Kotlin学习——hello kotlin & 函数function & 变量 & 类 + 泛型 + 继承
Kotlin 是一门现代但已成熟的编程语言,旨在让开发人员更幸福快乐。 它简洁、安全、可与 Java 及其他语言互操作,并提供了多种方式在多个平台间复用代码,以实现高效编程。
https://play.kotlinlang.org/byExample/01_introduction/02_Functions
目录
- 引出
- hello
- function函数
-
- Infix Functions 中缀函数
- Operator Functions 算术函数
- 变长参数vararg Parameters
- 变量
-
- kt中的null
- kt中的类
- 泛型 Generics
-
- 泛型函数Generic Functions
- 继承Inheritance
-
- 超类Asiatic
- 总结
引出
1.kotlin初识;
2.function函数,变量,null;
3.泛型,接口,继承,超类;
hello
package com.tianju.ktLearn
fun main() { // 2
println("Hello, World!") // 3
}
function函数
- 返回值为Unit,表示没有返回值, 类似与java里面的 void
- Unit可以省略不写,可以传两个参数,参数带有默认值
package com.tianju.ktLearn
// 返回值为Unit,表示没有返回值, 类似与java里面的 void
fun printMsg(msg: String): Unit {
println(msg)
}
// Unit可以省略不写,可以传两个参数,参数带有默认值
fun printMsgWithPrefix(msg: String, prefix:String = "info") {
println("[wtt--$prefix] $msg")
}
fun sum(x: Int, y: Int): Int {
return x+y;
}
fun multiply(x: Int,y: Int) = x*y
fun main() {
printMsg("Pet!")
// 可以不传参,带有默认参数的
printMsgWithPrefix("Hello")
printMsgWithPrefix("Hello","Peter")
printMsgWithPrefix(prefix = "MMDD", msg = "HTTP")
val sum = sum(100, 300)
println(sum)
println(multiply(3,30))
}
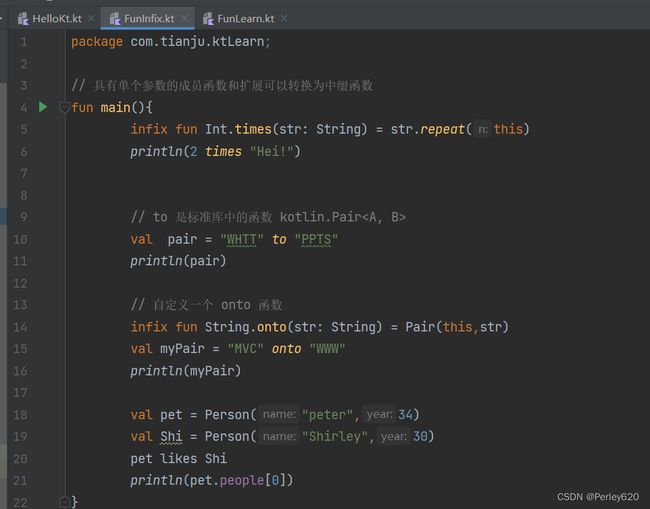
Infix Functions 中缀函数
具有单个参数的成员函数和扩展可以转换为中缀函数。
package com.tianju.ktLearn;
// 具有单个参数的成员函数和扩展可以转换为中缀函数
fun main(){
infix fun Int.times(str: String) = str.repeat(this)
println(2 times "Hei!")
// to 是标准库中的函数 kotlin.PairOperator Functions 算术函数
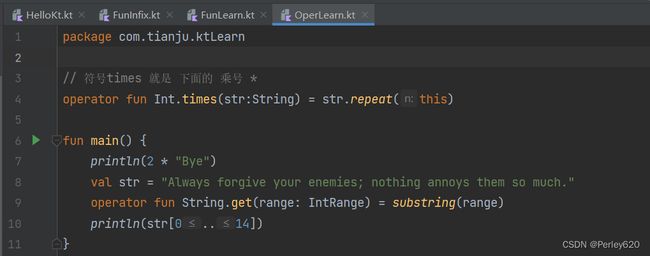
Certain functions can be “upgraded” to operators, allowing their calls with the corresponding operator symbol.
