复杂类型,查询--学习笔记
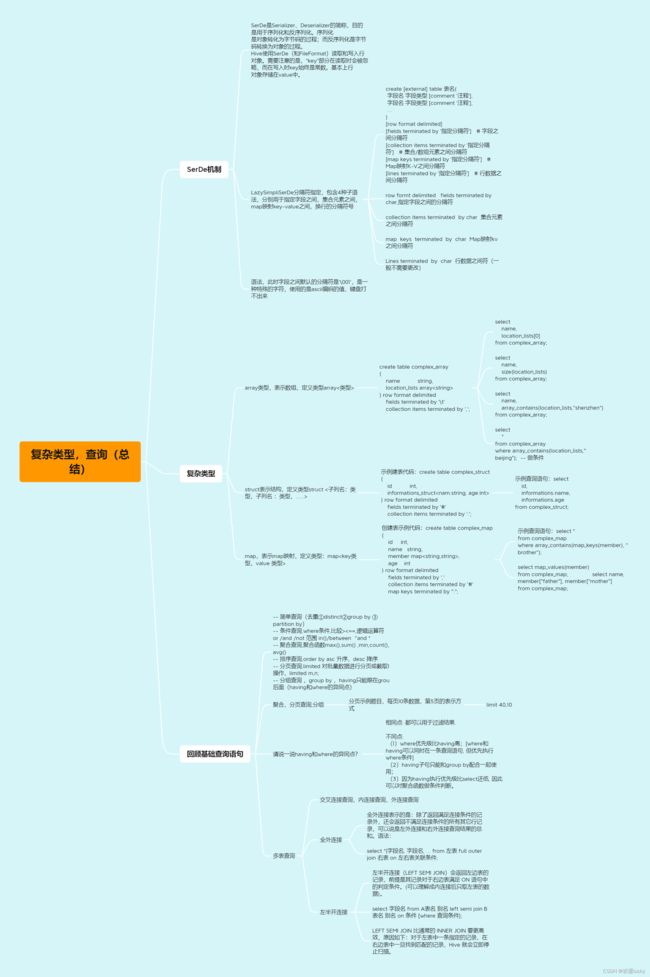
1,复杂类型
解决问题:一些不容易获取到的数据,例如数组类型,集合类型等,获取他们的数据
-- 1.创建表
create table tb_array_person(
name string,
city_array array<string>
)row format delimited
fields terminated by "\t"
collection items terminated by ",";
-- 2.上传数据到hdfs对应的表下
-- 3.查询数据结果
select * from tb_array_person;
1)当设定了复杂数据类型的字段后,需要给字段指定分隔符之外,还需要指定其他分隔符
2)注意,当使用原生数据类型指定字段名类型无法满足需求时,就可以考虑使用复杂数据类型。
1.1 SerDe机制
所谓SerDe,就是单词Serializer、Deserializer的简称。而Serializer表示序列化,Deserializer为反序列化。
(1)序列化是对象(或数据)转化为字节码的过程,相当于:加密
(2)反序列化是字节码转换为对象(或数据)的过程,好比是:解密
而上述问题中的[collection items terminated by “,”],就表示拥有了SerDe语法。可以通过命令查看:
desc formatted 表名;
2,这个序列化类中,一共包含4种子语法,分别用于指定不同内容的分隔符号,4种语法分别是:
[row format delimited]
[fields terminated by '指定分隔符'] # 字段之间分隔符
[collection items terminated by '指定分隔符'] # 集合/数组元素之间分隔符
[map keys terminated by '指定分隔符'] # Map映射K-V之间分隔符
[lines terminated by '指定分隔符'] # 行数据之间分隔符
(1)一般情况下,使用复杂类型时,要设定collection、map分隔符;
(2)fields字段、collection items集合/数组、map keys Map映射这几个使用较常见
1.2array数组
create [external] table 表名(
字段名 字段类型 [comment '注释'],
字段名 字段类型 [comment '注释'],
...
