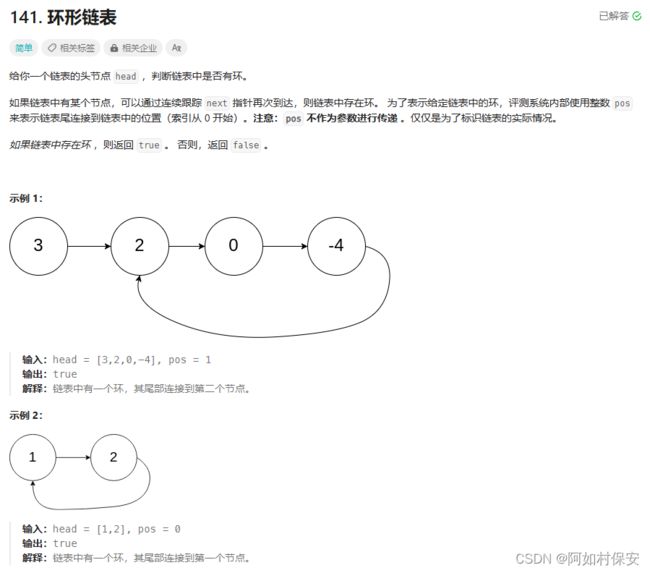
}快指针先走一步,每次快指针比慢指针多走一步,如果存在环,两个指针就必然相交,不会相交的就没有环。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null) return false;
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head.next;
while(slow!=fast && slow!=null && fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
}
return fast==slow? true:false;
}
}环形链表的进阶,找入环的第一个节点,这个可以参考左程云算法与数据结构代码汇总之链表(Java)-CSDN博客
快指针比慢指针先走一步,每次快指针都比慢指针多走一步,相遇就是有环,相遇后把快指针重置到头结点,再一起一步步往后,相遇的第一个节点就是入环的第一个节点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
// 检测到环路
fast = head; // 重置 fast 到头节点
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return fast; // 返回环路的起点
}
}
return null; // 没有环路
}
}简单题,快慢指针,快指针到达末尾的时候,慢指针在中间节点。注意一下,快指针的边界条件就好了。fast!=null && fast.next!=null
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
}先通过快慢指针找到中间节点,把后面的进行翻转,然后再一一连接。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//反转后半链表
ListNode tail = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
ListNode pre = null;
while(tail != null){
ListNode temp = tail.next;
tail.next = pre;
pre = tail;
tail = temp;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null && pre != null){
ListNode cur_next = cur.next, pre_next = pre.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre.next = cur_next;
cur = cur_next;
pre = pre_next;
}
}
}
这一题在之前左的链表笔记中也有写。
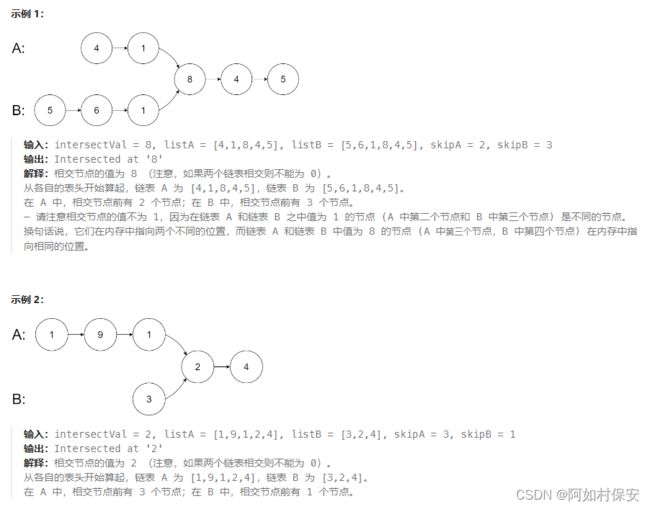
这里保证了没有环,使两个链表先到同一长度,长的先走他们的长度之差步,之后两个指针一起走,每走一步就对比一下,如果相同,就返回,一直走到最后,还没有就说明不相交。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 题目保证无环
int n=0;
ListNode a=headA;
ListNode b=headB;
while(a!=null){
n++;
a=a.next;
}
while(b!=null){
n--;
b=b.next;
}
ListNode x=headA;
ListNode y=headB;
while(n!=0){
if(n>0){
x=x.next;
n--;
} else{
y=y.next;
n++;
}
}
while(x!=null && y!=null){
if(x==y){
return x;
}
x=x.next;
y=y.next;
}
return null;
}
}总结
终于把链表总结完了,其实也是多敲敲就会了,全是套路啊,反转链表,链表的双指针...有个好现象就是越敲越也舒服了,掌握套路,多敲多练。