数据结构与算法实验(黑龙江大学)
实验一 顺序存储的线性表(2 学时)
一、实验目的
1 、掌握线性表的逻辑结构特征。
2、熟练掌握线性表的顺序存储结构的描述方法。
3 、熟练掌握顺序表上各种基本操作的实现。
二、实验内容
1 、设线性表的数据元素都为整数,存放在顺序表 S 中且递增有序。设计算法,将 x 插入
到顺序表 S 的适当位置上,以保持线性表的有序性。要求算法的时间复杂度为 O(n) ,空间复
杂度为 O(1) 。
2 、线性表使用顺序表作存储结构,设计算法,仅用一个辅助结点,实现将顺序表中的结
点循环右移 k 位的运算。
3 、设计算法,仅用一个辅助结点,实现将顺序存储的线性表中的数据元素逆置。
三、实验指导
1 、本实验所有题目中的向量可以用顺序表来描述,数据元素为整数。
2 、提示
( 1 )题目 1 中的顺序表在建立时即是有序表, x 的值由用户输入,应该考虑 3 种情况,
①小于原表中第一个元素的值;②介于最小元素值和最大元素值之间;③大于最大元素的值。
( 2 )对于题目 2 , k 的值由用户输入,如顺序表中元素为 1,2,3,4,5,6 ,当 k 的值为 4 时,
结果为 3,4,5,6,1,2 。
四、考核标准
1 、至少完成 2 个题目,设计合理,结果正确,按时完成;评定为 A 。
2 、完成部分题目或未按时完成,设计比较合理,结果正确;根据实际情况评定为 B 或 C 。
3 、未独立完成实验要求;评定为 D 。
(本单元共 2 分。未按时完成或算法的时间与空间复杂度过高也会酌情扣分。)
五、代码实现
MySeqListTest 类
package 实验一;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MySeqListTest {
private int[] arr;
private int len;//顺序表长度,记载元素个数
public MySeqListTest(int[] elem) {
if (elem == null || elem.length == 0) {
this.len = 0;
} else {
arr = elem;
len = elem.length;
}
}
/**
* @description: 插入并排序
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 19:59
* @param: [x]
* @return: void
**/
public void insert(int x) {
int[] newArr = new int[len + 1];
//将数组中元素按升序排列
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (arr[i] < arr[j]) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
int i = 0, j = 0;// i 为element数组下标,j为newArr数组元素下标
for (; i < arr.length; i++, j++) {//判断插入元素位置
if (arr[i] >= x) {//如果element元素大于x,则将x置于newArr数组第j个位置
newArr[j] = x;
break;
}else {//否则就将element数组中第i个元素置于newArr数组中第j个元素
newArr[newArr.length-1] = x;
newArr[j]=arr[i];
}
}
while (iRightMoveTest类
package 实验一;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RightMoveTest {
/**
* @description: 循环右移
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 19:59
* @param: [move, num]
* @return: void
**/
public void rightMove(int[] move, int num) {
int i, j, temp;
for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {
//将原数组最后一位存入临时变量temp
temp = move[move.length - 1];
for (j = move.length - 2; j >= 0; j--) {//将剩下所有元素右移num次
move[j + 1] = move[j];
}
move[0] = temp;//右移结束后temp存在数组第一位
}
System.out.println("循环右移结果如下:");
for (i = 0; i < move.length; i++) {
System.out.print(move[i] + "\t");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入数组元素个数:");
int n = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入循环右移次数:");
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n];
System.out.println("依次输入数组元素");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
RightMoveTest r = new RightMoveTest();
r.rightMove(arr, m);
}
}
ArrayReverse类
package 实验一;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayReverse {
/**
* @description: 数组逆置
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 19:58
* @param: [array]
* @return: void
**/
public void reverse(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length / 2; i++) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[array.length - i - 1];
array[array.length - i - 1] = temp;
}
System.out.println("数组逆置结果如下:");
for (int j = 0; j < array.length; j++) {
System.out.print(array[j] + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入数组元素个数:");
int num = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[num];
System.out.println("依次输入数组元素:");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
ArrayReverse a = new ArrayReverse();
a.reverse(arr);
}
}
实验二 单链表 (2 学时)
一、实验目的
1 、掌握线性表的链式存储结构。
2 、熟练掌握单链表的描述方法和建立方法。
3 、熟练掌握单链表上基本操作及其相关应用的实现。
二、实验内容
1 、已知带头结点的动态单链表 L 中的结点是按整数值递增排序的,试写一算法将值为 x
的结点插入到表 L 中,使 L 仍然有序。要求算法的时间复杂度为 O(n) ,空间复杂度为 O(1) 。
2 、设计一算法,逆置带头结点的动态链表 L 。要求利用原表的结点空间,并要求用尽可
能少的时间完成。 3 、假设有两个按元素值递增有序的线性表 A 和 B ,均以单链表作存储结构,试编写算法
将 A 表和 B 表归并成一个按元素值递减有序的线性表性表 C ,并要求利用原表的空间存放 C ,
并要求用尽可能少的时间完成。
三、实验指导
1 、本实验中的动态链表都用单链表实现,结点中 data 域类型假定为 int 。
2 、提示
( 1 )题目 1 中的单链表在建立时即为有序表, x 的值由用户输入,应该考虑 3 种情况,
①小于原表中第一个元素的值;②介于最小元素值和最大元素值之间;③大于最大元素的值。
( 2 )题目 2 可以考虑用头插法思想将单链表中每个结点“卸”下来再“挂”上去。
( 3 )题目 3 也可以考虑使用头插法思想,同时可参照两个递增有序单链表合成一个有序
单链表的算法。
四、考核标准
1 、至少完成 2 个题目,设计合理,结果正确;评定为 A 。
2 、完成部分题目或未按时完成,设计比较合理,结果正确;评定为 B 或 C 。
3 、未独立完成实验要求;评定为 D 。
(本单元共 2 分。未按时完成或算法的时间与空间复杂度过高也会酌情扣分。)
五、代码实现
Node类
package 实验二;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Node {
private int data;
private Node next;
public Node() {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
data= sc.nextInt();
next = null;
}
public Node(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node(int data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return data + " "+next+" ";
}
}
LinkList类
package 实验二;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LinkList {
private Node head;
private int num;
//初始化(建立)空链表
public LinkList() {
num = 0;
head = null;
}
public LinkList(Node head) {
this.head = head;
}
//初始化(建立)一个具有n个结点的链表
public LinkList(int n) {
num = n;
head = new Node();
Node p = head;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
p.setNext(new Node());
p = p.getNext();
}
}
/**
* @description: 插入
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:00
* @param: [x]
* @return: void
**/
public void insert(int x) {
Node temp = new Node(x);
num++;
if (head == null) {
head = temp;
} else {
if (x < head.getData()) {
temp.setNext(head);
head = temp;
} else {
Node p = head;
while (p.getNext() != null && p.getNext().getData() < x) {
p = p.getNext();
}
temp.setNext(p.getNext());
p.setNext(temp);
}
}
}
/**
* @description: 输出链表中所有结点data域的值
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:01
* @param: []
* @return: void
**/
public void linkPrint() {
Node p = head;
if (head != null) {
while (p.getNext() != null) {
System.out.print(p.getData() + " ");
p = p.getNext();
}
System.out.print(p.getData() + " ");
} else {
System.out.println("链表中没有数据!!!");
}
}
/**
* @description: 选择排序(升序)
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:01
* @param: [head]
* @return: void
**/
public void sortList(Node head) {
Node p = head;
int temp = 0;
while (p != null) {
Node next = p.getNext();
while (next != null) {
if (next.getData() < p.getData()) {
temp = p.getData();
p.setData(next.getData());
next.setData(temp);
}
next = next.getNext();
}
p = p.getNext();
}
}
/**
* @description: 选择排序(降序)
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:01
* @param: [head]
* @return: void
**/
public void sortList_2(Node head) {
Node q = head;
int temp = 0;
while (q != null) {
Node next = q.getNext();
while (next != null) {
if (next.getData() > q.getData()) {
temp = q.getData();
q.setData(next.getData());
next.setData(temp);
}
next = next.getNext();
}
q = q.getNext();
}
}
/**
* @description: 逆置 从原来的链表把第一个节点一个一个逮出来,然后头插到新链表中
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:01
* @param: [head]
* @return: void
**/
public void reverse(Node head) {
Node p = head; //head原链表头结点
Node temp = null;//暂时保存的原来的头结点
Node result = null;//新链表头结点
while (p != null) {
temp = p;
p = p.getNext();
temp.setNext(result);
result = temp;
}
if (head != null) {
while (result.getNext() != null) {
System.out.print(result.getData() + " ");
result = result.getNext();
}
System.out.print(result.getData() + " ");
} else {
System.out.println("链表中没有数据!!!");
}
}
/**
* @description: 连接
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:02
* @param: [p]
* @return: void
**/
public void connect(LinkList p) {
Node p1 = head;
num = p.num + num;
while (p1.getNext() != null) {
p1 = p1.getNext();
}
Node p2 = p.head;
while (p2 != null) {
p1.setNext(new Node(p2.getData()));
p1 = p1.getNext();
p2 = p2.getNext();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//插入测试
System.out.println("请输入链表1的初始长度: ");
int n1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请往链表1中输入数据: ");
LinkList l1 = new LinkList(n1);
System.out.println("显示链表1: ");
l1.linkPrint();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("请输入插入的数据:");
int x = sc.nextInt();
l1.insert(x);
l1.sortList(l1.head);
System.out.println("显示插入之后的链表:");
l1.linkPrint();
//逆置测试
System.out.println();
System.out.println("请输入链表2的初始长度: ");
int n2 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请往链表2中输入数据: ");
LinkList l2 = new LinkList(n2);
System.out.println("显示链表2: ");
l2.sortList(l2.head);
l2.linkPrint();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("逆置后链表为:");
l2.reverse(l2.head);
//归并降序测试
System.out.println();
System.out.println("请输入链表3的初始长度: ");
int n3 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请往链表3中输入数据: ");
LinkList l3 = new LinkList(n3);
System.out.println("显示链表3: ");
l3.linkPrint();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("请输入链表4的初始长度: ");
int n4 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请往链表4中输入数据: ");
LinkList l4 = new LinkList(n4);
System.out.println("显示链表4: ");
l4.linkPrint();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("连接链表3和链表4: ");
l3.connect(l4);
l3.linkPrint();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("将连接好的链表降序输出: ");
l3.sortList_2(l3.head);
l3.linkPrint();
}
}
实验三 循环链表和双链表(2 学时)
一、实验目的
1 、熟练掌握循环链表的存储特征和建立方法。
2 、熟练掌握双链表的存储特征和建立方法。
3 、掌握在循环链表以及双链表上基本应用的实现。
二、实验内容
1 、假设在长度大于 1 的单循环链表中,既无头结点也无头指针。 s 为指向某个结点的指
针,试编写算法删除结点 *s 的直接前驱结点。
2 、已知由单链表表示的线性表中,含有三类字符的数据元素(如:字母、数字和其它字
符),设计算法构造三个以循环链表示的线性表,使每一个表中只含同一类的字符,且利用原
表中的结点空间作为这三个表的空间。(头结点可以另辟空间)
3 、有一双链表,每个结点中除有 prior 、 data 和 next 域外,还有一访问频度域 freq ,在链
表被启用前,其值均初始化为零。每当在链表上进行一次 LOCATE(L,x) 运算,元素值为 x 的
结点中 freq 域的值增 1 ,并使此链表中结点保持按 freq 递减的顺序排列,以便使频繁访问的结
点总是靠近表头。设计满足上述要求的 LOCATE 算法。
三、实验指导
1 、认真阅读题目,根据题目内容要求建立好相应的链表。
2 、提示
( 1 )①题目 1 应该先建立好单循环链表,并返回主调函数该单循环链表的头指针或尾指
针;②用户输入某个整数,在建好的单循环链表中查找该整数,如找到将该结点的地址传给 s ;
③根据 s 删除其前驱结点,特别要注意删除的就是第一个结点的前驱;④参考测试用例:如
链表中为(1,2,3,4,5),用户输入 3,结果为(1,2,4,5);如链表中为(1,2,3,4,5),用户输
入 1,则结果应为(1,2,3,4)。 ( 2 )①题目 2 应事先建立好一个非循环单链表 L (该链表结点的 data 域类型为 char ),
该链表中含三种字符,例如该链表可为如下:
( ’1’->’c’->’!’->’h’->’$’->’2’->’3’->’i’->’n’->’#’->’a’ )
②建立三个空的循环单链表 h1、h2、h3,分别存储数字字符、字母字符、其它字符;③
按顺序扫描 L 中的每个结点,根据结点中 data 的特征将其链入相应的循环链表中;③按照上
述测试用例,h1 中应为( ’1’-> ’2’->’3’ ),h2 中应为( ’c’->’h’->’i’ ->’n’ ->’a’ ), h3 中应为( ’ !
