matlab实践(四):利用改进的遗传算法解决TSP问题
1.TSP问题
TSP问题可以描述为:现有一些节点,节点和节点之间均可相连形成边,节点之间的边存在距离,需要找到一个遍历方案先后访问所有的点,使的遍历的总距离最短。这里我们提供80个节点的经纬度,以便我们更好的计算点与点之间的距离。
2.数据
x=[850.712674289007 929.608866756663 582.790965175840 879.013904597178 0.522375356944771 612.566469483999 527.680069338442 801.347605521952 498.094291196390 574.661219130188 738.640291995402 246.734525985975 83.4828136026227 660.944557947342 890.752116325322 769.029085335896 928.313062314188 16.9829383372613 862.710718699670 844.855674576263 552.291341538775 31.9910157625669 362.411462273053 489.569989177322 123.083747545945 146.514910614890 42.6524109111434 281.866855880430 695.163039444332 535.801055751113 123.932277598070 852.998155340816 270.294332292698 564.979570738201 417.028951642886 947.933121293169 105.709426581721 166.460440876421 573.709764841198 931.201384608250 737.841653797590 860.440563038232 984.398312240972 785.558989265031 177.602460505865 133.931250987971 939.141706069548 295.533834475356 467.068187028852 25.2281814930363 559.032544988695 347.879194327261 54.2394844411296 662.808061960974 898.486137834300 988.417928784981 706.917419322763 287.849344815137 464.839941625137 818.204038907671 178.116953886766 56.7046890682912 335.848974676925 208.946673993135 675.391177336247 912.132474239623 745.546073701717 561.861425281637 597.211350337855 134.122932828682 894.941675440814 242.486558936719 441.722057064424 897.191350973572 93.3705167550930 456.057666843742 995.389727655092 297.346815887922 298.243971887764 505.428142457703];
y=[560.559527354885 696.667200555228 815.397211477421 988.911616079589 865.438591013025 989.950205708831 479.523385210219 227.842935706042 900.852488532005 845.178185054037 585.987035826476 666.416217319468 625.959785171583 729.751855317221 982.303222883606 581.446487875398 580.090365758442 120.859571098558 484.296511212103 209.405084020935 629.883385064421 614.713419117141 49.5325790420612 192.510396062075 205.494170907680 189.072174472614 635.197916859882 538.596678045340 499.116013482590 445.183165296042 490.357293468018 873.927405861733 208.461358751314 640.311825162758 205.975515532243 82.0712070977259 142.041121903998 620.958643935308 52.0778902858696 728.661681678271 63.4045006928182 934.405118961213 858.938816683866 513.377418587575 398.589496735843 30.8895487449515 301.306064586392 332.936281836175 648.198406466157 842.206612419335 854.099949273443 446.026648055103 177.107533789109 330.828995203305 118.155198446711 539.982099037929 999.491620097705 414.522538893108 763.957078491957 100.221540195492 359.634913482080 521.885673661279 175.669029675661 905.153559004464 468.468199903997 104.011574779379 736.267455596639 184.194097515527 299.936990089789 212.601533358843 71.4528127870445 53.7543922087138 13.2832004672525 196.658191367632 307.366899587920 101.669393624755 332.092833452499 62.0452213196326 46.3512648981808 761.425886690113];其中x代表经度,y代表纬度。
3.遗传算法
step1:初始化种群
step2:计算适应度
step3:选择,交叉,变异算子
step4: 判断是否为最优解
适应度函数
function [ fitnessvar, sumDistances,minPath, maxPath ] = fitness( distances, pop )