package com.tianju.ktLearn
// 符号times 就是 下面的 乘号 *
operator fun Int.times(str:String) = str.repeat(this)
fun main() {
println(2 * "Bye")
val str = "Always forgive your enemies; nothing annoys them so much."
operator fun String.get(range: IntRange) = substring(range)
println(str[0..14])
}
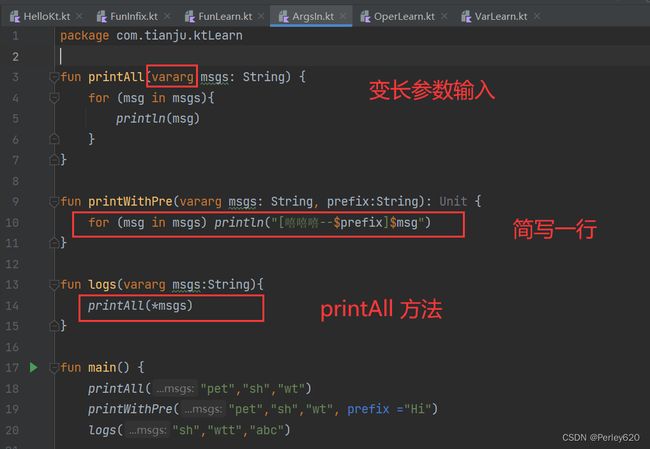
变长参数vararg Parameters
package com.tianju.ktLearn
fun printAll(vararg msgs: String) {
for (msg in msgs){
println(msg)
}
}
fun printWithPre(vararg msgs: String, prefix:String): Unit {
for (msg in msgs) println("[嘻嘻嘻--$prefix]$msg")
}
fun logs(vararg msgs:String){
printAll(*msgs)
}
fun main() {
printAll("pet","sh","wt")
printWithPre("pet","sh","wt", prefix ="Hi")
logs("sh","wtt","abc")
}
变量
Kotlin具有强大的类型推理能力。虽然你可以显式地声明变量的类型,但你通常会让编译器通过推断来完成这项工作。Kotlin不强制执行不变性,但建议这样做。本质上使用val而不是var。
val b: Int = 1 // 2
val c = 3 // 3
声明一个不可变变量并对其进行初始化。
声明一个不可变变量并在不指定类型的情况下对其进行初始化。编译器推断类型Int。
kt中的null
- 在kt里面,如果有一个可以为null,需要在类型后面加上 问号 ?
- 函数只能传入不为null的值
- 参数类型后面加个 ? 问号后,传入的值可以为null
package com.tianju.ktLearn
fun main() {
var neverNull : String = "never Null"
// neverNull = null
println(neverNull)
// 在kt里面,如果有一个可以为null,需要在类型后面加上 问号 ?
var nullable:String? = "can be null"
nullable = null
println(nullable)
fun strLength(notNull:String ): Int {
return notNull.length
}
// 函数只能传入不为null的值
strLength(neverNull)
// strLength(nullable) // 爆红
val str = descStr(null)
println(str)
println(descStr("hello are you ok?"))