’->’
$’->’#’ )。
( 3 )题目 3 要求先建立好双链表 DL1 , DL1 中内容假设为( 1,2,3,4,5,6 ),每个结点的 freq
值都为 0 ;用户每输入一个值, DL1 应该做出相应的调整,并把调整结果供用户直观查看。
四、考核标准
1 、至少完成 2 个题目,设计合理,结果正确;评定为 A
2 、完成部分题目或未按时完成,设计比较合理,结果正确;评定为 B 或 C
3 、未独立完成实验要求;评定为 D
(本单元共 3 分。只完成前两个题目最多得 2 分,高质量完成 3 个题目给 3 分,未按时
完成或算法的时间与空间复杂度过高也会酌情扣分。)
五、代码实现
题目一
Node类
package 实验三.题目一;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Node {
private Object data;
Node next;
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node() {
}
public Node(Object data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return data + " ";
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Node)) return false;
Node node = (Node) o;
return Objects.equals(getData(), node.getData()) &&
Objects.equals(getNext(), node.getNext());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getData(), getNext());
}
}
LinkedList1类
package 实验三.题目一;
public class LinkedList1 {
private Node head;
public LinkedList1() {
}
public LinkedList1(Node head) {
this.head = head;
}
public void create(int len) {
head = new Node();
Node p = head;
if (len == 1) {
p.setData(null);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (i < len - 1) {
p.setData(i);
p.setNext(new Node());
p = p.getNext();
}
if (i==len-1){
p.setData(i);
p.setNext(head);
}
}
}
}
public Node get (int index){
if (head != null) {
int i = 0;
Node tmp = head;
while (tmp.getNext() != null) {
if (i == index) {
return tmp;
}
i++;
tmp = tmp.getNext();
}
if (i == index) {
return tmp;
}
}
return null;
}
public void delete(int n){
Node curr=head;
while(!curr.getNext().getData().equals(n)){
curr=curr.getNext();
}
curr.setNext(curr.getNext().getNext());
curr.setData(n);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList1 l=new LinkedList1();
l.create(2);
System.out.println("显示链表:");
for (int i=0;i<2;i++){
System.out.print(l.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("删除后的链表:");
l.delete(0);
for (int i=0;i<1;i++){
System.out.print(l.get(i));
}
}
}
题目二
Node类
package 实验三.题目二;
public class Node {
private char data;
private Node next;
public Node() {
this('0',null);
}
public Node(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
public Node(char data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node(char data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public char getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(char data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return data + " "+next+" ";
}
}
LinkedList2类
package 实验三.题目二;
public class LinkedList2 {
private Node head;
int size;
public LinkedList2() {
this.head = new Node('0', null);
this.size = 0;
}
public void create(Node head, int len) {
head = new Node();
Node p = head;
if (len == 1) {
p.setData('\0');
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (i < len - 1) {
p.setNext(new Node());
p = p.getNext();
}
if (i == len - 1) {
p.setNext(head);
}
}
}
}
public void insert(char t) {
Node n = head;
while (n.getNext() != null) {
n = n.getNext();
}
Node newNode = new Node(t, null);
n.setNext(newNode);
size++;
}
public Node get(int i) {
Node p = head;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {
p = p.getNext();
}
return p;
}
public void linkPrint() {
Node p = head.getNext();
if (head != null) {
while (p.getNext() != null) {
System.out.print(p.getData() + " ");
p = p.getNext();
}
System.out.print(p.getData() + " ");
System.out.println();
} else {
System.out.println("链表中没有数据!!!");
}
}
public void result() {
Node current = head;
LinkedList2 a1 = new LinkedList2();
LinkedList2 a2 = new LinkedList2();
LinkedList2 a3 = new LinkedList2();
while (current != null) {
if ((current.getData() >= 'A' && current.getData() <= 'Z') || (current.getData() >= 'a' && current.getData() <= 'z')) {
a1.insert(current.getData());
} else if (current.getData() >= '0' && current.getData() <= '9') {
a2.insert(current.getData());
} else {
a3.insert(current.getData());
}
current = current.getNext();
}
System.out.print("字母:");
a1.linkPrint();
System.out.print("数字:");
a2.linkPrint();
System.out.print("符号:");
a3.linkPrint();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList2 l = new LinkedList2();
l.insert('1');
l.insert('2');
l.insert('a');
l.insert('e');
l.insert('f');
l.insert('b');
l.insert('5');
l.insert('c');
l.insert('7');
l.insert('9');
l.insert('d');
l.insert('e');
l.insert('@');
l.insert('#');
l.insert('$');
l.insert('%');
l.insert('^');
l.insert('&');
l.insert('*');
l.insert('?');
l.create(l.head, 20);
l.linkPrint();
l.result();
}
}
题目三
Node类
package 实验三.题目三;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Node {
private Object data;
private int freq;
Node prior;
Node next;
public Node(Object data, int freq, Node prior, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.freq = freq;
this.prior = prior;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(Object data) {
this.data=data;
}
public Node(){
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public int getFreq() {
return freq;
}
public void setFreq(int freq) {
this.freq = freq;
}
public Node getPrior() {
return prior;
}
public void setPrior(Node prior) {
this.prior = prior;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return data+" " ;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Node)) return false;
Node node = (Node) o;
return getFreq() == node.getFreq() && Objects.equals(getData(), node.getData()) && Objects.equals(getPrior(), node.getPrior()) && Objects.equals(getNext(), node.getNext());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getData(), getFreq(), getPrior(), getNext());
}
}
LinkList类
package 实验三.题目三;
public class LinkList {
private Node head;
public LinkList() {
}
public LinkList(Node head) {
this.head = head;
}
public Node getHead() {
return head;
}
public void setHead(Node head) {
this.head = head;
}
public Node get(int index) {
if (head != null) {
int count = 0;
Node temp = head;
while (temp.getNext() != null) {
if (count == index) {
return temp;
}
count++;
temp = temp.getNext();
}
if (count == index) {
return temp;
}
}
return null;
}
public void add(Object data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
} else {
Node temp = head;
while (temp.getNext() != null) {
temp = temp.getNext();
}
temp.setNext(node);
}
}
public int size() {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
} else {
Node temp = head;
int count = 0;
while (temp.getNext() != null) {
temp = temp.getNext();
count++;
}
count++;
return count;
}
}
public void Locate(LinkList l, int x) {
Node temp = l.head;
while (temp.getNext() != null) {
if (temp.getData().equals(x)) {
temp.setFreq(temp.getFreq() + 1);
}
temp = temp.getNext();
}
if (temp.getData().equals(x)) {
temp.setFreq(temp.getFreq() + 1);
}
}
//冒泡排序(升序)
public void order(LinkList l) {
int size = l.size();
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size - 1 - i; j++) {
if (l.get(j).getFreq() <= l.get(j + 1).getFreq()) {
temp = (int) l.get(j + 1).getData();
l.get(j + 1).setData(l.get(j).getData());
l.get(j).setData(temp);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkList l1 = new LinkList();
l1.add(1);
l1.add(2);
l1.add(3);
l1.add(4);
l1.Locate(l1, 1);
l1.Locate(l1, 1);
l1.Locate(l1, 1);
l1.Locate(l1, 2);
l1.Locate(l1, 2);
l1.Locate(l1, 2);
l1.Locate(l1, 2);
l1.Locate(l1, 3);
System.out.println("链表为:");
System.out.println(l1.get(0) + " " + l1.get(1) + " " + l1.get(2) + " " + l1.get(3));
System.out.println("该链表中个数据频度为:");
System.out.println(l1.get(0).getFreq() + " " + l1.get(1).getFreq() + " " + l1.get(2).getFreq() + " " + l1.get(3).getFreq());
System.out.println("排序后:");
l1.order(l1);
System.out.println(l1.get(0) + " " + l1.get(1) + " " + l1.get(2) + " " + l1.get(3));
}
}
实验四 栈和队列(2 学时)
一、实验目的
1 、掌握栈和队列的逻辑特征。
2 、熟练掌握在两种存储结构上实现栈和队列的基本运算。
3 、学会利用栈和队列解决一些实际问题。
二、实验内容
1 、设单链表中存放着 n 个字符,设计算法,判断该字符串中是否有中心对称关系。例如:
xyzzyx 、 xyzyx 都算是中心对称的字符串。
2 、设计算法判断一个算术表达式的圆括号是否配对。(提示:对表达式进行扫描,遇‘ ( ’
进栈,遇‘ ) ’退掉栈顶的‘ ( ’,表达式被扫描完毕,栈为空 )
3 、假设以带头结点的循环链表表示队列,并只设一个指针指向队尾,编写相应的置队空、
入队和出队算法。
三、实验指导
1 、题目 1 可用顺序栈或链栈实现;题目 2 可以用顺序栈实现;题目 3 用单循环链表实现。
2 、提示
( 1 )题目 1 重点考虑①哪些字符进栈;②如何利用栈判断中心对称关系。
( 2 )题目 2 重点考虑①遇到左括号如何处理,遇到右括号如何处理,遇到其它字符如何
处理,何时结束?②当栈空时如果扫描到右括号时应如何处理?
