Unity数据持久化之XML
本博客主要记录PlayerPrefs的使用,比较长
1、什么是数据持久化
数据持久化就是将内存中的数据模型转化为存储模型,以及将存储模型转化为内存中数据模型的通称
简述:将游戏中的数据存储到硬盘,然后可以下次进游戏的时候读取硬盘中的数据到内存。
2、什么是XML
首先XML是可扩展性标记语言,被用来传输和存储数据。
具体语法和规范不再赘述,可自行查找资料。
XML资料
3、将类中属性转化为XML写法
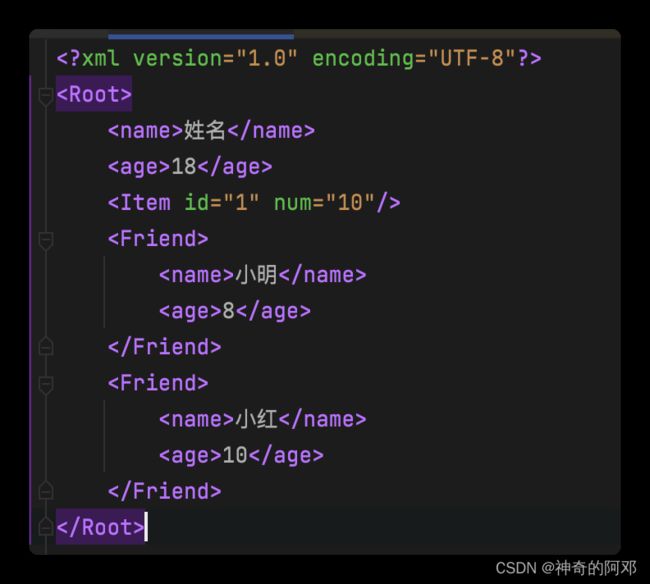
<PlayerInfo>
<name>name哥name>
<atk>10atk>
<def>5def>
<moveSpeed>20moveSpeed>
<roundSpeed>20roundSpeed>
<weapon>
<id>1id>
<num>1num>
weapon>
<listInt>
<int>1int>
<int>2int>
<int>3int>
listInt>
<itemList>
<Item id="1" num="10"/>
<Item id="2" num="20"/>
<Item id="3" num="30"/>
<Item id="4" num="40"/>
itemList>
<itemDic>
<int>1int>
<Item id="1" num="1"/>
<int>2int>
<Item id="2" num="1"/>
<int>3int>
<Item id="3" num="1"/>
itemDic>
PlayerInfo>
4、C#读取XML文件的方法
- 1、XmlDocument (把数据加载到内存中,方便读取)
- 2、XmlTextReader (以流形式加载,内存占用更少,但是是单向只读,使用不是特别方便,除非有特殊需求,否则不会使用)
- 3、Linq 待补充
4.1 XmlDocument
//使用XmlDocument类读取是较方便最容易理解和操作的方法
#region 知识点一 读取xml文件信息
XmlDocument xml = new XmlDocument();
//通过XmlDocument读取xml文件 有两个API
//1.直接根据xml字符串内容 来加载xml文件
//存放在Resorces文件夹下的xml文件加载处理
TextAsset asset = Resources.Load("TestXml");
print(asset.text);
//通过这个方法 就能够翻译字符串为xml对象
xml.LoadXml(asset.text);
//2.是通过xml文件的路径去进行加载
xml.Load(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/TestXml.xml");
#endregion
#region 知识点二 读取元素和属性信息
//节点信息类
//XmlNode 单个节点信息类
//节点列表信息
//XmlNodeList 多个节点信息类
//获取xml当中的根节点,注意Root是节点的名字而不是其他意思
XmlNode root = xml.SelectSingleNode("Root");
//再通过根节点 去获取下面的子节点
XmlNode nodeName = root.SelectSingleNode("name");
//如果想要获取节点包裹的元素信息 直接 .InnerText
print(nodeName.InnerText);
XmlNode nodeAge = root.SelectSingleNode("age");
print(nodeAge.InnerText);
//对于内部有多组数据的
XmlNode nodeItem = root.SelectSingleNode("Item");
//第一种方式 直接用 中括号获取信息
print(nodeItem.Attributes["id"].Value);
print(nodeItem.Attributes["num"].Value);
//第二种方式
print(nodeItem.Attributes.GetNamedItem("id").Value);
print(nodeItem.Attributes.GetNamedItem("num").Value);
//这里是获取 一个节点下的同名节点的方法
XmlNodeList friendList = root.SelectNodes("Friend");
//遍历方式一:迭代器遍历
//foreach (XmlNode item in friendList)
//{
// print(item.SelectSingleNode("name").InnerText);
// print(item.SelectSingleNode("age").InnerText);
//}
//遍历方式二:通过for循环遍历
//通过XmlNodeList中的 成员变量 Count可以得到 节点数量
for (int i = 0; i < friendList.Count; i++)
{
print(friendList[i].SelectSingleNode("name").InnerText);
print(friendList[i].SelectSingleNode("age").InnerText);
}
#endregion
4.2 XmlDocument总结
//1.读取XML文件
//XmlDocument xml = new XmlDocument();
//读取文本方式1-xml.LoadXml(传入xml文本字符串)
//读取文本方式2-xml.Load(传入路径)
//2.读取元素和属性
//获取单个节点 : XmlNode node = xml.SelectSingleNode(节点名)
//获取多个节点 : XmlNodeList nodeList = xml.SelectNodes(节点名)
//获取节点元素内容:node.InnerText
//获取节点元素属性:
//1.item.Attributes["属性名"].Value
//2.item.Attributes.GetNamedItem("属性名").Value
