《算法系列》之队列与堆
简介
队列和堆也是基础的数据结构,无论刷不刷题都需要了解的数据结构。其中堆可以看做是优先队列,在很多语言中,都有优先队列或者说堆的的容器可以直接使用,但是在面试中,面试官更倾向于让更面试者自己实现一个堆。所以建议读者掌握大小根堆的实现方法,尤其要搞懂建堆、调整和删除的过程。
理论基础
队列(Queue)是一种先进先出(FIFO,First-In-First-Out)的线性表。和栈一样,队列是一种操作受限制的线性表。在具体应用中通常用链表或者数组来实现。队列只允许在后端(称为 rear)进行插入操作,在前端(称为 front)进行删除操作。队列的学习可以类比栈。队列是实现广度优先搜索的重要数据结构。
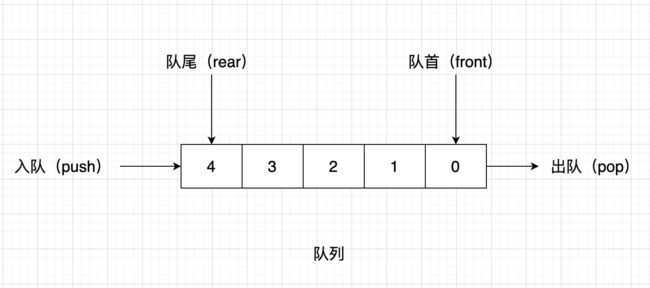
基于链表实现队列:
public class Queue implements Iterable{
private Node head;
private Node last;
private int N;
// 内部类
private class Node{
// 链表所存元素
public T item;
public Node next;
// Node的有参构造
public Node(T item,Node next){
this.item=item;
this.next=next;
}
}
// 队列的构造
public Queue(){
// head结点不存储元素
this.head=new Node(null,null);
this.last=null;
this.N=0;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return N==0;
}
public int size(){
return N;
}
// 尾插
public void enqueue(T t){
// 尾结点为null
if(last==null){
last=new Node(t,null);
head.next=last;
}else{
// 尾结点不为null
// 记录旧尾结点
Node oldlast=last;
// 更新尾结点
last=new Node(t,null);
// 旧的尾结点指向新的尾结点
oldlast.next=last;
}
N++;
}
// 头取
public T dequeue(){
if(isEmpty()){
return null;
}else{
// 旧的首结点的下一个结点
Node oldFirst=head.next;
// 更新首结点的下一个结点
head.next=oldFirst.next;
N--;
// 因为取元素是在删除,如果删完了就需要重置last=null
if(isEmpty()){
last=null;
}
// 先进先出,头取
return oldFirst.item;
}
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new MyIterator();}
private class MyIterator implements Iterator{
// 记录每次遍历的结点
private Node n;
MyIterator(){
this.n=head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next!=null;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
n=n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue q=new Queue();
q.enqueue("a");
q.enqueue("b");
q.enqueue("c");
q.enqueue("d");
for(String k:q){
System.out.println(k);
}
// 删除一个元素(先进先出)
System.out.println(q.dequeue());
for(String k:q){
System.out.println(k);
}
}
}
堆(Heap)是计算机科学中一类特殊的数据结构,是最高效的优先级队列。 堆通常是一个可以被看做一棵完全二叉树的数组对象。 堆是非线性数据结构,相当于一维数组,有两个直接后继。将根结点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根结点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。堆总是满足下列性质:
public class MyPriorityQueue {
public static void shiftDown(int[] arr,int parent){
// 首先的记录孩子的节点位置,parent元素的下表是0
// 左孩子节点的下标是2*parent + 1只需要记录左孩子的节点位置即可,如果父节点的值,大于子节点的值
// 需要将节点进行交换,交换的时候,是将两个子节点中最小的节点进行交换
int child = 2* parent + 1;
// 记录数组长度,也就是堆的长度
int size = arr.length;
while (child < size){
// 找到节点中的最大值
if(child + 1 < size && arr[child] < arr[child + 1]){
child = child + 1;
}
// 找到之后将节点进行交换
if(arr[parent] < arr[child]){
int temp = arr[parent];
arr[parent] = arr[child];
arr[child] = temp;
}else {
// 此时不用进行调整
break;
}
// 完成之后让节点parent指向子节点继续向下执行
parent = child;
child = 2*parent + 1;
}
}
public static void shiftUp(int[] arr, int child) {
// 父节点的元素下标正是child - 1 再除以2
int parent = (child-1) / 2;
while (child > 0){
// 大堆的方式,把子节点向上调整
if(arr[parent] < arr[child]){
int temp = arr[parent];
arr[parent] = arr[child];
arr[child] = temp;
}else {
break;
}
child = parent;
parent = (child-1) / 2;
}
}
// 建堆操作
public static void createHeap(int[] array){
for(int i = (array.length - 1 -1) / 2; i >= 0;i--){
shiftDown(array,i);
}
}
private int[] arr = new int[100];
// 记录对的元素个数
private int size = 0;
// 往堆中插入元素
public void offer(int val){
if(size >= arr.length){
return;
}
arr[size] = val;
size ++;
// 插入之后,需要将元素进行向上调整
// 将刚插入的最后一个元素向上调整
shiftUp(arr, size-1);
}
// 获取堆顶元素
public Integer peek(){
if(size == 0){
return null;
}
return arr[0];
}
// 删除操作,一定是删除堆顶元素
public Integer poll(){
if(size == 0){
return null;
}
// 获取堆顶元素
int popElement = arr[0];
// 和堆的最后一个元素进行交换
int temp = popElement;
popElement = arr[size -1];
arr[size - 1] = popElement;
// 交换完成之后,删除即可
size--;
// 删除之后,进行shiftUp操作
shiftUp(arr, size - 1);
return popElement;
}
解题心得
- 单纯的队列与堆的题其实并不算多,但我们仍要重点了解这两种基础数据结构。
- 堆排序在很多大公司的面试中很常见,需要重点学习。
- 队列在广度优先搜索中很有用。
- 这里的堆是指数据结构,和操作系统的“堆栈”概念是两种概念。
- 堆可以看做是优先队列。
- 堆通常是一个可以被看做一棵完全二叉树的数组对象。
算法题目
215. 数组中的第K个最大元素

