DirtyPipe(CVE-2022-0847) 脏管漏洞复现分析
DirtyPipe(CVE-2022-0847) 漏洞复现分析
1. 概述
1.1 漏洞简述
DirtyPipe(CVE-2022-0847),脏管漏洞,攻击者可以利用该漏洞实现低权限用户提升至 root 权限,且能对主机任意可读文件进行读写。这是Linux kernel 存在安全漏洞,该漏洞源于新管道缓冲区结构的“flag”变量在 Linux 内核中的 copy_page_to_iter_pipe() 和 push_pipe() 函数中缺乏正确的初始化。
该漏洞在原理上与2016年10月18日由黑客 Phil Oester 提出的 “Dirty Cow”脏牛漏洞类似,其本质上是由于 Kernel 内核中编写的匿名管道限制不严导致的问题,两个漏洞触发的点都在于linux内核对文件读写操作的优化(写时拷贝/零拷贝),所以将其命名为 “DirtyPipe”,中文音译为:脏管漏洞或脏管道漏洞。
值得注意的是, 该内核漏洞不仅影响了linux各个发行版, Android或其他使用linux内核的IoT系统同样会受到影响。
本实验分为概述、实验环境介绍、DirtyPipe(CVE-2022-0847) 漏洞复现分析、漏洞防范与补丁分析和总结几个部分。
希望通过本次详细的分析,能够锻炼自己的漏洞分析和剖析问题原理的的能力,同时提升发现漏洞、挖掘漏洞和处理漏洞的思维,为以后的工作打下良好的基础。
1.2 危害等级
高危(CVSS 评分7.8)
利用难度::容易
类型:LPE
远程利用:否
威胁等级: 高危
1.3 影响范围
Linux Kernel版本 >= 5.8
Linux Kernel版本 < 5.16.11 / 5.15.25 / 5.10.102
CentOS 8 默认内核版本受该漏洞影响
CentOS 7 及以下版本不受影响
1.4 适用条件
- 攻击者必须有读权限(因为它需要通过 splice() 方法将将页输入管道中)
- 偏移量不能在页边界上(因为页上至少有一个字节已经拼接到管道中)
- 写入不能跨越页边界(因为这将为其余部分创建一个新的匿名缓冲区)
- 文件无法调整大小(因为管道有自己的页面填充管理,并且不会告诉页面缓存附加了多少数据)
- 单次写入的长度不能超过一页(因为页大小为4K)
2.实验环境
虚拟机:Linux kali 5.10.0-kali7-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 5.10.28-1kali1 (2021-04-12) x86_64 GNU/Linux
内核版本:5.01.28
调试工具:gcc
3.DirtyPipe(CVE-2022-0847) 漏洞复现分析
3.1 概述
2022年3月7日,安全研究员 Max Kellermann提出一个 Linux 内核提权漏洞 CVE-2022-0847,攻击者可以利用该漏洞实现低权限用户提升至 root 权限,且能对主机任意可读文件进行读写。该漏洞在原理上与2016年10月18日由黑客 Phil Oester 提出的 “Dirty Cow”脏牛漏洞类似,由于本质上是由于 Kernel 内核中编写的匿名管道限制不严导致的问题。
它允许覆盖任意只读文件中的数据,非特权用户通过替换/etc/passwd文件中root用户的hash值达到权限提升的目的。
在3月7日, 漏洞发现者Max Kellermann详细披露了该漏洞细节以及完整POC。Paper中不光解释了该漏洞的触发原因, 还说明了发现漏洞的故事, 以及形成该漏洞的内核代码演变过程, 由浅入深,非常适合深入研究学习。
3.2 前导知识
3.2.1 管道(Pipe)
• 管道(Pipe)是一种经典的进程间通信方式, 它包含一个输入端和一个输出端, 程序将数据从一段输入, 从另一端读出。
图1 linux中的的管道机制
• 在内核中, 为了实现这种数据通信,需要以页面(Page)为单位维护一个环形缓冲区(被称为ring_buffer), 里面存了16个pipe_buf结构,每个pipe_buf结构又有一个指针指向一个表示物理内存页Page的结构体。每个Page大小为4KB,页面之间并不连续,而是通过数组进行管理,形成一个环形链表。维护两个链表指针,一个用来写(pipe->head),一个用来读(pipe->tail),可以被循环利用(即当当前页面带有PIPE_BUF_FLAG_CAN_MERGE flag时将标记且续写后的数据长度不超过一页时,可以进行续写)。
//C
// >>> include/linux/pipe_fs_i.h:17
/**
* struct pipe_buffer - a linux kernel pipe buffer
* @page: the page containing the data for the pipe buffer
* @offset: offset of data inside the @page
* @len: length of data inside the @page
* @ops: operations associated with this buffer. See @pipe_buf_operations.