//通过迭代器遍历或者循环遍历XmlNodeList对象 可以获取到各单个元素节点
4.3 利用XmlDocument将XML转成类对象
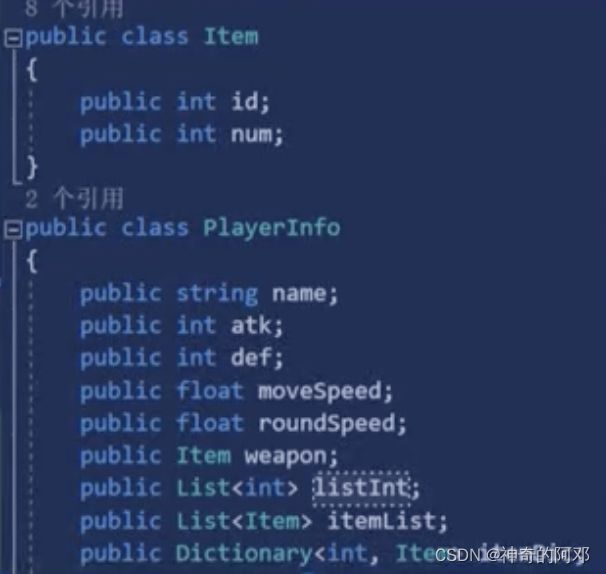
参考图1
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Xml;
using UnityEngine;
public class Item
{
public int id;
public int num;
}
public class PlayerInfo
{
public string name;
public int atk;
public int def;
public float moveSpeed;
public float roundSpeed;
public Item weapon;
public List listInt;
public List- itemList;
public Dictionary
itemDic;
public void LoadData(string fileName)
{
//加载XML文件信息
XmlDocument xml = new XmlDocument();
//加载
xml.Load(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/" + fileName + ".xml");
//从文件中加载出具体的数据
//加载根节点 才能加载后面的内容
XmlNode playerInfo = xml.SelectSingleNode("PlayerInfo");
//通过根节点 去加载具体的信息
this.name = playerInfo.SelectSingleNode("name").InnerText;
this.atk = int.Parse(playerInfo.SelectSingleNode("atk").InnerText);
this.def = int.Parse(playerInfo.SelectSingleNode("def").InnerText);
this.moveSpeed = float.Parse(playerInfo.SelectSingleNode("moveSpeed").InnerText);
this.roundSpeed = float.Parse(playerInfo.SelectSingleNode("roundSpeed").InnerText);
XmlNode weaponNode = playerInfo.SelectSingleNode("weapon");
this.weapon = new Item();
this.weapon.id = int.Parse(weaponNode.SelectSingleNode("id").InnerText);
this.weapon.num = int.Parse(weaponNode.SelectSingleNode("num").InnerText);
XmlNode listIntNode = playerInfo.SelectSingleNode("listInt");
XmlNodeList intList = listIntNode.SelectNodes("int");
this.listInt = new List();
for (int i = 0; i < intList.Count; i++)
{
this.listInt.Add(int.Parse(intList[i].InnerText));
}
XmlNode itemList = playerInfo.SelectSingleNode("itemList");
XmlNodeList items = itemList.SelectNodes("Item");
this.itemList = new List- ();
foreach (XmlNode item in items)
{
Item item2 = new Item();
item2.id = int.Parse(item.Attributes["id"].Value);
item2.num = int.Parse(item.Attributes["num"].Value);
this.itemList.Add(item2);
}
XmlNode itemDic = playerInfo.SelectSingleNode("itemDic");
XmlNodeList keyInt = itemDic.SelectNodes("int");
XmlNodeList valueItem = itemDic.SelectNodes("Item");
this.itemDic = new Dictionary
();
for (int i = 0; i < keyInt.Count; i++)
{
int key = int.Parse(keyInt[i].InnerText);
Item value = new Item();
value.id = int.Parse(valueItem[i].Attributes["id"].Value);
value.num = int.Parse(valueItem[i].Attributes["num"].Value);
this.itemDic.Add(key, value);
}
}
}
5、存储XML
注意:存储xml文件 在Unity中一定是使用各平台都可读可写可找到的路径
1.Resources 可读 不可写 打包后找不到 ×
2.Application.streamingAssetsPath 可读 PC端可写 找得到 ×
3.Application.dataPath 打包后找不到 ×
4.Application.persistentDataPath 可读可写找得到 √
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Xml;
using UnityEngine;
public class SaveXml : MonoBehaviour
{
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