字段名 array<类型>
)
[row format delimited]
[fields terminated by '指定分隔符'] # 字段之间分隔符
[collection items terminated by '指定分隔符']; # 集合/数组元素之间分隔符
array类型属于集合/数组,设定分隔符用collection items。
1,数组变量名[index]
以索引值形式访问数组的某元素。其中,index表示索引值,索引值从0开始计算。
2,size(数组变量名)
获取数组变量的总长度或元素总个数。
3,array_contains(数组变量名, value)
判断value值是否存在数组变量中。若存在,则返回true;否则返回false。
create table complex_array(
name string,
location_lists array<string>
)row format delimited
fields terminated by "\t"
collection items terminated by ",";
load data local inpath "/root/day09_hive/array/01-data_for_array_type.txt" into table complex_array;
select * from complex_array;
select
name,
location_lists[0]
from complex_array;
select
name,
size(location_lists)
from complex_array;
select
name,
array_contains(location_lists,"shenzhen")
from complex_array;
select
name,
array_contains(location_lists,"beijing")
from complex_array;
select
*
from complex_array
where array_contains(location_lists,"beijing"); -- 做条件
array<类型> 数组元素之间的分隔符:collection items terminated by ‘分隔符’;
1.3struct集合
在Hive中,以struct类型对结构字段之间设定分隔符的建表语句:
create [external] table 表名(
字段名 字段类型 [comment '注释'],
字段名 字段类型 [comment '注释'],
...
字段名 struct<子列名 类型, 子列名 类型, ...>
)
[row format delimited]
[fields terminated by '指定分隔符'] # 字段之间分隔符
[collection items terminated by '指定分隔符']; # 集合/数组元素之间分隔符
struct值得形式是key:value的形式
create table complex_struct(
id int,
informations struct<name:string, age:int>
)row format delimited
fields terminated by "#"
collection items terminated by ":";
load data inpath "/itheima/02-data_for_struct_type.txt" into table complex_struct;
select * from complex_struct;
select
id,
informations.name,
informations.age
from complex_struct;
struct
1.4map映射
在Hive中,以map类型对映射字段之间设定分隔符的建表语句:
create [external] table 表名(
字段名 字段类型 [comment '注释'],
字段名 字段类型 [comment '注释'],
...
字段名 map<key类型, value类型>
)
[row format delimited]
[fields terminated by '指定分隔符'] # 字段之间分隔符
[collection items terminated by '指定分隔符'] # 集合/数组元素之间分隔符
[map keys terminated by '指定分隔符']; # Map映射K-V之间分隔符
map类型属于Map映射,设定分隔符用map keys。
1,变量名[key]
以key键访问map映射的值。其中,key表示指定类型的键。
2,map_keys(变量名)
以数组形式返回Map变量的所有键。
3,map_values(变量名)
以数组形式返回Map变量的所有值。
4,array_contains(数组变量名, value)
判断value值是否存在数组变量中,可作为where条件处理。若存在,则返回true;否则返回false
create table complex_map(
id int,
name string,
members map<string, string>,
age int
)row format delimited
fields terminated by ","
collection items terminated by "#"
map keys terminated by ":";
select * from complex_map;
select
*,
members["father"],
members["mother"]
from complex_map;
select
map_keys(members)
from complex_map;
select
map_values(members)
from complex_map;
select
*
from complex_map
where
array_contains(map_keys(members),"brother");
map类型的字段主要存储K-V键值对;
操作map
2.区别SQL的join查询
(1)全外连接
全外连接表示的是:除了返回满足连接条件的记录外,还会返回不满足连接条件的所有其它行记录,可以说是左外连接和右外连接查询结果的总和。语法:
select *|字段名, 字段名, ... from 左表 full outer join 右表 on 左右表关联条件;
通俗地说,全外连接就是:(左表有,右表没有的null补全;右表有,左表没有的null补全)。
常用于合并显示所有数据内容。
(2)左半开连接
左半开连接(LEFT SEMI JOIN)会返回左边表的记录,前提是其记录对于右边表满足 ON 语句中的判定条件。(可以理解成内连接后只取左表的数据)。
select 字段名 from A表名 别名 left semi join B表名 别名 on 条件 [where 查询条件];
LEFT SEMI JOIN 比通常的 INNER JOIN 要更高效,原因如下:对于左表中一条指定的记录,在右边表中一旦找到匹配的记录,Hive 就会立即停止扫描。
select
*
from tb_users u
full join tb_orders `to` on u.createTime = `to`.createTime;
select
*
from tb_users u
left semi join tb_orders o on u.userid=o.userid;