* @flags: pipe buffer flags. See above.
* @private: private data owned by the ops.
**/
struct pipe_buffer {
struct page *page;
unsigned int offset, len;
const struct pipe_buf_operations *ops;
unsigned int flags;
unsigned long private;
};
• 管道可以分为命名管道和匿名管道。命名管道是一个有名字的实体文件,匿名管道就是我们常使用的管道符创建的管道。本质上来讲,管道就是一种进程间的通信手段,让两个进程可以通过pipe发送和接收数据。
图2 管道工作示意图
3.2.2 Page Cache机制
Page Cache即缓存管理机制,我们知道,磁盘的IO读写速度是很慢的,所以一般当我们访问一个磁盘文件的时候,首先操作系统会将其内容装载到内存中,后续的访问都是直接取内存中的副本来读取数据。因为一个文件的内存副本,后续可能会被很多进程打开和使用。为了保证大家都能快速的访问,Linux设计了这样一个Page Cache机制管理物理内存中映射的页框。如果用户进程使用read/write读写文件,那么内核会先将载入数据的物理内存映射到内核虚拟内存buffer。然后再将内核的buffer数据拷贝到用户态。
如果追求效率,内核也提供一种零拷贝模式(不发生系统调用,跨越用户和内核的边界做上下文切换)。用户进程可以使用mmap直接将用户态的buffer 映射到 物理内存,不需要进行系统调用,直接访问自己的mmap区域即可访问到那段物理内存内容。
在Linux中,不光是文件使用了Page cache, 前面提到的Pipe也用到了Page Cache机制。在内核中,pipe有一个大小为16的ring buffer数组,里面存了16个pipe_buf结构,每个pipe_buf结构又有一个指针指向一个表示物理内存页Page的结构体。每个Page大小为4KB,且不连续存放。这也说明管道一般大小为4KB*16。
3.2.3 splice()
splice 函数(系统调用)通过一种"零拷贝"的方法将文件内容输送到管道之中,相比传统的直接将文件内容送入管道性能更好。
比如在linux下实现文件的拷贝,用户调用splice()函数使用了 pipe 机制,从而不需要硬件的支持就能实现两个 fd 间的零拷贝。它也只涉及 2 次上下⽂切换,2 次 DMA 拷⻉。效率要比我们使用传统的read()/write()效率高。

图3 linux下的splice()拷贝
//C代码
#define _GNU_SOURCE /* See feature_test_macros(7) */
#include • splice()用于在两个文件描述符之间移动数据,即零拷贝。
• fd_in参数是待输入描述符。如果它是一个管道文件描述符,则off_in必须设置为NULL;否则off_in表示从输入数据流的何处开始读取,此时若为NULL,则从输入数据流的当前偏移位置读入。
• fd_out/off_out与上述相同,不过是用于输出。len参数指定移动数据的长度。flags参数则控制数据如何移动:
• SPLICE_F_NONBLOCK:splice操作不会被阻塞。然而,如果文件描述符没有被设置为不可被阻塞方式的 I/O ,那么调用 splice 有可能仍然被阻塞。
• SPLICE_F_MORE:告知操作系统内核下一个 splice 系统调用将会有更多的数据传来。
• SPLICE_F_MOVE:如果输出是文件,这个值则会使得操作系统内核尝试从输入管道缓冲区直接将数据读入到输出地址空间,这个数据传输过程没有任何数据拷贝操作发生。
• 使用splice时, fd_in和fd_out中必须至少有一个是管道文件描述符,否则将会报错。