#region 知识点一 决定存储在哪个文件夹下
string path = Application.persistentDataPath + "/PlayerInfo2.xml";
print(Application.persistentDataPath);
#endregion
#region 知识点二 存储xml文件
//关键类 XmlDocument 用于创建节点 存储文件
//关键类 XmlDeclaration 用于添加版本信息
//关键类 XmlElement 节点类
//存储有5步
//1.创建文本对象
XmlDocument xml = new XmlDocument();
//2.添加固定版本信息
//这一句代码 相当于就是创建这句内容
XmlDeclaration xmlDec = xml.CreateXmlDeclaration("1.0", "UTF-8", "");
//创建完成过后 要添加进入 文本对象中
xml.AppendChild(xmlDec);
//3.添加根节点
XmlElement root = xml.CreateElement("Root");
xml.AppendChild(root);
//4.为根节点添加子节点
//加了一个 name子节点
XmlElement name = xml.CreateElement("name");
name.InnerText = "唐老狮";
root.AppendChild(name);
XmlElement atk = xml.CreateElement("atk");
atk.InnerText = "10";
root.AppendChild(atk);
XmlElement listInt = xml.CreateElement("listInt");
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
{
XmlElement childNode = xml.CreateElement("int");
childNode.InnerText = i.ToString();
listInt.AppendChild(childNode);
}
root.AppendChild(listInt);
XmlElement itemList = xml.CreateElement("itemList");
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
{
XmlElement childNode = xml.CreateElement("Item");
//添加属性
childNode.SetAttribute("id", i.ToString());
childNode.SetAttribute("num", (i * 10).ToString());
itemList.AppendChild(childNode);
}
root.AppendChild(itemList);
//5.保存
xml.Save(path);
#endregion
#region 知识点三 修改xml文件
//1.先判断是否存在文件
if( File.Exists(path) )
{
//2.加载后 直接添加节点 移除节点即可
XmlDocument newXml = new XmlDocument();
newXml.Load(path);
//修改就是在原有文件基础上 去移除 或者添加
//移除
XmlNode node;// = newXml.SelectSingleNode("Root").SelectSingleNode("atk");
//这种是一种简便写法 通过/来区分父子关系
node = newXml.SelectSingleNode("Root/atk");
//得到自己的父节点
XmlNode root2 = newXml.SelectSingleNode("Root");
//移除子节点方法
root2.RemoveChild(node);
//添加节点
XmlElement speed = newXml.CreateElement("moveSpeed");
speed.InnerText = "20";
root2.AppendChild(speed);
//改了记得存
newXml.Save(path);
}
#endregion
#region 总结
//1.路径选取
//在运行过程中存储 只能往可写且能找到的文件夹存储
//故 选择了Application.persistentDataPath
//2.存储xml关键类
//XmlDocument 文件
// 创建节点 CreateElement
// 创建固定内容方法 CreateXmlDeclaration
// 添加节点 AppendChild
// 保存 Save
//XmlDeclaration 版本
//XmlElement 元素节点
// 设置属性方法SetAttribute
//3.修改
//RemoveChild移除节点
//可以通过 /的形式 来表示 子节点的子节点
#endregion
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
}
}
6、XML的优缺点
6.1 优点
6.2 缺点
7、XML序列化反序列化
从上面可以看出自己写xml转换,是无比麻烦的。C#提供了一些API可以直接进行转化,能转化大部分
的类型的数据,(引用类型初始化为空的)不会被序列化,dictionary也不会被序列化
7.1 序列化
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using UnityEngine;
public class Lesson1Test
{
[XmlElement("testPublic123123")]
public int testPublic;
private int testPrivate;
protected int testProtected;
internal int testInternal;
public string testPUblicStr;
public int testPro { get; set; }