}
/**
* 返回值为String,
* 参数类型后面加个 ? 问号后,传入的值可以为null
*/
fun descStr(maybeStr: String?): String {
if (maybeStr !=null && maybeStr.length>0){
return "StrLength is ${maybeStr.length}"
}
return "null"
}
kt中的类
- 在kt里面没有 new 关键字
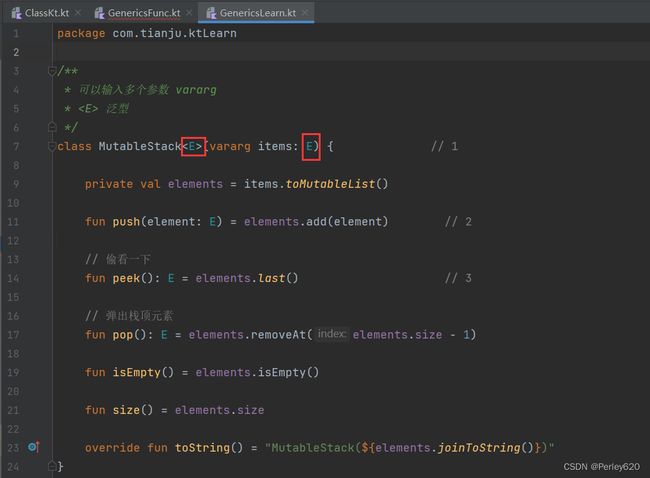
泛型 Generics
package com.tianju.ktLearn
/**
* 可以输入多个参数 vararg
* 泛型
*/
class MutableStack<E>(vararg items: E) { // 1
private val elements = items.toMutableList()
fun push(element: E) = elements.add(element) // 2
// 偷看一下
fun peek(): E = elements.last() // 3
// 弹出栈顶元素
fun pop(): E = elements.removeAt(elements.size - 1)
fun isEmpty() = elements.isEmpty()
fun size() = elements.size
override fun toString() = "MutableStack(${elements.joinToString()})"
}
fun main() {
val mut = MutableStack<String>("hello","pet")
println("is mut empty?---> " + mut.isEmpty())
print(mut)
mut.push("wtt")
println(mut)
mut.peek()
println(mut)
val pop = mut.pop()
println(pop)
println(mut)
println("is mut empty?---> " + mut.isEmpty())
}
泛型函数Generic Functions
如果函数的逻辑独立于特定类型,则也可以生成函数。例如,您可以编写一个实用程序函数来创建可变堆栈:
继承Inheritance
超类Asiatic
package com.tianju.ktLearn
/**
* open 关键字就表示是接口 interface
*/
open class Dog{
open fun fake(){
println("wow wow !")
}
}
class YourDog : Dog(){
override fun fake() {
println("miao wu ,wow")
}
}
/**
* 带参数的接口
* interface with par
*/
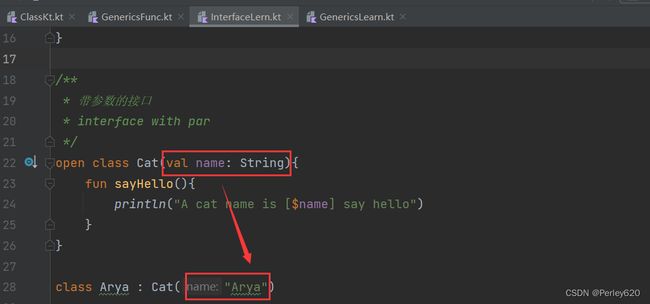
open class Cat(val name: String){
fun sayHello(){
println("A cat name is [$name] say hello")
}
}
class Arya : Cat("Arya")
/**
* 超类 :将构造函数参数传递给超类
*/
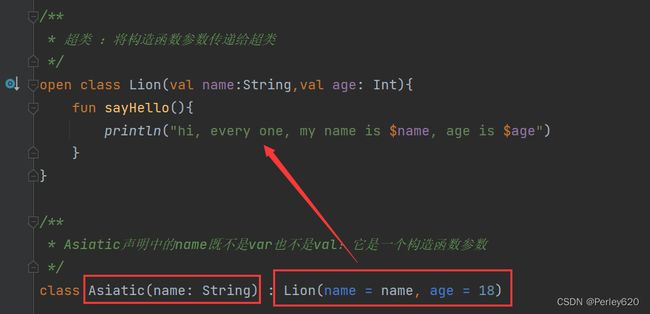
open class Lion(val name:String,val age: Int){
fun sayHello(){
println("hi, every one, my name is $name, age is $age")
}
}
/**
* Asiatic声明中的name既不是var也不是val:它是一个构造函数参数
*/
class Asiatic(name: String) : Lion(name = name, age = 18)
fun main() {
val dog = YourDog()
dog.fake()
val cat : Cat = Arya()
cat.sayHello()
println(cat.name)
val lion: Lion = Asiatic("Peter")
lion.sayHello()
}
总结
1.kotlin初识;
2.function函数,变量,null;
3.泛型,接口,继承,超类;