力扣第1020题 飞地的数量 C++ 深度优先搜索 附Java代码
题目
1020. 飞地的数量
中等
相关标签
深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 并查集 数组 矩阵
给你一个大小为 m x n 的二进制矩阵 grid ,其中 0 表示一个海洋单元格、1 表示一个陆地单元格。
一次 移动 是指从一个陆地单元格走到另一个相邻(上、下、左、右)的陆地单元格或跨过 grid 的边界。
返回网格中 无法 在任意次数的移动中离开网格边界的陆地单元格的数量。
示例 1:
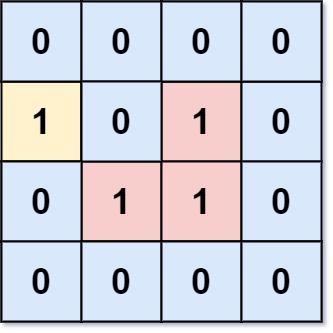
输入:grid = [[0,0,0,0],[1,0,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,0,0,0]] 输出:3 解释:有三个 1 被 0 包围。一个 1 没有被包围,因为它在边界上。
示例 2:
输入:grid = [[0,1,1,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,0]] 输出:0 解释:所有 1 都在边界上或可以到达边界。
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500grid[i][j]的值为0或1
思路和解题方法
私有成员变量
dir和count:
dir数组保存了四个方向的偏移量,分别表示向上、向下、向左和向右移动。count用于统计符合条件的陆地单元格数量。私有方法
dfs:
dfs方法实现了深度优先搜索,用于标记相邻的陆地单元格并统计它们的数量。- 首先将当前单元格标记为已访问(即将其值设为 0),并增加
count的计数。- 然后遍历四个方向,对符合条件的相邻单元格进行递归调用。
公有方法
numEnclaves:
numEnclaves方法是解决问题的入口。- 首先获取地图的行数
n和列数m。- 然后从地图的左右两侧边界开始,对边界上的陆地进行深度优先搜索,并将符合条件的陆地标记为已访问。
- 接着从地图的上下两侧边界开始,同样对边界上的陆地进行深度优先搜索并标记。
- 最后,再次遍历整个地图,对剩余的未访问的陆地进行深度优先搜索,统计符合条件的陆地数量,并将结果返回。
复杂度
时间复杂度:
O(n*m)
时间复杂度:假设网格的维度为 n×m。
- 在深度优先搜索过程中,最坏情况下,我们可能需要访问所有的陆地格子。因此,时间复杂度为 O(n*m)。
空间复杂度
O(n*m)
- 空间复杂度:深度优先搜索所需的栈空间是其递归调用的最大深度。在这个问题中,最坏情况下,我们可能需要访问所有的陆地格子,因此递归调用的最大深度为 O(nm)。因此,总的空间复杂度也是 O(nm)。
c++ 代码
class Solution {
private int[][] directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}; // 保存四个方向的偏移量
private int count; // 统计符合题目要求的陆地空格数量
private void dfs(int[][] grid, int x, int y) {
grid[x][y] = 0; // 将当前位置标记为已访问
count++; // 统计陆地空格数量
for (int[] dir : directions) { // 向四个方向遍历
int nextX = x + dir[0];
int nextY = y + dir[1];
// 超过边界
if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= grid.length || nextY < 0 || nextY >= grid[0].length) {
continue;
}
// 不符合条件,不继续遍历
if (grid[nextX][nextY] == 0) {
continue;
}
dfs(grid, nextX, nextY); // 递归遍历相邻陆地
}
return;
}
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
// 从左右两侧向中间遍历
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (grid[i][0] == 1) {
dfs(grid, i, 0);
}
if (grid[i][m - 1] == 1) {
dfs(grid, i, m - 1);
}
}
// 从上下两侧向中间遍历
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[0][j] == 1) {
dfs(grid, 0, j);
}
if (grid[n - 1][j] == 1) {
dfs(grid, n - 1, j);
}
}
count = 0;
// 统计剩余未被访问的陆地空格数量
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
dfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
c++代码广度优先搜索
class Solution {
private:
int count = 0;
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
// 使用广度优先搜索遍历陆地格子
void bfs(vector>& grid, int x, int y) {
queue> que;
que.push({x, y});
grid[x][y] = 0; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记
count++;
while(!que.empty()) {
pair cur = que.front(); que.pop();
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
if (grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) {
que.push({nextx, nexty});
count++;
grid[nextx][nexty] = 0; // 只要加入队列立刻标记
}
}
}
}
public:
int numEnclaves(vector>& grid) {
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
// 从左侧边,和右侧边 向中间遍历
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (grid[i][0] == 1) bfs(grid, i, 0);
if (grid[i][m - 1] == 1) bfs(grid, i, m - 1);
}
// 从上边和下边 向中间遍历
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[0][j] == 1) bfs(grid, 0, j);
if (grid[n - 1][j] == 1) bfs(grid, n - 1, j);
}
count = 0;
// 统计剩余未被访问的陆地空格数量