public Lesson1Test2 testClass = new Lesson1Test2();
public int[] arrayInt;
[XmlArray("IntList")]
[XmlArrayItem("Int32")]
public List listInt;
public List listItem;
//不支持字典
//public Dictionary testDic = new Dictionary() { { 1, "123" } };
}
public class Lesson1Test2
{
//添加上这个特性后是有点区别的,这些会按照属性去写,而不是直接按照node,见下面图
[XmlAttribute("Test1")]
public int test1 = 1;
[XmlAttribute()]
public float test2 = 1.1f;
[XmlAttribute()]
public bool test3 = true;
}
public class XmlSerialize : MonoBehaviour
{
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
#region 知识点一 什么是序列化和反序列化
//序列化:把对象转化为可传输的字节序列过程称为序列化
//反序列化:把字节序列还原为对象的过程称为反序列化
//说人话:
//序列化就是把想要存储的内容转换为字节序列用于存储或传递
//反序列化就是把存储或收到的字节序列信息解析读取出来使用
#endregion
#region 知识点二 xml序列化
//1.第一步准备一个数据结构类
Lesson1Test lt = new Lesson1Test();
//2.进行序列化
// 关键知识点
// XmlSerializer 用于序列化对象为xml的关键类
// StreamWriter 用于存储文件
// using 用于方便流对象释放和销毁
//第一步:确定存储路径
string path = Application.persistentDataPath + "/Lesson1Test.xml";
print(Application.persistentDataPath);
//第二步:结合 using知识点 和 StreamWriter这个流对象 来写入文件
// 括号内的代码:写入一个文件流 如果有该文件 直接打开并修改 如果没有该文件 直接新建一个文件
// using 的新用法 括号当中包裹的声明的对象 会在 大括号语句块结束后 自动释放掉
// 当语句块结束 会自动帮助我们调用 对象的 Dispose这个方法 让其进行销毁
// using一般都是配合 内存占用比较大 或者 有读写操作时 进行使用的
using ( StreamWriter stream = new StreamWriter(path) )
{
//第三步:进行xml文件序列化
XmlSerializer s = new XmlSerializer(typeof(Lesson1Test));
//这句代码的含义 就是通过序列化对象 对我们类对象进行翻译 将其翻译成我们的xml文件 写入到对应的文件中
//第一个参数 : 文件流对象
//第二个参数: 想要备翻译 的对象
//注意 :翻译机器的类型 一定要和传入的对象是一致的 不然会报错
s.Serialize(stream, lt);
}
#endregion
#region 知识点三 自定义节点名 或 设置属性
//可以通过特性 设置节点或者设置属性 并且修改名字
#endregion
#region 总结
//序列化流程
//1.有一个想要保存的类对象
//2.使用XmlSerializer 序列化该对象
//3.通过StreamWriter 配合 using将数据存储 写入文件
//注意:
//1.只能序列化公共成员
//2.不支持字典序列化
//3.可以通过特性修改节点信息 或者设置属性信息
//4.Stream相关要配合using使用 否则可能出现内存相关的错误
//5、注意如果类型是引用类型,而且初始化没有放入值,那么xml里面就没这个属性
#endregion
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
}
}
7.2 反序列化
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using UnityEngine;
public class Lesson2 : MonoBehaviour
{
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
#region 知识回顾
// 序列化 就是把类对象 转换为可存储和传输的数据
// 反序列化 就是把存储或收到的数据 转换为 类对象
// xml序列化关键知识
// 1.using 和 StreamWriter
// 2.XmlSerializer 的 Serialize序列化方法
#endregion
#region 知识点一 判断文件是否存在
string path = Application.persistentDataPath + "/Lesson1Test.xml";
if( File.Exists(path) )
{
#region 知识点二 反序列化
//关键知识
// 1.using 和 StreamReader
// 2.XmlSerializer 的 Deserialize反序列化方法
//读取文件
using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(path))
{
//产生了一个 序列化反序列化的翻译机器
XmlSerializer s = new XmlSerializer(typeof(Lesson1Test));
Lesson1Test lt = s.Deserialize(reader) as Lesson1Test;
}
#endregion
}
#endregion
#region 总结
//1.判断文件是否存在 File.Exists