( 3 )题目 3 除了完成基本运算还要考虑设计直观的界面使用户清晰操作并直观看到操作
结果。
四、考核标准
1 、至少完成 2 个题目,设计合理,结果正确,时间与空间复杂度低;评定为 A
2 、完成部分题目或未按时完成,设计比较合理,结果正确;评定为 B 或 C
3 、未独立完成实验要求;评定为 D
(本单元共 2 分。未按时完成或算法的时间与空间复杂度过高也会酌情扣分。)
五、代码实现
题目一
Node类
package 实验四.题目一;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Node {
private Object data;
Node next;
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node(Object data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public Node() {
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return data + "" ;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Node)) return false;
Node node = (Node) o;
return Objects.equals(getData(), node.getData()) && Objects.equals(getNext(), node.getNext());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getData(), getNext());
}
}
Stack类
package 实验四.题目一;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Stack {
private Node head;
private int N;
public Stack() {
this.head = new Node(null, null);
this.N = 0;
}
/**
* @description: 判断当前栈中元素个数是否为0
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:04
* @param: []
* @return: boolean
**/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0;
}
/**
* @description: 获取栈中元素个数
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:03
* @param: []
* @return: int
**/
public int size() {
return N;
}
/**
* @description: 把t元素压入栈
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:03
* @param: [t]
* @return: void
**/
public void push(Object t) {
//找到首结点指向的第一个结点
Node oldFirst = head.getNext();
//创建新节点
Node newNode = new Node(t, null);
//让首结点指向新结点
head.setNext(newNode);
//让新结点指向原来的第一个结点
newNode.setNext(oldFirst);
//元素个数+1
N++;
}
/**
* @description: 弹出栈顶元素
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:04
* @param: []
* @return: java.lang.Object
**/
public Object pop() {
//找到首结点指向的第一个结点
Node oldFirst = head.getNext();
if (oldFirst == null) {
return null;
}
//让首结点指向原来的第一个结点的下一个结点
head.setNext(oldFirst.getNext());
//元素个数-1
N--;
return oldFirst.getData() + "";
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Stack)) return false;
Stack stack = (Stack) o;
return N == stack.N && Objects.equals(head, stack.head);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(head, N);
}
}
LinkedList类
package 实验四.题目一;
import java.util.Objects;
public class LinkedList {
private Node head;
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Node head) {
this.head = head;
}
public Node getHead() {
return head;
}
public void setHead(Node head) {
this.head = head;
}
public Node get(int index) {
if (head != null) {
int count = 0;
Node temp = head;
while (temp.getNext() != null) {
if (count == index) {
return temp;
}
count++;
temp = temp.getNext();
}
if (count == index) {
return temp;
}
}
return null;
}
public int size() {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
} else {
Node temp = head;
int count = 1;
while (temp.getNext() != null) {
temp = temp.getNext();
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
public void add(Object data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
} else {
Node temp = head;
while (temp.getNext() != null) {
temp = temp.getNext();
}
temp.setNext(node);
}
}
public boolean isCentrallySymmetric(LinkedList l) {
int size = l.size();
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size / 2; i++) {
if (l.get(i).getData().equals(l.get(size - 1 - i).getData())) {
count++;
}
}
if (count == size / 2 || count == (size / 2) + 1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public void linkPrint() {
Node p = head;
if (head != null) {
while (p.getNext() != null) {
System.out.print(p.getData() + "");
p = p.getNext();
}
System.out.print(p.getData() + "");
} else {
System.out.println("链表中没有数据!!!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList l = new LinkedList();
l.add('a');
l.add('b');
l.add('a');
l.add('b');
l.add('a');
boolean b = l.isCentrallySymmetric(l);
l.linkPrint();
System.out.println("是否为中心对称的字符串:");
System.out.println(b);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof LinkedList)) return false;
LinkedList that = (LinkedList) o;
return Objects.equals(getHead(), that.getHead());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getHead());
}
}
CentrallySymmetric类
package 实验四.题目一;
public class CentrallySymmetric {
public static boolean isCentrallySymmetric(LinkedList l) {
Stack s = new Stack();
Node p = l.getHead();
for (int i = 0; i < l.size() / 2; i++) {
s.push(p.getData());
p = p.getNext();
}
if (l.size()%2==1){
p=p.getNext();
}
int count=0;
for (int i = 0; i < l.size() / 2; i++) {
Object pop = s.pop();
if (p!=null&&pop.equals(p.getData())){
count++;
p=p.getNext();
}
}
System.out.println(count);
if (count== l.size()/2){
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList l = new LinkedList();
l.add("a");
l.add("a");
l.add("b");
l.add("b");
l.add("a");
l.add("a");
boolean b = CentrallySymmetric.isCentrallySymmetric(l);
l.linkPrint();
System.out.println("是否为中心对称的字符串:");
System.out.println(b);
}
}
题目二
Node类
package 实验四.题目二;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Node {
private Object data;
Node next;
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node() {
}
public Node(Object data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return data + " " ;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Node)) return false;
Node node = (Node) o;
return Objects.equals(getData(), node.getData()) &&
Objects.equals(getNext(), node.getNext());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getData(), getNext());
}
}
Stack类
package 实验四.题目二;
public class Stack {
private Node head;
private int N;
public Stack() {
this.head = new Node(null, null);
this.N = 0;
}
//判断当前栈中元素个数是否为0
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0;
}
//获取栈中元素个数
public int size() {
return N;
}
//把t元素压入栈
public void push(Object t) {
//找到首结点指向的第一个结点
Node oldFirst = head.getNext();
//创建新节点
Node newNode = new Node(t, null);
//让首结点指向新结点
head.setNext(newNode);
//让新结点指向原来的第一个结点
newNode.setNext(oldFirst);
//元素个数+1
N++;
}
//弹出栈顶元素
public String pop() {
//找到首结点指向的第一个结点
Node oldFirst=head.getNext();
if (oldFirst==null){
return null;
}
//让首结点指向原来的第一个结点的下一个结点
head.setNext(oldFirst.getNext());
//元素个数-1
N--;
return oldFirst.getData()+"";
}
}
BracketsMatchTest类
package 实验四.题目二;
public class BracketsMatchTest {
public static boolean isMatch(String str) {
//建栈
Stack chars = new Stack();
//从左到右遍历字符串
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
String currChar = str.charAt(i) + "" ;
//如果检测到左括号,压入栈中
if (currChar.equals("(")) {
chars.push(currChar);
//如果检测到右括号,从栈中弹出一个左括号
} else if (currChar.equals(")")) {
String pop = chars.pop();
if (pop == null) {
return false;
}
}
}
//栈中是否有剩余的左括号
if (chars.size() == 0){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "({[]})" ;
boolean match = isMatch(str);
System.out.println(str + " 中的括号是否配对: "+"\t");
System.out.println(match+"\t");
}
}
题目三
Node类
package 实验四.题目三;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Node {
private Object data;
Node next;
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node(Object data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
public Node() {
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return data + "" ;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Node)) return false;
Node node = (Node) o;
return Objects.equals(getData(), node.getData()) && Objects.equals(getNext(), node.getNext());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(getData(), getNext());
}
}
LinkedList类
package 实验四.题目三;
public class LinkedList {
private Node head;
public LinkedList(Node head) {
this.head = head;
}
public LinkedList() {
}
public Node getHead() {
return head;
}
public void setHead(Node head) {
this.head = head;
}
public void createList(int size) {
head = new Node();
Node temp = head;
if (size == 1) {
temp.setData(null);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if ((i < size - 1)) {
temp.setData(i);
temp.setNext(new Node());
temp = temp.getNext();
} else if (i == size - 1) {
temp.setData(i);
temp.setNext(head);
}
}
}
}
public Node get(int index) {
if (head != null) {
int count = 0;
Node tmp = head;
while (tmp.getNext() != null) {
if (count == index) {
return tmp;
}
count++;
tmp = tmp.getNext();
}
if (count == index) {
return tmp;
}
}
return null;
}
public int size() {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
} else {
Node tmp = head;
int count = 1;
while (tmp.getNext() != null) {
tmp = tmp.getNext();
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
public void delete(int num) {
Node tmp = head;
while (!tmp.getNext().getData().equals(num)) {
tmp = tmp.getNext();
}
tmp.setNext(tmp.getNext().getNext());
tmp.setData(num);
}
//置队空
public LinkedList setNull(LinkedList l) {