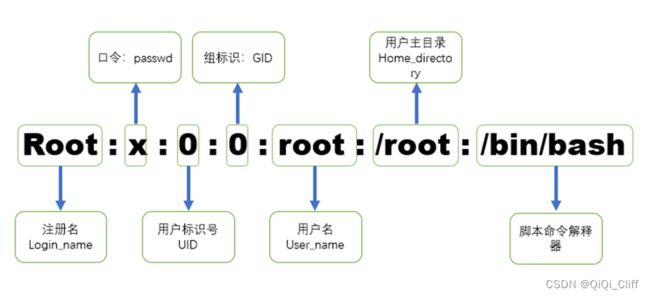
3.2.4 linux密码配置文件(/etc/passwd)格式
因为本次实验是通过篡改/etc/passwd文件的内容实现提权到root,所以了解Linux密码配置文件的格式很有必要。
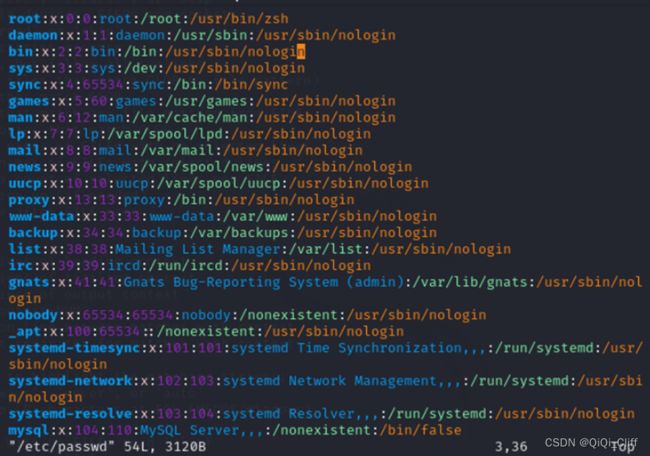
图5 /etc/passwd文件密码存储格式
3.3 漏洞原理分析
在作者的paper中可以了解到, 发现该漏洞的起因不是因为专门的漏洞挖掘工作, 而是关于日志服务器多次出现的文件错误, 用户下载的包含日志的gzip文件多次出现CRC校验位错误, 排查后发现CRC校验位总是被一段ZIP头覆盖。
根据作者介绍, 可以生成ZIP文件的只有主服务器的一个负责HTTP连接的服务(为了兼容windows用户, 需要把gzip封包即时封包为ZIP文件), 而该服务没有写入gzip文件的权限。
即主服务器同时存在一个writer进程与一个splicer进程, 两个进程以不同的用户身份运行, splicer进程并没有写入writer进程目标文件的权限, 但存在splicer进程的数据写入文件的bug存在。
splice()系统调用将包含文件的页面缓存(page cache),链接到pipe的环形缓冲区(pipe_buffer)时,在copy_page_to_iter_pipe 和 push_pipe函数中未能正确清除页面的"PIPE_BUF_FLAG_CAN_MERGE"属性,导致后续进行pipe_write()操作时错误的判定"write操作可合并(merge)“,从而将非法数据写入文件页面缓存,导致任意文件覆盖漏洞。
简单来说就是调用splice 函数可以通过"零拷贝"的形式将文件发送到pipe,代码层面的零拷贝是直接将文件缓存页(page cache)作为pipe 的buf页使用。但这里引入了一个变量未初始化漏洞,导致文件缓存页会在后续pipe 通道中被当成普通pipe缓存页而被"续写"进而被篡改。然而,在这种情况下,因为没有其他可写权限的程序进行write操作,所以内核并不会将这个缓存页判定为"脏页”,短时间内(到下次重启之类的)不会刷新到磁盘。在这段时间内所有访问该文件的场景都将使用被篡改的文件缓存页,也就达成了一个"短时间内对任意可读文件任意写"的操作。可以完成本地提权。
splice 函数(系统调用)通过一种"零拷贝"的方法将文件内容输送到管道之中,相比传统的直接将文件内容送入管道性能更好。
splice()源代码。调用链接为:
C
//code:fs/splice.c
SYSCALL_DEFINE6(splice...)
->__do_splice->do_splice...
->copy_page_to_iter
-> copy_page_to_iter_pipe
调用链比较复杂,但是最终的实现在copy_page_to_iter_pipe()中,即漏洞所在位置。copy_page_to_iter_pipe()函数会将文件的缓存页拷贝替换给pipe的缓存页。在分析copy_page_to_iter_pipe()函数之前,先看管道写的机制。
pipe_write()源码:
//C
//fs/pipe.c
static ssize_t
pipe_write(struct kiocb *iocb, struct iov_iter *from)
{
struct file *filp = iocb->ki_filp;
struct pipe_inode_info *pipe = filp->private_data;
unsigned int head;
ssize_t ret = 0;
size_t total_len = iov_iter_count(from);
ssize_t chars;
...
