用Java实现图书管理系统(类,抽象类,封装,继承,多态,接口,顺序表)
我们实现的主要内容就是对图书的增删改查,分为了管理员用户和普通的用户,分别对他们进行操作。
流程图如下:
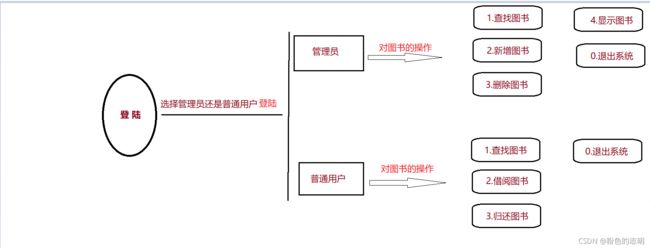
目录
- 创建图书相关的类
-
- Book类
- BookList类
- 创建操作相关的类
-
- IOperation接口
- AddOperation 新增图书
- DelOperation 删除图书
- FindOperation 查找图书
- DisplayOperation 显示图书
- BorrowOperation 借阅图书
- ReturnOperation 归还图书
- ExitOperation 退出系统
- 创建用户相关的类
-
- User父类
- AdminUser子类
- NormalUser子类
- TestDemo测试类
- 总结
创建图书相关的类
既然是面向对象进行操作的,那么我们就分成几块在分别进行操作就行了
创一个book包,里面放书相关的东西
 先创一个Book类,里面放书相关的东西,创建 Book 类, 表示一本书
先创一个Book类,里面放书相关的东西,创建 Book 类, 表示一本书
创建 BookList 类, 用来保存 N 本书.

Book类
public class Book {
private String name; //书的名字
private String author;//作者
private int price;//价格
private String type;//类型
private boolean isBorrowed;//是否被借出
}
接下来就是封装
public class Book {
private String name;
private String author;
private int price;
private String type;
private boolean isBorrowed;
public Book(String name, String author, int price, String type) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public boolean isBorrowed() {
return isBorrowed;
}
public void setBorrowed(boolean borrowed) {
isBorrowed = borrowed;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
((isBorrowed == true) ? " 已经被借出" : " 未被借出")+
'}';
}
}
BookList类
public class BookList {
private Book[] books = new Book[10]; //存放书的数组
private int usedSize;//放了多少本书
public BookList(){ //放一些初始值
books[0] = new Book("三国演义","罗贯中",17,"小说");
books[1] = new Book("西游记","吴承恩",47,"小说");
books[2] = new Book("水浒传","施耐庵",37,"小说");
books[3] = new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹",35,"小说");
this.usedSize = 4;
}
public int getUsedSize() {
return usedSize;
}
public void setUsedSize(int usedSize) {
this.usedSize = usedSize;
}
public Book getPos(int pos){ //获取pos位置的一本书
if(pos < 0 || pos >getUsedSize()){
System.out.println("位置不合法!");
return null;
}
return books[pos];
}
public void setBooks(int pos,Book book){ //设置pos下标为一本书
if(pos < 0 || pos > getUsedSize()){
return;
}
books[pos] = book;
}
}
创建操作相关的类
首先创个包operation里面放相关操作的类
这里我把每个操作该实现的内容先展示出来,更直观的去感受他。
IOperation接口
用接口的目的是因为后续的增删查改都要用到这种方法,对后面的管理员和普通用户分开调用要帮助。
public interface IOperation {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public void work(BookList bookList);
}
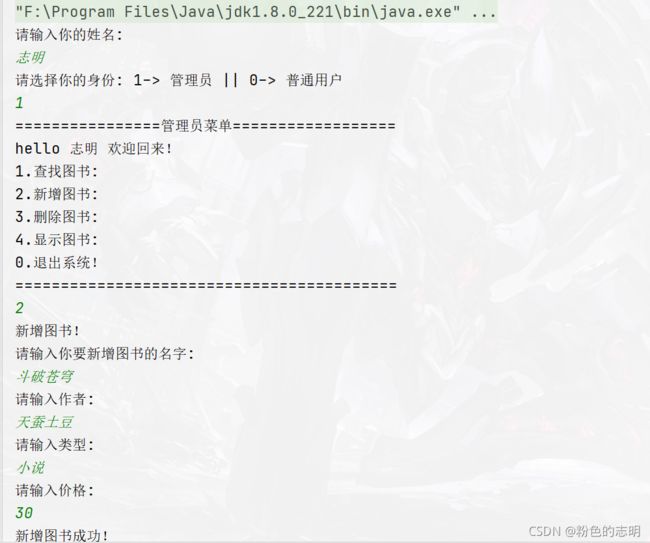
AddOperation 新增图书
public class AddOperation implements IOperation{
public void work(BookList bookList){ //对n本书进行操作的方法
System.out.println("新增图书!");
System.out.println("请输入你要新增图书的名字: ");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入作者: ");
String author = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入类型: ");
String type = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入价格: ");
int price = scanner.nextInt();
Book book = new Book(name,author,price,type); //创建一本书这个对象
int size = bookList.getUsedSize(); //有多少本书
bookList.setBooks(size,book); //在数组末尾位置添加这本书(我们这里添加就默认从最后位置添加)