// l.createList(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
l.get(i).setData(null);
}
return l;
}
//进队
public void enqueue(LinkedList l, int data) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (l.get(i).getData() == null) {
l.get(i).setData(data);
break;
}
}
}
//出队
public void dequeue(LinkedList l, int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
l.delete((int) l.get(1).getData());
}
}
}
Test类
package 实验四.题目三;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList l=new LinkedList();
l.createList(5);
LinkedList l1=l.setNull(l);
for (int i=0;i<5;i++){
System.out.print(l1.get(i)+" ");
}
l1.enqueue(l1,4);
l1.enqueue(l1,5);
l1.enqueue(l1,6);
l1.enqueue(l1,7);
l1.enqueue(l1,8);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("入队之后链表里的数据为");
for (int i=0;i<5;i++){
System.out.print(l1.get(i)+" ");
}
l1.dequeue(l1,2);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("出队之后的数据为");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.print(l1.get(i)+" ");
}
}
}
实验五 树的应用(2 学时)
一、实验目的
1 、掌握二叉树的各种存储结构的特点及适用范围。
2 、掌握建立二叉树的方法。(包括顺序存储、二叉链表存储)
3 、熟练掌握二叉树的前序、中序、后序遍历的递归及非递归算法;灵活运用递归的遍历
算法实现二叉树的应用。
二、实验内容
1 、以二叉链表作存储结构,设计求二叉树高度的算法。
2 、一棵 n 个结点的完全二叉树用向量作存储结构,用非递归算法实现对该二叉树进行前
序遍历。
3 、以二叉链表作存储结构,编写非递归的前序、中序、后序遍历算法。
三、实验指导
1 、题目 1 和题目 3 要求事先建立好二叉树(以二叉链表作存储结构);题目 2 要求事先
建立好二叉树(采用顺序存储结构)。
2 、提示
( 1 )题目 1 可参考二叉树的递归遍历算法进行设计。
( 2 )题目 2 考虑是否可以借助其他辅助结构进行设计。
( 3 )题目 3 可以考虑利用栈来实现,难点在于后序遍历的非递归算法的实现(何时入栈,
如何标识何时出栈)。
四、考核标准
1 、至少完成 2 个题目,设计合理,结果正确;评定为 A
2 、完成部分题目或未按时完成,设计比较合理,结果正确;评定为 B 或 C
3 、未独立完成实验要求;评定为 D
(本单元共 3 分。只完成前两个题目最多得 2 分,高质量完成 3 个题目给 3 分,未按时
完成或算法的时间与空间复杂度过高会酌情扣分。)
五、代码实现
题目一
BinaryTree类
package 实验五.题目一;
public class BinaryTree, Value> {
private Node root;
private int N;
private class Node {
public Key key;//存储键
private Value value;//存储值
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(Key key, Value value, Node left, Node right) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
//获取树中元素个数
public int size() {
return N;
}
//向树中添加元素key-value
public void put(Key key, Value value) {
root = put(root, key, value);
}
//向指定树x中添加 key-value,并返回添加元素后的新树
private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value value) {
//如果x子树为空
if (x == null) {
N++;
return new Node(key, value, null, null);
}
//如果x子树不为空
//比较x结点的键和key的大小
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
//如果key大于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的右子树
x.right = put(x.right, key, value);
} else if (cmp < 0) {
//如果key小于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的左子树
x.left = put(x.left, key, value);
} else {
//如果key等于x结点的键,则替换x结点的值为value
x.value = value;
}
return x;
}
//查询树中指定key对应的value
public Value get(Key key) {
return get(root, key);
}
//从指定的树x中,查找key对应的值
public Value get(Node x, Key key) {
//x树为空
if (x == null) {
return null;
}
//x树不为空
//比较x结点的键和key的大小
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
//如果key大于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的右子树
return get(x.right, key);
} else if (cmp < 0) {
//如果key小于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的左子树
return get(x.left, key);
} else {
//如果key等于x结点的键,就找到了键为key的结点,只需要返回x结点的值即可
return x.value;
}
}
//获取整个树的最大深度
public int maxDepth() {
return maxDepth(root);
}
//获取指定树x的最大深度
private int maxDepth(Node x) {
if (x == null) {
return 0;
}
int max = 0;//x的最大深度
int maxL = 0;//的最大深度
int maxR = 0;//的最大深度
//计算x结点左子树的最大深度
if (x.left != null) {
maxL = maxDepth(x.left);
}
//计算x结点右子树的最大深度
if (x.right != null) {
maxR = maxDepth(x.right);
}
//比较左右子树最大深度,取最大值+1
if (maxL > maxR) {
max = maxL + 1;
} else {
max = maxR + 1;
}
return max;
}
}
BinaryTreeMaxDepthTest类
package 实验五.题目一;
public class BinaryTreeMaxDepthTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建树对象
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree<>();
//往树中添加数据
tree.put("E", "5");
tree.put("B", "2");
tree.put("G", "7");
tree.put("A", "1");
tree.put("D", "4");
tree.put("F", "6");
tree.put("H", "8");
tree.put("C", "3");
int maxDepth = tree.maxDepth();
System.out.println(maxDepth);
}
}
题目二
LinkedList类
package 实验五.题目二;
public class LinkedList {
public void preorder(int[] tree) {
int p = 0;
int k = 0;
while (k != tree.length) {
if (p < tree.length) {
System.out.println(tree[p] + " ");
p = 2 * p + 1;
k++;
} else {
p = p / 2;
if (p % 2 == 0) {
p = p / 4 - 1;
p = 2 * p + 2;
} else {
p = p + 1;
if (p >= tree.length) {
p = 2 * p + 1;
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedlist = new LinkedList();
int[] tree = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
linkedlist.preorder(tree);
}
}
题目三
BinaryTree类
package 实验五.题目三;
public class BinaryTree, Value> {
public Node root;
public int N;
public class Node {
public Key key;
public Value value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(Key key, Value value, Node left, Node right) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
public int size() {
return N;
}
public void put(Key key, Value value) {
root = put(root, key, value);
}
//向指定的树x中添加key-value,并返回添加元素后新的树
private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value value) {
if (x == null) {
N++;
return new Node(key, value, null, null);
}
//如果x子树不为空,比较x结点的键和key的大小
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp > 0) {
//如果key大于x节点的键,则继续找x节点的右子树
x.right = put(x.right, key, value);
} else if (cmp < 0) {
x.left = put(x.left, key, value);
} else {
x.value = value;
}
return x;
}
public int maxDepth() {
return maxDepth(root);
}
//获取指定树x的最大深度
private int maxDepth(Node x) {
if (x == null) {
return 0;
}
int max = 0;
int maxL = 0;
int maxR = 0;
if (x.left != null) {
maxL = maxDepth(x.left);
}
if (x.right != null) {
maxR = maxDepth(x.right);
}
max = maxL > maxR ? maxL + 1 : maxR + 1;
return max;
}
}
LinkedList类
package 实验五.题目三;
import java.util.Stack;
public class LinkedList {
/**
* @description: 前序
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/27 22:56
* @param: [root]
* @return: void
**/
static void preOrder(BinaryTree.Node root) {
if (root == null) return;
Stack s = new Stack<>();
while (!s.isEmpty() || root != null) {
while (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.value + " ");
s.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
if (!s.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTree.Node t = s.pop();
root = t.right;
}
}
}
/**
* @description: 中序
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/27 22:56
* @param: [root]
* @return: void
**/
static void inOrder(BinaryTree.Node root) {
if (root == null) return;
Stack s = new Stack<>();
while (!s.isEmpty() || root != null) {
while (root != null) {
s.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
if (!s.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTree.Node t = s.pop();
System.out.print(t.value + " ");
root = t.right;
}
}
}
/**
* @description: 后序
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/27 22:56
* @param: [root]
* @return: void
**/
static void postOrder(BinaryTree.Node root) {
if (root == null) return;
Stack s = new Stack<>();
BinaryTree.Node last = null;
while (!s.isEmpty() || root != null) {
while (root != null) {
s.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
if (!s.isEmpty()) {
BinaryTree.Node t = s.pop();
if (t.right == null || last == t.right) {//在这里面打印t并处理last之后,并不用处理root,因为之所以能进入这里,是因为root一定等于null,所以下一轮循环一定还能进入这里,然后弹出t的父结点做处理
System.out.print(t.value + " ");
last = t;
} else {//右孩子还没有打印过
s.push(t);//因为当前结点未打印,所以要重新放回去,等右孩子打印完之后回来打印
root = t.right;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree<>();
tree.put("E", "5");
tree.put("B", "2");
tree.put("G", "7");
tree.put("A", "1");
tree.put("D", "4");
//
preOrder(tree.root);
System.out.println();
//
inOrder(tree.root);
System.out.println();
//
postOrder(tree.root);
}
}
实验六 综合设计与应用一(个人项目) (6 学时)
本单元为个人综合项目,上机实现部分占 5 分,报告占 3 分,总计 8 分,共占 6 学时。
一、实验目的
1 .熟练掌握线性结构(线性表、栈、队列等)的存储方式,及在其上进行复杂操作的方
式。
2 .熟练掌握非线性结构 ---- 树形结构的存储方式,及在其上进行复杂操作的方式。
3 .提高学生设计能力以及编写综合性大实验的编程能力。
二、实验内容 (以下题目任选其中一个)
1 .表达式求值问题
2 .哈夫曼编码译码器
三、实验指导
1 . 表达式求值问题
( 1 )问题描述
表达式求值是程序设计语言编译中的一个最基本问题。人们在书写表达式时通常采用将
运算符放在两个操作数中间的“中缀”表示形式,称为中缀表达式。但是这种表达式形式对
计算机处理来说是不太适合的。在计算机领域,经常将算术表达式表示成“后缀”表示形式,
称为后缀表达式。如 : 中缀表达式 3+2*(7-5) 对应的后缀表达式为 3275-*+ 。
表达式是由操作数、运算符、界限符组成的。操作数既可以是常数,也可以是说明为变
量或常量的标示符;运算符可以分为算术运算符、关系运算符和逻辑运算符 3 类;基本界限
符有左右括号和表达式结束符等。
(2) 功能与界面要求
要求以字符序列的形式从终端输入或从文件输入语法正确的、不含变量的整数或小数表
达式,并根据输入表达式实现:① 算数四则运算中缀表达式到后缀表达式的转换;② 后缀
表达式的求值;③ 中缀表达式的求值。
要求演示在求值过程中运算符栈、操作数栈、输入字符和主要操作过程及运算结果。
在本题目中可将表达式中的操作数规定为 1 位数字字符 。也可根据个人的能力对这部分功能
进行扩充,使得操作数可以是多位数甚至是小数。
算法应该能够过滤掉输入符号之间的空格。 也可对本算法功能进行扩充,使其具有对对
输入表达式进行语法检查的功能 。
为了简化问题,运算符可只包含 + 、 - 、 * 、 / 四种基本运算,括号只有圆括号。 可根据需
要及个人能力对算法的功能进行扩充,允许有其它运算符。
本项目可使用控制台界面或可视化图形界面,若使用可视化图形界面有加分。要求配备
菜单,至少含如下选项:
------------------------------------------------------