//2.文件流获取 StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(path)
//3.根据文件流 XmlSerializer通过Deserialize反序列化 出对象
//注意:List对象 如果有默认值 反序列化时 不会清空 会往后面添加
#endregion
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
}
}
7.3 对序列化进行改进 IXmlSerializable
从上面可以得知有些数据是不能被序列化的,可以通过实现IXmlSerializable接口实现
7.31 IXmlSerializable的作用
可以让一些不能被序列化和反序列化的特殊类能被处理
让特殊类继承 IXmlSerializable 接口 实现其中的方法即可
7.311 IXmlSerializable只继承不实现
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Schema;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using UnityEngine;
public class TestLesson3 : IXmlSerializable
{
public int test1 = 10;
public int test2 = 99;
public XmlSchema GetSchema()
{
}
public void ReadXml(XmlReader reader)
{
}
public void WriteXml(XmlWriter writer)
{
}
}
public class Lesson3 : MonoBehaviour
{
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
TestLesson3 t = new TestLesson3();
print(Application.persistentDataPath + "/test.xml");
using (StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(Application.persistentDataPath + "/test.xml"))
{
XmlSerializer s = new XmlSerializer(typeof(TestLesson3));
s.Serialize(writer, t);
}
using(StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(Application.persistentDataPath + "/test.xml"))
{
XmlSerializer s = new XmlSerializer(typeof(TestLesson3));
t = s.Deserialize(reader) as TestLesson3;
}
#endregion
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
}
}
7.312 IXmlSerializable不继承
public class TestLesson3
{
public int test1 = 10;
public int test2 = 99;
}
7.312 IXmlSerializable继承重写
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Schema;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using UnityEngine;
public class TestLesson3 : IXmlSerializable
{
public int test1 = 10;
public int test2 = 99;
public XmlSchema GetSchema()
{
return null;
}
///
///自己重写,就不会自动了,所有的都需要自己去整理
///
///
public void ReadXml(XmlReader reader)
{
//读属性
//test1 = int.Parse(reader["Test1"]);
//test2 = int.Parse(reader["Test2"]);
//读节点
//方式一
//reader.Read();//这时读到的是节点
//reader.Read();//这时读到的才是值
//test1 = int.Parse(reader.Value);//得到值内容
//reader.Read();//得到节点尾部配对
//reader.Read();//读到节点开头
//reader.Read();//读到值
//test2 = int.Parse(reader.Value);//获取值内容
//方式二
//while (reader.Read())
//{
// if(reader.NodeType == XmlNodeType.Element)
// {
// switch (reader.Name)
// {
// case "Test1":
// reader.Read();
// test1 = int.Parse(reader.Value) ;
// break;
// case "Test2":
// reader.Read();
// test2 = int.Parse(reader.Value);
// break;
// }
// }
//}
//推荐的写法,正常写法应该是循环(看下面改进段),这里面只是写死的,2次检测
//读包裹点
//例如Test1、Test2
XmlSerializer s = new XmlSerializer(typeof(int));
//去到根节点的下一个节点
reader.Read();
//检查当前节点是否为元素并将读取器推进到下一个节点。 找到以Test1的节点
reader.ReadStartElement("Test1");
test1 = (int)s.Deserialize(reader);