% 计算整个种群的适应度值
[popSize, col] = size(pop);
sumDistances = zeros(popSize,1);
fitnessvar = zeros(popSize,1);
for i=1:popSize
for j=1:col-1
sumDistances(i) = sumDistances(i) + distances(pop(i,j),pop(i,j+1));
end
end
minPath = min(sumDistances);
maxPath = max(sumDistances);
for i=1:length(sumDistances)
fitnessvar(i,1)=(maxPath - sumDistances(i,1)+0.000001) / (maxPath-minPath+0.00000001);
end
end交叉
function [childPath] = crossover(parent1Path, parent2Path, prob)
% 交叉
random = rand();
if prob >= random
[l, length] = size(parent1Path);
childPath = zeros(l,length);
setSize = floor(length/2) -1;
offset = randi(setSize);
for i=offset:setSize+offset-1 %交叉段
childPath(1,i) = parent1Path(1,i); %先将交叉段复制
end
iterator = i+1;
j = iterator;
while any(childPath == 0) %对于交叉段以外位置操作
if j > length
j = 1;
end
if iterator > length
iterator = 1;
end
if ~any(childPath == parent2Path(1,j))
childPath(1,iterator) = parent2Path(1,j);
iterator = iterator + 1;
end
j = j + 1;
end
else
childPath = parent1Path;
end
end更新
function [ mutatedPath ] = mutate( path, prob )
%对指定的路径利用指定的概率进行更新
random = rand();
if random <= prob
[l,length] = size(path);
index1 = randi(length);
index2 = randi(length);
%交换
temp = path(l,index1);
path(l,index1) = path(l,index2);
path(l,index2)=temp;
end
mutatedPath = path;
end计算距离
function [ distances ] = calculateDistance( city )
%计算距离
[~, col] = size(city);
distances = zeros(col);
for i=1:col
for j=1:col
distances(i,j)= distances(i,j)+ sqrt( (city(1,i)-city(1,j))^2 + (city(2,i)-city(2,j))^2 );
end
end
end画图
function [ output_args ] = paint( cities, pop, minPath, totalDistances,gen)
gNumber=gen;
[~, length] = size(cities);
xDots = cities(1,:);
yDots = cities(2,:);
%figure(1);
title('GA TSP');
plot(xDots,yDots, 'p', 'MarkerSize', 14, 'MarkerFaceColor', 'blue');
xlabel('经度');
ylabel('纬度');
axis equal
hold on
[minPathX,~] = find(totalDistances==minPath,1, 'first');
bestPopPath = pop(minPathX, :);
bestX = zeros(1,length);
bestY = zeros(1,length);
for j=1:length
bestX(1,j) = cities(1,bestPopPath(1,j));
bestY(1,j) = cities(2,bestPopPath(1,j));
end
title('GA TSP');
plot(bestX(1,:),bestY(1,:), 'red', 'LineWidth', 1.25);
legend('城市', '路径');
axis equal
grid on
%text(5,0,sprintf('迭代次数: %d 总路径长度: %.2f',gNumber, minPath),'FontSize',10);
drawnow
hold off
end主函数
clear;
clc;
tStart = tic; % 算法计时器
%%%%%%%%%%%%自定义参数%%%%%%%%%%%%%
cities=importdata('cities80.mat');
cityNum=80;
maxGEN = 500; % 最大迭代步长
popSize = 100; % 遗传算法种群大小
crossoverProbabilty = 0.9; %交叉概率
mutationProbabilty = 0.1; %变异概率
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
gbest = Inf; %初始最佳路径距离
distances = calculateDistance(cities); %计算两两城市之间距离,生成一个方阵
% 生成种群,每个个体代表一个路径
pop = zeros(popSize, cityNum); %生成 popSize x cityNum 方阵,存储种族群
for i=1:popSize
pop(i,:) = randperm(cityNum); %随机生成一个解,即城市-城市-...链,初始种群
end
offspring = zeros(popSize,cityNum); %子代
%保存每代的最小路劲便于画图
minPathes = zeros(maxGEN,1);
% GA算法
for gen=1:maxGEN
% 计算适应度的值,即路径总距离
[fval, sumDistance, minPath, maxPath] = fitness(distances, pop);
% 轮盘赌选择