表达式求值
1. 中缀表达式到后缀表达式的转换
2. 后缀表达式的计算
3. 中缀表达式的计算
4. 退出
-------------------------------------------------------
( 3 )数据结构要求
要求输入表达式采用字符串存储,操作数和运算符采用栈存储,待输出的表达式用队列
存储。
( 4 )算法与数据结构设计指导
① 中缀表达式到后缀表达式的转换
问题分析
若一个中缀表达式中没有括号(如 4+2*3 ,它的后缀表达式为 423*+ )。在扫描到中缀表
达式中的 2 后,能立即输出 + ,因为 * 具有较高优先级,必须先运算,因此需先保存 + 。也就是
说,新扫描运算符优先级必须与前一个运算符的优先级做比较,如果新的运算符优先级高, 就要像前一个运算符那样保存它,直到扫描到第二个操作数,将它输出后才能将该运算符输
出。因此,在转化中必须保存两个运算符,后保存的运算符先输出。用计算机来实现这个转
化过程,就需要用到能后进先出的数据结构 ---- 栈。
若在中缀表达式中含小括号,那么由于括号隔离了优先级规则,它在整个表达式的内部
产生了完全独立的子表达式。因此,前面的算法就需要有所改变。当扫描到一个左括号时,
需要将其压入栈中,使其在栈中产生一个“伪栈底”。这样算法就可以像前面一样进行。但当
扫描到一个右括号时,需要将栈中从栈顶到“伪栈底”之间的所有运算符弹出,然后再将这
个“伪栈底”删除。
数据结构与算法设计思想
顺序扫描中缀表达式, 当读到数字时, 直接将其送至 输出队列 中; 当读到运算符时 ,将
运算符 栈 中所有优先级高于或等于当前运算符的运算符弹出,送至输出队列中,再将当前运
算符入栈; 当读入左括号时, 将其入运算符栈; 当读到右括号时, 将运算符符栈中从栈顶到
靠近栈顶的第一个左括号 ( “伪栈底”)之间的所有运算符全部依次弹出,送至输出队列中,
再删除栈中的左括号。
为了简化算法,可认为扫描到的任何运算符,其优先级都比栈顶的 左括号 优先级高。为
了方便边界条件(栈空)判断,提高算法运行效率,在扫描中缀表达式之前,在空栈中预先
压入一个‘ # ’字符作为栈底元素,另外,在中缀表达式的最后增加一个‘ # ’字符作为中缀
表达式的结束标志,当扫描到结束符‘ # ’时,将栈中从栈顶到‘ # ’之间的所有运算符全部
依次弹出,送至输出队列中,再删除栈中的‘ # ’,并结束算法。
除了显示算法的运行结果外,最好能在算法运行过程中演示运算符栈和存放后缀表达式
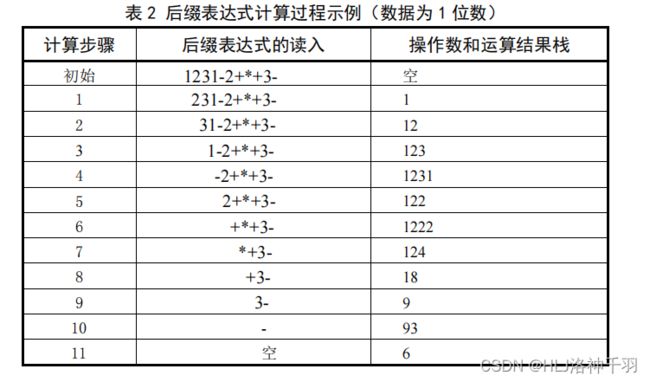
的队列的变化情况。如,若输入的中缀表达式字符串: 1+2* ( 3-1+2 ) -3# ,就会得到后缀表
达式: 1231-2+*+3- ,在算法运行过程中,运算符栈和存放后缀表达式的队列变化过程如表 1
所示。
②后缀表达式的计算
问题分析
在后缀表达式中,不仅不需要括号,而且还完全免除了运算符优先规则。后缀表达式只
需要从左到右顺序计算。
后缀表达式中可能有多个运算符,如 1231-2+*+3- ,因此必须像输入字符一样保存中间结
果。在计算后缀表达式时,最后保存的值最先取出参与运算,所以需要用 栈 来存储操作数及
中间结果。
因为在生成的后缀表达式 队列 中,存放的是字符序列,因此在算法中要有一个数字字符
到数值的转换。
数据结构与算法设计思想
利用栈(操作数和运算结果栈)计算后缀表达式。顺序扫描后缀表达式, 当读到数字时,
将其送至 栈 中; 当读到运算符 θ 时 ,将栈顶字符弹出,将其转换成对应的数值并赋给变量 y ,
再将次栈顶字符弹出,将其转换成对应的数值,并赋给变量 x ,之后计算 x θ y ,将运算结果转
换成对应的数字字符送入 栈 中。
本算法可以对任意输入的后缀表达式进行计算,也可以 以前一个中缀表达式到后缀表达
式转换算法的输出为输入,计算该后缀表达式 。
除了显示算法的运行结果外,最好能在算法运行过程中演示(操作数和运算结果)栈的
变化情况。以输入的后缀表达式为 1231-2+*+3- 的情况为例,在算法运行过程中,操作数及运
算结果栈变化过程如表 2 所示。
③中缀表达式的计算
问题分析
要把一个表达式翻译成正确求值的机器指令序列,首先要能够正确解释表达式。要对算
术表达式求值,首先要了解算术四则运算规则。即:先乘除,后加减;同级从左到右计算;
先括号内,后括号外。
例如, 1+2* ( 3-1+2 ) -3=1+2* ( 2+2 ) -3=1+2*4-3=1+8-3=9-3=6
为了简化算法,可认为扫描到的任何运算符,其优先级都比栈顶的左括号优先级高。算 符之间的优先关系如表 3 所示。
数据结构与算法设计思想
算法伪代码:
将输入的算术表达式存储到字符串 S 中;
建立并初始化操作数栈和运算符栈,并将‘#’压入运算符栈;
建立二维数组存储算术运算符的优先关系;
建立并初始化一个临时栈 T 用来处理多位数或小数;
依次(循环)读入表达式中的每个字符,存到字符变量 ch 中;
当读入的字符 ch 是操作数 ,将其入临时栈;
当读入的字符 ch 是运算符 :
将临时栈中的数据转化为整数或小数(这需要编写个函数),
并将转化后的数据入操作数栈,清空临时栈;
根据运算符栈的栈顶元素和 ch 的优先权比较结果,做不同的处理:
a)若是小于,则 ch 压入运算符栈,读入下一个字符;
b)若是大于,则弹出运算符栈顶的运算符,从操作数栈弹出两个数,进行相
应运算,将结果压入操作数栈;
c)若是等于,则运算符栈顶元素是‘(’且 ch 是‘)’,这时弹出运算符栈顶的
‘(’,相当于去括号,然后读入下一个字符;
d) 当读入的字符 ch 是‘#’ ,且运算符栈顶元素也是‘#’时,
算法结束。
除了显示最终运算结果外,最好能在算法运行过程中演示运算符栈和操作数栈的变化情
况。
( 4 )考核标准
若本实验项目占 8 分,其中 :
基本功能占 3.6 分,具体分值分布如下:
中缀表达式到后缀表达式的转换 ( 1.2 分)
后缀表达式的计算( 1.2 分)
中缀表达式的计算 (1.2 分 )
附加功能占 1.4 分,具体分值分部如下:
具有语法检查功能(含滤空格、除零异常处理、括号匹配判断等功能)。( 0.3 分)
除了用键盘输入数据外,还可以将前一个运算的结果(以指定特定文件形式)作 为下一个运算的输入。( 0.3 分)
能演示算法运行过程中运算符栈和操作数栈的变化情况。( 0.2 分)
能处理多位数、负数及小数的运算。( 0.2 分)
能实现加减乘除运算以外的其他运算。( 0.2 分)
界面友好,使用方便,最好能有图形界面。( 0.2 分)
设计报告占 3 分。
2.哈夫曼编码译码器
( 1 )问题描述
设计一个哈夫曼编码译码系统,对某个英文文本文件( .txt )中的字符进行哈夫曼编码,
并将该 txt 文件生成编码文件( .cod );反过来还可将一个编码文件( .cod )还原为一个文本文
件( .txt )。
( 2 )功能及界面要求
本题可采用 console 控制台或可视化界面, console 控制台参考界面如下:
**********************************************************************
* 哈夫曼编码译码器 *
* 1、选择需要进行编码的文件 *
* 2、建立哈夫曼树 *
* 3、建立密码本并对文件编码 *
* 4、选择需要进行解码的文件并解码 *
* 5、按位压缩方式对文件进行压缩 *
* *
**********************************************************************
功能说明:
①“选择需要进行编码的文件”:选择该选项后,提示用户输入(或选择)要进行编码(加密)
的文件(包括路径和文件名)。
②“建立哈夫曼树”: 选择该选项后,程序根据 1 中确定的文件建立哈夫曼树。
③“建立密码本并对文件编码”: 选择该选项后,程序根据 2 中建立好的哈夫曼树为 1 中出
现的每个字符建立编码,并对文件进行编码,在进行编码前提示用户将编码文件存放在哪个
文件(文件扩展名为 cod)中。
④“选择需要进行解码的文件并解码”: 选择该选项后,提示用户输入(或选择)需要进行
解码(译码)的文件(文件扩展名为 cod),并输入(或选择)将解码(译码)后的文件存放
到哪个文件(文件扩展名为 txt),程序将 cod 文件根据 3 建立的密码本进行解码,解码到 txt
文件中。
⑤“按位压缩方式对文件进行压缩”:对 cod 文件进行压缩,显示压缩比(即压缩后的编码文
件字节数/编码前的原 txt 文件字节数),并能对压缩后的 cod 文件进行解码。
( 3 )存储要求
哈夫曼树采用数组存储。
密码本在内存中采用数组存储,也可根据用户选择将密码本存到文件中。
编码文件和译码文件都采用文本文件存储。 ( 4 )数据结构与算法设计指导
①为实现功能 2 ,首先用对原 txt 文件进行扫描,得到每个字符(包括空格、标点符号和回车
换行)出现的次数,并根据教材提供的算法得到哈夫曼树。
②为实现功能 3 ,首先根据哈夫曼树及教材提供的算法得到每个出现字符的哈夫曼编码( 即
建立密码本),并对原 txt 文件重新进行扫描,扫描到某个字符时在密码本中找到该字符的哈
夫曼编码,写入到编码文件中。
③为实现功能 4 ,要扫描编码文件,扫描(读)到‘ 0 ’或‘ 1 ’时,根据哈夫曼树进行相应
的处理,直到扫描(读)到某个‘ 0 ’或‘ 1 ’后,哈夫曼树已经到达某个叶子,将该叶子对
应的字符写入到解码文件中。
④为实现功能 5 ,对编码后的 cod 文件进行处理,将每 8 个(‘ 0 ’或‘ 1 ’)字符串转化为相
应的整数(用 1 个字节存储)并写入压缩文件中,注意对最后一个 01 串(长度 <=8 )的处理。
( 5 )考核标准
若本实验项目占 8 分,其中 :
基本功能占 4 分,具体分值分布如下:
建立哈夫曼树。 ( 1 分)
产生字符 - 哈夫曼编码对照表,并显示每个字符对应的哈夫曼编 码。( 1 分)
对文件或从键盘输入的字符串进行编码,产生发送方的编码电文并显示或存
入指定的文件中。( 1 分)
接收方译码,显示译码结果或将译码结果存入指定文件。 (1 分 )
附加功能占 1 分,具体分值分部如下:
发送方按位压缩存储电文,接收方根据压缩电文解压译码,并显示压缩比。( 0.5
分)
界面友好,使用方便,最好能有可视化界面。( 0.5 分)
设计报告占 3 分。
四、代码实现
Operation类
package 实验六;
/**
* @author LiuHe
* @version 1.0
* @ClassName Operation
* @date 2023/10/27 22:26
*/
public class Operation {
/**
* @description: 写一个方法 返回对应的优先级
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/27 22:27
* @param: [operation]
* @return: int
**/
public static int get(String operation) {
int result = 0;
if ("+".equals(operation) || "-".equals(operation)) {
result = 1;
} else if ("*".equals(operation) || "/".equals(operation)) {
result = 2;
} else {
result = 0;
}
return result;
}
}
SuffixExpression类
package 实验六;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
public class SuffixExpression {
public static List zhongZhuiList(String s) {
/**
* @description: 先将中缀表达式转 换成list集合
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:05
* @param: [s]
* @return: java.util.List
**/
List list = new ArrayList<>();
String str;//用于拼接多位数
char c;//每遍历到一个字符,就放入到c
int i = 0;//指针,用于遍历中缀表达式
do {
//先判断是不是运算符
if ((c = s.charAt(i)) < 48 || (c = s.charAt(i)) > 57) {//ASCII码48~57为0到9十个阿拉伯数字
list.add(c + "");
i++;
} else {//是数字,需要考虑多位数
str = "";
while (i < s.length() && (c = s.charAt(i)) >= 48 && (c = s.charAt(i)) <= 57) {
str = str + c;
i++;
}
list.add(str);
}
} while (i < s.length());
return list;
}
/**
* @description: 将得到的中缀表达式对应的list转换成后缀表达式对应的list
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:04
* @param: [list]
* @return: java.util.List
**/
public static List houZhuiList(List list) {
Stack s1 = new Stack<>();
List s2 = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历中缀表达式集合
for (String item : list) {
//如果是一个数字,加入到s2
if (item.matches("\\d+")) {//matches() 方法用于检测字符串是否匹配给定的正则表达式
s2.add(item);
} else if (item.equals("(")) {
s1.push(item);
} else if (item.equals(")")) {
//如果是右括号,则依次弹出s1栈顶的运算符,并压入s2,直到遇到左括号为止,此时将这对括号丢弃
while (!s1.peek().equals("(")) {
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
s1.pop();//将(弹出s1
} else {
//当item的优先级小于等于s1栈顶运算符的优先级时,将s1栈顶的运算符弹出并压入到s2
while (s1.size() != 0 && Operation.get(s1.peek()) >= Operation.get(item)) {
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
s1.push(item);//还需要将item压入栈
}
}
while (s1.size() != 0) {//将s1中剩余的运算符依次弹出并加入s2
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
return s2;
}
/**
* @description: 计算中缀表达式
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:05
* @param: [list]
* @return: java.util.List
**/
public static List calzhongZhui(List list) {
Stack s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack num = new Stack<>();
List s2 = new ArrayList<>();
for (String item : list) {
if (item.matches("\\d+")) {
num.push(item);
} else if (item.equals("(")) {
s1.push(item);
} else if (item.equals(")")) {
while (!s1.peek().equals("(")) {
cal2(s1, num);
s1.pop();
}
s1.pop();
} else {
while (s1.size() != 0 && Operation.get(s1.peek()) >= Operation.get(item)) {
cal2(s1, num);
s1.pop();
}
s1.push(item);
}
}
while (s1.size() != 0) {
cal2(s1, num);
s1.pop();
}
s2.add(num.pop());
return s2;
}
public static Stack cal2(Stack s1, Stack s2) {
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(s2.pop());
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(s2.pop());
int res = 0;
if (s1.peek().equals("+")) {
res = num1 + num2;
} else if (s1.peek().equals("-")) {
res = num1 - num2;
} else if (s1.peek().equals("*")) {
res = num1 * num2;
} else if (s1.peek().equals("/")) {
res = num1 / num2;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("运算符有错误");
}
//把计算结果入栈
s2.push(res + "");
return s2;
}
/**
* @description: 完成对后缀表达式的运算
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/28 20:07
* @param: [list]
* @return: int
**/
public static int cal(List list) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
//遍历list
for (String p : list) {
//使用正则表达式来取数
if (p.matches("\\d+")) {//匹配的是多位数
stack.push(p);//如果是数字,则入栈,如果是符号则进行运算
} else {
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int res = 0;
if (p.equals("+")) {
res = num1 + num2;
} else if (p.equals("-")) {
res = num1 - num2;
} else if (p.equals("*")) {
res = num1 * num2;
} else if (p.equals("/")) {
res = num1 / num2;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("运算符有错误");
}
//把计算结果入栈
stack.push(res + "");
}
}
return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "1+((2+3)*4)-5";