/*
* If it wasn't empty we try to merge new data into
* the last buffer.
*
* That naturally merges small writes, but it also
* page-aligns the rest of the writes for large writes
* spanning multiple pages.
*/
head = pipe->head;
was_empty = pipe_empty(head, pipe->tail);
chars = total_len & (PAGE_SIZE-1);
if (chars && !was_empty) {
//如果缓存页不为空 (要走进这个分支,说明我们得提前把pipe申请满一遍,然后再将内容都读完,保留buf结构体)
unsigned int mask = pipe->ring_size - 1;
struct pipe_buffer *buf = &pipe->bufs[(head - 1) & mask];
int offset = buf->offset + buf->len;//接着写cache的位置
//如果pipe_buf的Flag为PIPE_BUF_FLAG_CAN_MERGE(初始化时设置的), 则允许在当前页面续写
if ((buf->flags & PIPE_BUF_FLAG_CAN_MERGE) && offset + chars <= PAGE_SIZE) {
//如果续写不会引发写跨页,则写入。否则goto out, 那里会分配一个新的内存页来装数据。
ret = pipe_buf_confirm(pipe, buf);
if (ret)
goto out;
//将数据从用户传来的from, 拷贝到 pipe_buf->page
//这里的pipe_buf->page 和 攻击目标的只读文件 共享 缓存页!
ret = copy_page_from_iter(buf->page, offset, chars, from);
if (unlikely(ret < chars)) {
ret = -EFAULT;
goto out;
}
buf->len += ret;
if (!iov_iter_count(from))
goto out;
}
}
...
}
程序分析:
- 检查 如果当前管道(pipe)中不为空(head==tail判定为空管道),则说明现在管道中有未被读取的数据,则获取head 指针,也就是指向最新的用来写的页,查看该页的len、offset(为了找到数据结尾)。接下来尝试在当前页面续写
- 判断 当前页面是否带有 PIPE_BUF_FLAG_CAN_MERGE flag标记,如果不存在则不允许在当前页面续写。或当前写入的数据拼接在之前的数据后面长度超过一页(即写入操作跨页),如果跨页,则无法续写。
- 如果无法在上一页续写,则另起一页
- 调用alloc_page() 申请一个新的页
- 将新的页放在数组最前面(可能会替换掉原有页面),对相关值进行初始化。
- buf->flag 默认初始化为PIPE_BUF_FLAG_CAN_MERGE ,因为出于内存高效利用的考虑,默认状态是允许页可以续写的。
- 拷贝写入的数据,并设置相应的偏移量字段;没拷贝完重复上述操作。
漏洞利用的关键就是在splice 中pipe_buf带有未被初始化的PIPE_BUF_FLAG_CAN_MERGE flag标记,允许我们继续往一个"没写完"的pipe页面续写数据。
上面提到了,pipe 就是通过管理16 个页来作为缓存。splice 的零拷贝方法就是,直接用文件缓存页来替换pipe 中的缓存页(更改pipe缓存页指针指向文件缓存页)。
而漏洞所在的copy_page_to_iter_pipe 函数主要做的工作就是将pipe 缓存页结构指向要传输的文件的文件缓存页。
copy_page_to_iter_pipe()源码:
//C代码
// Code: lib/iov_iter.c
static size_t copy_page_to_iter_pipe(struct page *page, size_t offset, size_t bytes,
struct iov_iter *i)
{
struct pipe_inode_info *pipe = i->pipe;
struct pipe_buffer *buf;
unsigned int p_tail = pipe->tail;
unsigned int p_mask = pipe->ring_size - 1;
unsigned int i_head = i->head;
size_t off;
if (unlikely(bytes > i->count))
bytes = i->count;
if (unlikely(!bytes))
return 0;
if (!sanity(i))
return 0;
off = i->iov_offset;
//获取当前bufs数组中 写入index的pipe_buf
buf = &pipe->bufs[i_head & p_mask];
if (off) {
if (offset == off && buf->page == page) {
/* merge with the last one */
buf->len += bytes;
i->iov_offset += bytes;
goto out;
}
i_head++;
buf = &pipe->bufs[i_head & p_mask];
}