//检查当前内容节点是否为结束标记并将读取器推进到下一个节点
reader.ReadEndElement();
reader.ReadStartElement("Test2");
test1 = (int)s.Deserialize(reader);
reader.ReadEndElement();
}
///
/// 序列化的自定义规则
///
///
public void WriteXml(XmlWriter writer)
{
//写属性
//writer.WriteAttributeString("Test1", test1.ToString());
//writer.WriteAttributeString("Test2", test2.ToString());
//写节点
//writer.WriteElementString("Test1", test1.ToString());
//writer.WriteElementString("Test2", test2.ToString());
//写包裹节点
XmlSerializer s = new XmlSerializer(typeof(int));
//Test1的开始节点
writer.WriteStartElement("Test1");
//写入数据
s.Serialize(writer, test1);
//Test1的结束节点
writer.WriteEndElement();
writer.WriteStartElement("Test2");
s.Serialize(writer, test2);
writer.WriteEndElement();
}
}
public class Lesson3 : MonoBehaviour
{
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
#region 知识点一 IXmlSerializable是什么
//C# 的XmlSerializer 提供了可拓展内容
//可以让一些不能被序列化和反序列化的特殊类能被处理
//让特殊类继承 IXmlSerializable 接口 实现其中的方法即可
#endregion
#region 知识点二 自定义类实践
TestLesson3 t = new TestLesson3();
print(Application.persistentDataPath + "/test.xml");
using (StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(Application.persistentDataPath + "/test.xml"))
{
XmlSerializer s = new XmlSerializer(typeof(TestLesson3));
s.Serialize(writer, t);
}
using(StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(Application.persistentDataPath + "/test.xml"))
{
XmlSerializer s = new XmlSerializer(typeof(TestLesson3));
t = s.Deserialize(reader) as TestLesson3;
}
#endregion
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
}
}
7.4 对字典dictionary序列化进行改进 IXmlSerializable
由于字典不能被直接用来序列化,所以需要特殊处理。
思路就是自己定义一个类型,这个类型需要有所有字典的功能,也需要继承IXmlSerializable,
所以这个类就是继承Dictionary,实现接口IXmlSerializable
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Schema;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using UnityEngine;
public class SerizlizerDictionary : Dictionary, IXmlSerializable
{
public XmlSchema GetSchema()
{
return null;
}
//自定义字典的 反序列化 规则
public void ReadXml(XmlReader reader)
{
XmlSerializer keySer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(TKey));
XmlSerializer valueSer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(TValue));
//要跳过根节点
reader.Read();
//判断 当前不是元素节点 结束 就进行 反序列化
while (reader.NodeType != XmlNodeType.EndElement)
{
//反序列化键 , 拿到的就是确切的值
TKey key = (TKey)keySer.Deserialize(reader);
//反序列化值,拿到的就是确切的值
TValue value = (TValue)valueSer.Deserialize(reader);
//存储到字典中
this.Add(key, value);
}
//根节点的尾结点
reader.Read();
}
//自定义 字典的 序列化 规则
public void WriteXml(XmlWriter writer)
{
XmlSerializer keySer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(TKey));
XmlSerializer valueSer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(TValue));
//this就是这个字典