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("中缀表达式转成后缀表达式:");
List list = houZhuiList(zhongZhuiList(s));
for (String str : list) {
System.out.print(str + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("计算后缀表达式:");
System.out.println(cal(houZhuiList(zhongZhuiList(s))));
System.out.println("计算中缀表达式:");
List strings = calzhongZhui(zhongZhuiList(s));
for (String string : strings) {
System.out.println(string);
}
}
} 实验七 图的应用(2 学时)
一、实验目的
1 、掌握图的各种存储结构的特点及适用范围。
2 、掌握建立图的方法。(包括邻接矩阵、邻接表)
3 、熟练掌握图的深度优先搜索算法和广度优先搜索算法,并能灵活运用这两个算法解决
实际问题。
二、实验内容
1. 在图中求一条从顶点 i 到顶点 j 的简单路径。
2. 在图中求从顶点 i 到顶点 j 的最短路径。
三、实验指导
实现上述两个功能时要求图分别用邻接矩阵和邻接表表示。
求简单路径问题,可利用图得深度优先搜索遍历算法实现,从顶点 i 出发,开始遍历,访
问到顶点 j 时遍历结束。在遍历的过程中,需要将访问过的顶点压入栈,当在遍历过程中遇
到一个访问过的顶点 k 时,需要依次删除栈中元素,直到栈顶为 k 。遍历结束后,将栈中的
顶点倒着输出即为顶点 i 到顶点 j 的简单路径。 求最短路径问题,可利用图得广度优先搜索遍历算法实现,为实现图得广度优先搜索算法,
需要用到队列。
四、考核标准
1 、完成全部题目,设计合理,结果正确;评定为 A
2 、完成部分题目或未按时完成,设计比较合理,结果正确;评定为 B 或 C
3 、未独立完成实验要求;评定为 D
(本单元共 3 分。未按时完成或算法的时间与空间复杂度过高会酌情扣分。)
五、代码实现
first
Queue类
package 实验七.first;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Queue implements Iterable {
private Node head;
private Node last;
private int N;
private class Node {
public T item;
public Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
public Queue() {
this.head = new Node(null, null);
this.last = null;
this.N = 0;
}
public Queue(Node head, Node last, int n) {
this.head = head;
this.last = last;
N = n;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N == 0;
}
public int size() {
return N;
}
public void enqueue(T t) {
if (last == null) {
last = new Node(t, null);
head.next = last;
} else {
Node oldLast = last;
last = new Node(t, null);
oldLast.next = last;
}
N++;
}
public T dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Node oldFirst = head.next;
head.next = oldFirst.next;
N--;
if (isEmpty()) {
last = null;
}
return oldFirst.item;
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new QIterator();
}
private class QIterator implements Iterator {
private Node n;
private QIterator() {
this.n = head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next != null;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
n = n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
} Graph类
package 实验七.first;
public class Graph {
private final int v;//顶点数目
private int e;//边的数目
private Queue[] adj;//邻接表
public Graph(int v) {
this.v = v;//初始化顶点数目
this.e = 0;//初始化边的数目
this.adj = new Queue[v];//初始化邻接表
for (int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++) {
adj[i] = new Queue();
}
}
//获取顶点数目
public int V() {
return v;
}
//获取边的数目
public int E() {
return e;
}
//向图中添加一条边v-w
public void addEdge(int v, int w) {
adj[v].enqueue(w);
adj[w].enqueue(v);
//边的数量+1
e++;
}
//获取和顶点v相邻的所有顶点
public Queue adj(int v) {
return adj[v];
}
} DepthFirstPaths类
package 实验七.first;
import java.util.Stack;
public class DepthFirstPaths {
//索引代表顶点,值表示当前顶点是否已经被搜索
private boolean[] marked;
//起点
private int s;
//索引代表顶点,值代表从起点s到当前顶点路径上的最后一个顶点
private int[] edgeTo;
//构造深度优先搜索对象,使用深度优先搜索找出G图中起点为s的所有路径
public DepthFirstPaths(Graph g, int s) {
//初始化marked数组
this.marked = new boolean[g.V()];
//初始化起点
this.s = s;
//初始化edgeTo数组
this.edgeTo = new int[g.V()];
dfs(g, s);
}
//使用深度优先搜索找出G图中v顶点的所有相邻顶点
private void dfs(Graph g, int v) {
//把v顶点标识为已搜索
marked[v] = true;
//遍历顶点v的邻接表,拿到每一个相邻的顶点,继续递归搜索
for (Integer w : g.adj(v)) {
//如果顶点w没有被搜索,则继续递归搜索
if (!marked[w]) {
edgeTo[w] = v;//到达顶点w的路径上的最后一个顶点是v
dfs(g, w);
}
}
}
//判断w顶点与s顶点是否存在路径
public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
return marked[v];
}
//找出从起点s到顶点v的路径(就是该路径经过的顶点)
public Stack pathTo(int v) {
if (!hasPathTo(v)) {
return null;
}
//创建栈对象,保存路径中的所有顶点
Stack path = new Stack<>();
//通过循环,从顶点v开始,一直往前找直到找到起点为止
for (int x = v; x != s; x = edgeTo[x]) {
path.push(x);
}
path.push(s);
return path;
}
}
DepthFirstPathsTest类
package 实验七.first;
import java.util.Stack;
public class DepthFirstPathsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
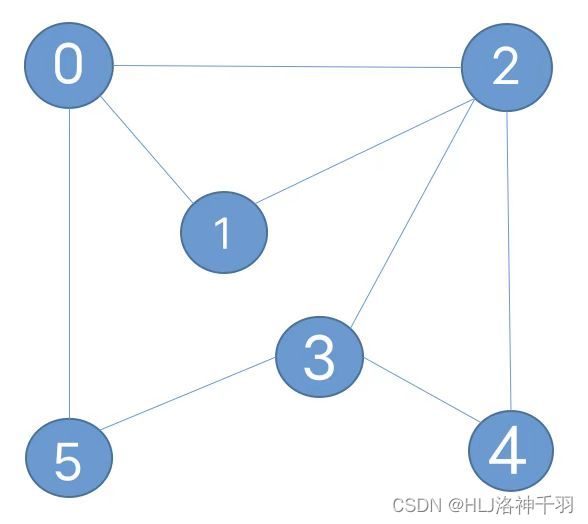
Graph graph = new Graph(6);
graph.addEdge(0, 2);
graph.addEdge(0, 1);
graph.addEdge(2, 1);
graph.addEdge(2, 3);
graph.addEdge(2, 4);
graph.addEdge(3, 5);
graph.addEdge(3, 4);
graph.addEdge(0, 5);
DepthFirstPaths paths = new DepthFirstPaths(graph, 0);
Stack path = paths.pathTo(4);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (!path.empty()) {
// System.out.print(path.pop()+"-");
sb.append(path.pop()).append("-");
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
two
GraphBfs类
package 实验七.two;
import java.util.*;
public class GraphBfs {
private Map> adjList = new HashMap<>();//key是编号 value是邻居
LinkedList list = new LinkedList<>();
/**
* @description: 初始化图
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/27 22:44
* @param: []
* @return: void
**/
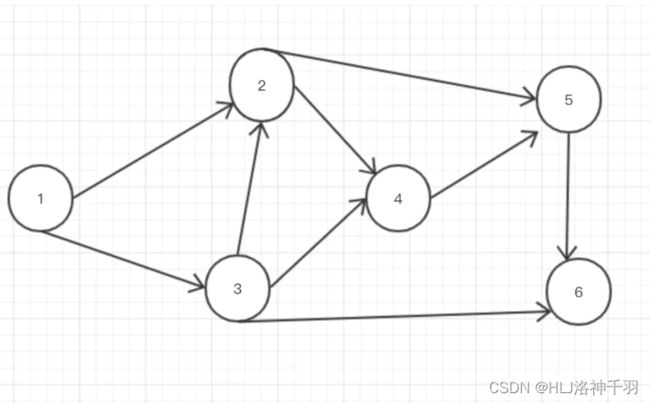
public void createGraph() {
List l1 = new LinkedList<>();
l1.add(2);
l1.add(3);
List l2 = new LinkedList<>();
l2.add(4);
l2.add(5);
List l3 = new LinkedList<>();
l3.add(4);
l3.add(6);
List l4 = new LinkedList<>();
l4.add(5);
List l5 = new LinkedList<>();
l5.add(6);
List l6 = new LinkedList<>();
this.adjList.put(1, l1);
this.adjList.put(2, l2);
this.adjList.put(3, l3);
this.adjList.put(4, l4);
this.adjList.put(5, l5);
this.adjList.put(6, l6);
}
/**
* @description: 广度优先 寻找最短路径
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/27 22:44
* @param: [startId, endId]
* @return: void
**/
public void bfs(int startId, int endId) {
Queue waitSearchQueue = new LinkedList<>();//等待被搜索的队列
Map visitedList = new HashMap<>(); //访问过的节点列表
waitSearchQueue.offer(new Node(startId, -1));//将开始节点入队
while (!waitSearchQueue.isEmpty()) {//队列不空
Node currentNode = waitSearchQueue.poll();//从队列头弹出
System.out.println("当前目标:" + currentNode.id);
if (currentNode.id == endId) {//如果找到了
System.out.println("找到目标:" + currentNode.id);
printPath(currentNode, visitedList); //打印出来路径
return;
}
if (visitedList.containsKey(currentNode.id)) { //如果搜索过的就不第二次搜索了
continue;
}
//将当前节点的邻居都入队
for (int i = 0; i < this.adjList.get(currentNode.id).size(); i++) {
int nodeId = this.adjList.get(currentNode.id).get(i);
//如果访问过的就不用入队了。入队的话parentId就错了
if (!visitedList.containsKey(nodeId)) {
waitSearchQueue.offer(new Node(nodeId, currentNode.id));
}
}
//标示当前节点访问过了
visitedList.put(currentNode.id, currentNode);
}
System.out.println("没有路径");
}
/**
* @description: 打印出路径
* @author: LiuHe
* @date: 2023/10/27 22:43
* @param: [targetNode, visitList]
* @return: void
**/
public void printPath(Node targetNode, Map visitList) {
int parentId = targetNode.parentId;
while (parentId != -1) {
int id = visitList.get(parentId).id;
parentId = visitList.get(parentId).parentId;
list.add(id);
}
ListIterator it = list.listIterator(list.size());
while (it.hasPrevious()) {
Object O = it.previous();
System.out.print(O + "-->");
}
System.out.print(targetNode.id);
}
//每一个节点的抽象 这里只存储id
static class Node {
private final int id;
private final int parentId;
public Node(int id, int parentId) {
this.id = id;
this.parentId = parentId;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphBfs g = new GraphBfs();
g.createGraph();
g.bfs(1, 5);
}
}
实验八 综合设计与应用二(团队项目)(4 学时)
本单元为团队项目,系统设计与实现占 3 分, PPT、答辩情况、团队合作、创新性、实
用性占 2 分,总计 5 分。
一、实验目的
综合运用所学的数据结构与算法实现一个小系统。
二、实验内容
1 .校园导游系统 ( 求最短路径算法 : Dijkstra,Floyd)
2 .最小生成树模拟程序 ( 求最小生成树算法 : Prim 、 Kruskal)
3 .迷宫问题模拟程序(栈、队列、堆的应用,各种树形搜索算法)
4 .内部排序性能分析演示程序(各种排序算法)
5 .通讯录管理系统的设计与实现(各种查找算法)
6 . (拓扑排序算法)
7. 自选题目
三、实验指导
1.校园导游系统
( 1 )问题描述
设计一个校园导游程序,为来学校的用户提供景点信息及路径查询服务。
( 2 )功能及界面要求
本题可采用 console 控制台或可视化界面, console 控制台参考界面如下:
**********************************************************************
* 校园导游程序 *
* *
* 这段区域显示各顶点的编号、名称并画出校园地图 *
* *
* 1、景点信息查询 *
* 2、校门口到其他景点的路经查询(单源最短路径) *
* 3、校园各景点间的路经查询(各顶点对间最短路径) *
* *
********************************************************************* 功能说明 :
① “景点信息查询”
系统为来访客人提供图中任意景点相关信息的查询功能。
用户选择该选项后,提示用户输入要查询的景点编号,根据景点编号显示出该景点的名
称和简介。
② “校门口到其他景点的路经查询”
系统为来访客人提供从校门口到图中任意景点的问路查询功能。
用户选择该选项后,提示用户输入要到达的景点编号,根据该景点编号显示出从校门口到
该景点的最短路径长度及路径信息(即路径上的顶点序列)
③ “校园各景点间的路经查询”
系统为为来访客人提供图中任意景点间的问路查询;
用户选择该选项后,提示用户输入起点编号及终点编号,根据起点和终点编号确定起点到
终点的最短路径及长度并直观显示。
( 3 )数据结构要求
校园地图中的景点信息采用一维结构体数组存储,各条边的信息采用邻接矩阵存储。
路径采用栈或队列存储。
( 4 )数据结构与算法设计指导
①设计学校的校园平面图(有向图,任意两点间的去边和回边长度相等),所含景点不少
于 10 个,以图中顶点表示校内各景点,存放景点名称、代号、简介等信息,以边表示路径,
存放路径长度等相关信息。
②利用教材上建立图的邻接矩阵的算法实现图的存储。
③根据查找算法实现功能 1。
④根据迪杰斯特拉算法和教材上的参考程序实现功能 2。
⑤根据弗洛伊德算法和教材上的参考程序实现功能 3。
( 5 )考核标准
系统设计与实现占 3 分, PPT 、答辩情况、团队合作、创新性、实用性等占 2 分,总计
5 分。
2.最小生成树模拟程序
( 1 )问题描述
已知一个无向连通网表示 n 个城市以及城市间可能设置的通信线路,其中网的顶点表示
城市,边表示两个城市之间的线路,赋于边上的权值表示相应的代价。对于 n 个点的连通网
可以建立许多不同的生成树,每一棵生成树都可以是一个通信网。现在,我们要选择这样一
棵生成树,使总的耗费最小,即构造连通网的最小生成树。
( 2 )功能及界面要求
本题可采用 console 控制台或可视化界面, console 控制台参考界面如下:
**********************************************************************
* 最小生成树模拟程序 *