if (pipe_full(i_head, p_tail, pipe->max_usage))
return 0;
//buf->flag的默认值是 PIPE_BUF_FLAG_CAN_MERGE
//这里没有将 buf->flag 设置为 0,漏洞点!后面会提到
buf->ops = &page_cache_pipe_buf_ops;
//获取文件的缓存页,存放到page里。
get_page(page);
//将pipe的page指向文件的缓存page
buf->page = page;
buf->offset = offset;
buf->len = bytes;
pipe->head = i_head + 1;
i->iov_offset = offset + bytes;
i->head = i_head;
out:
i->count -= bytes;
return bytes;
}
程序分析:
- 首先根据pipe 页数组环形结构,找到当前写指针(pipe->head) 的位置
- 将当前需要写入的页指向准备好的文件缓存页,并设置其他信息,比如len 是由splice 系统调用的传入参数决定的
上面的代码实现了把pipe的缓存页结构指向要传输文件的page cache,但是遗漏了flag的初始化0操作。Linux 4.9, 添加了iov_iter对Pipe的支持, 其中copy_page_to_iter_pipe()与push_pipe()函数实现中缺少对pipe buffer中flag的初始化操作, 但在当时并无大碍, 因为此时的can_merge标识还在ops即pipe_buf_operations结构体中。此时的buf->ops = &page_cache_pipe_buf_ops操作会使can_merge属性为0, 此时并不会触发漏洞, 但为之后的代码迭代留下了隐患。这也就是该漏洞只在Linux 内核大于等于5.8以后才存在的原因。
综合上面的分析,得到如下的利用思路:
当使用 pipe进行read/write,我们可以让目标 pipe 的每个 pipe buffer 都带上PIPE_BUF_FLAG_CAN_MERGE flag。之后再次打开目标文件,并使用 splice 写到之前处理过的 pipe 中,splice 底层会帮助我们把目标文件的 page cache 设置到 pipe buffer 的 page 字段,但却没有初始化flags 字段。之后我们再调用 pipe write 时由于存在PIPE_BUF_FLAG_CAN_MERGE flag 字段,内容会接着上次被写入同一个 page 中,但 page 其实已经变成了目标文件的 page cache,导致直接修改了目标文件 page cache。如果之后有其他文件尝试读取这个文件,kernel 会优先返回 page cache 中的内容,也就是被我们修改后的 page cache。但由于这个修改并不会触发 page 的 dirty 属性,因此若由于内存紧张后或系统重启等原因,就会导致这个 cache 内 kernel 丢弃,再次读取文件内核就会重新从磁盘中取出未被我们修改的内容,这也是和脏牛漏洞的不同点。
这时根据上面分析过的pipe_write 代码,如果重新调用pipe_write 向pipe 中写数据,写指针(pipe->head) 指向目标文件的Page Cache,flag 为 PIPE_BUF_FLAG_CAN_MERGE ,则会认为可以接着该页继续写,只要写入长度不跨页、写入点不在页边界。从而就实现了向目标文件缓存页写入任意内容!短时间内访问(读取)该文件的操作都会读到被我们篡改的文件缓存页上,因此可以修改/etc/passwd、sshkey 或者一些suid 文件之类的系统文件实现提权的目的。
3.4 漏洞复现
我们以一个实例来更清晰的理解上述原理。
比如当我们要篡改一个只读权限的文件,如 /etc/passwd。POC的思路大概为以下5个步骤。
- 创建一个管道。调用pipe()函数将一块内存区域划分为一个管道数据结构。
- 将管道填充满(通过pipe_write()任意写入数据),这样所有的buf(pipe 缓存页)都初始化过了,flag 默认初始化为PIPE_BUF_FLAG_CAN_MERGE。
- 将管道清空(通过pipe_read()),这样通过splice 系统调用传送文件的时候就会使用原有的初始化过的buf结构。
- 调用splice() 函数将想要篡改的文件传送入。
- 继续向pipe写入内容(pipe_write()),这时就会覆盖到文件缓存页了,完成目标文件缓存页篡改。
参考Max Kellermann给出的poc,我们本次实验的poc源码如下:
//C代码
/* SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0 */
/*
* Copyright 2022 CM4all GmbH / IONOS SE
*
* author: Max Kellermann
*
* Proof-of-concept exploit for the Dirty Pipe
* vulnerability (CVE-2022-0847) caused by an uninitialized
* "pipe_buffer.flags" variable. It demonstrates how to overwrite any
* file contents in the page cache, even if the file is not permitted
* to be written, immutable or on a read-only mount.