bookList.setUsedSize(size + 1); //书加一
System.out.println("新增图书成功!");
}
}
DelOperation 删除图书
public class DelOperation implements IOperation{
public void work(BookList bookList){
System.out.println("删除图书!");
//1、根据书名找到书的位置 index
System.out.println("请输入你要删除图书的名字: ");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int currentSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
int index = 0;//存储找到的下标
int i = 0;
for (; i < currentSize; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getPos(i); //得到i下标的书
if(book.getName().equals(name)) { //是要删的书(这里用了equal这个函数,他就是判断值是否相同,不考虑地址)
index = i;
break;
}
}
if(currentSize <= i){
System.out.println("没有你要删除的这本书!");
return;
}
//2、进行删除
for (int j = index;j < currentSize - 1;j++) {
Book book = bookList.getPos(j + 1); //后面的书往前挪
bookList.setBooks(j,book);
}
bookList.setBooks(currentSize,null);
bookList.setUsedSize(currentSize - 1);
System.out.println("删除成功!");
}
}
FindOperation 查找图书
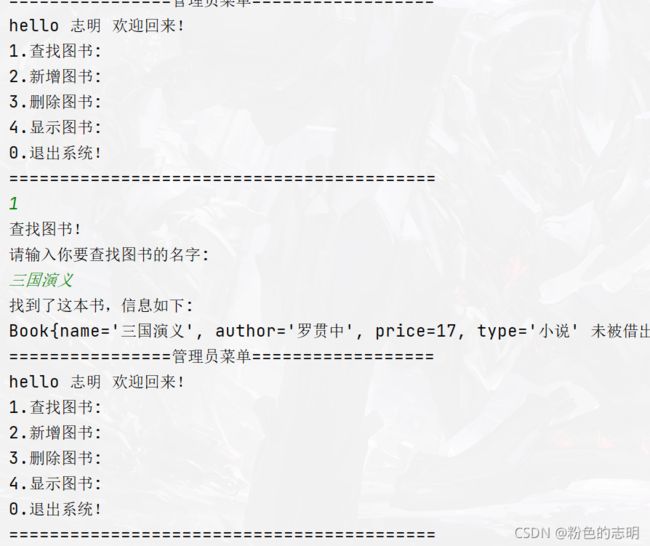
public class FindOperation implements IOperation{
public void work(BookList bookList){
System.out.println("查找图书!");
System.out.println("请输入你要查找图书的名字: ");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int size = bookList.getUsedSize();
int i = 0;
for(;i < size;i++){
Book book = bookList.getPos(i);
if(name.equals(book.getName())){
System.out.println("找到了这本书,信息如下: ");
System.out.println(book);
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有你要找的这本书!");
}
}
DisplayOperation 显示图书
public class DisplayOperation implements IOperation{
public void work(BookList bookList){
System.out.println("显示图书!");
int size = bookList.getUsedSize();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getPos(i);
System.out.println(book);
}
}
}
BorrowOperation 借阅图书
public class BorrowOperation implements IOperation{
public void work(BookList bookList){
System.out.println("借阅图书!");
System.out.println("请输入你要借阅的图书名字: ");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int size = bookList.getUsedSize();
int i = 0;
for(;i < size;i++){
Book book = bookList.getPos(i);
if(name.equals(book.getName())){
System.out.println("你要借书的信息如下: ");
System.out.println(book);
book.setBorrowed(true);
System.out.println("借阅成功!");
System.out.println(book);
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有你要借的书!");
}
}
ReturnOperation 归还图书
public class ReturnOperation implements IOperation{
public void work(BookList bookList){
System.out.println("归还图书!");
System.out.println("请输入你要归还图书的名字: ");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
int i = 0;
int size = bookList.getUsedSize();
for(;i < size;i++){
Book book = bookList.getPos(i);
if(name.equals(book.getName())){
book.setBorrowed(false);
System.out.println("归还成功!");
System.out.println(book);
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有你要归还的书!");
}
}
ExitOperation 退出系统