* *
* 这段区域可以显示出一个设计好的无向连通网络 *
* *
* *
* 1、普里姆(Prim)算法构造最小生成树 *
* 2、克鲁斯卡尔(Kruscal)算法构造最小生成树 *
* *
*********************************************************************
功能说明:
① 提示用户输入起点编号,根据普里姆(Prim)算法构造出最小生成树,按顺序显示选出的
各条边,把构造出的最小生成树直观显示出来,并显示出该最小生成树上各边权值之和。
② 根据克鲁斯卡尔(Kruscal)算法构造出最小生成树,按顺序显示选出的各条边,把构造
出的最小生成树直观显示出来,并显示出该最小生成树上各边权值之和。
( 3 )数据结构要求
无向连通图采用邻接矩阵存储。
最小生成树采用一维结构体数组存储(边)。
实现 Kruskal 算法时,最好用并查集实现,并用树形结构存储并查集。
( 4 )数据结构与算法设计指导
① 设计无向连通图(顶点数不小于 6)并存储。
③ 根据邻接矩阵和教材中相应的算法实现功能 1。
③ 根据邻接矩阵和教材中相应的算法实现功能 2。
( 5 )考核标准
系统设计与实现占 3 分, PPT 、答辩情况、团队合作、创新性、实用性等占 2 分,总计
5 分。
3.迷宫问题模拟程序
( 1 ) 问题描述
老鼠走迷宫是心理学中的一个经典试验。设有一只无盖大箱,箱中设置一些隔断,形成
弯弯曲曲的通道作为迷宫,如图 1 。箱子还设有一个入口和一个出口。试验时,先在出口处
放一些奶酪之类的可以吸引老鼠的东西,然后将一只老鼠放到入口处,这样,老鼠受到美味
的吸引,向着出口走去。心理学家就观察老鼠如何由入口到达出口。
这个试验可以用来考查老鼠记忆力的强弱。如果它记忆力很好,那么在迷宫中对先前尝
试过的失败路径就不会再去尝试。
( 2 )功能及界面要求
设计一个模拟小动物走迷宫的程序,为小动物寻找一条从迷宫入口到迷宫出口的通路。
最好能以高运行效率找到一条从入口到出口的最短路径。假设老鼠具有稳定记忆力,能记住
以前走过的失败路径,而不会重蹈覆辙。
要求:
用户可以设置迷宫的行数或列数。
随机产生迷宫的状态。
用户设置小动物的入口下标和出口下标。
根据迷宫状态和入、出口位置直观显示出从入口到出口的通路或“不存在通路”的信
息。最好能将所设置的整个迷宫的状态也显示出来。
( 3 )数据结构要求
迷宫采用二维数组存储。
通路上的各个坐标可用队列或栈存储。
( 4 )数据结构与算法设计指导
整个算法分为四个子算法:迷宫生成算法;搜索路径算法;输出路径算法;恢复迷宫算
法。其中路径搜索算法可以基于广度优先搜索,也可以基于深度优先搜索(即回溯法) , 也可
以基于其它优化搜索策略(如: A* 算法、爬山法等),以提高搜索效率。如果按照深度优先
搜索(回溯法),找到的路径并不一定是最短的。如果要找到一条从入口到出口的最短路径,
就得采用广度优先搜索。
① 基于广度优先搜索迷宫问题求解方法指导
迷宫的表示及迷宫的生成算法
在平面图上迷宫是由一些小方格组成的,所以可以用一个 maze[m][n] 来表示迷宫,数组
的每个元素 maze[i][j] 的值取 0 或 1 ,取 0 表示此路可通,取 1 表示此路不通。不失一般性,
若设迷宫入口是 maze[1][1] ,出口是 maze[m][n] ,且 maze[1][1]=0 , maze[m][n]=0 。一个迷宫
的示意图如图 2 所示。
( 3 )数据结构要求
采用顺序存储的线性表。
( 4 )算法设计指导
在各种排序算法中增加比较次数和移动次数的统计功能。
需要设计一个逆置算法,将正序表变成逆序表。
需要设计一个算法,产生 n 个随机数 (n 是用户指定的元素个数 ) 。
( 5 )考核标准
系统设计与实现占 3 分, PPT 、答辩情况、团队合作、创新性、实用性等占 2 分,总
计 5 分。
通讯录管理系统的设计与实现
(1) 问题描述
设计与实现一个通讯录管理系统,实现按姓名、电话号、 QQ 号查找。
(2) 功能及界面要求
要求能够管理通讯录,即具有通讯录的建立、增、删、改记录功能;
要求实现在指定通讯录中按姓名、电话号、 QQ 号查找功能。
本题可采用控制台界面,若能用可视化界面更好。控制台参考界面(一级界面)如下:
************************************************
* 通 讯 录 管 理 系 统 *
* *
* 1. 通讯录编辑 *
* 2. 通讯录查找 *
* 3. 退出 *
************************************************
控制台参考界面(通讯录管理子系统二级界面)如下:
************************************************
* 通讯录编辑子系统 *
* *
* 1. 建立通讯录并录入记录 *
* 2. 增加记录 *
* 3. 删除记录 *
* 4. 修改记录 *
* 5. 返回主菜单 *
***********************************************
对应功能说明:
① 从无到有建立一个通讯录,以文件形式存储。在建立通讯录的同时允许录入记录。
② 在通讯录(文件)尾部增加若干记录。
③ 通过姓名找到指定记录,删除指定记录。
④ 通过姓名找到指定记录,修改该记录后保存到文件。
控制台参考界面(通讯录查找子系统二级界面)如下:
************************************************
* 通讯录查找子系统 *
* *
* 1. 按姓名查找(散列表查找) *
* 2. 按电话号查找(二叉排序树查找) *
* 3. 按 QQ 号查找(二分查找) *
* 4. 返回主菜单 *
************************************************ 对应功能说明:
① 读指定文件内容,以用户名为关键字建立 散列表 ,要求完成下列功能:
采用一定的方法解决冲突;
查找并显示给定用户的记录;
设计不同的散列函数,比较冲突率;在散列函数确定的前提下,尝试各种不同处理冲突
的方法,考察平均查找长度的变化。
②读指定文件内容,以电话号码为关键字建立 二叉排序树 。在二叉排序树上查找并显示
给定电话号码的记录。
③对从键盘输入的各记录,以 QQ 号为关键字建立 有序表 。在有序表上二分查找并显示
给定 QQ 号的记录。
(3) 数据结构要求
可分别用散列表、二叉排序树、有序表等存储通讯录,若能用 键树 、 B 树 、 B+ 树 等存储
通讯录更好。每个记录至少有下列数据项:姓名、手机号、 QQ 号、单位、地址。
(4) 数据结构与算法设计指导
具体数据结构与算法设计方法见教材。
(5) 考核标准
系统设计与实现占 3 分, PPT 、答辩情况、团队合作、创新性、实用性等占 2 分,总计
5 分。
6. 教学计划编制系统的设计与实现
(1) 问题描述
大学的专业都要指定教学计划。假设任何专业都有固定的学习年限,每学年含两学期,
每学期的时间长度和学分上限值均相等。每个专业开设的课程都是确定的,而且课程开设时
间安排必须满足先修关系。每门课程有哪些先修课程是确定的,可以有任意多门,也可以没
有。每门课程恰好占 1 学期。在这样的前提下设计与实现一个教学计划编制系统。
(2) 功能与界面要求
输入:学期总数,学分上限,专业开设课程门数,每门课程的编号(整型)、课程名称、学分,
先修关系(用课程编号序对给出)。
输出:教学计划。
( 3 )数据结构要求
要求用图表示课程及课程间先修关系。
(4)数据结构与算法设计指导
可设学期总数不超过 10 ,课程总数不超过 50 。如果输入的先修课程号不在该专业开设
的课程序列中,则作为错误处理。
可用拓扑排序算法先将该专业的课程进行拓扑排序,然后按拓扑序列将课程分配到各个
学期,每学期开设的课程不能超过学分上限。
(4)考核标准
系统设计与实现占 3 分, PPT 、答辩情况、团队合作、创新性、实用性等占 2 分,总计 5
分。
四、代码实现
PrimTree类
package 实验八;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class PrimTree {
public void t1() {
char[] vertex = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G'};
int vertexSize = vertex.length;
int[][] edges = {
{0, 7, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0},
{7, 0, 8, 9, 7, 0, 0},
{0, 8, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0},
{5, 9, 0, 0, 15, 6, 0},
{0, 7, 5, 15, 0, 8, 9},
{0, 0, 0, 6, 8, 0, 11},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 9, 11, 0}
};
//生成一个图
Graph graph = new Graph(vertexSize);
//最小生成树
MinTree minTree = new MinTree();
minTree.createGraph(graph, vertexSize, vertex, edges);
//显示邻接矩阵
minTree.showGraph(graph);
//显示路径
minTree.prim(graph, 3);
}
static class MinTree {
//生成一个邻接矩阵
/* graph 图对象
* vertexSize 图中顶点个数
* vertex 图中顶点值
* edges 图权值(邻接矩阵)
*/
public void createGraph(Graph graph, int vertexSize, char[] vertex, int[][] edges) {
for (int i = 0; i < vertexSize; i++) {
graph.vertex[i] = (char) vertex[i];
for (int j = 0; j < vertexSize; j++) {
graph.edges[i][j] = edges[i][j];
}
}
}
public void showGraph(Graph graph) {
for (int[] edge : graph.edges) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(edge));
}
}
/*
* graph 一个图
* v 当前我们开始顶点的下标
*/
public void prim(Graph graph, int v) {
//用来标记当前顶点是否被访问
int[] visited = new int[graph.vertexSize];
//当前顶点记录成访问
visited[v] = 1;
//用于记录存放未被遍历的顶点中与已被遍历顶点的最小权值的顶点
int minV = -1;
int minI = -1;
//寻找最小权值并记录 默认为无穷大
int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//循环遍历k个顶点
for (int k = 1; k < graph.vertexSize; k++) {
//我们需要确定每一次生成子图中最短一条路径并记录
for (int i = 0; i < graph.vertexSize; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < graph.vertexSize; j++) {
if (visited[i] == 1 && visited[j] == 0 && graph.edges[i][j] != 0 && graph.edges[i][j] < minDistance) {
//找到当前子图最小路径并记录
minDistance = graph.edges[i][j];
//记录最小路径的下标
minV = i;
minI = j;
}
}
}
System.out.println(graph.vertex[minV] + "-->" + graph.vertex[minI] + " " + minDistance);
visited[minI] = 1;
minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
}
static class Graph {
int vertexSize;//存放顶点个数
char[] vertex;//存放顶点的数据
int[][] edges;//存放权值
public Graph(int vertexSize) {
this.vertexSize = vertexSize;
this.vertex = new char[vertexSize];
this.edges = new int[vertexSize][vertexSize];
}
}
}
KruskalTree类
package 实验八;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class KruskalTree {
public void t2() {
char[] vertexes = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G'};
int vertexSize = vertexes.length;
int[][] edges = {
{0, 7, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0},
{7, 0, 8, 9, 7, 0, 0},
{0, 8, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0},
{5, 9, 0, 0, 15, 6, 0},
{0, 7, 5, 15, 0, 8, 9},
{0, 0, 0, 6, 8, 0, 11},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 9, 11, 0}
};
//创建一个图
Graph graph = new Graph(vertexSize);
//定义KruskalMinTree
KruskalMinTree kruskalMinTree = new KruskalMinTree();
//初始化参数
int edgeNum = kruskalMinTree.createGraph(graph, vertexSize, vertexes, edges);
//遍历我们的邻接数组
kruskalMinTree.showGraph(graph);
//输出边
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(kruskalMinTree.getEdges(edgeNum, vertexes, edges)));
kruskalMinTree.Kruskal(edgeNum, vertexes, edges);
}
static class KruskalMinTree {
public int createGraph(Graph graph, int vertexSize, char[] vertexes, int[][] edges) {
int edgeNum = 0;
//初始化 vertexes edges
for (int i = 0; i < vertexSize; i++) {
graph.vertexes[i] = vertexes[i];
for (int j = 0; j < vertexSize; j++) {
graph.edges[i][j] = edges[i][j];
}
}
//找到所有边数
for (int i = 0; i < vertexSize; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < vertexSize; j++) {
if (edges[i][j] != 0) {
edgeNum++;
}
}
}
return edgeNum;
}
public void showGraph(Graph graph) {
for (int[] edge : graph.edges) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(edge));
}
}
/**
* @param ch 传入的顶点
* @param vertexes 字符数组
* @return 给一个字符,如果找到,返回相应的下标,反之,返回-1
*/
public int getPosition(char ch, char[] vertexes) {
for (int i = 0; i < vertexes.length; i++) {
if (vertexes[i] == ch) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* @param edgeNum 边的数目
* @param vertexes 字符数组
* @param edges 权值
* @return 返回 Edge{ start=A end=D weight=5 }
*/
public Edge[] getEdges(int edgeNum, char[] vertexes, int[][] edges) {
int index = 0;
//存放边的数组 Edge{ start=A end=D weight=5 }
Edge[] edge = new Edge[edgeNum];
for (int i = 0; i < vertexes.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < vertexes.length; j++) {
if (edges[i][j] != 0) {
edge[index++] = new Edge(vertexes[i], vertexes[j], edges[i][j]);
}
}
}
return edge;
}
/**
* @param ends 对应终点数组
* @param i 起点下标
* @return
*/
public int getEnd(int[] ends, int i) {
while (ends[i] != 0) {
i = ends[i];
}
return i;
}
/**
* @param edgeNum 边的数目
* @param vertexes 字符数组
* @param edges 权值
*/
public void Kruskal(int edgeNum, char[] vertexes, int[][] edges) {
//当前结果序列的索引
int index = 0;
//存放结果数组
Edge[] rets = new Edge[edgeNum];
//存放每个顶点在最小生成树中的终点
int[] ends = new int[edgeNum];
//边的序列
Edge[] edge = getEdges(edgeNum, vertexes, edges);
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(edge));
Arrays.sort(edge);
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(edge));