*
* This exploit requires Linux 5.8 or later; the code path was made
* reachable by commit f6dd975583bd ("pipe: merge
* anon_pipe_buf*_ops"). The commit did not introduce the bug, it was
* there before, it just provided an easy way to exploit it.
*
* There are two major limitations of this exploit: the offset cannot
* be on a page boundary (it needs to write one byte before the offset
* to add a reference to this page to the pipe), and the write cannot
* cross a page boundary.
*
* Example: ./write_anything /root/.ssh/authorized_keys 1 $'\nssh-ed25519 AAA......\n'
*
* Further explanation: https://dirtypipe.cm4all.com/
*/
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include 3.5 复现与调试展示
将3.4所编写的poc在kali上编译运行。
首先查看linux内核,然后运行脚本。
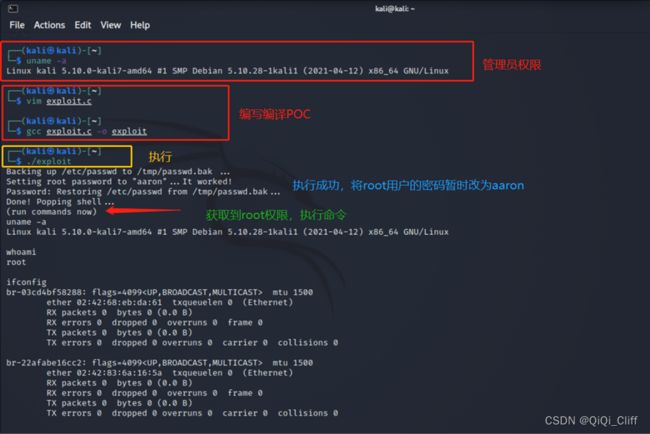
图6 poc执行示意图
上图中,我们已经从普通用户权限提权至管理员root权限,从而可以执行任意命令。
4 漏洞防范与补丁分析
可以具体通过以下命令排查范围:
uname -a
因为该漏洞属于内核漏洞,查看当前使用的内核版本,如果该版本在大于5.8则需要更新内核版本到对应的 5.16.11/5.15.25/5.10.102 及之后版本。
通过分析linux内核补丁,发现补丁增加了对copy_page_to_iter_pipe()和push_pipe()函数中buf->flags的初始化操作,因此推定Dirtypipe漏洞本质上为变量未初始化漏洞。
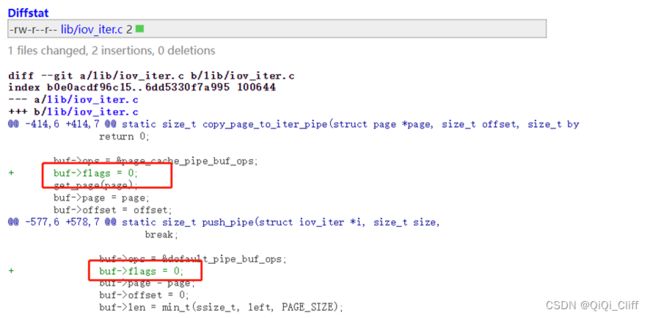
图7 漏洞补丁关键代码
5 总结
- 传统防御思路中默认只读文件是安全的,但是目前已经出现几例能够覆写只读文件内容的漏洞利用,运行时系统包括重要只读文件的完整性保护也是值得思考的。
- 生态链安全仍需持续关注,Linux内核层发现的安全漏洞,影响了所有对应版本Linux乃至Android的厂商和设备。
- CVE漏洞的安全影响依旧巨大,一方面是信息公开会吸引大量安全人员关注研究——包括黑灰产;另一方面如果修复发版不及时,会遭到外界大量的质疑和安全舆论风险。
- DirtyPipe(CVE-2022-0847),脏管漏洞是一个linux内核层漏洞,是内核调用函数中零拷贝机制存在的参数未初始化的高危漏洞。
6 参考文献
- CVE-2022-0847 Linux 脏管漏洞分析与利用 https://www.freebuf.com/vuls/331378.html
- [漏洞分析] CVE-2022-0847 Dirty Pipe linux内核提权分析https://blog.csdn.net/Breeze_CAT/article/details/123393188
- The Dirty Pipe Vulnerability:https://dirtypipe.cm4all.com/
- 详解 CVE-2022-0847 DirtyPipe 漏洞 https://xie.infoq.cn/article/cd7a2f7d7c8a8f96153471a5d