foreach (KeyValuePair kv in this)
{
//可以理解为在不断的将 键和值 转化为xml放到总得xml中
//键值对 的序列化
keySer.Serialize(writer, kv.Key);
valueSer.Serialize(writer, kv.Value);
}
}
}
------------------------------
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using UnityEngine;
public class TestLesson4
{
public int test1;
public SerizlizerDictionary dic;
}
public class Lesson4 : MonoBehaviour
{
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
#region 知识点一 思考如何让Dictionary支持xml序列和反序列化
//1.我们没办法修改C#自带的类
//2.那我们可以重写一个类 继承Dictionary 然后让这个类继承序列化拓展接口IXmlSerializable
//3.实现里面的序列化和反序列化方法即可
#endregion
#region 知识点二 让Dictionary支持序列化和反序列化
TestLesson4 tl4 = new TestLesson4();
//tl4.dic = new SerizlizerDictionary();
//tl4.dic.Add(1, "123");
//tl4.dic.Add(2, "234");
//tl4.dic.Add(3, "345");
string path = Application.persistentDataPath + "/TestLesson4.xml";
//using(StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(path))
//{
// XmlSerializer s = new XmlSerializer(typeof(TestLesson4));
// s.Serialize(writer, tl4);
//}
using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(path))
{
XmlSerializer s = new XmlSerializer(typeof(TestLesson4));
tl4 = s.Deserialize(reader) as TestLesson4;
}
#endregion
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
}
}
经过测试,如果TestLesson4也实现了IXmlSerializable,
那么内部的public SerizlizerDictionary dic;
内部的那个WriteXml就不会运行,只会执行TestLesson4自己的WriteXml
8、对XML进行封装
8.2 XMLManager
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
using UnityEngine;
public class XmlDataMgr :BaseManager
{
///
/// 保存数据到xml文件中
///
/// 数据对象
/// 文件名
public void SaveData(object data, string fileName)
{
//1.得到存储路径
string path = Application.persistentDataPath + "/" + fileName + ".xml";
Debug.Log("文件被存储在"+path);
//2.存储文件
using(StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(path))
{
//3.序列化
XmlSerializer s = new XmlSerializer(data.GetType());
s.Serialize(writer, data);
}
}
///
/// 从xml文件中读取内容
///
/// 对象类型
/// 文件名
/// 8.3 XMLTest
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Unity.VisualScripting;
using UnityEngine;
public class ItemList
{
public string name = "111";
public int age = 11;
}
public class TestClass
{
public string test1;
public ItemList[] array;
public List list;
public SerizlizerDictionary dic;
}
public class XMLTest : MonoBehaviour
{
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
TestClass ts = new TestClass();
//存放数据
// ts.test1 = "名字";
// ts.array = new[] { new ItemList(), new ItemList() };
// ts.list = new List(){new ItemList()};
// XmlDataMgr.GetInstance().SaveData(ts,"测试功能");
//取出数据
TestClass testClass = XmlDataMgr.GetInstance().LoadData(typeof(TestClass),"测试功能")as TestClass;
Debug.Log(testClass.test1);
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
}
}