数据结构与算法-树和森林
树和森林
- 1.线索二叉树
- 2.树和森林
-
- 2.1树的存储结构
- 2.2双亲表示法
- 2.3孩子链表表示法
-
- 2.3.1孩子链表表示法的实现
- 2.3.2查找结点x在树中的下标
- 2.3.3创建k个结点的树
- 2.3.4计算结点x的度数
- 2.3.5插入结点u的孩子v
- 2.4孩子兄弟表示法
-
- 2.4.1例题
- 3.二叉树的小练笔
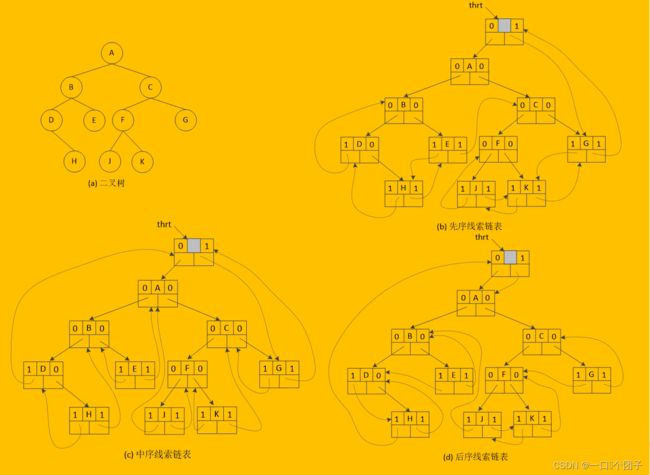
1.线索二叉树
遍历二叉树是以一定的规则将二叉树中的结点排列成一个线性序列的过程。与线性表相比,二叉树的遍历存在以下问题:
(1).遍历算法复杂而费时
(2).为检索或查找二叉树中某结点在某种遍历下的前驱结点和后继结点,必须从根结点开始遍历,直到找到该结点的前驱结点和后继结点。
为此,我们引入线索二叉树的概念,线索二叉树可以简化遍历算法,提高遍历效率。
其中,
ltag为0时,lchild域指向结点的左孩子,ltag为1时,lchild指向结点的前驱;rtag为0时,rchild域指向结点的右孩子,rtag为1时,rchild域指向结点的后继。
2.树和森林
2.1树的存储结构
树的存储结构常分为:
- 双亲表示法
- 孩子链表表示法
- 孩子兄弟表示法
2.2双亲表示法
由树的定义知,除根结点之外,树中的每个结点都有唯一的双亲。根据这一特点,双亲表示法可以用一组连续的存储空间存放结点信息,即用一维数组来存储树中的各个结点。数据元素为结构体类型,其中包括结点本身信息以及指示其双亲结点在数组中的位置信息。
双亲表示法在类型定义如下:
#define MaxSize 100
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct PtNode
{
ElemType data;
int parent;
}PtNode;
typedef struct
{
PtNode nodes[MaxSize];
int r, n;
}PTree;
2.3孩子链表表示法
孩子链表表示法存储单元的主体是一个与结点个数一样大小的一维数组,数组的每一个元素由两个域组成,一个域用来存放结点自身的数据信息,另一个用来存放指针,该指针指向由该结点孩子组成的单链表的表头。单链表的结点结构也有两个域组成,一个存放孩子结点在一维数组中的下标,另一个是指针域,指向下一个孩子。
2.3.1孩子链表表示法的实现
#define MaxSize 100
typedef struct CtNode
{
int child;
CtNode* next;//指向下一个孩子结点
}CtNode;
typedef struct
{
char data;
int parent;
CtNode* firstchild;//指向第一个孩子
int r, n;
}CtBox;
class CTree
{
private:
CtBox nodes[MaxSize];
int r, n;
public:
int LocateNode(char x);//查找结点x在树中的下标
void CreateCtree(int k);//创建k个结点的树
int DegreeNode(char x);//计算结点x的度数
void InsertNode(char u, char v);//插入结点u的孩子v
};
2.3.2查找结点x在树中的下标
int CTree::LocateNode(char x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (x == nodes[i].data)
return i;
else
return -1;
}
}
2.3.3创建k个结点的树
void CTree::CreateCtree(int k)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
cin >> nodes[i].data;
nodes[i].firstchild = NULL;
}
n = k;
r = 0;
char u, v;
int h, t;
CtNode* p;
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
cin >> u;
h = LocateNode(u);
cin >> v;
while (v != '.')
{
t = LocateNode(v);
p = new CtNode;
p->child = t;
p->next = nodes[h].firstchild;
nodes[h].firstchild = p;
cin >> v;
}
}
}
2.3.4计算结点x的度数
int CTree::DegreeNode(char x)
{
int h = LocateNode(x);
CtNode* p = nodes[h].firstchild;
int count = 0;
while (p)
{
count++;
p = p->next;
}
return count;
}
2.3.5插入结点u的孩子v
void CTree::InsertNode(char u, char v)
{
int h = LocateNode(u);
if (h == -1)
return;
nodes[n].data = v;
nodes[n].firstchild = NULL;
n++;
CtNode* p = new CtNode;
int t = LocateNode(v);
p->child = t;
p->next = nodes[h].firstchild;
nodes[h].firstchild = p;
}
2.4孩子兄弟表示法
孩子兄弟表示法又称二叉链表表示法或二叉树表示法。即以二叉链表作为树的存储结构,链表中结点的两个链域分别指向结点的第一个孩子结点和下一个兄弟结点。
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct CSNode
{
ElemType data;
CSNode* firstchild;
CSNode* nextsibling;
}CSNode;
2.4.1例题
已知一棵树以孩子兄弟表示法为其存储结构,设计一个递归算法计算树的高度。
int CSTreeHeight(CSNode* t)
{
int m, max = 0;
CSNode* p;
if (t == NULL)
return 0;
else
{
p = t->firstchild;
while (p)
{
m = CSTreeHeight(p);
if (max < m)
max = m;
p = p->nextsibling;
}
return 1 + max;
}
}
3.二叉树的小练笔
题目:递归创建一棵二叉树,中序输出二叉树序列,计算树的深度,计算度数为1的结点数,计算度数为1的结点数以及判断两棵树是否相似。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include