题目解析:我们也可以使用堆排序来解决这个问题,即建立一个大根堆,做 k - 1次删除操作后堆顶元素就是我们要找的答案。
代码如下:
/**
* 基于堆排序的选择方法
*/
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
int heapSize = nums.length;
buildMaxHeap(nums, heapSize);
for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= nums.length - k + 1; --i) {
swap(nums, 0, i);
--heapSize;
maxHeapify(nums, 0, heapSize);
}
return nums[0];
}
public void buildMaxHeap(int[] a, int heapSize) {
for (int i = heapSize / 2; i >= 0; --i) {
maxHeapify(a, i, heapSize);
}
}
public void maxHeapify(int[] a, int i, int heapSize) {
int l = i * 2 + 1, r = i * 2 + 2, largest = i;
if (l < heapSize && a[l] > a[largest]) {
largest = l;
}
if (r < heapSize && a[r] > a[largest]) {
largest = r;
}
if (largest != i) {
swap(a, i, largest);
maxHeapify(a, largest, heapSize);
}
}
public void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
218. 天际线问题

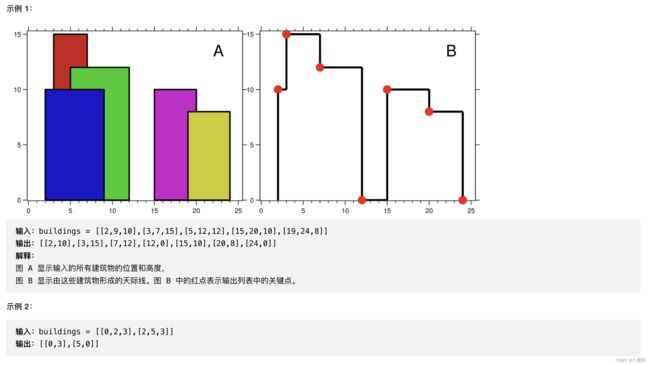
题目解析:如果将所有的建筑的边界作为一条线,那么所有的答案都在这些线上。考虑任意一条线,那么这条线和所有相交的建筑(这里排除掉刚好和建筑右边界相交),取一个最高的高度,然后判断这个高度是否和ans末尾最后一个元素的高度相等,不相等就加入进去,在这里为了快速得到最高的高度,使用一个堆来进行记录。
代码如下:
/**
* 扫描线 + 优先队列
*/
class Solution {
public List> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) {
// 得到所有由建筑边界构成的边界线,并升序
int[] boundaries = new int[buildings.length * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < buildings.length; i++) {
boundaries[2 * i] = buildings[i][0];
boundaries[2 * i + 1] = buildings[i][1];
}
Arrays.sort(boundaries);
// 创建一个堆,维护一个边界-高度值对
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b[1] - a[1]);
List> ans = new ArrayList<>(); // 返回答案
int index = 0; // 指向buildings
for (int boundary : boundaries) {
// 对于一个建筑,如果其左边界在当前判断的边界线左边或重叠,那么向堆加入右边界-高度值对
while (index < buildings.length && buildings[index][0] <= boundary) {
pq.offer(new int[] { buildings[index][1], buildings[index][2] });
index++;
}
// 对于那些加入了堆中的建筑,从堆的顶部移出建筑右边界在边界线左边或重叠的边界-高度值对
while (!pq.isEmpty() && pq.peek()[0] <= boundary) {
pq.poll();
}
// 经过上面的两步操作之后,当前边界线穿过的建筑(不含右边界)全都在堆中,并且堆的顶端是所有穿过的建筑中,高度最高的,也就是天际线高度
// 如果此时的堆为空,证明边界线没有穿过任何建筑,来到了建筑的分割位置,天际线为0
int maxHeight = pq.isEmpty() ? 0 : pq.peek()[1];
// 按照这种算法,每一条边界线都会产生一个天际线高度,如果这个高度和ans末尾元素的高度一致,那么就说明两条边界线穿过了同一个建筑,并且相邻,那么按照规则只取最左端
if (ans.size() == 0 || maxHeight != ans.get(ans.size() - 1).get(1)) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(boundary, maxHeight));
}
}
return ans;
}
}
225. 用队列实现栈

题目解析:这题多少有点多此一举的感觉,为了满足栈的特性,即最后入栈的元素最先出栈,在使用队列实现栈时,应满足队列前端的元素是最后入栈的元素。可以使用两个队列实现栈的操作,其中 queue1用于存储栈内的元素,queue2作为入栈操作的辅助队列。
代码如下:
/**
* 两个队列
*/
class MyStack {
Queue queue1;
Queue queue2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList();
queue2 = new LinkedList();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
queue2.offer(x);
while (!queue1.isEmpty()) {
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
Queue temp = queue1;
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = temp;
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return queue1.poll();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
回到首页
刷 leetcode 500+ 题的一些感受
下一篇
《算法系列》之并查集
