springboot项目基本配置
接口入口日志
参数校验
业务逻辑执行
异常捕获-统一异常处理
统一数据返回体
接口返回日志
使用的是springboot2.x版本。
Mybatisplus
官网地址:https://baomidou.com/
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidougroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>3.5.2version>
dependency>
xml路径配置
mybatisplus默认的路径是:classpath*:/mapper/**/*.xml。
这个路径表示在classpath下寻找mapper目录及其所有子目录下的所有xml文件
根据自己的xml位置去选择是否配置,否则不用配置,使用默认路径即可。
classpath包括两个路径,第一个是src/main/resources,第二个是src/main/java。
classpath*会递归查询类路径的子目录,classpath则不会。
** 表示递归地匹配任意多个子目录。
所以mybatisplus默认会递归查询类路径下的mapper包中所有子目录的xml文件。
需要注意的是,一般情况下我们会把mapper包放在另一个文件夹中,这个时候默认的路径就会找不到xml,需要将路径改成

xml文件模板
DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.mapper.StudentMapper">
mapper>
mapper标签的namespace用来给xml指定关联的mapper接口
Invalid bound statement (not found)的坑
很多人都碰过这个问题。
第一种:打的文件包taget里没有xml
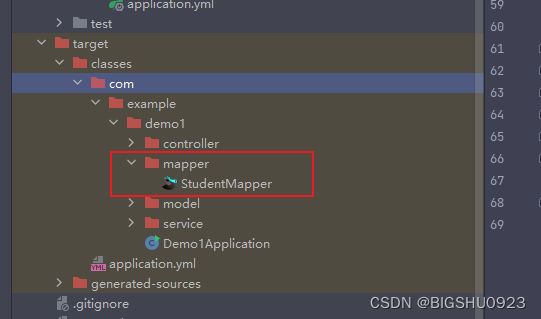
在pom文件的build标签下指定打包的资源
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/javadirectory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xmlinclude>
includes>
<filtering>truefiltering>
resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resourcesdirectory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*include>
includes>
resource>
resources>
然后用maven的clean把原来的target包删掉,再用下面的install重新打包

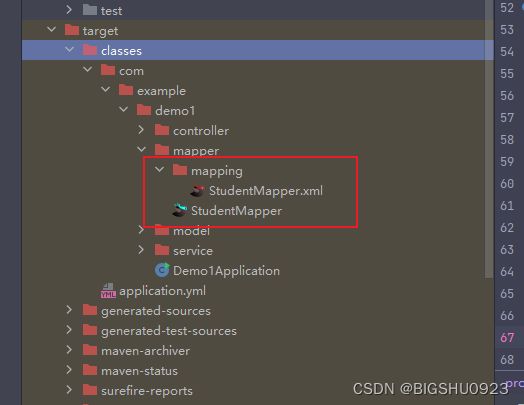
在新的target中看到了xml
第二种:配置的xml路径有问题。
统一数据返回体
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class ResponseResult<T> {
private Integer code;
private String message;
private T data;
private static <T> ResponseResult<T> buildResponse(Integer code, String message, T data){
ResponseResult<T> response = new ResponseResult<>();
response.setCode(code);
response.setMessage(message);
response.setData(data);
return response;
}
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> success(T data){
return buildResponse(ResponseEnum.SUCCESS.getCode(), ResponseEnum.SUCCESS.getMsg(), data);
}
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> success(Integer code, String message, T data){
return buildResponse(code, message, data);
}
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> error(){
return buildResponse(ResponseEnum.SERVICE_ERROR.getCode(), ResponseEnum.SERVICE_ERROR.getMsg(), null);
}
public static <T> ResponseResult<T> error(Integer code, String message, T data){
return buildResponse(code, message, data);
}
}
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public enum ResponseEnum {
/**
* 响应的枚举类
*/
SUCCESS(200, "响应成功"),
SERVICE_ERROR(500, "服务端响应异常");
private final Integer code;
private final String msg;
}
统一异常处理
在这里可以通过@ExceptionHandler处理指定的异常
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice(basePackages = "com.zou.metabox")
public class ExceptionControllerAdvice {
/**
* 处理验证异常的方法
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public ResponseResult<Map<String,String>> handlerValidExecption(MethodArgumentNotValidException e){
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
e.getFieldErrors().forEach(fieldError-> map.put(fieldError.getField(),fieldError.getDefaultMessage()));
return ResponseResult.error(BusinessCodeEnum.VALID_EXCEPTION.getCode(), BusinessCodeEnum.VALID_EXCEPTION.getMsg(), map);
}
/**
* 系统其他的异常处理
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Throwable.class)
public ResponseResult<String> handlerExecption(Throwable throwable){
log.error("错误信息:",throwable);
return ResponseResult.error(BusinessCodeEnum.UNKNOW_EXCEPTION.getCode(), BusinessCodeEnum.UNKNOW_EXCEPTION.getMsg(), throwable.getMessage());
}
/**
* 指定异常去处理,这里处理了自己定义的异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = MyException.class)
public ResponseResult<Map<String, String>> handlerMyException(MyException e){
return ResponseResult.error(BusinessCodeEnum.MYEXCEPTION.getCode(), BusinessCodeEnum.MYEXCEPTION.getMsg(), null);
}
}
日志
设置日志级别
在application.yml中设置
logging:
level:
root: INFO
com.zou.metabox.mapper: DEBUG
AOP日志
使用aop做日志记录,记录输入的参数名及参数值,并且记录接口响应结果。
package com.zou.metabox.common.aspect;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
/**
* @author BIGSHU0923
* @description com.zou.metabox 中Controller层的的日志切面
* @since 7/30/2023 5:32 PM
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LoggingAspect {
/**
* com.zou.metabox.controller 包中公共方法的切入点
*/
@Pointcut("execution(public * com.zou.metabox.controller.*.*(..))")