public class ExitOperation implements IOperation{
public void work(BookList bookList){
System.out.println("退出系统!");
System.exit(0);
}
}
创建用户相关的类
先创建 package user
创建 User 类, 这是一个抽象类,创建普通用户类, 是 User 的子类,创建管理员用户类
User父类
public abstract class User {
protected String name;
protected IOperation[] iOperations; //创建接口数组未实例化
public User(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public abstract int menu(); //抽象菜单方法(这里因为父类不需要对他进行实例化,所以用抽象更好一点)
public void doWork(int choice, BookList bookList){ //对进行哪种操作的选择
iOperations[choice].work(bookList); //调用你选择的操作
}
}
AdminUser子类
public class AdminUser extends User{
public AdminUser(String name){
super(name);
this.iOperations = new IOperation[]{ //创建接口数组实例化(继承父类的方法)
new ExitOperation(),
new FindOperation(),
new AddOperation(),
new DelOperation(),
new DisplayOperation()
};
}
public int menu(){
System.out.println("================管理员菜单==================");
System.out.println("hello "+this.name+" 欢迎回来!");
System.out.println("1.查找图书:");
System.out.println("2.新增图书:");
System.out.println("3.删除图书:");
System.out.println("4.显示图书:");
System.out.println("0.退出系统!");
System.out.println("==========================================");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice; //返回你选择的操作,对应数组下标
}
}
NormalUser子类
public class NormalUser extends User{
public NormalUser(String name){
super(name);
this.iOperations = new IOperation[]{
new ExitOperation(),
new FindOperation(),
new BorrowOperation(),
new ReturnOperation(),
};
}
public int menu(){
System.out.println("================普通用户菜单==================");
System.out.println("hello "+this.name+" 欢迎回来!");
System.out.println("1.查找图书:");
System.out.println("2.借阅图书:");
System.out.println("3.归还图书:");
System.out.println("0.退出系统!");
System.out.println("============================================");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
}
}
TestDemo测试类
public class TestDemo {
public static User login() { //登陆页面
System.out.println("请输入你的姓名: ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请选择你的身份: 1-> 管理员 || 0-> 普通用户");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
if(choice == 1){ //选择管理员用户还是普通用户
return new AdminUser(name);
}else{
return new NormalUser(name);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookList bookList = new BookList();
User user = login();//向上转型
while(true){
int choice = user.menu();//发生了动态绑定 -》 多态
//根据你的choice 调用合适的操作
user.doWork(choice,bookList);
}
}
}
总结
注意一点,我们实现每一个类可能调用的是其他包里面的类,用的时候要自己导入相应包中的类才能正常使用,像这样
这点非常重要,千万不要导错了包。
好了,今天的图书管理系统就到这里了,如果你觉得不是很好理解,那肯定是前面的知识点掌握的不是很牢固,你可以看看我下面两篇博客,都是对基础知识的总结,看完之后再来看这个效果会更好。
https://blog.csdn.net/chenbaifan/article/details/121322372?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/chenbaifan/article/details/121098374?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
感谢观看,你的鼓励是我学习最大的动力,加油!让我们一起进步吧!