//判断是否形成回路
for (int i = 0; i < edgeNum; i++) {
// 给一个字符,如果找到,返回相应的下标,反之,返回-1
//拿到第一个顶点的起始位置
int p1 = getPosition(edge[i].start, vertexes);
//拿到第一个顶点的终点位置
int p2 = getPosition(edge[i].end, vertexes);
//拿到第一个顶点的起始位置的终点
int m = getEnd(ends, p1);
//拿到第一个顶点的终点位置的终点
int n = getEnd(ends, p2);
if (m != n) {
ends[m] = n;
rets[index++] = edge[i];
}
}
System.out.println("最小生成树");
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
System.out.println(rets[i]);
}
}
}
static class Edge implements Comparable {
char start;//边的起始位置
char end;//边的结束位置
int weight;//权值
public Edge(char start, char end, int weight) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Edge{" +
"start=" + start +
", end=" + end +
", weight=" + weight +
'}';
}
}
static class Graph {
int vertexSize;//存放顶点个数
char[] vertexes;//存放顶点的数据
int[][] edges;//存放权值
public Graph(int vertexSize) {
this.vertexSize = vertexSize;
this.vertexes = new char[vertexSize];
this.edges = new int[vertexSize][vertexSize];
}
}
}
Test类
package 实验八;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
PrimTree primTree = new PrimTree();
KruskalTree kruskalTree = new KruskalTree();
int option;
while (true){
System.out.println("***********************************************");
System.out.println("* 1、普里姆(Prim)算法构造最小生成树 *");
System.out.println("* 2、克鲁斯卡尔(Kruskal)算法构造最小生成树 *");
System.out.println("* 3、退出 *");
System.out.println("************************************************");
option=scanner.nextInt();
switch (option) {
case 1:
primTree.t1();
continue;
case 2:
kruskalTree.t2();
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("成功退出!");
System.exit(0);
default:
}
}
}
}
实验九 排序和查找(2 学时)
一、实验目的
1 、掌握快速排序和二路归并排序的实现方法。
2 、掌握二叉排序树的建立过程以及二叉排序树上的基本操作。
二、实验内容
1 、随机生成若干个正整数,分别使用快速排序算法和二路归并排序算法对这些数据进行
排序。
2 、根据随机生成的正整数序列建立二叉排序树,在二叉排序树上进行插入、查找及删除
等操作。
三、实验指导
1 、题目 1 可以使用一维整型数组存储待排序的数据;要求随机生成 3 组数据,每组数据
的整数个数和取值范围由用户输入,对每组数据要求输出两种排序算法的排序结果、比较次
数及移动次数。
2 、题目 2 的二叉排序树使用二叉链表存储,要求随机生成若干个正整数,正整数的个数
和取值范围由用户输入,用户可以根据菜单进行各种操作,例如 :
1 —建立 2 —输出【中序遍历】 3 —插入 4 —查找【要求输出比较次数】 5 —删除 0 —退出
3 、提示:
( 1 )题目 1 可参考教材中关于快速排序算法和二路归并排序算法的思想和实现过程加以
完善来实现。
( 2 )题目 2 可参考教材中关于二叉排序树的建立、插入、删除及删除的思想和实现过程
加以自己的设计和整合并实现。
四、考核标准
1 、完成全部题目,设计合理,结果正确;评定为 A
2 、完成部分题目或未按时完成,设计比较合理,结果正确;评定为 B 或 C
3 、未独立完成实验要求;评定为 D
(本实验共 2 分。一个实验题目 1 分,未按时完成或算法的时间与空间复杂度过高也会酌情
扣分。)
五、代码实现
二叉排序树
BinarySearchTree类
package 实验九.二叉排序树;
public class BinarySearchTree {
private int data;
private BinarySearchTree left;
private BinarySearchTree right;
public BinarySearchTree() {
}
public BinarySearchTree(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public BinarySearchTree getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(BinarySearchTree left) {
this.left = left;
}
public BinarySearchTree getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(BinarySearchTree right) {
this.right = right;
}
}
BinarySearchTreeOpts类
package 实验九.二叉排序树;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BinarySearchTreeOpts {
static BinarySearchTree root;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("************************");
System.out.println("* 1—建立 *");
System.out.println("* 2—输出 *");
System.out.println("* 3—插入 *");
System.out.println("* 4—查找 *");
System.out.println("* 5—删除 *");
System.out.println("* 0—退出 *");
System.out.println("************************");
while (true) {
System.out.println("请选择:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int option = scanner.nextInt();
switch (option) {
case 1://建立
Random random = new Random();
int[] dataS = new int[7];
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
int randNum = random.nextInt(90) + 10;
dataS[i] = randNum;
}
System.out.println("随机数据:" + Arrays.toString(dataS));
for (int data : dataS) {
insert(data);
}
break;
case 2://输出
System.out.println("中序遍历输出:");
mid(root);
System.out.println();
break;
case 3://插入
System.out.println("请输入要插入的数据:");
int in = scanner.nextInt();
insert(in);
break;
case 4://查找
System.out.println("请输入要查找的数据:");
int fn = scanner.nextInt();
find(fn);
break;
case 5://删除
System.out.println("请输入要删除的数据:");
int rn = scanner.nextInt();
remove(rn);
break;
case 0://退出
System.exit(0);
default:
System.out.println("请重新选择!");
}
}
}
//插入
public static void insert(int data) {
if (root == null) {
root = new BinarySearchTree(data);
return;
}
BinarySearchTree node = root;
while (node != null) {
if (data < node.getData()) {
if (node.getLeft() == null) {
node.setLeft(new BinarySearchTree(data));
return;
}
node = node.getLeft();
} else {
if (node.getRight() == null) {
node.setRight(new BinarySearchTree(data));
return;
}
node = node.getRight();
}
}
}
//中序
public static void mid(BinarySearchTree cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return;
}
mid(cur.getLeft());
System.out.print(cur.getData() + " ");
mid(cur.getRight());
}
//查找
public static void find(int data) {
BinarySearchTree node = root;
while (node != null) {
if (data < node.getData()) {
node = node.getLeft();
} else if (data > node.getData()) {
node = node.getRight();
} else {
System.out.println("找到数据!");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没找到数据!");
}
//删除
public static void remove(int data) {
BinarySearchTree node = root;
BinarySearchTree parent = null;
//查找要删除的结点,并且记录其父节点
while (node != null && node.getData() != data) {
parent = node;
if (data < node.getData()) {
node = node.getLeft();
} else {
node = node.getRight();
}
}
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//找到该节点
//删除的节点有两个子结点
if (node.getLeft() != null && node.getRight() != null) {
//找最小的节点
BinarySearchTree minNode = node.getRight();
BinarySearchTree minNodeParent = node;
while (minNode.getLeft() != null) {
minNodeParent = minNode;
minNode = minNode.getLeft();//找最小节点
}
node.setData(minNode.getData());//节点转换节点,删除实际数据
node = minNode;//真正要删除的节点
parent = minNodeParent;
}
//删除结点
BinarySearchTree child = null;
if (node.getLeft() != null) {
child = node.getLeft();
} else if (node.getRight() != null) {
child = node.getRight();
} else {
child = null;
}
if (parent == null) {//删除根节点,并且根节点没有右子树
root = child;
} else if (parent.getLeft() == node) {
parent.setLeft(child);
} else if (parent.getRight() == node) {
parent.setRight(child);
}
}
}
二路归并排序
MergeSort类
package 实验九.二路归并排序;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
int[] arr = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int randNum = random.nextInt(90) + 10;
arr[i] = randNum;
}
System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
int[] temp = new int[arr.length];
sort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, temp);
System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
/**
* @param arr 要排序的数组
* @param left 数组左边索引
* @param right 数组右边索引
* @param temp 临时数组
*/
public static void sort(int[] arr, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = (right + left) / 2;
//左边
sort(arr, left, mid, temp);
//右边
sort(arr, mid + 1, right, temp);
merger(arr, left, mid, right, temp);
}
}
/**
* @param arr 要排序的数组
* @param left 数组左边索引
* @param mid 数组中间索引
* @param right 数组右边索引
* @param temp 临时数组
*/
public static void merger(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right, int[] temp) {
int leftIndex = left;
int rightIndex = mid + 1;
int k = 0;
//把左边和右边两个序列合并成一个有序的序列
while (leftIndex <= mid && rightIndex <= right) {
//如果左边元素大于右边,交换,索引++
if (arr[leftIndex] <= arr[rightIndex]) {
temp[k++] = arr[leftIndex++];
} else {
temp[k++] = arr[rightIndex++];
}
}
//把左边剩余数据放入temp
while (leftIndex <= mid) {
temp[k++] = arr[leftIndex++];
}
//把右边剩余数据放入temp
while (rightIndex <= right) {
temp[k++] = arr[rightIndex++];
}
//把temp数组里的数据赋值给原数组
k = 0;
int tempLeft = left;
while (tempLeft <= right) {
arr[tempLeft++] = temp[k++];
}
}
}
快速排序
QuickSort类
package 实验九.快速排序;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
int[] arr = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int randNum = random.nextInt(90) + 10;
arr[i]=randNum;
}
System.out.println("排序前:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
sort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
System.out.println("排序后:" + Arrays.toString(arr));
}
/**
* @param arr 传进来的数组int
* @param begin 左位置
* @param end 右位置
*/
public static void sort(int[] arr, int begin, int end) {
if (begin < end) {
//定义一个基准数
int temp = arr[begin];
int left = begin;
int right = end;
while (left < right) {
//处理右边找到右边所有大于基准数的元素
//退出循环时,右边都是大于基准数的元素
while (left < right && arr[right] >= temp) {
right--;
}
//把右边小于基准数的元素给左边
arr[left] = arr[right];
//处理左边找到左边所有小于基准数的元素
//退出循环时,左边都小于基准数的元素
while (left < right && arr[left] < temp) {
left++;
}
//把左边大于基准数的元素给右边
arr[right] = arr[left];
}
arr[left] = temp;
//划分为两部分
//处理左边用到递归
sort(arr, begin, left - 1);
//处理右边用到递归
sort(arr, left + 1, end);
}
}
}
本文章仅供学习交流使用,如有侵权,联系删除