public void loggingPointcut(){
// 暂不用处理
}
/**
* 此方法用于在日志中记录请求和返回信息。
*
* @param pjp ProceedingJoinPoint对象,用于执行目标方法
* @return 目标方法的返回结果
* @throws Throwable 抛出异常时,将它传递给调用方
*/
@Around("loggingPointcut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
// 获取类名
String className = pjp.getTarget().getClass().getTypeName();
// 获取方法名
String methodName = pjp.getSignature().getName();
// 获取参数名
String[] parameterNames = ((MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature()).getParameterNames();
Object result = null;
// 获取参数值
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
// 获取请求
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
// 获取请求的url
String url = request.getRequestURL().toString();
// 请求参数,以参数名和值为键值对
Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
IntStream.range(0, parameterNames.length).forEach(i -> paramMap.put(parameterNames[i], args[i]));
// header参数
Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames();
Map<String, Object> headerMap = new HashMap<>();
while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String headerName = headerNames.nextElement();
String headerValue = request.getHeader(headerName);
headerMap.put(headerName, headerValue);
}
// 打印请求参数,记录起始时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// log.info("请求| 请求接口:{} | 类名:{} | 方法:{} | header参数:{} | 参数:{} | 请求时间:{}", url, className, methodName, headerMap, paramMap, LocalDateTime.now());
log.info("请求| 请求接口:{} | 类名:{} | 方法:{} | 参数:{} | 请求时间:{}", url, className, methodName, paramMap, LocalDateTime.now());
try {
result = pjp.proceed();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("返回| 处理时间:{} 毫秒 | 返回结果 :{}", (System.currentTimeMillis() - start), "failed");
throw e;
}
// 获取执行完的时间 打印返回报文
log.info("返回| 处理时间:{} 毫秒 | 返回结果 :{}", (System.currentTimeMillis() - start), "success");
return result;
}
}
Springboot事务
单数据源
配置单数据源
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/xinyan
port: 3306
username: root
password: root
使用事务
代码:
下面这代码会更新,但是传入的id>5时,会抛出个异常,如果没有加事务,则不会回滚。
public void testRollback(Long id) {
MyRecord myRecord = new MyRecord();
myRecord.setId(id);
myRecord.setRecord("66666");
myRecordMapper.updateRecord(myRecord);
if(id > 5){
int a = 10/0;
}
}
使用事务前,使用事务后。
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void testRollback(Long id) {
MyRecord myRecord = new MyRecord();
myRecord.setId(id);
myRecord.setRecord("66666");
myRecordMapper.updateRecord(myRecord);
if(id > 5){
int a = 10/0;
}
}
如果抛异常后,会回滚更改。
多数据源
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidougroupId>
<artifactId>dynamic-datasource-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>3.4.1version>
dependency>
配置多数据源
spring:
datasource:
dynamic:
primary: master
strict: true
lazy: true
datasource:
master:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/xinyan
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
slave:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/metabox
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
使用事务
@DSTransactional
// @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
@DS("slave")
public void testRollback2(Integer id){
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(id);
student.setAge(100);
studentMapper.updateStudent(student);
if(id == 3){
int a = 10/0;
}
}
多数据源,所以使用@DSTransactional才有用,使用@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)没用