tournamentSize=4; %设置大小
for k=1:popSize
% 选择父代进行交叉
tourPopDistances=zeros( tournamentSize,1);
for i=1:tournamentSize
randomRow = randi(popSize); %生成1-popSize之间的一个伪随机数
tourPopDistances(i,1) = sumDistance(randomRow,1);
end
% 选择最好的,即距离最小的
parent1 = min(tourPopDistances);
[parent1X,parent1Y] = find(sumDistance==parent1,1, 'first');
%找到parent1的下标,即个体序号,[parent1X,parent1Y]=[row,col]
parent1Path = pop(parent1X(1,1),:);
for i=1:tournamentSize
randomRow = randi(popSize);
tourPopDistances(i,1) = sumDistance(randomRow,1);
end
parent2 = min(tourPopDistances);
[parent2X,parent2Y] = find(sumDistance==parent2,1, 'first');
parent2Path = pop(parent2X(1,1),:);
subPath = crossover(parent1Path, parent2Path, crossoverProbabilty);%交叉
subPath = mutate(subPath, mutationProbabilty);%变异
offspring(k,:) = subPath(1,:);
minPathes(gen,1) = minPath;
end
fprintf('代数:%d 最短路径:%.2fKM \n', gen,minPath);
% 更新
pop = offspring;
% 画出当前状态下的最短路径
if minPath < gbest
gbest = minPath;
paint(cities, pop, gbest, sumDistance,gen);
end
end
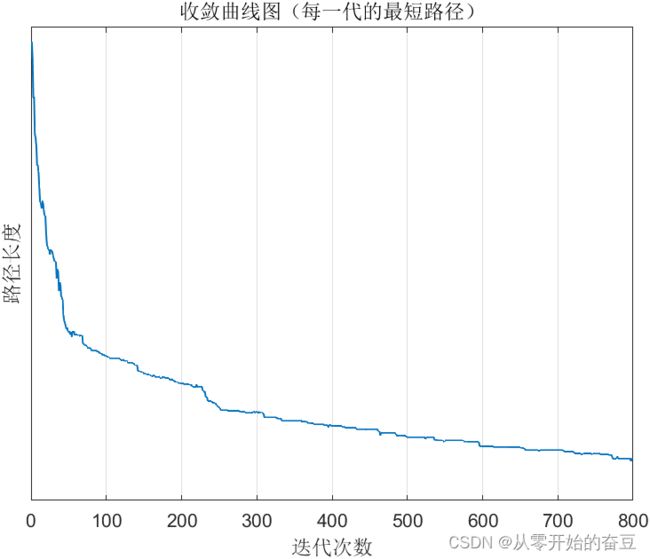
figure
plot(minPathes, 'MarkerFaceColor', 'red','LineWidth',1);
title('收敛曲线图(每一代的最短路径)');
set(gca,'ytick',500:100:5000);
ylabel('路径长度');
xlabel('迭代次数');
grid on
tEnd = toc(tStart);
fprintf('时间:%d 分 %f 秒.\n', floor(tEnd/60), rem(tEnd,60));结果
4.改进的遗传算法
clc;clear;
tStart = tic; % 算法计时器
%%%%%初始化参数
C= importdata('cities80.mat')';
NP=200;
N=size(C,1);
G=500;
%%%%%初始种群
f=zeros(N,NP);
for i=1:NP
f(:,i)=randperm(N);
end
len=zeros(1,NP);
%%%%%任意城市间距离
D=zeros(N);
for i=1:N
for j=1:N
D(i,j)=((C(i,1)-C(j,1))^2 + (C(i,2)-C(j,2))^2)^0.5;
end
end
%%%%%计算路径长度--亲和度
for i=1:NP
len(i)=func3(D,f(:,i),N);
end
[sortlen ,index]=sort(len);
sortf=f(:,index);
NC=10;
gen=1;
%%%%%免疫循环
while gen<=G
%%%%%选择激励度前NP/2个体进入免疫操作
for i=1:NP/2
a=sortf(:,i);
ca=repmat(a,1,NC);
for j=1:NC
p1=floor(1+N*rand);
p2=floor(1+N*rand);
while p1==p2
p1=floor(1+N*rand);
p2=floor(1+N*rand);
end
tmp=ca(p1,j);
ca(p1,j)=ca(p2,j);
ca(p2,j)=tmp;
end
ca(:,1)=a;
%%%%%克隆抑制
for j=1:NC
calen(j)=func3(D,ca(:,j),N);
end
[sortcalen,index]=sort(calen);
sortca=ca(:,index);
af(:,i)=sortca(:,1);
alen(i)=sortcalen(1);
end
%%%%%免疫种群与新生种群合并--种群刷新
for i=1:NP/2
bf(:,i)=randperm(N);
blen(i)=func3(D,bf(:,i),N);
end
f=[af bf];
len=[alen blen];
[sortlen, index]=sort(len);
sortf=f(:,index);
fprintf('代数:%d 最短路径:%.2fKM \n', gen,trace(gen));
gen=gen+1;
trace(gen)=sortlen(1);
paint(C', f, trace(end), len,gen);
end
%%%%%输出优化结果
bestf=sortf(:,1);
bestlen=trace(end);
% for i=1:N-1
% plot([C(bestf(i),1),C(bestf(i+1),1)],[C(bestf(i),2),C(bestf(i+1),2)],'o-');
% hold on;
% end
% plot([C(bestf(N),1),C(bestf(1),1)],[C(bestf(N),2),C(bestf(1),2)],'ro-');
% title(['最短距离:',num2str(bestlen)]);
figure
plot(trace, 'MarkerFaceColor', 'red','LineWidth',1);
title('收敛曲线图(每一代的最短路径)');
set(gca,'ytick',0:10000:50000);
ylabel('路径长度');
xlabel('迭代次数');
grid on
tEnd = toc(tStart);
fprintf('时间:%d 分 %f 秒.\n', floor(tEnd/60), rem(tEnd,60));
%%%%%路径长度函数
function result = func3(D,f,N)
len=D(f(1),f(N));
for j=2:N
len=D(f(j),f(j-1))+len;
end
result=len;
end结果