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) bfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
return count;
}
};
附Java代码
深度优先搜索
class Solution {
int count = 0;
int[][] dir ={
{0, 1},
{1, 0},
{-1, 0},
{0, -1}
};
// 深度优先搜索函数
private void dfs(int[][] grid, int x, int y){
// 如果当前单元格为海洋(0),则返回
if(grid[x][y] == 0)
return;
// 将当前单元格标记为已访问过,并增加计数
grid[x][y] = 0;
count++;
// 对当前单元格的四个相邻方向进行搜索
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int nextX = x + dir[i][0];
int nextY = y + dir[i][1];
// 检查相邻单元格是否在地图范围内,若超出范围则跳过
if(nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= grid.length || nextY >= grid[0].length)
continue;
// 递归搜索相邻单元格
dfs(grid, nextX, nextY);
}
}
// 计算被围绕的陆地数量的函数
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
// 从左右两侧边界开始搜索并标记符合条件的陆地
for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++){
if(grid[i][0] == 1)
dfs(grid, i, 0);
if(grid[i][grid[0].length - 1] == 1)
dfs(grid, i, grid[0].length - 1);
}
// 从上下两侧边界开始搜索并标记符合条件的陆地
for(int j = 1; j < grid[0].length - 1; j++){
if(grid[0][j] == 1)
dfs(grid, 0, j);
if(grid[grid.length - 1][j] == 1)
dfs(grid, grid.length - 1, j);
}
// 重新初始化计数器
count = 0;
// 遍历整个地图,搜索并标记剩余的未访问陆地
for(int i = 1; i < grid.length - 1; i++){
for(int j = 1; j < grid[0].length - 1; j++){
if(grid[i][j] == 1)
dfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
// 返回被围绕的陆地数量
return count;
}
}
广度优先搜索
class Solution {
// 四个方向
private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};
// 广度优先遍历,把可以通向边缘部分的 1 全部标记成 true
public void bfs(int[][] grid, Queue queue, boolean[][] visited) {
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] curPos = queue.poll();
for (int[] current: position) {
int row = curPos[0] + current[0], col = curPos[1] + current[1];
// 下标越界直接跳过
if (row < 0 || row >= grid.length || col < 0 || col >= grid[0].length)
continue;
// 当前位置不是 1 或者已经被访问了就直接跳过
if (visited[row][col] || grid[row][col] == 0) continue;
visited[row][col] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{row, col});
}
}
}
// 计算被包围的陆地数量
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
int rowSize = grid.length, colSize = grid[0].length, ans = 0; // ans 记录答案
// 标记数组记录每个值为 1 的位置是否可以到达边界,可以为 true,反之为 false
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize];
Queue queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 搜索左侧边界和右侧边界查找 1 存入队列
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
if (grid[row][0] == 1) {
visited[row][0] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{row, 0});
}
if (grid[row][colSize - 1] == 1) {
visited[row][colSize - 1] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{row, colSize - 1});
}
}
// 搜索上边界和下边界遍历,但是四个角不用遍历,因为上面已经遍历到了
for (int col = 1; col < colSize - 1; col++) {
if (grid[0][col] == 1) {
visited[0][col] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{0, col});
}
if (grid[rowSize - 1][col] == 1 && !visited[rowSize - 1][col]) {
visited[rowSize - 1][col] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{rowSize - 1, col});
}
}
bfs(grid, queue, visited); // 广度优先遍历
// 查找没有标记过的 1,记录到 ans 中
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
if (grid[row][col] == 1 && !visited[row][col]) ++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
觉得有用的话可以点点赞,支持一下。
如果愿意的话关注一下。会对你有更多的帮助。
每天都会不定时更新哦 >人< 。